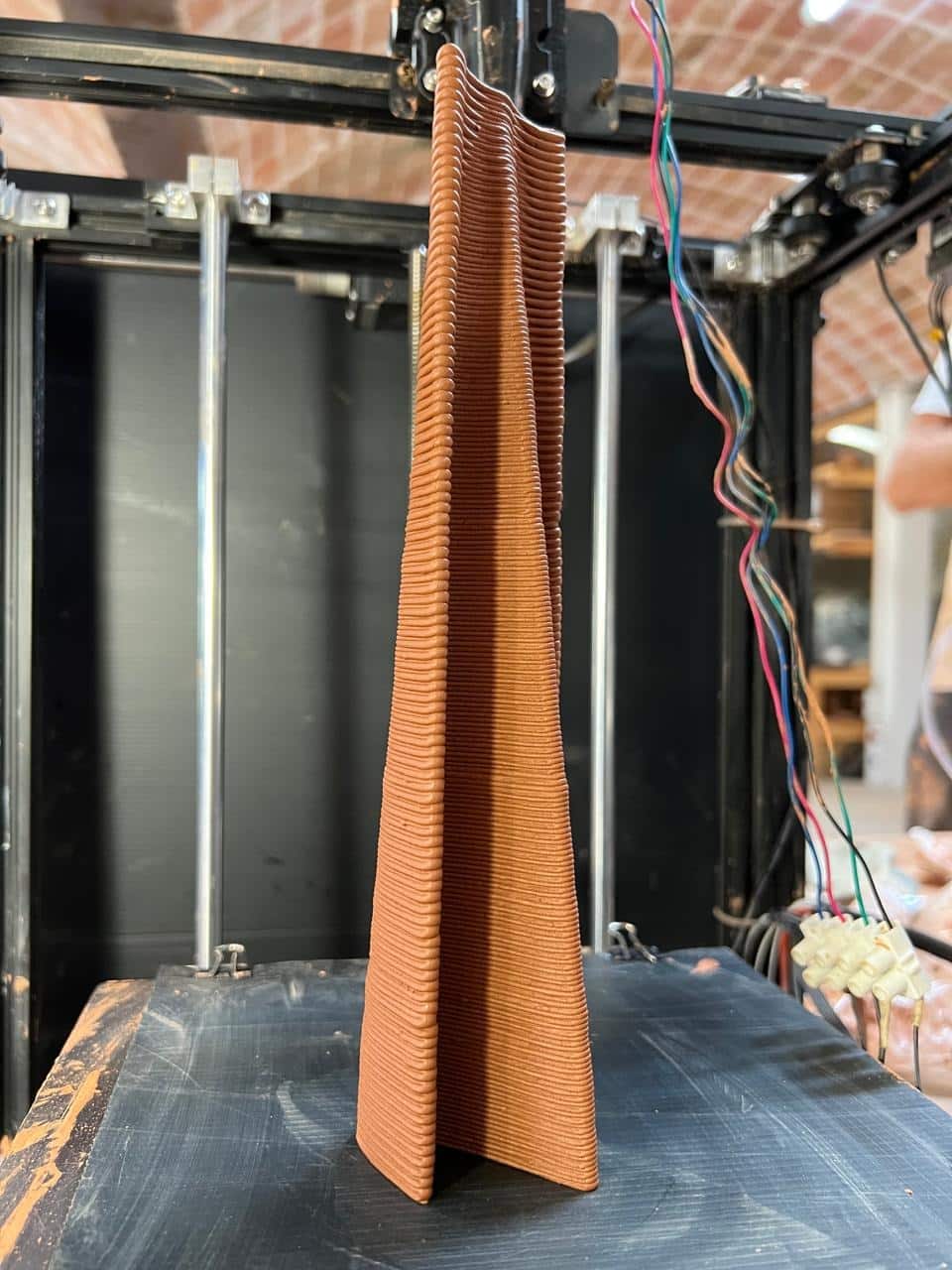
The TECHNE series is a four-week journey through the principles and practices of 3D printing with earth — from material discovery to full-scale design performance. Each week builds on the previous one, combining theory, experimentation, and digital craftsmanship to explore how computational design and material intelligence can shape the future of architecture.
Week 1: Matter – Amanda Rivera & Secil Afsar
Exploring the Materiality of Earth
The workshop begins with earth itself — a material of ancient tradition and renewed relevance. Students investigate its components, physical and mechanical properties, and how additives affect performance in 3D printing. Through testing and iteration, participants learn how to develop sustainable, high-performing earth mixes suitable for printing.
Learning Outcomes
-
Understand the sustainability potential of earth in architecture
-
Learn traditional and contemporary earthen construction techniques
-
Analyse material properties and water interactions
-
Experiment with additives, fibres, and stabilisers
-
Develop, test, and refine 3D printable earth mixes
Week 2: Machine – Secil Afsar
Mastering Additive Manufacturing Tools
This week focuses on the technology that brings ideas into form — the 3D printer. Students work across scales, from small desktop machines to large robotic systems like the WASP Crane, learning how to control and maintain these tools while refining printing parameters and materials.
Learning Outcomes
-
Master the workflow of clay and earth-based 3D printing
-
Generate and execute G-code for different printing scales
-
Calibrate and maintain 3D printers
-
Understand Cartesian and polar mechatronics systems
-
Prepare and adapt materials for both small- and large-scale printing
Week 3: Structure – Nestor Beguin & Alicia Huguet
Designing with Strength and Logic
This module examines how geometry and material interact to create structurally sound 3D printed forms. Through computational simulation and physical testing, students analyse how printed geometries behave under load, discovering how form and structure can evolve together.
Learning Outcomes
-
Understand structural behaviour in 3D printed architecture
-
Apply Finite Element Method (FEM) analysis to evaluate strength
-
Integrate structural principles into design
-
Conduct physical testing and interpret performance data
-
Build a toolkit of structural logics for future design stages
Week 4: Climate- Nestor Beguin, Xavi Aguilo, Marti Riera
Designing with Performance and Environment
The final week introduces performative design — creating geometry that responds to environmental forces. Students design a 3D printed wall that adapts to light, heat, or airflow using parametric modelling in Grasshopper, exploring how digital design can translate environmental data into architectural form.
Learning Outcomes
-
Develop 3D parametric models based on performance criteria
-
Manipulate geometry through attractor points and vector data
-
Relate form generation to climatic performance
-
Evaluate the environmental behaviour of printed designs
-
Combine computation and materiality into performative architecture