A passive cooling system

Project Agua Mobility is an innovative endeavor that utilizes 3D printing technology to integrate plaster and mortar materials around bricks, enabling the simultaneous construction and finishing of structures. The project’s primary objective is to develop an alternative water transportation system based on capillary action, employing a multimaterial manifold. In this system, plaster acts as a medium for water transport, while mortar effectively retains moisture, preventing it from reaching the core structure. The key focus is on harnessing evaporative cooling, a sustainable approach that requires minimal water usage and operates without external energy sources. Project Agua Mobility represents a significant advancement towards sustainable water management and energy-efficient cooling solutions.
Need For Passive Design

Buildings use the largest portion of the energy consumed in a city forheating and coolingspace, so employing a passive design strategy for construction can be a good way to deal with this situation.
Capillary Action
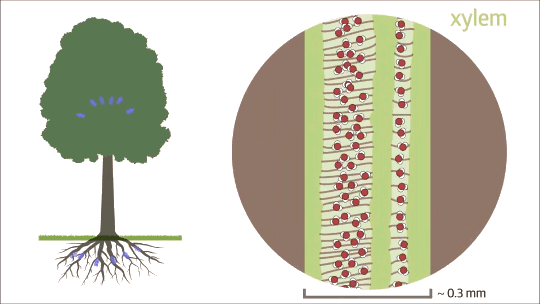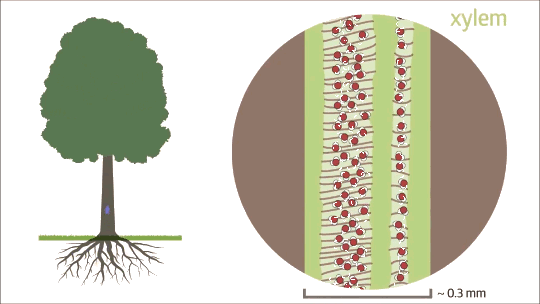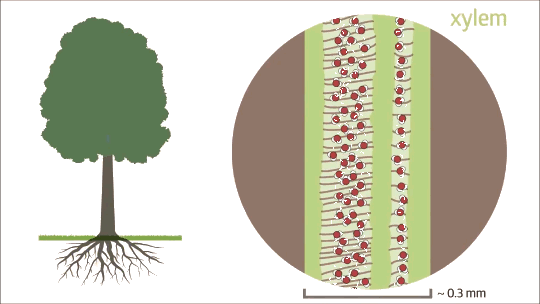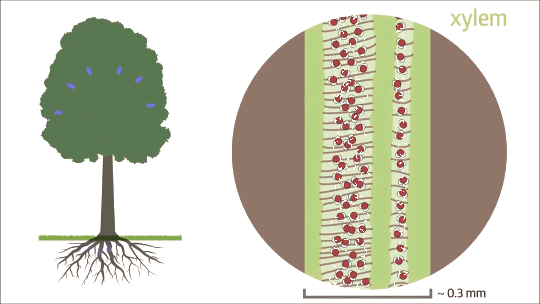
Capillary action is fluid flow through a narrow tube or space from surface tension, cohesion, and adhesion.
Capillary action does not require the force of gravity. In fact, liquids often rise in narrow tube in opposition to gravity.
State Of the Art
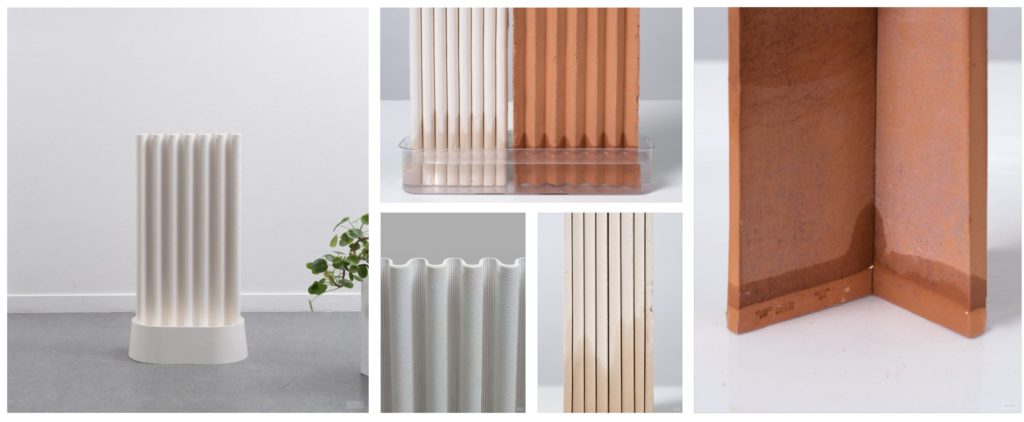

The paper clay air-humidifier is an earthenware object designed for the home environment. To work, it simply uses capillarity and evaporation.
Material : Composite earthenware paper clay

Liu says that his humidifier was inspired by the way trees work in nature: “The bottom water storage part is like the ground and soil. The extension curves [which are inside the water container] are like the roots of a tree absorbing water. The main part carries water upwards and radiates, like tree trunks and branches.”
Material : Clay & Ceramic
State Of the Art Conclusion
- Incorporation of this system in different scale has yet to be explored.
- If applied on the bigger scale, what is the structural stability of the material.
- If the system is placed in exterior wall or environment what will be the Weathering effects
Property Study of Material Selection
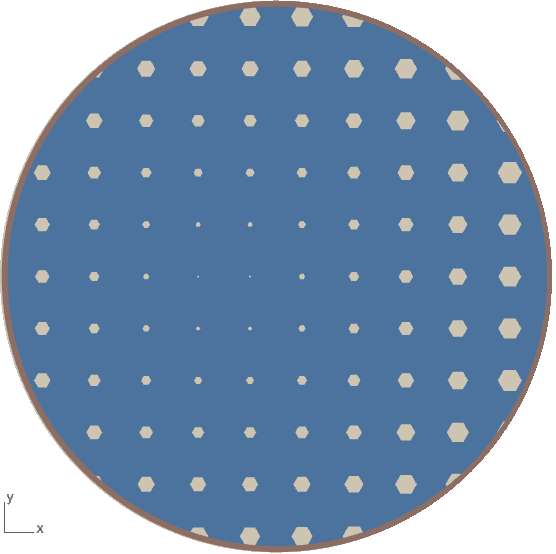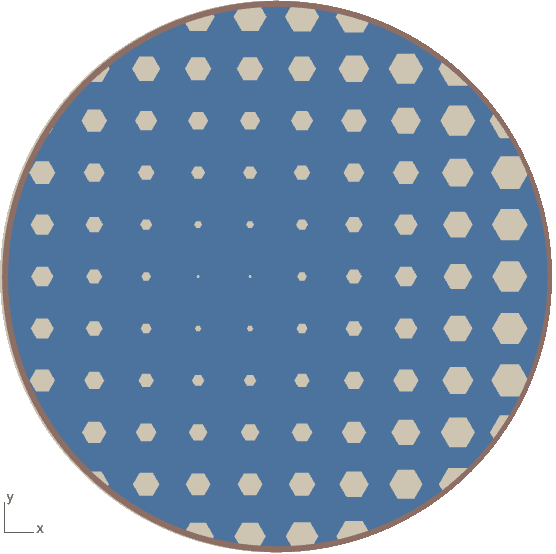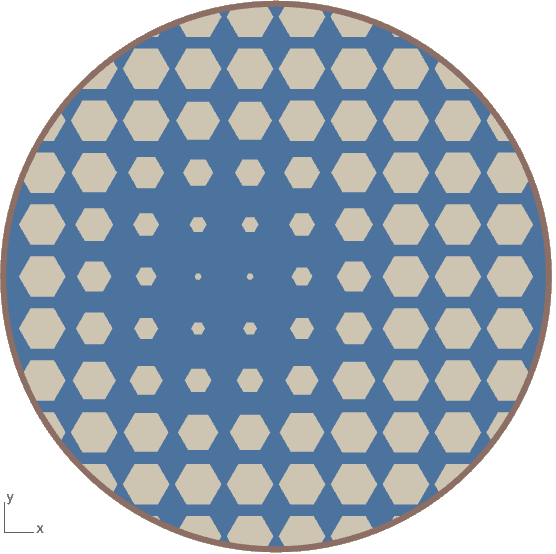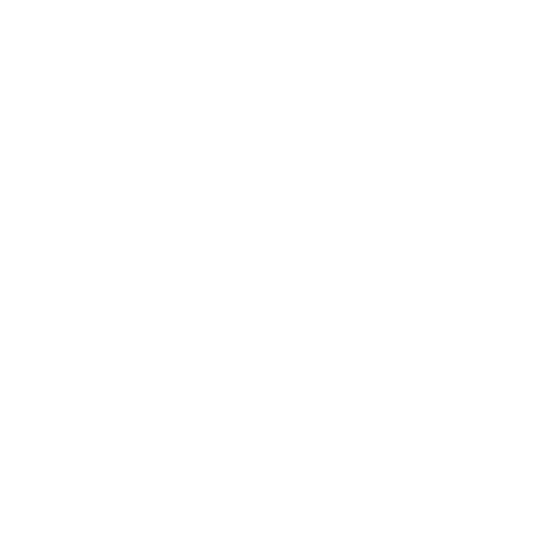
Porosity Of the Material
More the porosity more the water absorption in the material here are few list of material with maximum porosity:
- Gas Concrete
- Gypsum Plaster (Lime Putty)
- Fly ash
- Clay Bricks
- Sponge
Water Absorption
- Sponge
- Paper
- Gypsum Plaster
- Clay Bricks
- Cotton
- Concrete
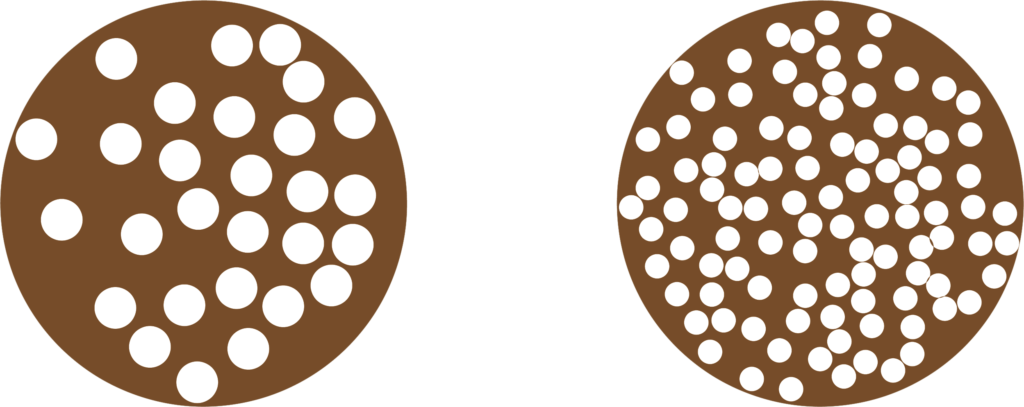
Bulk Density of material
More the bulk density less the porosity, hence less water absorption
- Paper
- Clay Bricks
- Lime Plaster
- Gypsum Plaster
- Gas Concrete
After the cumulative analysis of the properties and the material it was evident that plaster is best material for capillary action.
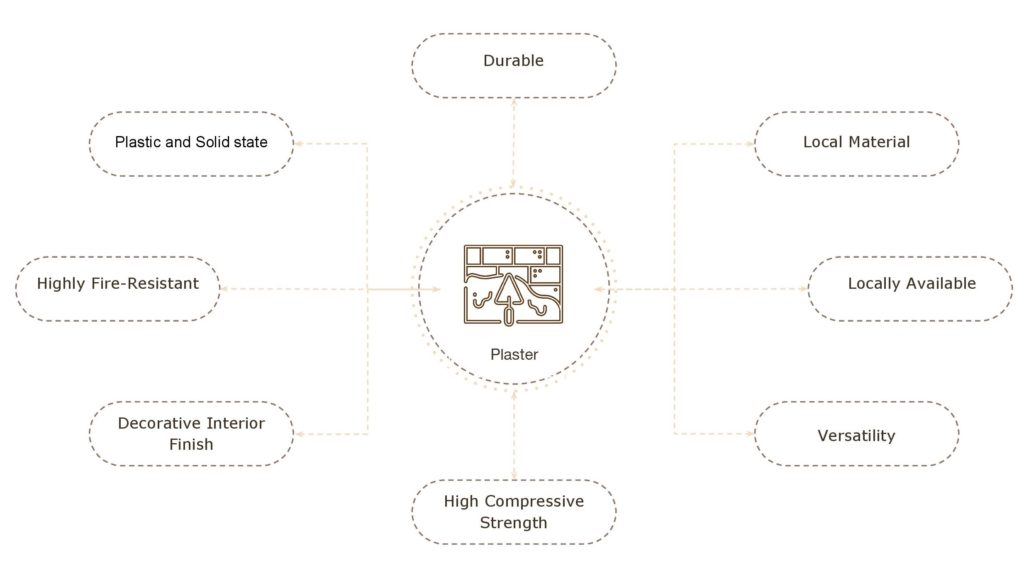
Study Of Plaster

Properties & Advantages of plaster
Material Experimentation Of Plaster

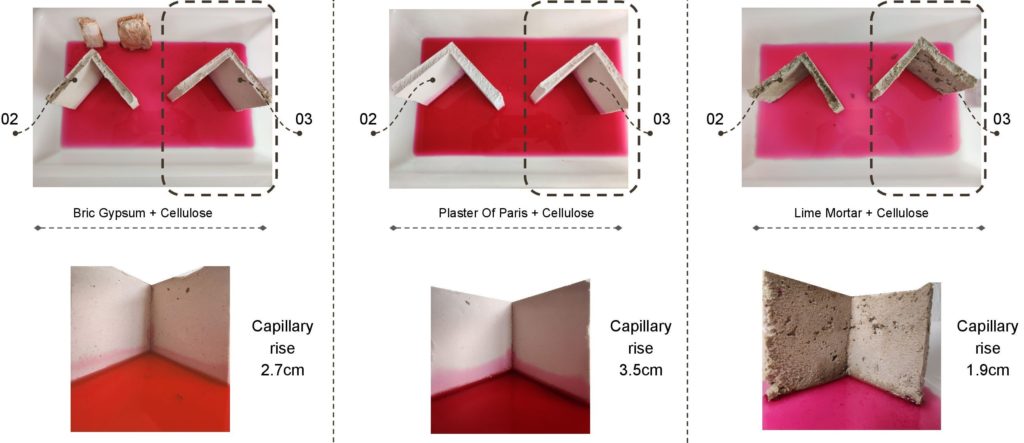
Conclusion: After keeping for 6 hrs in the water it was evident that POP had the highest amount of capillary movement and water absorption in all 3.
Project Statement
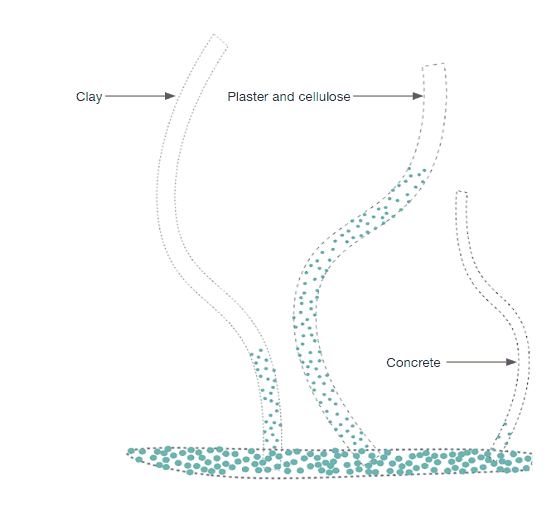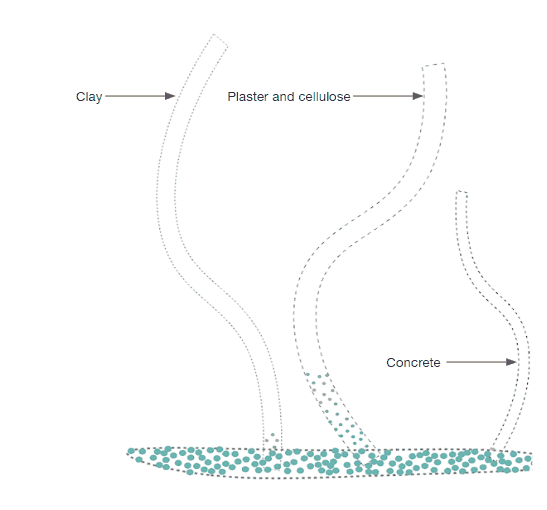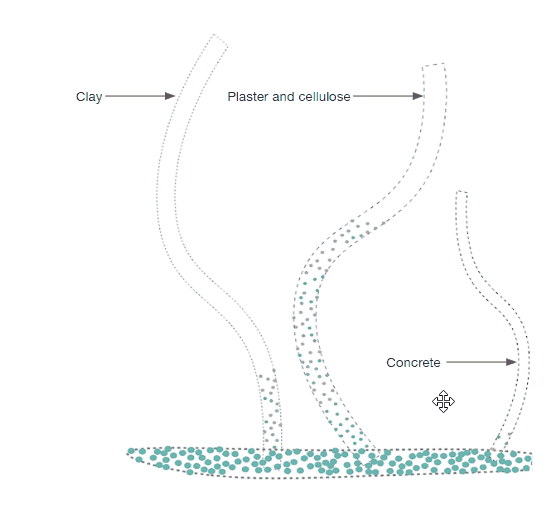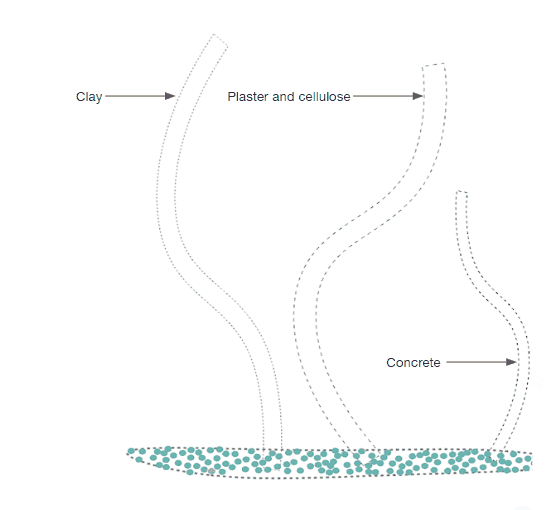
The project’s goal is to investigate alternative water transportation methods in structures to irrigate surfaces that can operate as passive cooling through capillary action. It specifically suggests using a multi-material manifold consisting of plaster and concrete that can controllably transport moisture by capillary action over extended distances with the best structural durability.
Fabrication
Plaster Fabrication
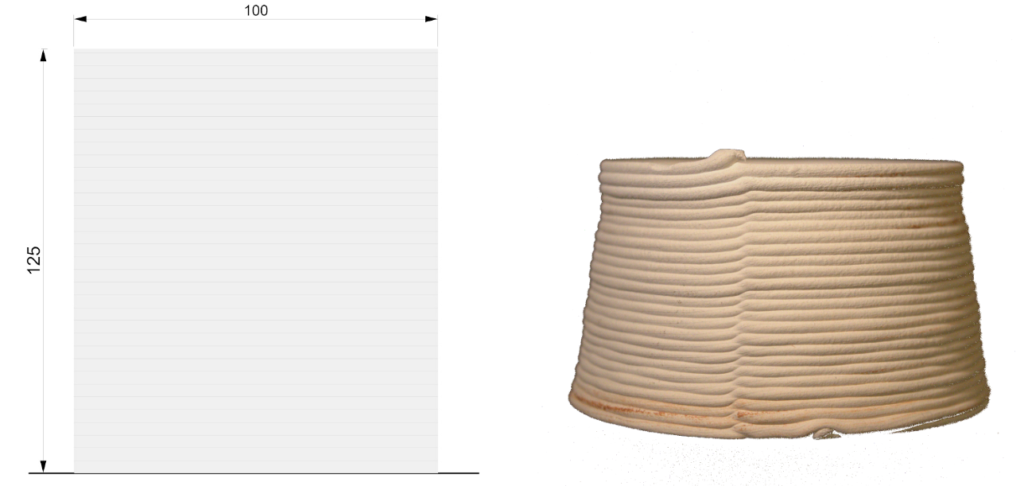

PARAMETER – First test
Material Plaster + Cellulose
Robotic arm ABB 120
Nozzle size 6mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 1.75 mm

PARAMETER- Infill Test
Material Plaster + Cellulose
Robotic arm ABB 120
Nozzle size 6mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 1.75 mm
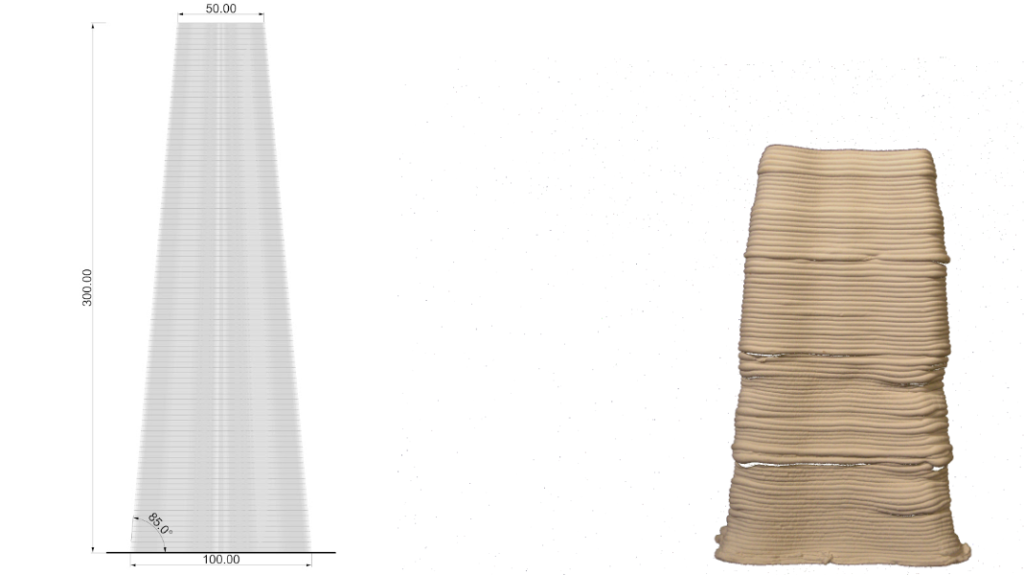


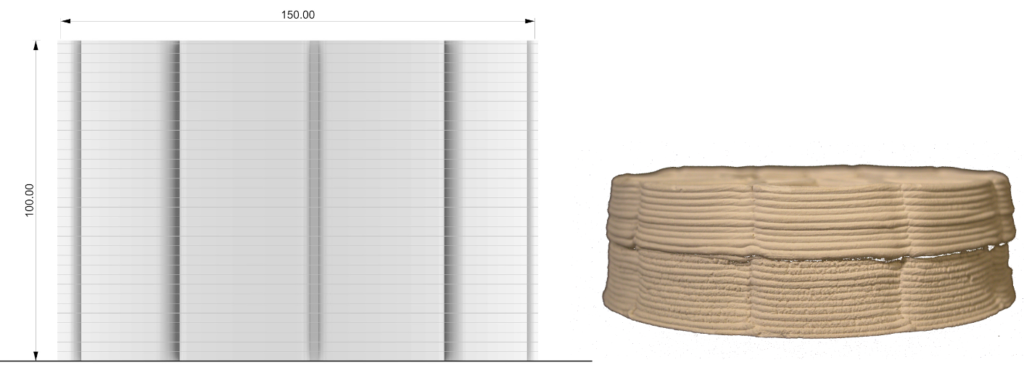
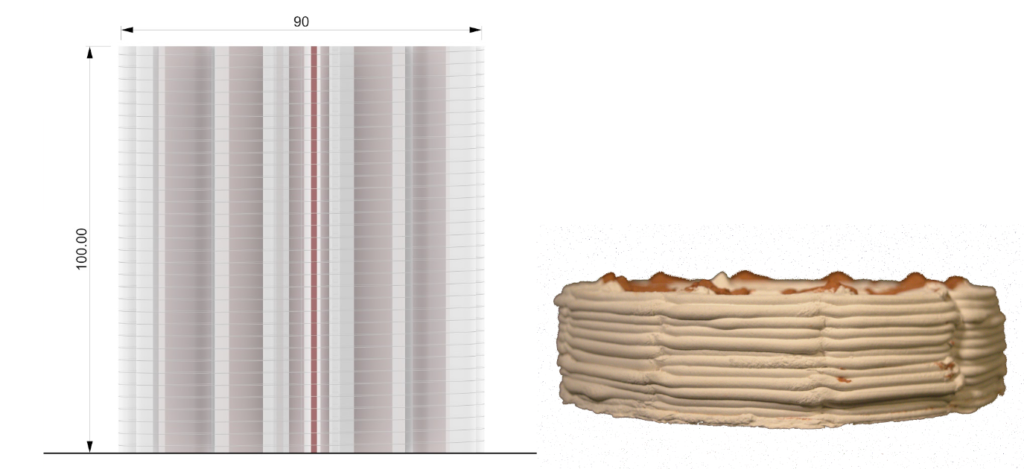
PARAMETER – Height Test
Material Plaster + Cellulose
Robotic arm ABB 120
Nozzle size 6mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 1.75 mm
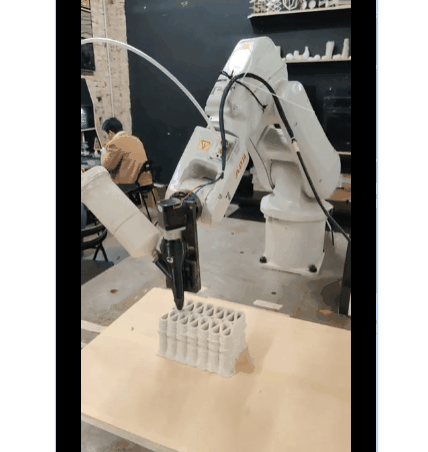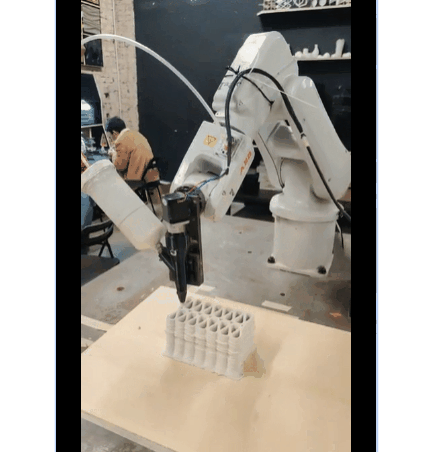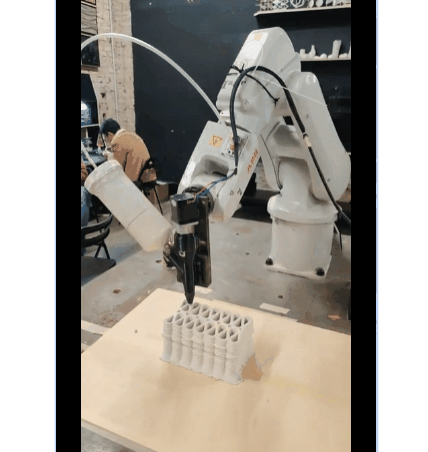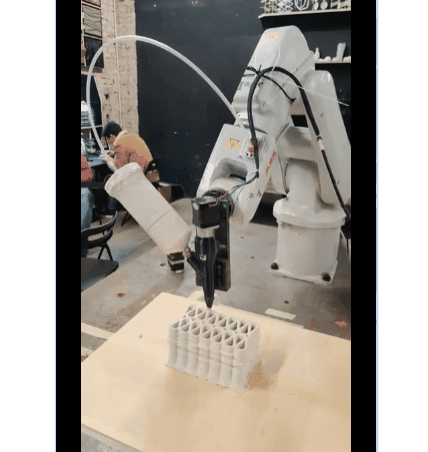
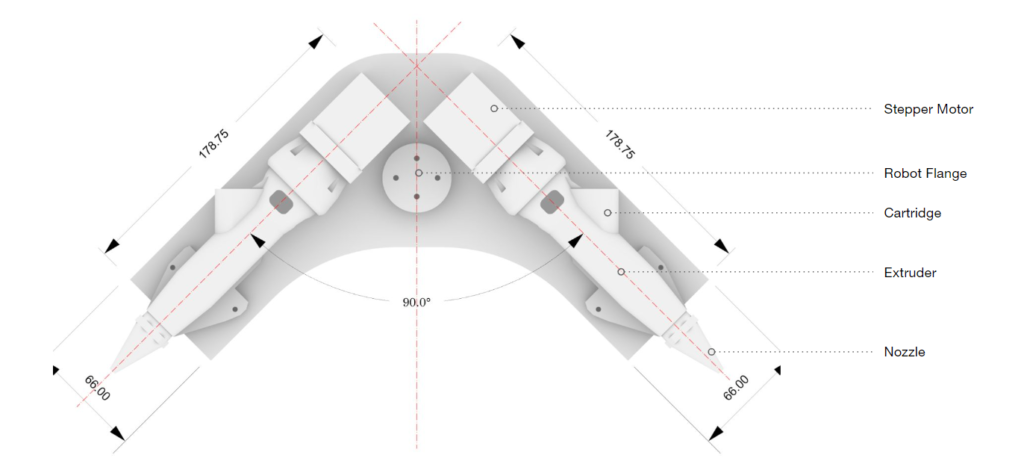
Dual Extruder Setup
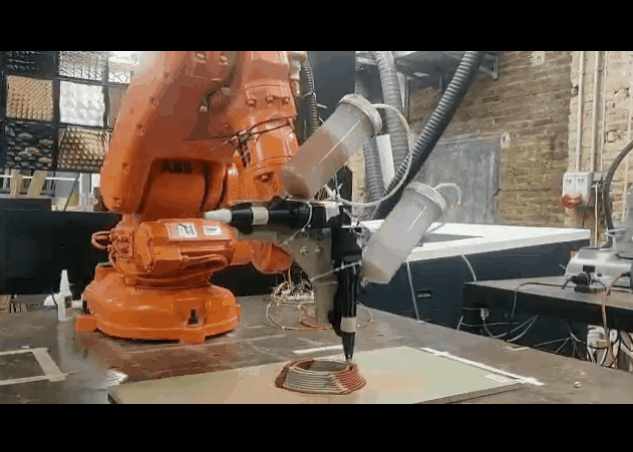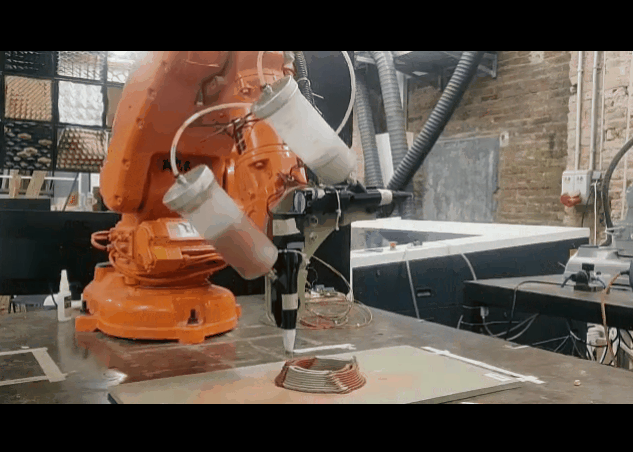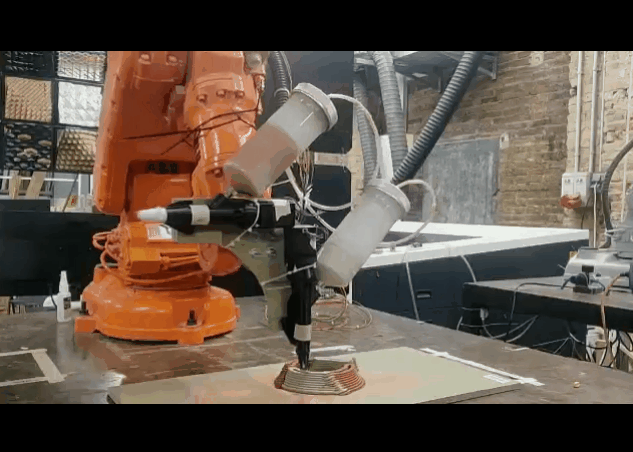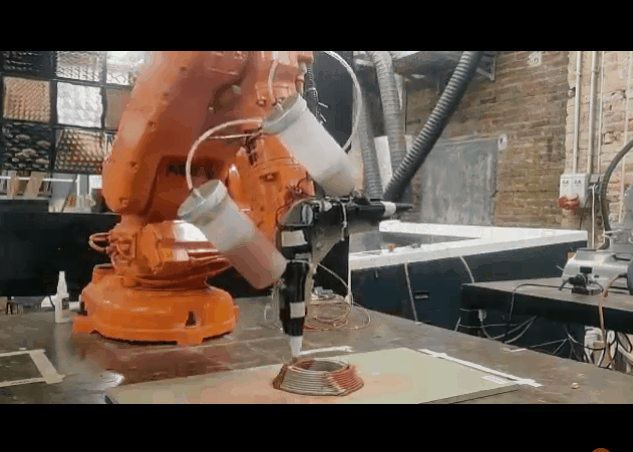
First Exploration Of Dual Extrusion
PARAMETER – Dual Extruder Infill Set-up
Material Plaster + Cellulose + Clay
Robotic arm ABB 120
Nozzle size 6mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 1.75 mm

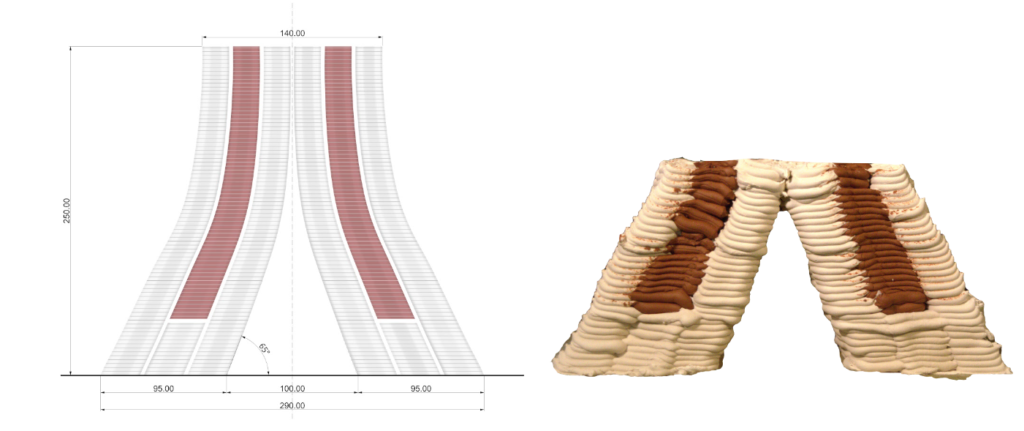
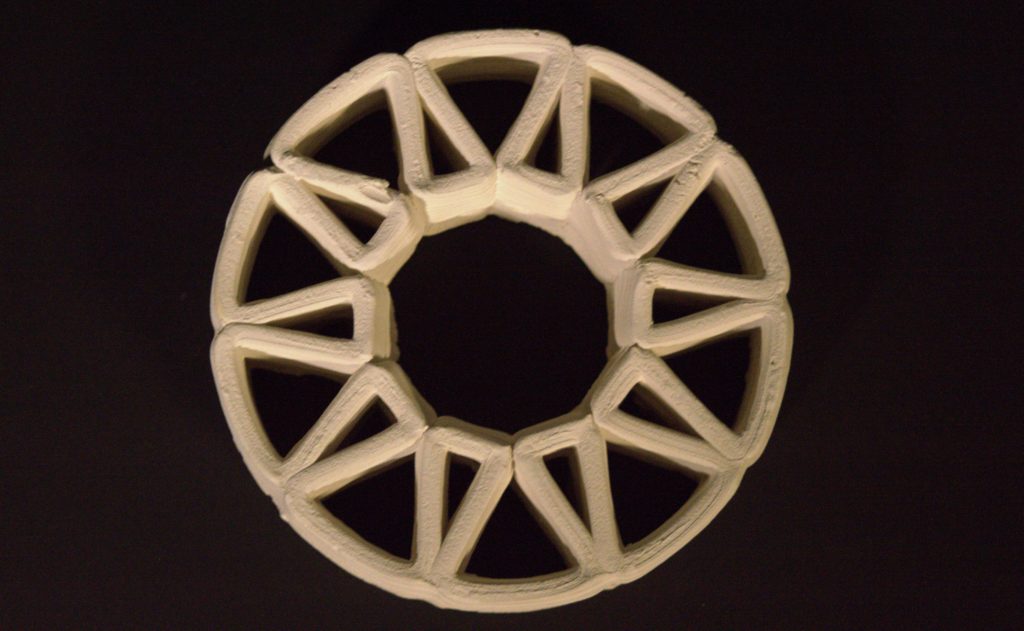
PARAMETER – Geometry Based on Above Observations
Material Plaster + Cellulose + clay
Robotic arm ABB 120
Nozzle size 6mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 1.75 mm

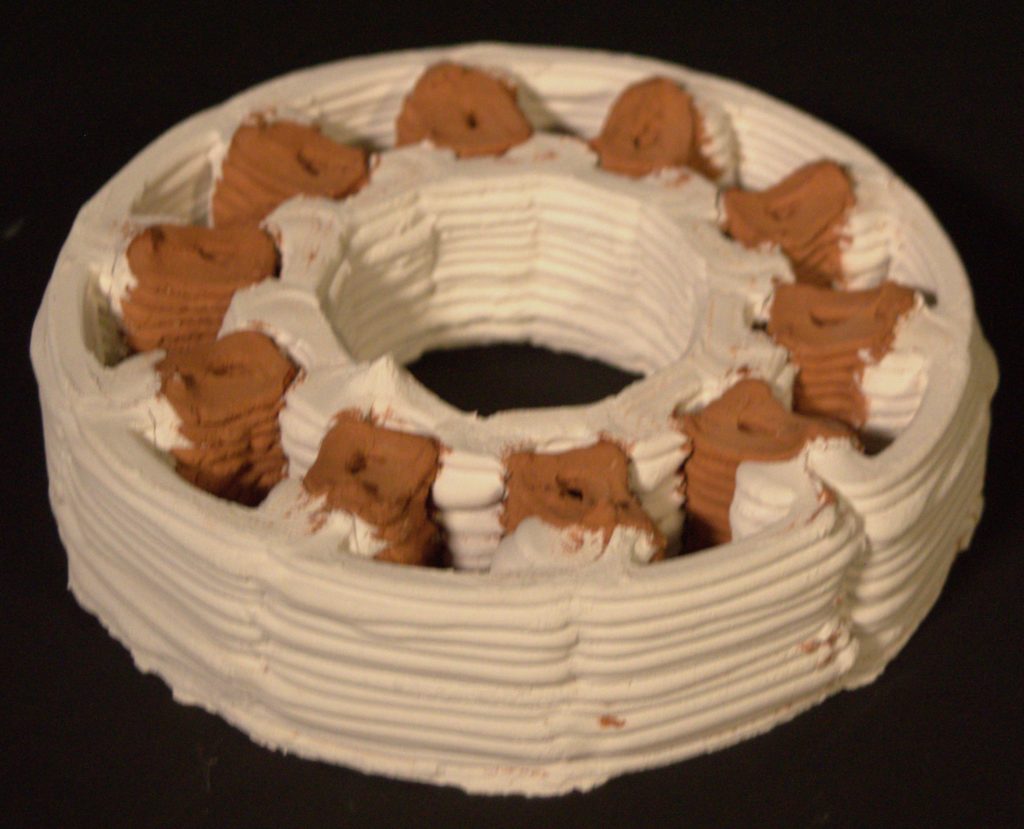
Capillary Test

Testing prototypes in 2 cm deep water to test the capillary action and water movement in the geometry

Factors Impacting Design
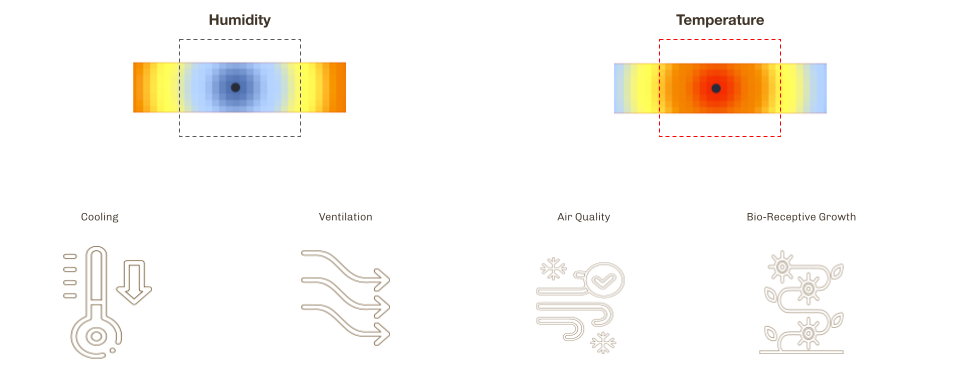
Site Selection based on climate analysis

Final Site (Granada, Alhambra)
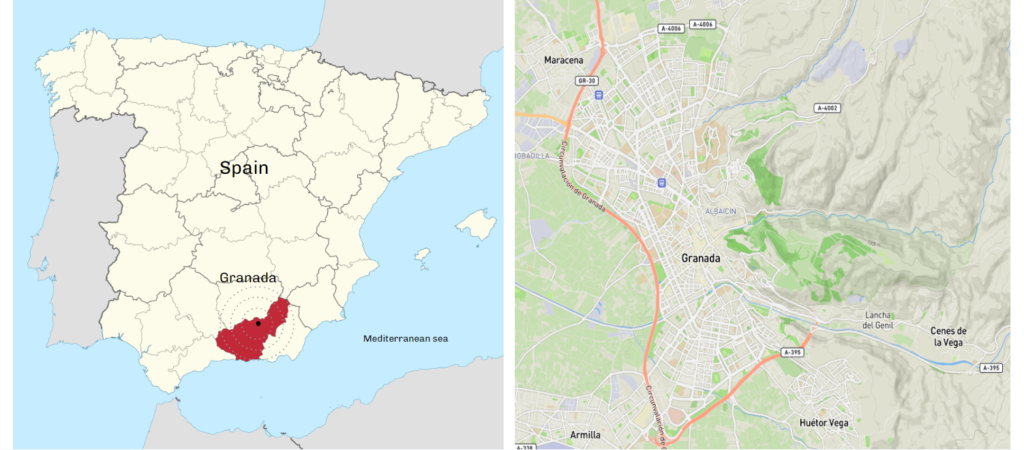
The Site was selected keeping in the mind the hot & dry climate of the city. Moreover, to also have kind of incorporation of culture of the city and palace Alhambra was selected. The entrance tourist information center of Alhambra was not developed in a way that can work sustainably and also no trace of vernacular architecture of the palace.
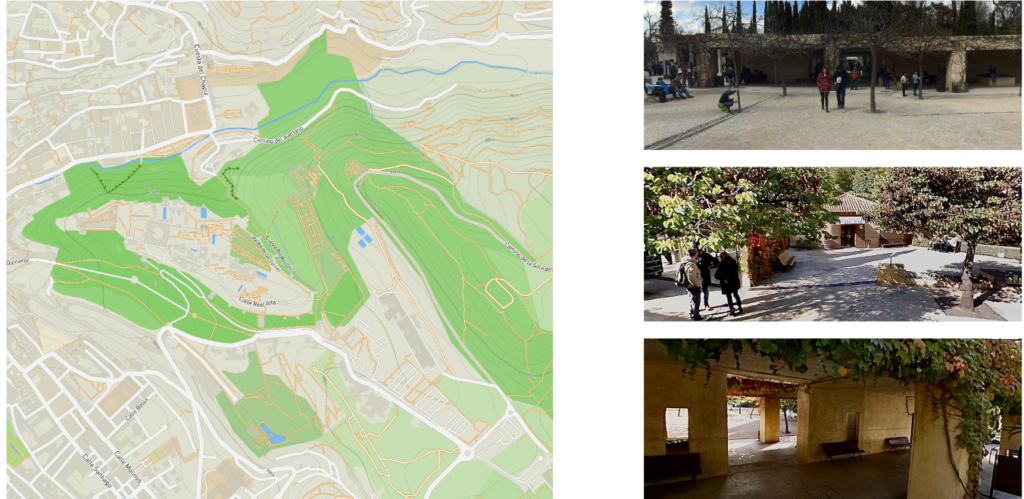

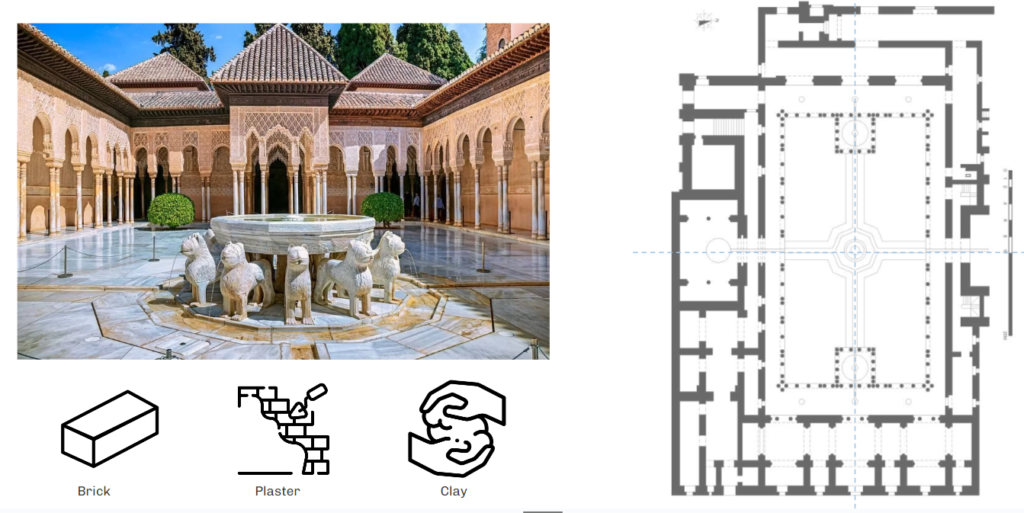
After selecting the site the study of material that has been used in vernacular architecture came into the picture as that also changes the approach towards design, fabrication and many more parameters. Hence incorporation of brick was necessary.
Optimized Dual extruder Set-up
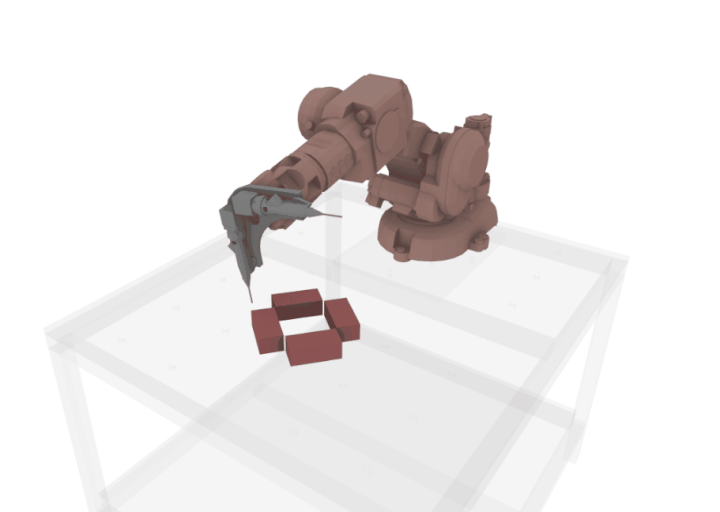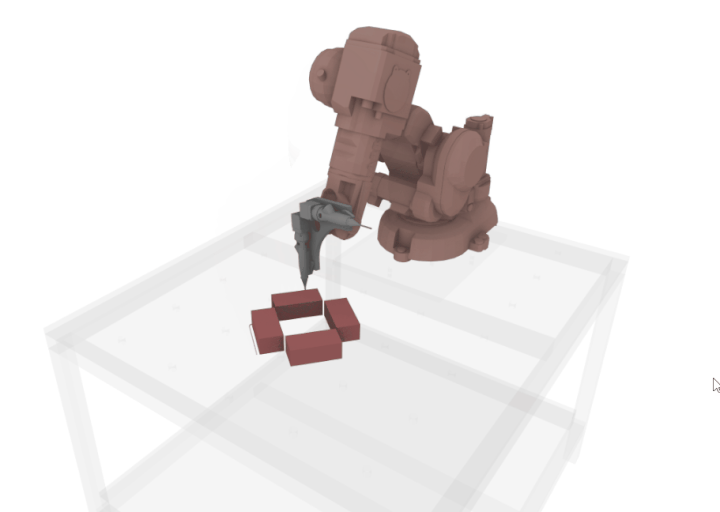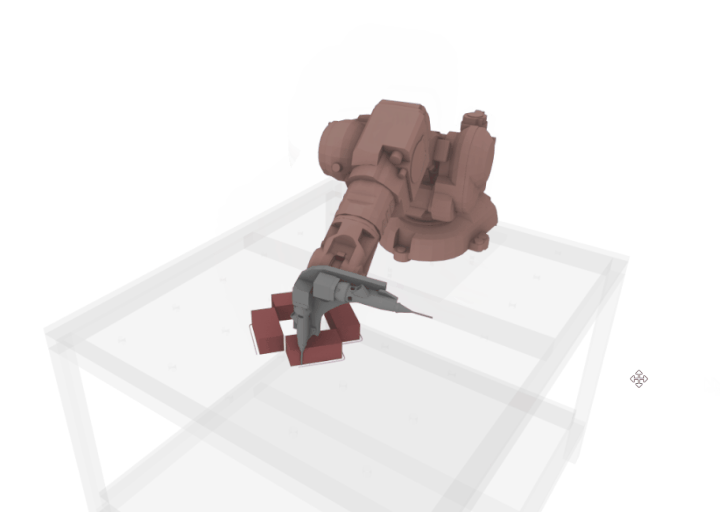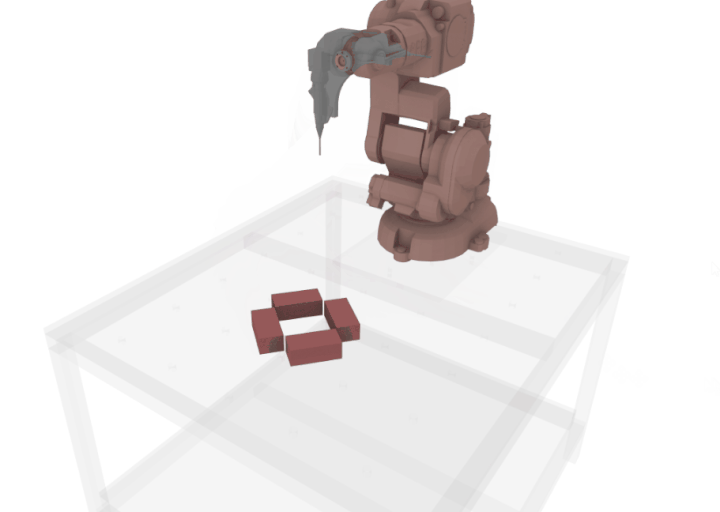
An extended nozzle was designed specifically to develop an extruder which can print next to the bricks without colliding the bricks as it is tricky to work with plaster because of issue of fast drying, hence it is necessary to develop a workflow where the collision is avoided as much as possible.
First Brick Printing Exploration
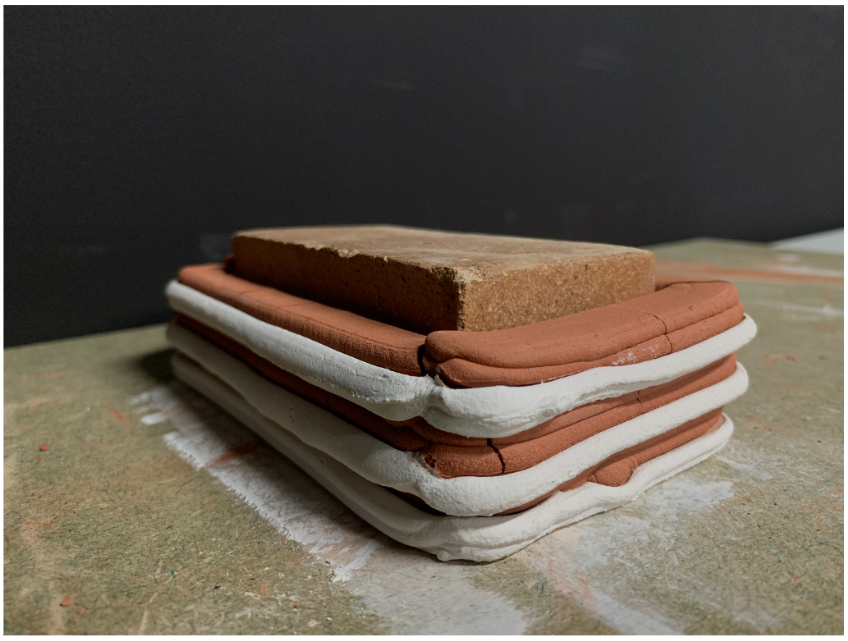
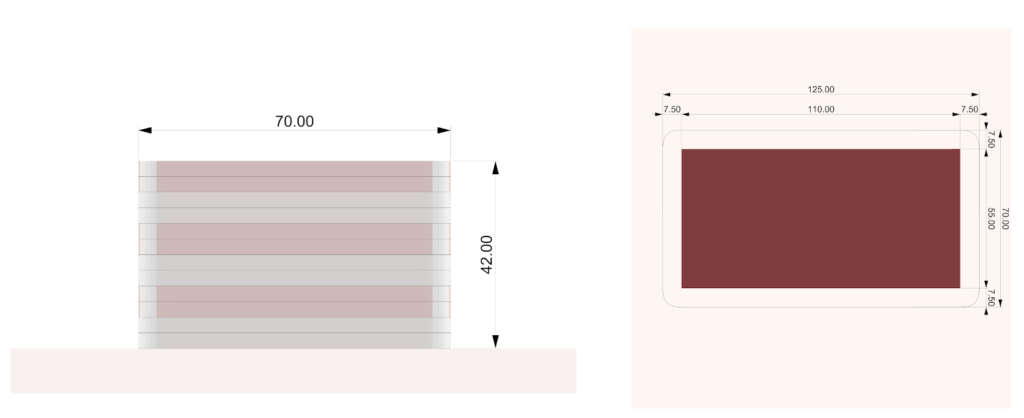

PARAMETER
Material Plaster + Cellulose + clay
Robotic arm ABB 140
Nozzle size 8mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 4 mm
Infill Exploration


PARAMETER
Material Plaster + Cellulose + Clay
Robotic arm ABB 140
Nozzle size 8mm
Speed 15% to 20%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 4 mm
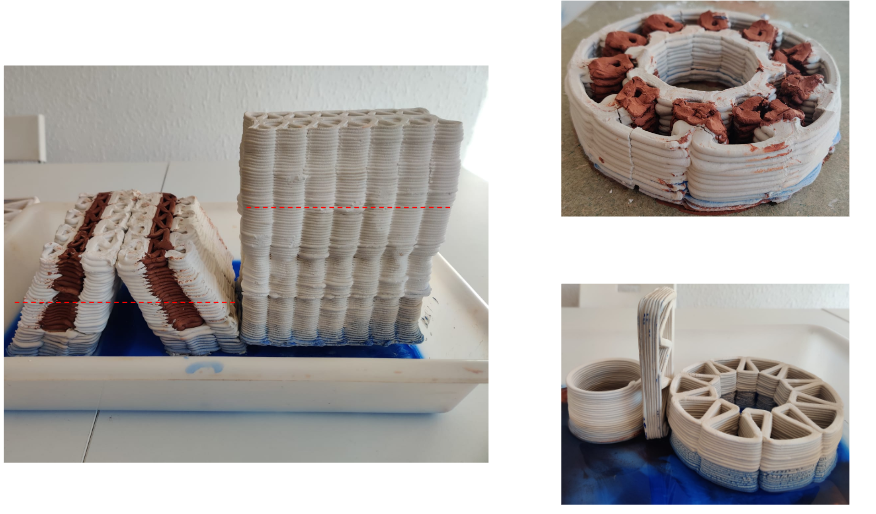
Initial Observations

- Clay is not getting enough space to shrink leading it to crack.
- Necessity of the material with the same properties is very important.
- Hence a mix of plaster and mortar was developed in order to form the bond between plaster and other material.
Mortar Exploration with bricks and Plaster

PARAMETER
Material Plaster + Cellulose + Mortar
Robotic arm ABB 140
Nozzle size 8mm
Speed 15% to 50% (15% for plaster, 50% for mortar)
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 4 mm
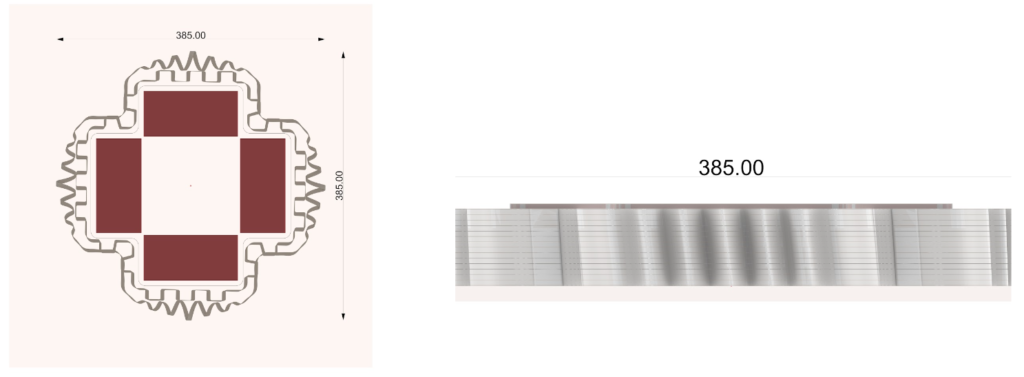
Final Fabrication
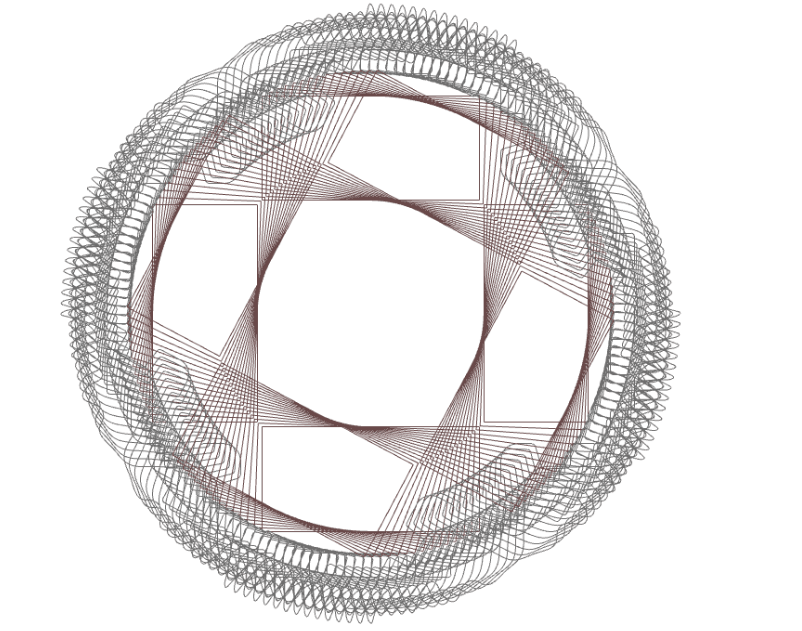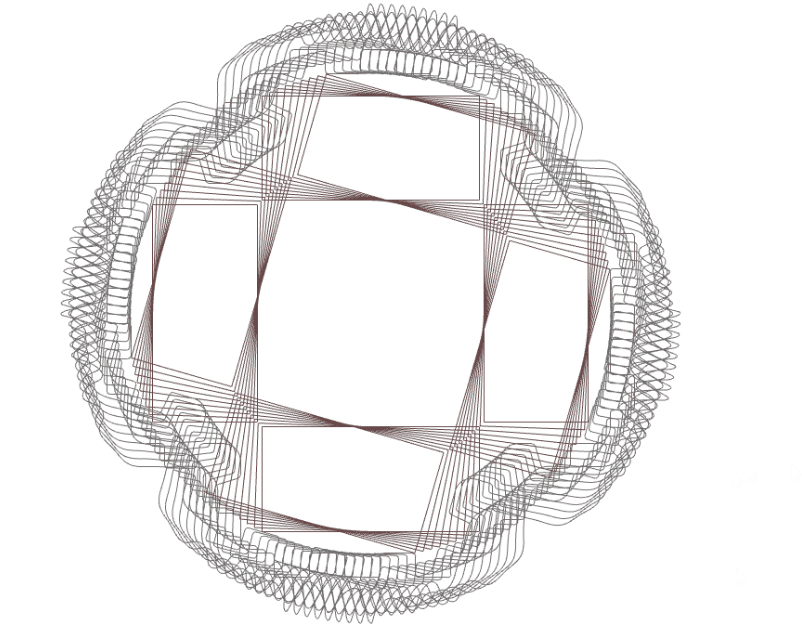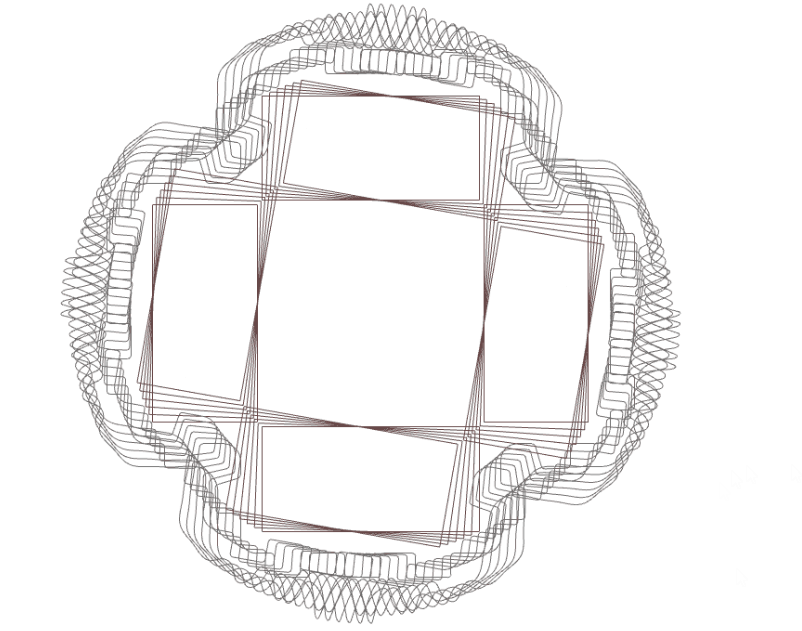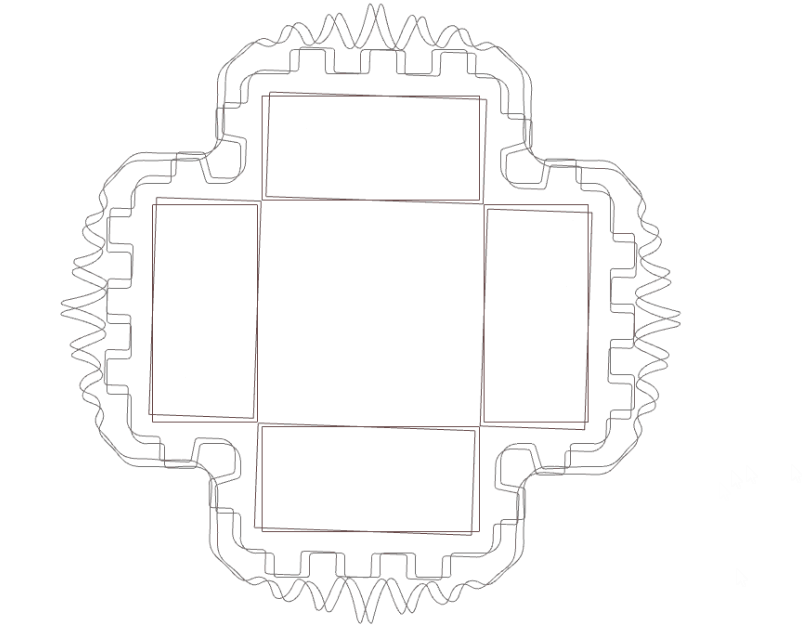
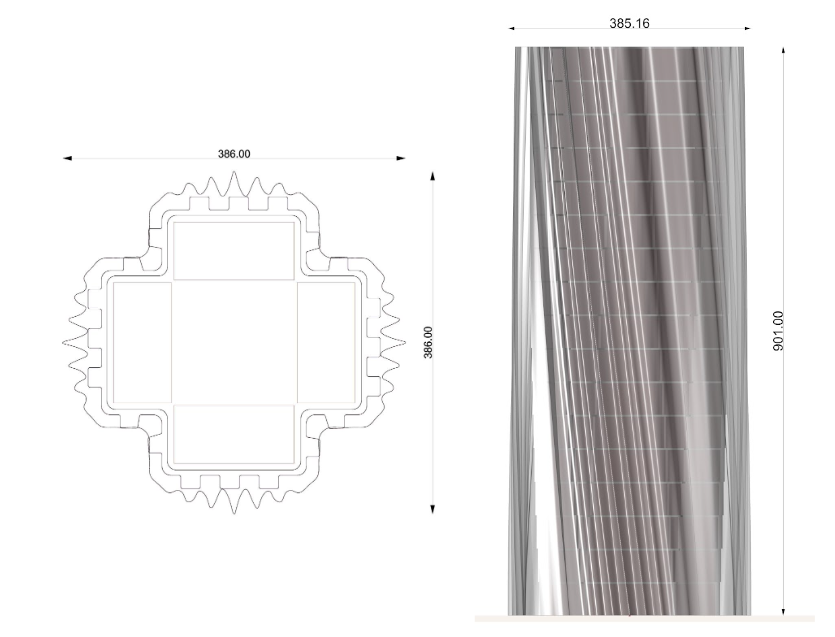
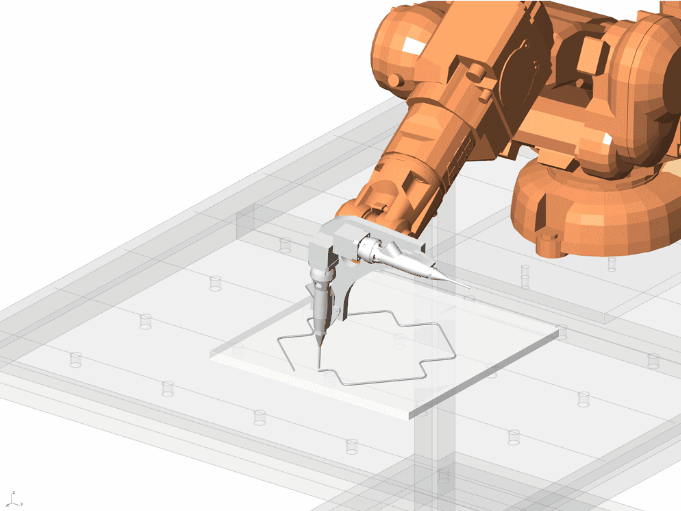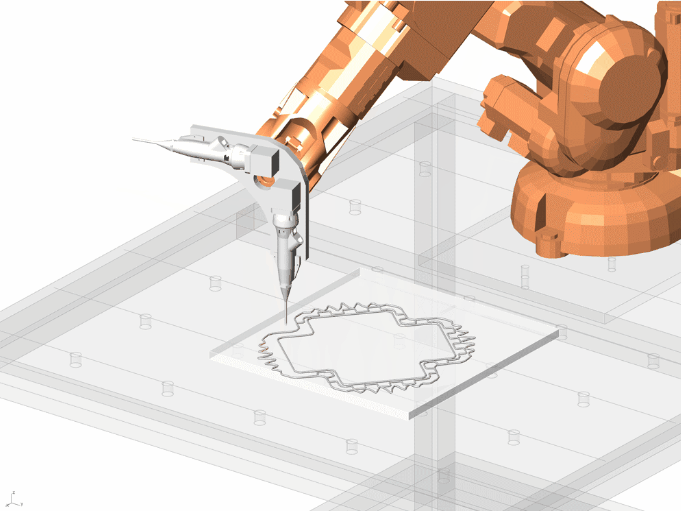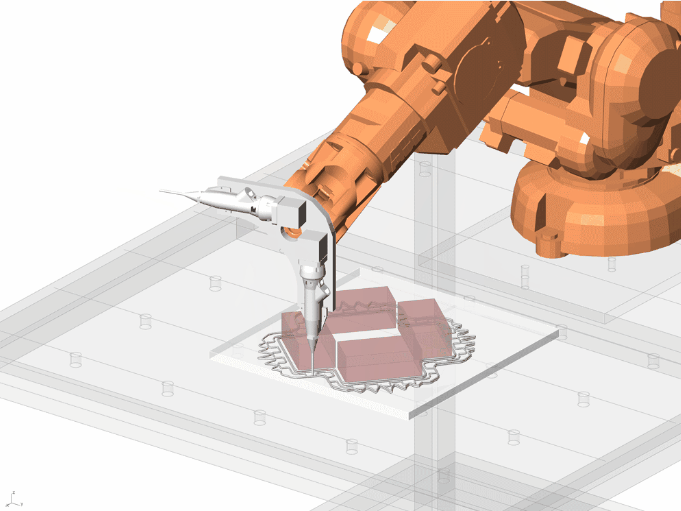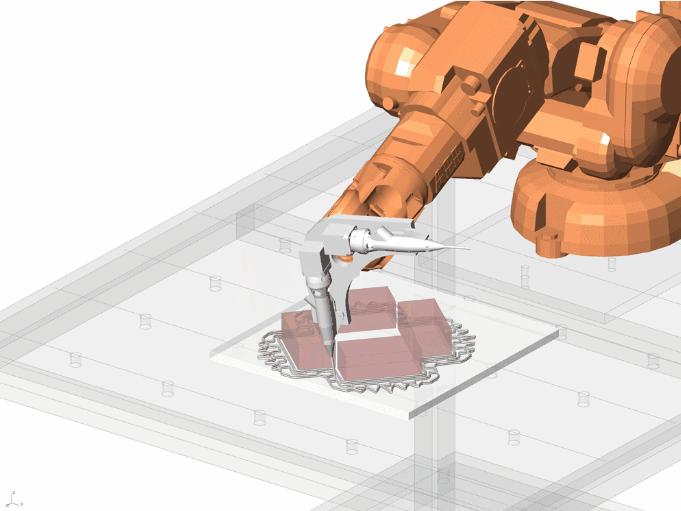

Important features of the Design
- Capturing rain water.
- collecting water and storing
- Using that water for the purpose of capillary action
- Prominent grooves have ben kept in the design in order to quantify the movement of water.
- Passive cooling of the surrounding
Final fabrication Process And Models
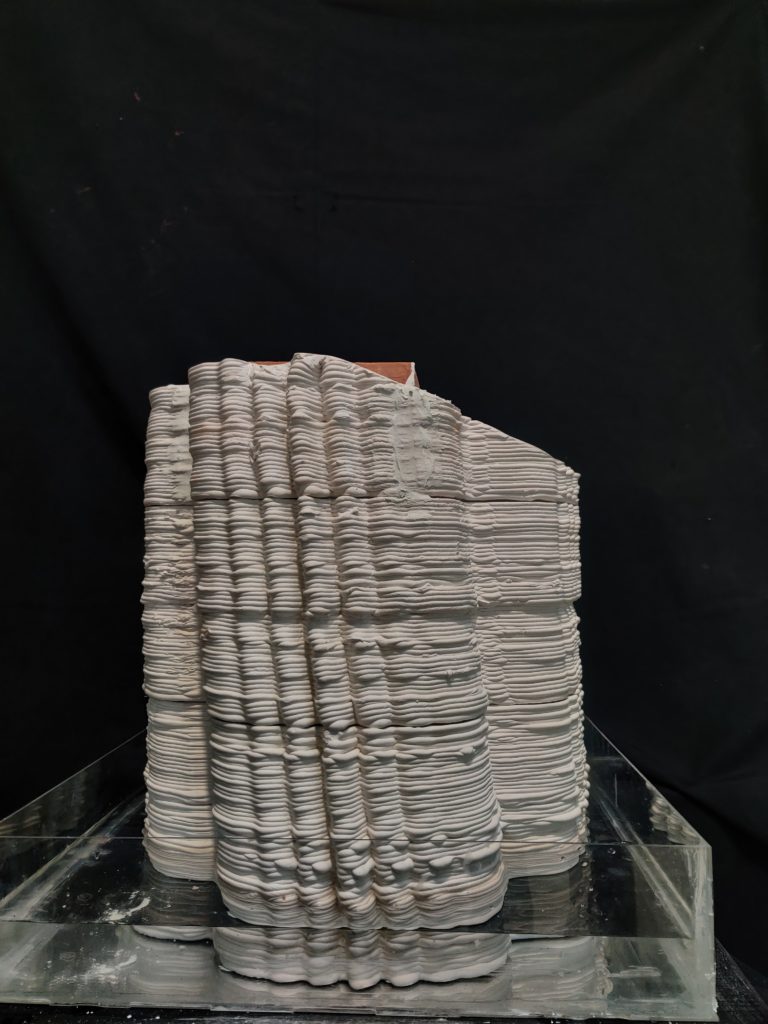
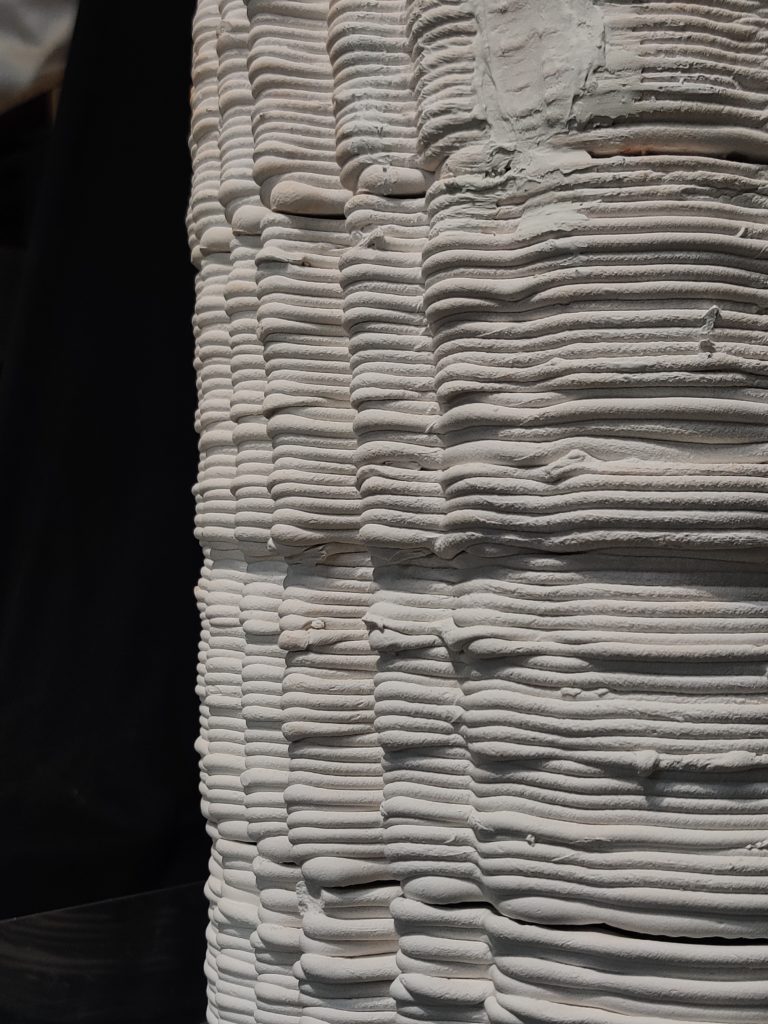
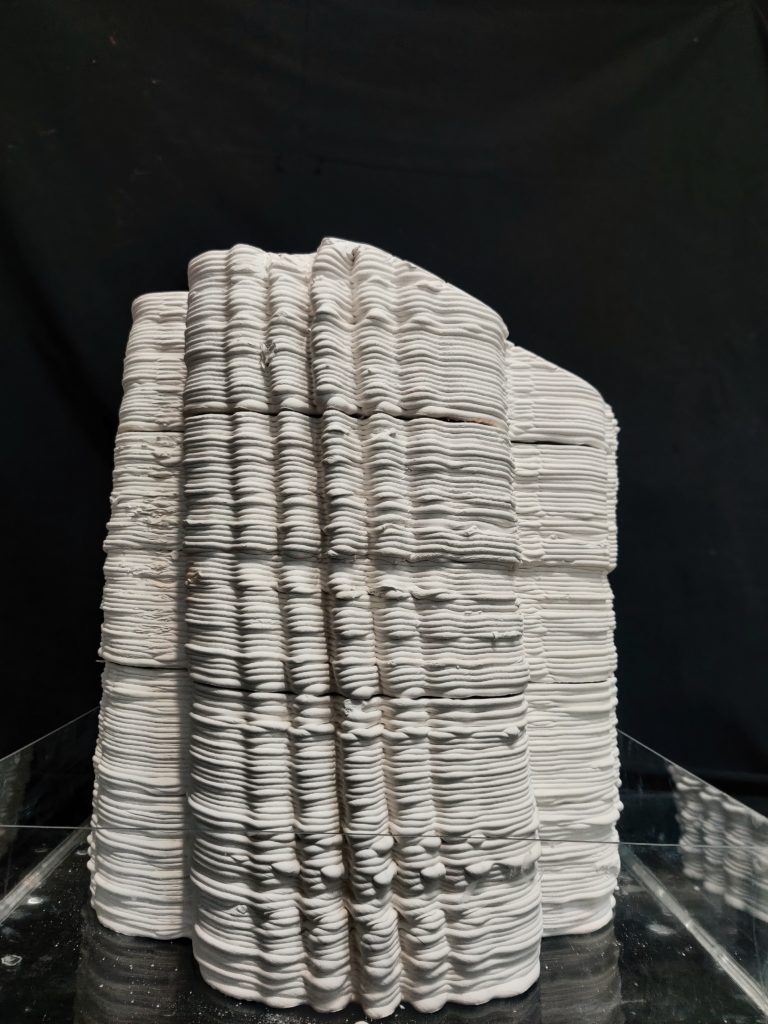
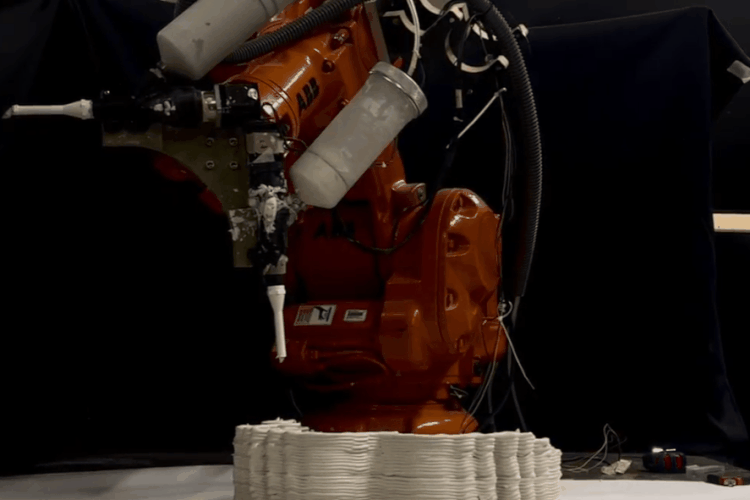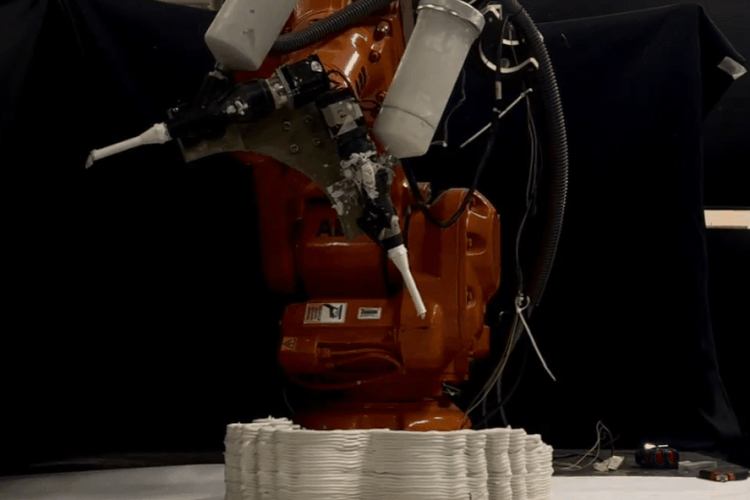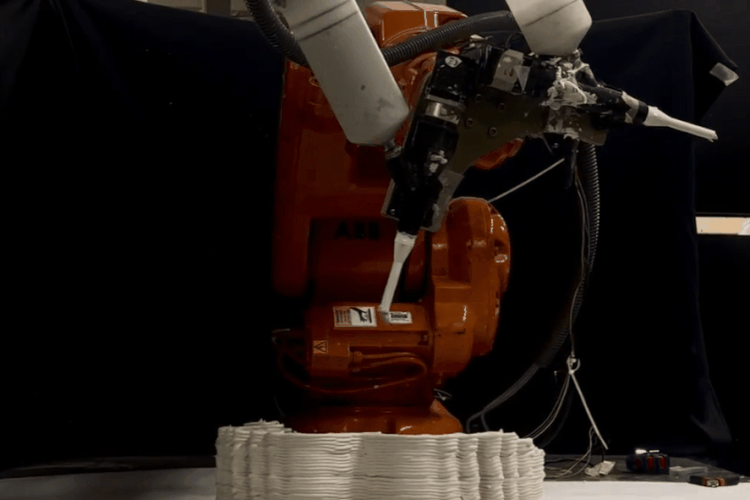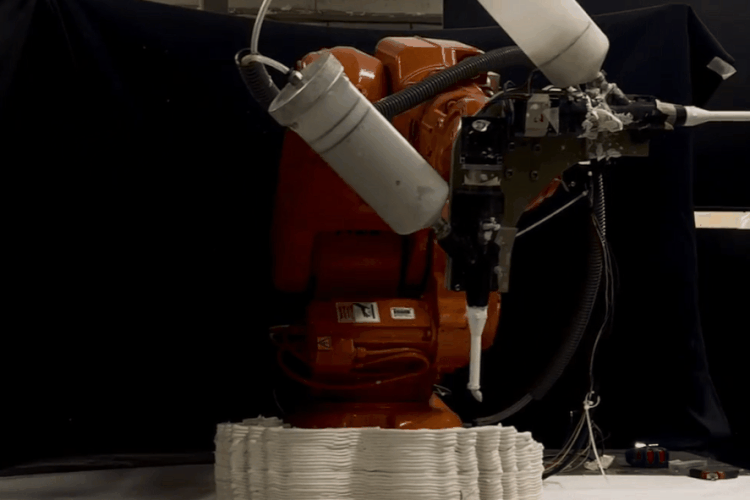



PARAMETER – Final Prototype
Material Plaster + Cellulose + Mortar
Robotic arm ABB 140
Nozzle size 8mm
Speed 15% to 50%
Pressure 2.5
Layer distance 3.75 mm
Thermal Imaging of the prototype Before and After Pouring Water
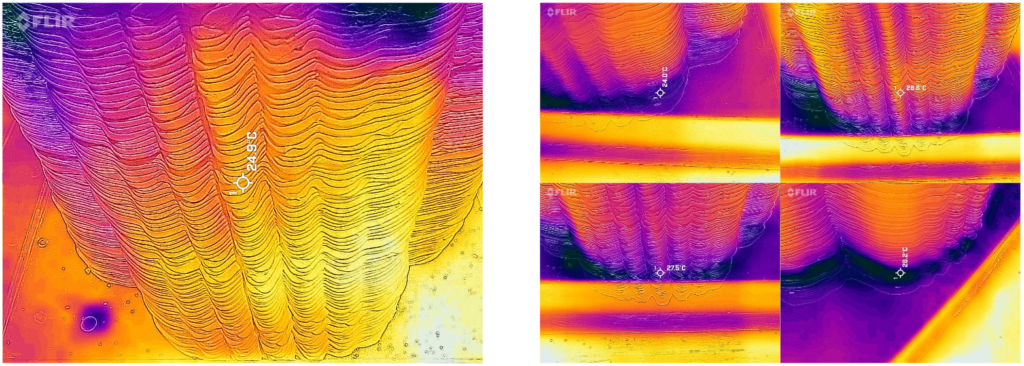
As it is seen in the images on the right the water on the bottom of the box has started to rise above in the material. And as per the design consideration of keeping prominent grooves is very impactful as the water movement is seen more in the grooves compared to the surface of the model
Final Design
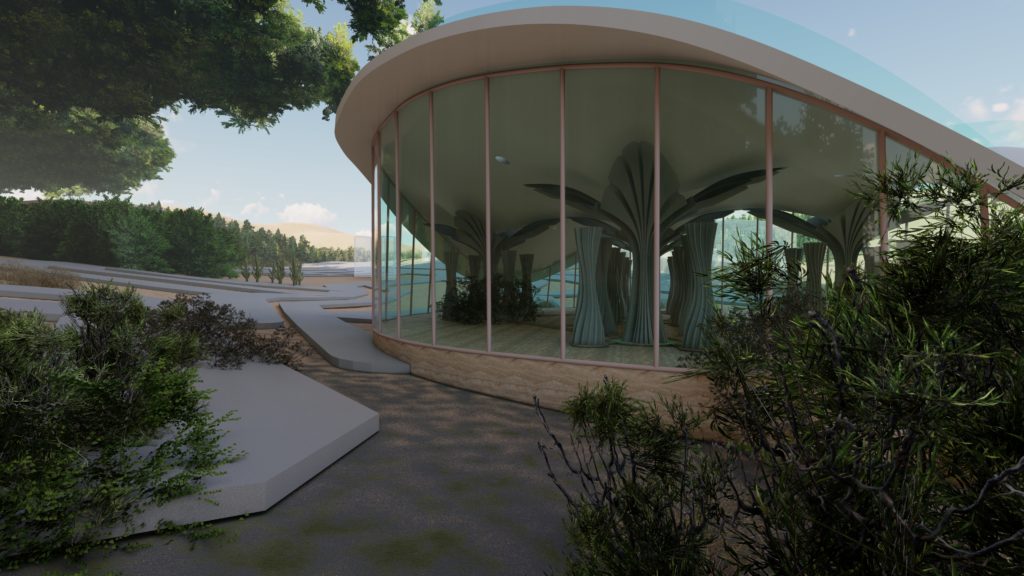

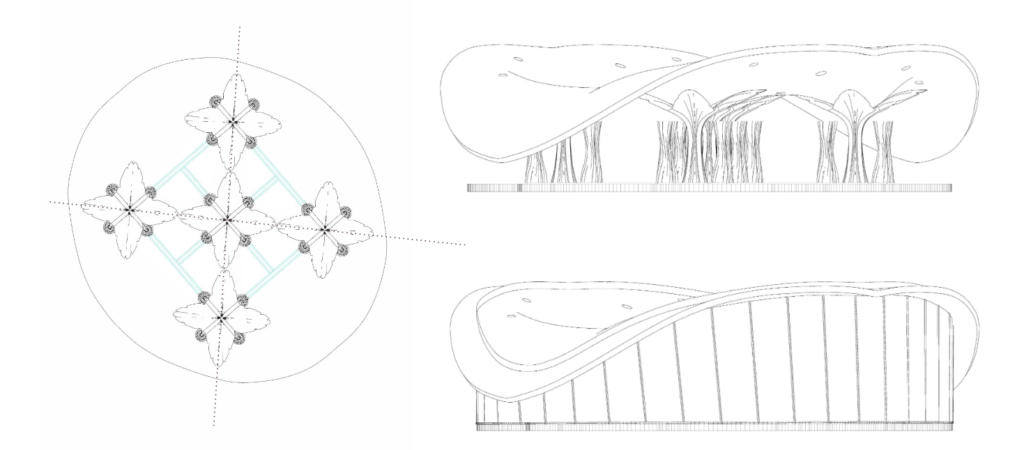
Typical Layout and drawings of the Proposal
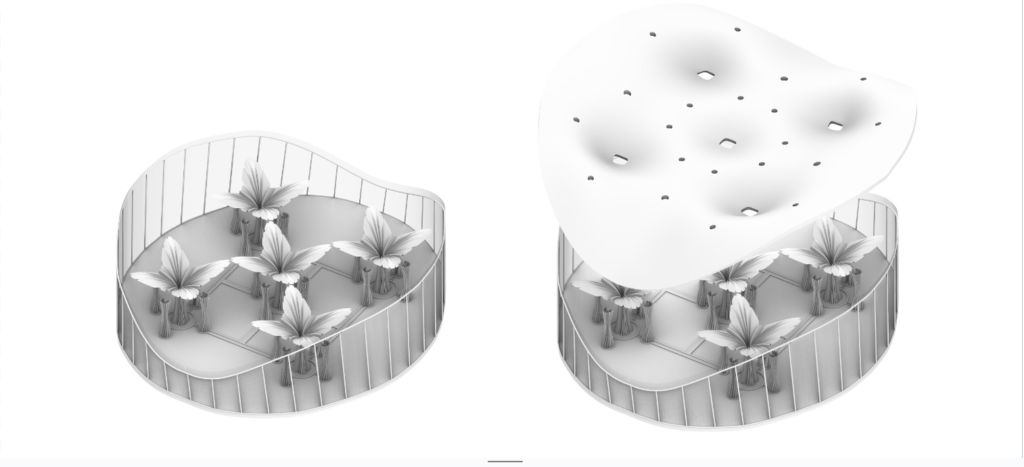
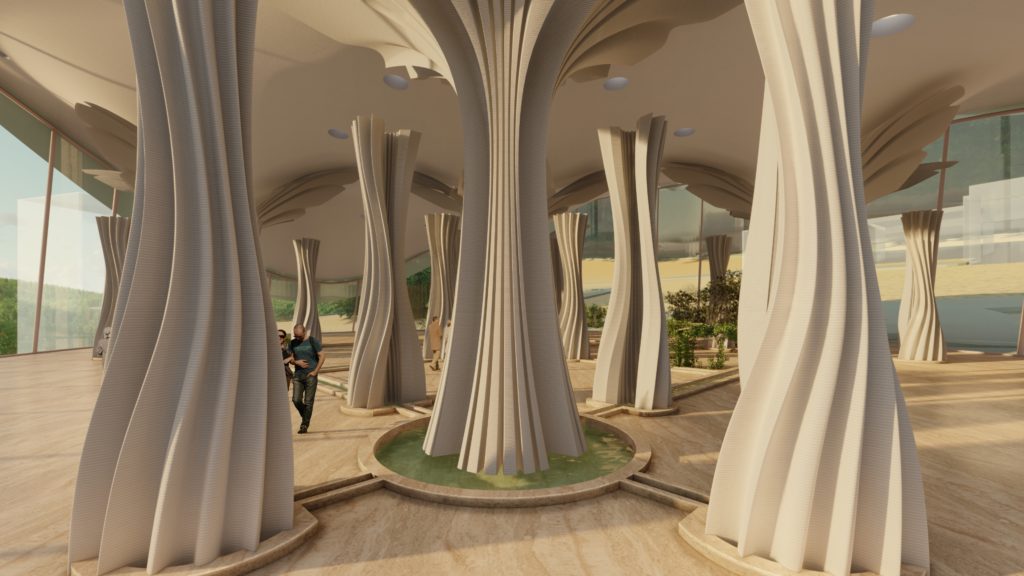
Axonometric view of the pavilion
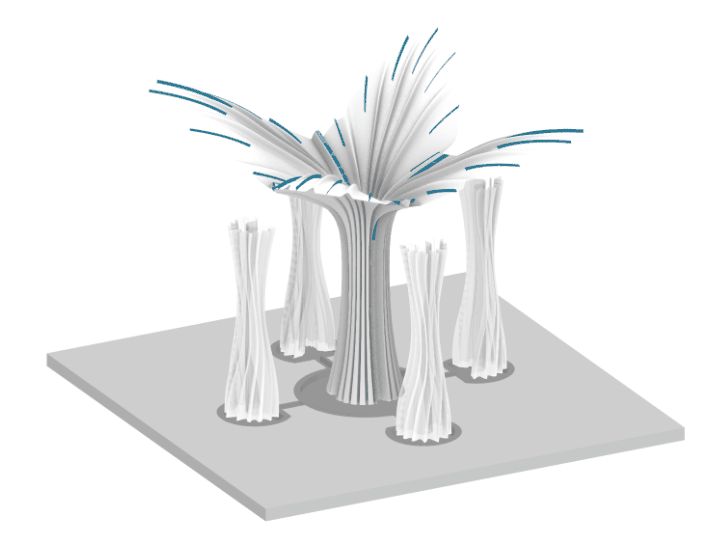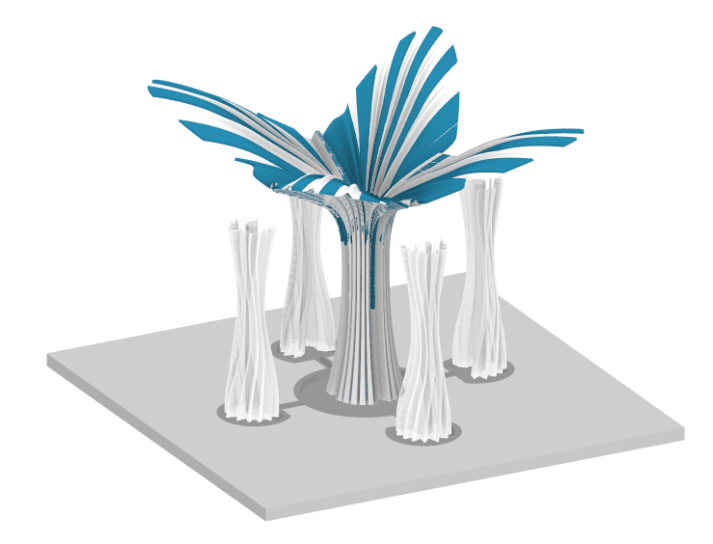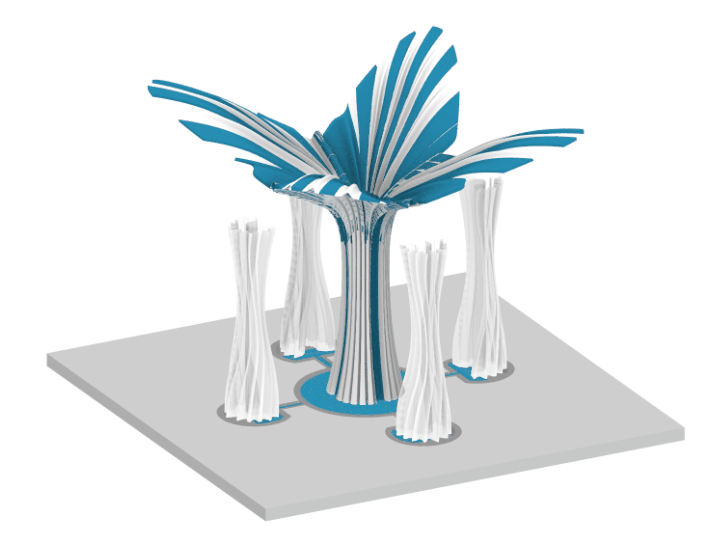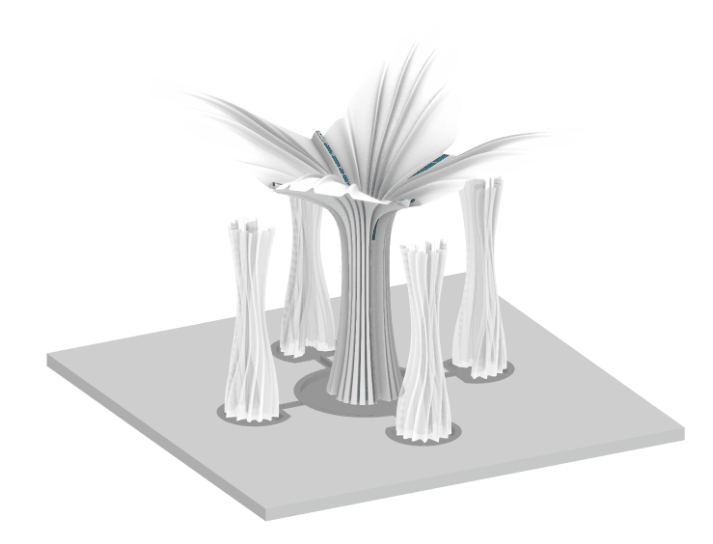
Digital Simulation of the system
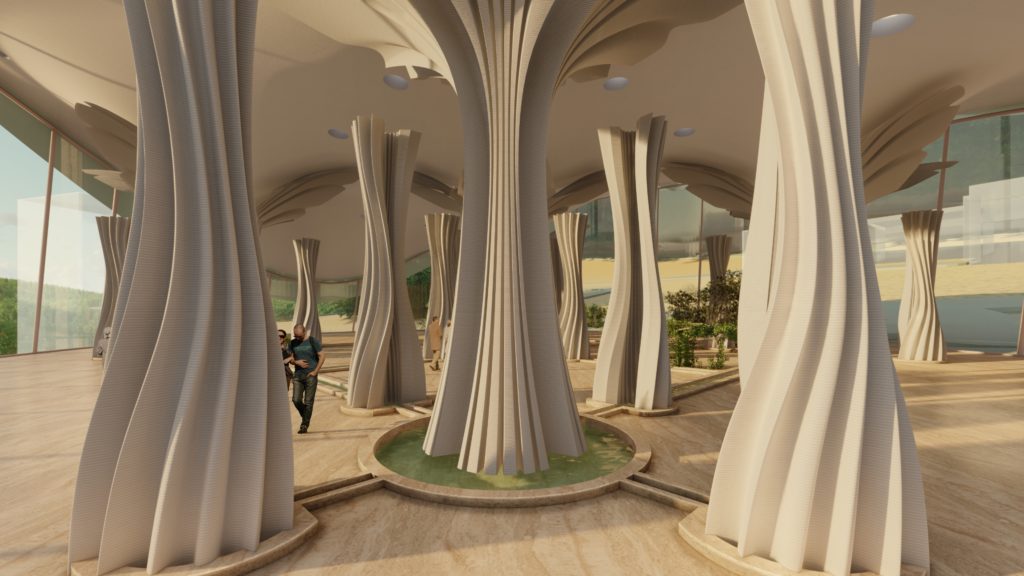
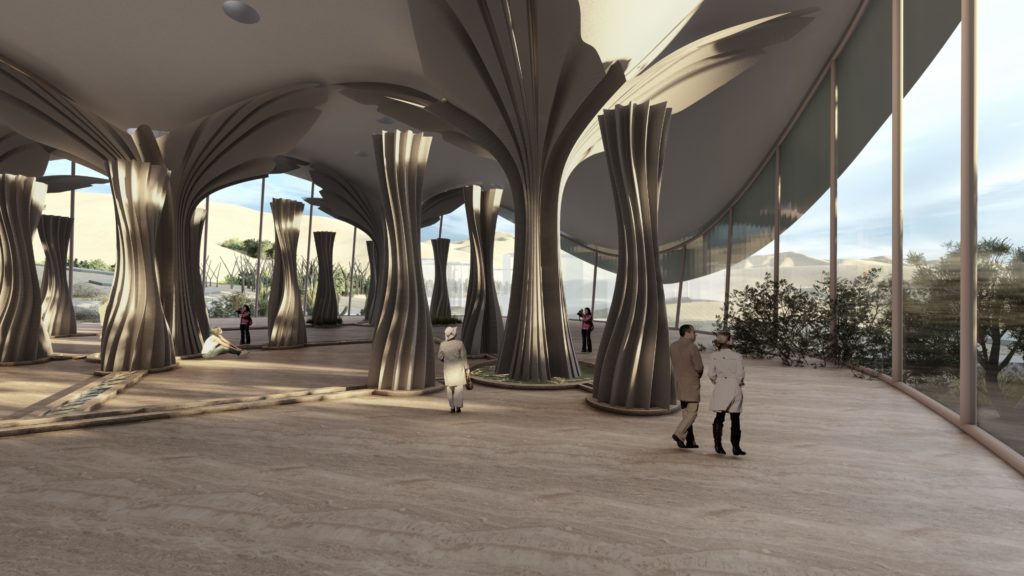


Visual Representation of the Design
Future Exploration
- Explore the brittleness of the material and try to resolve
- Explore different structural system like wall beams
- Also with different material like concrete, wood and any other structural material
- Work with continuous feeding system for material fabrication

