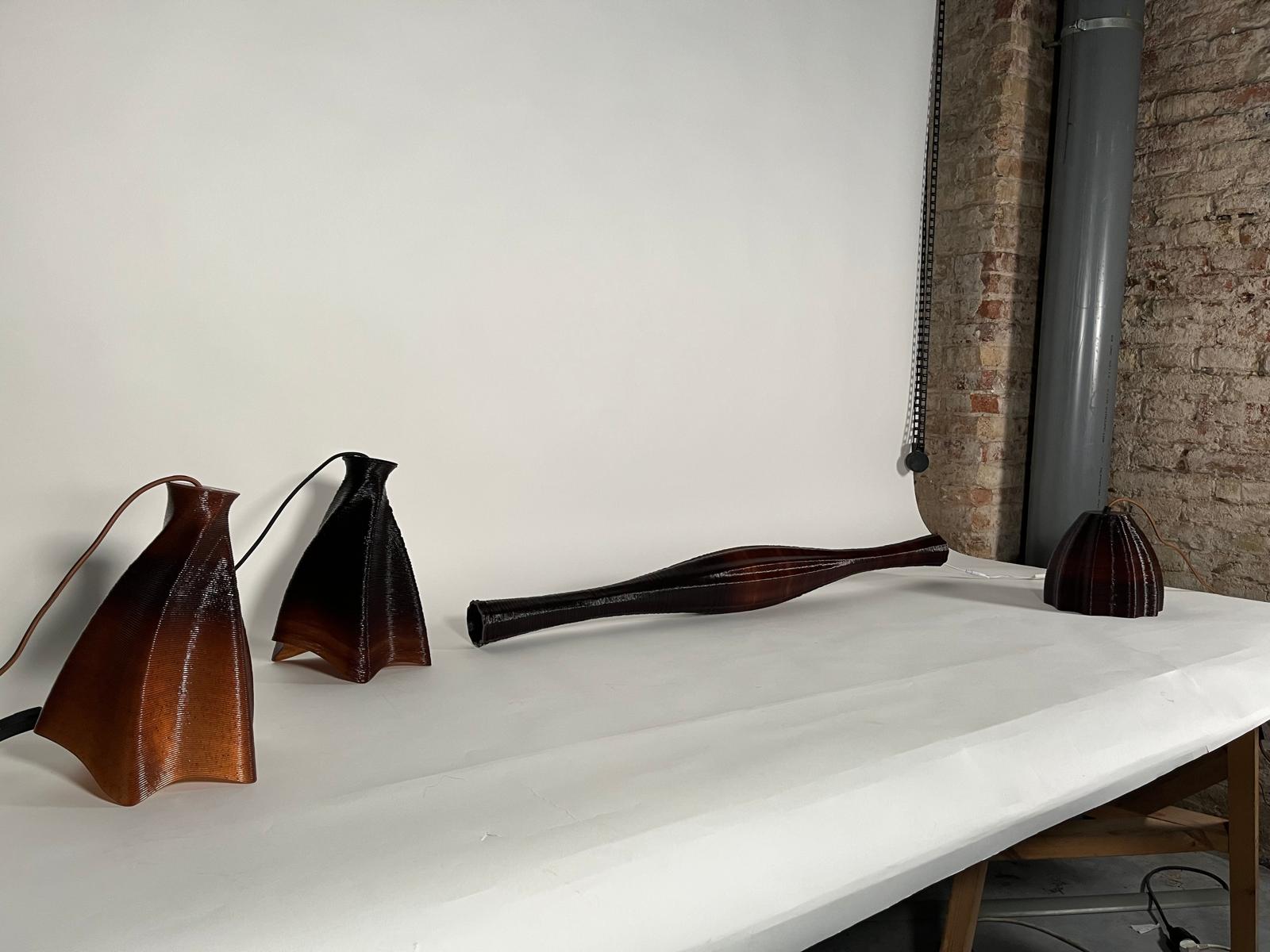
Terraweave
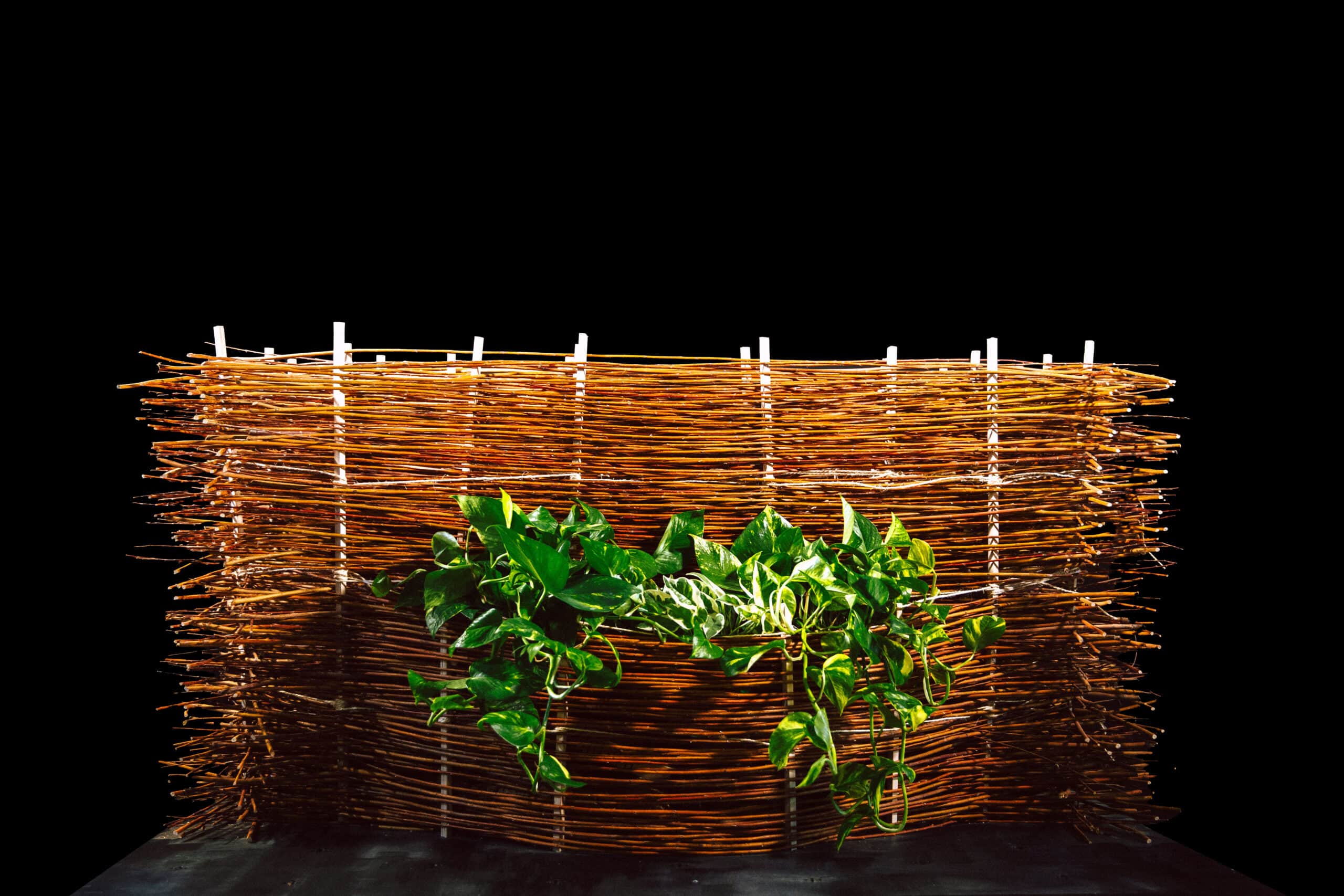
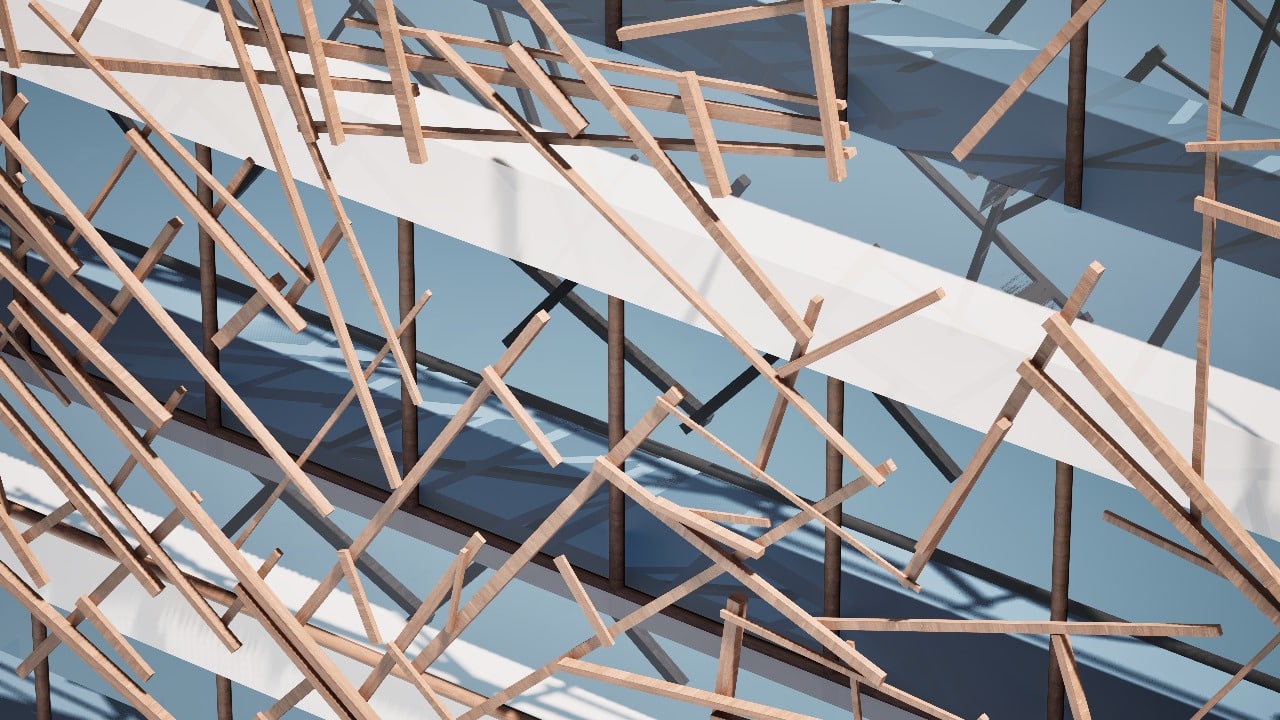
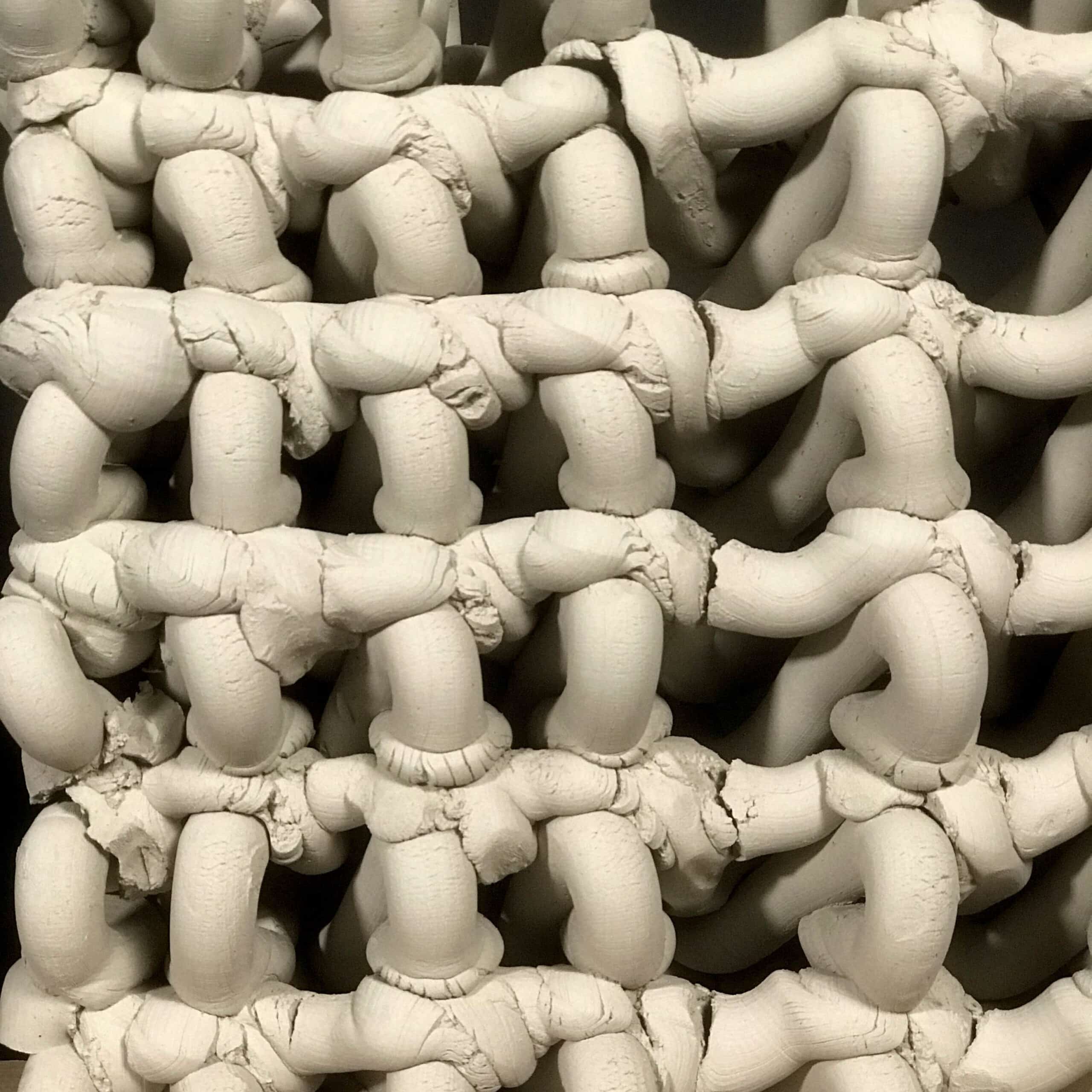
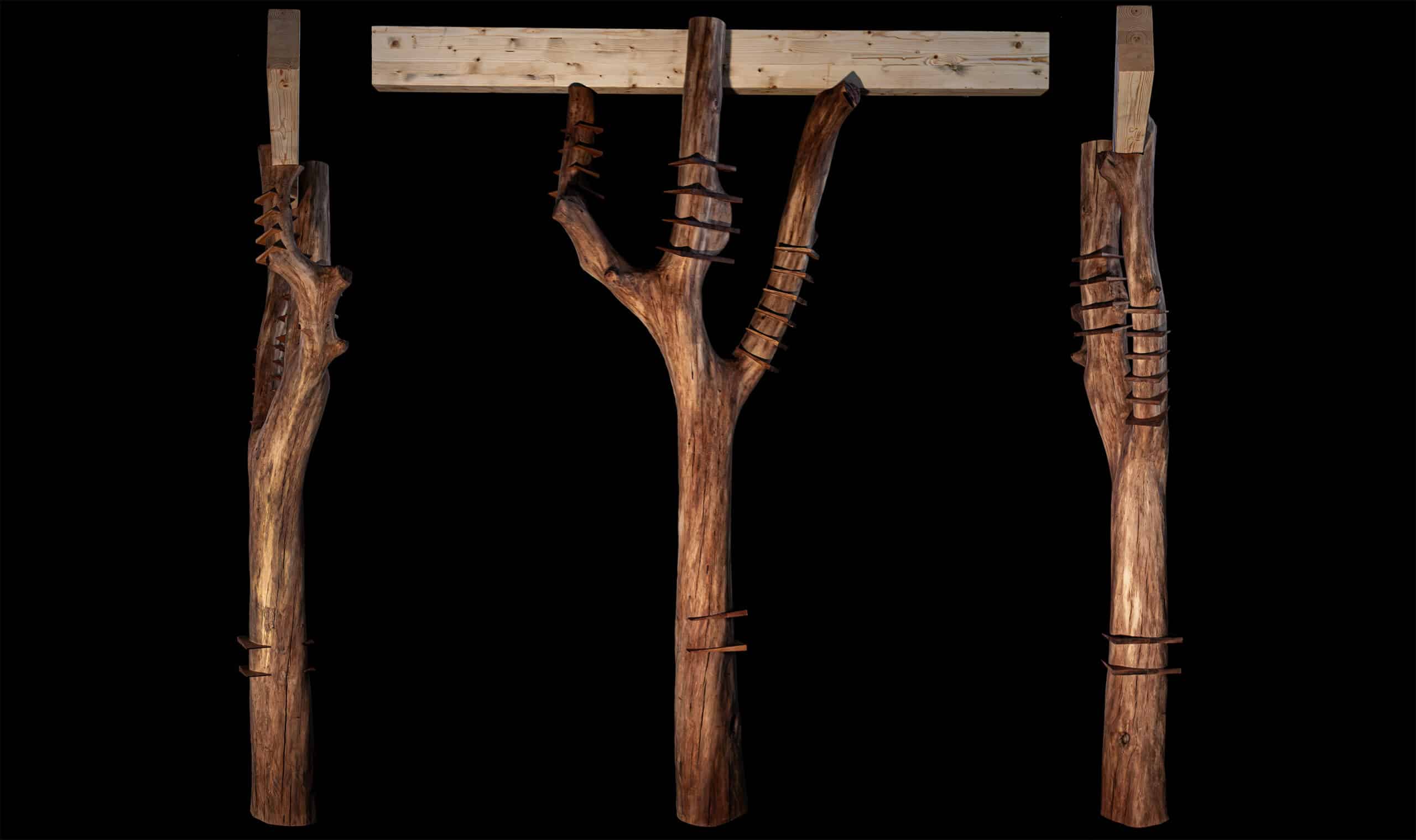
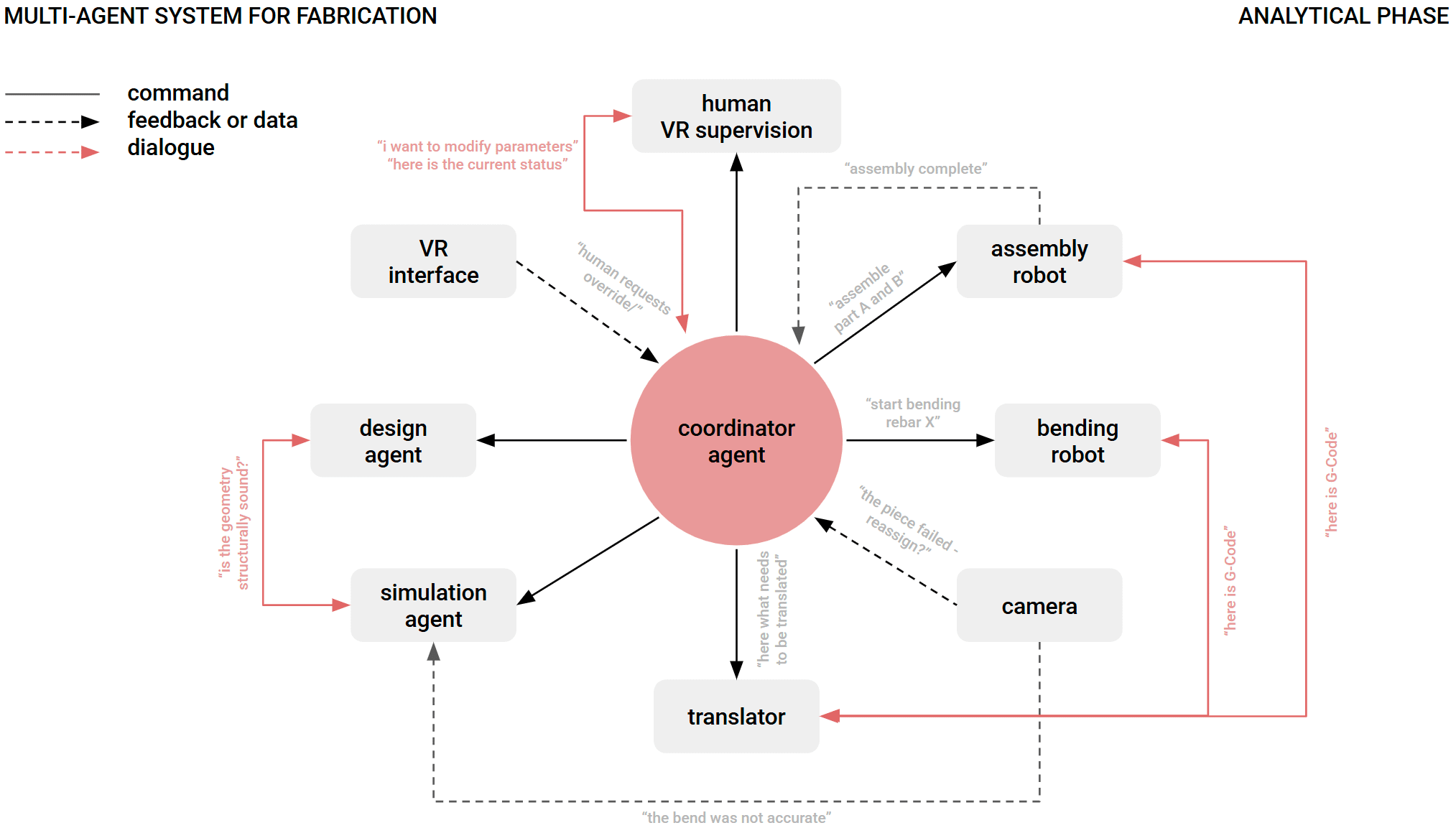
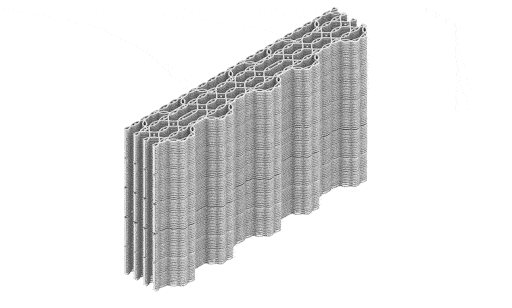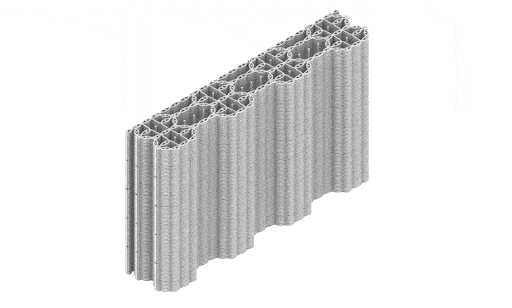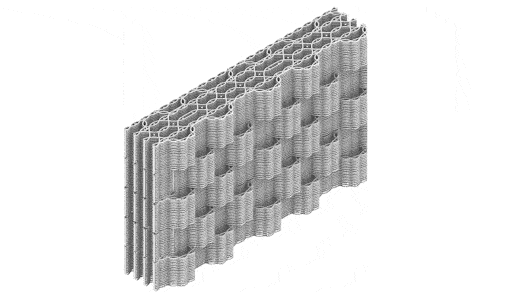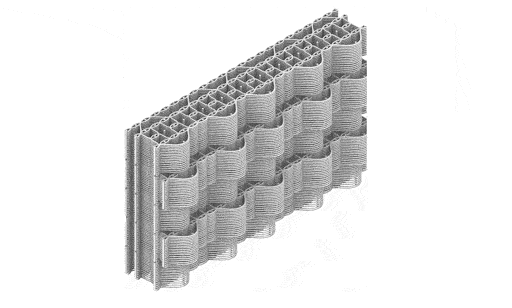
Crafting performative structures through robotic earth injection in dynamic fiber scaffolds Terraweave is an architectural research project that explores how robotic additive manufacturing can enhance the performance of natural building materials. Conducted as part of the Master in Robotics and Advanced Construction at IAAC, the project investigates the integration of willow scaffolds and earth injection … Read more