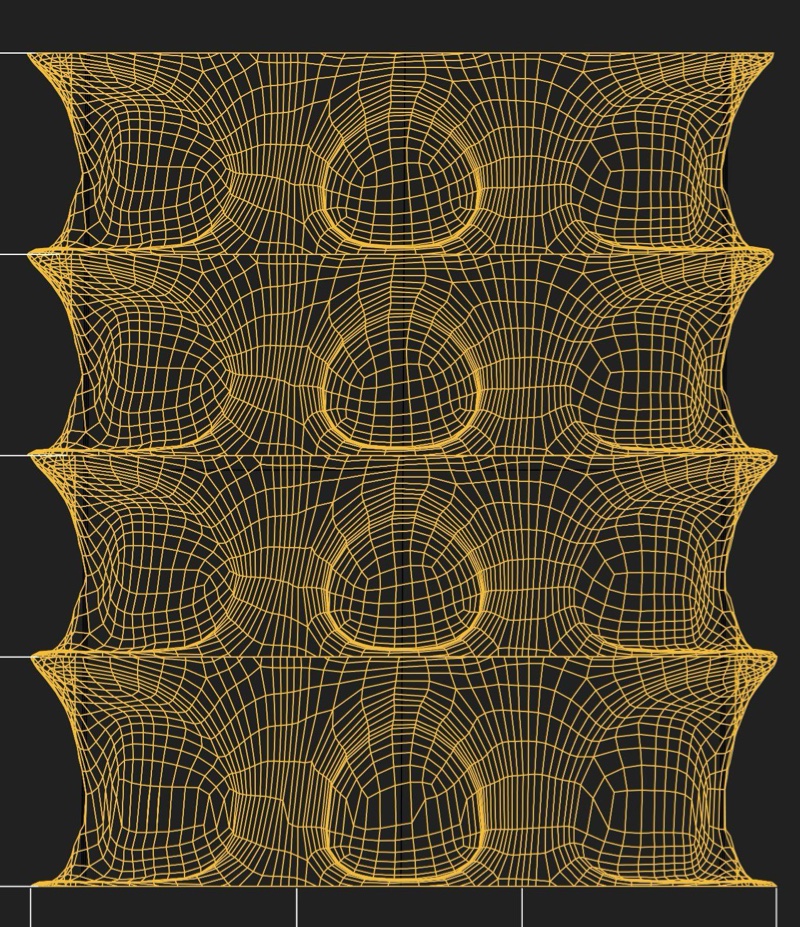
Credits: UCL
Intro Description & Structure
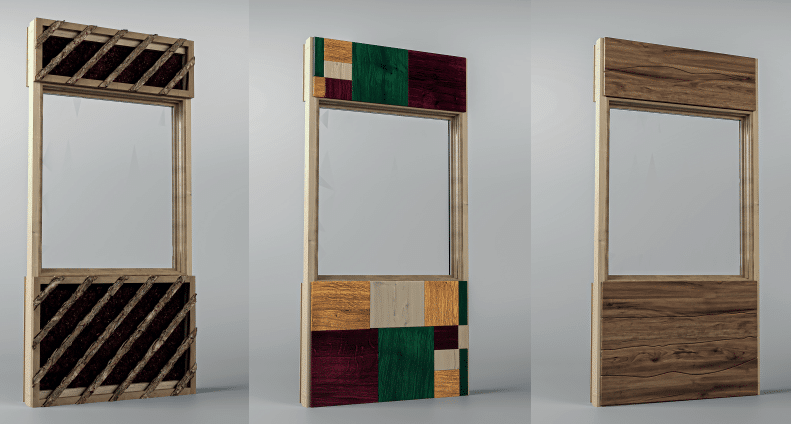
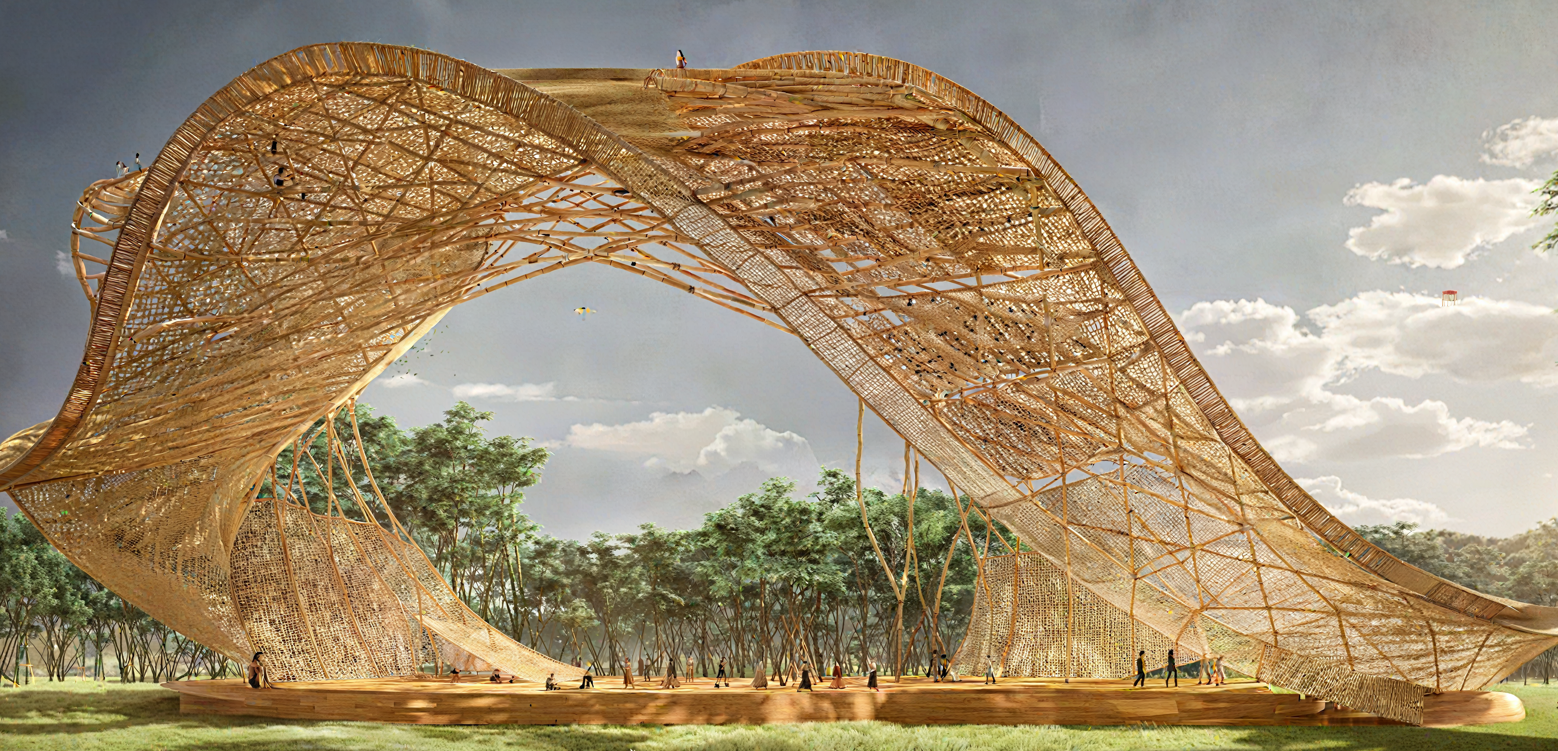
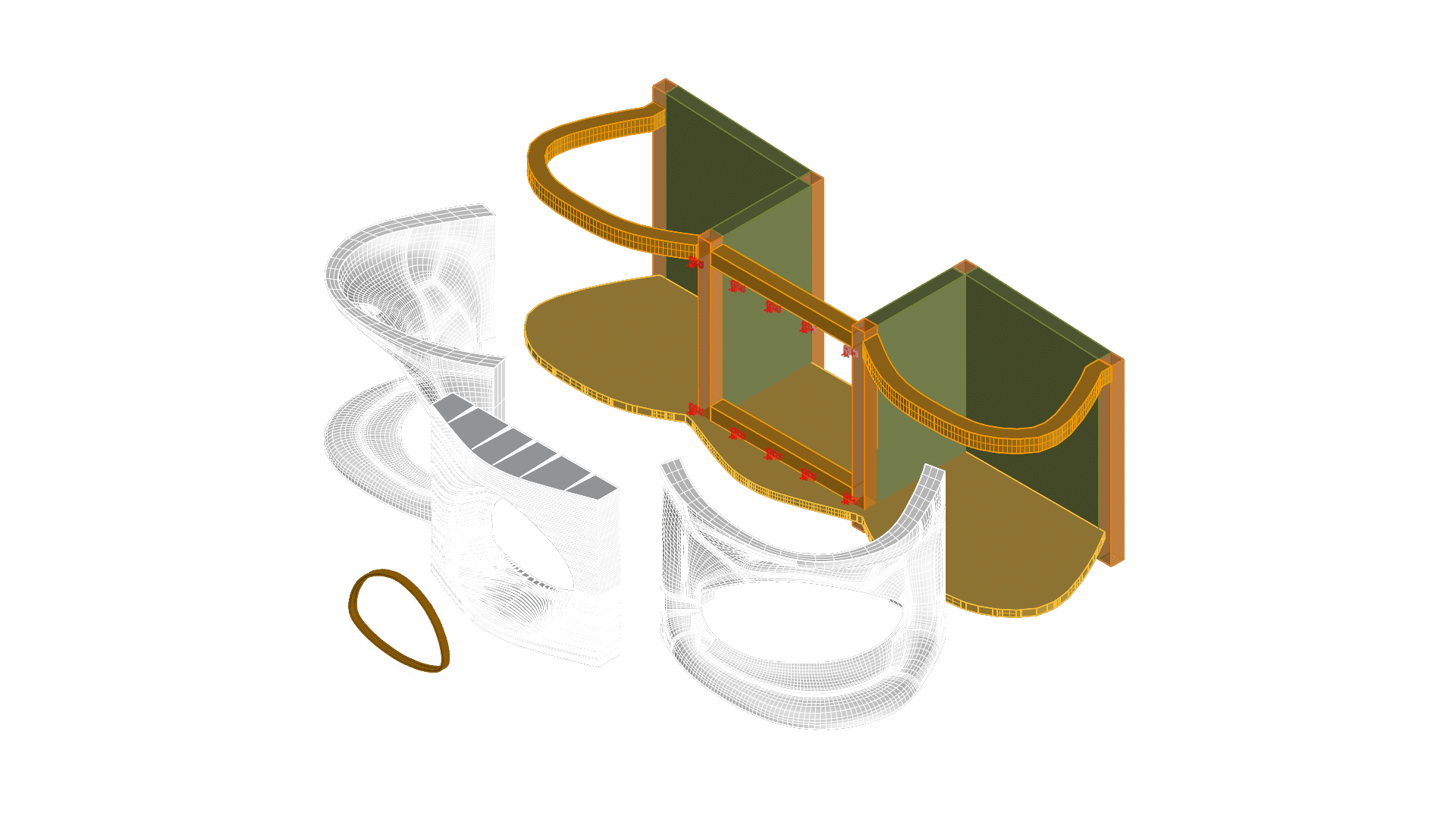
Advanced manufacturing encompasses the use of innovative technologies and methodologies to enhance the production and design of products or processes. In the AEC (architecture, engineering, & construction) sector, it specifically refers to the integration of cutting-edge fabrication technologies and methodologies into the design and construction of built environments. This offers new solutions for construction methods, design processes, and components, among other examples that involve contemporary fabrication methods. This approach leverages digital fabrication, additive manufacturing, and automation to create precise, customised and often more sustainable architectural components and construction systems.
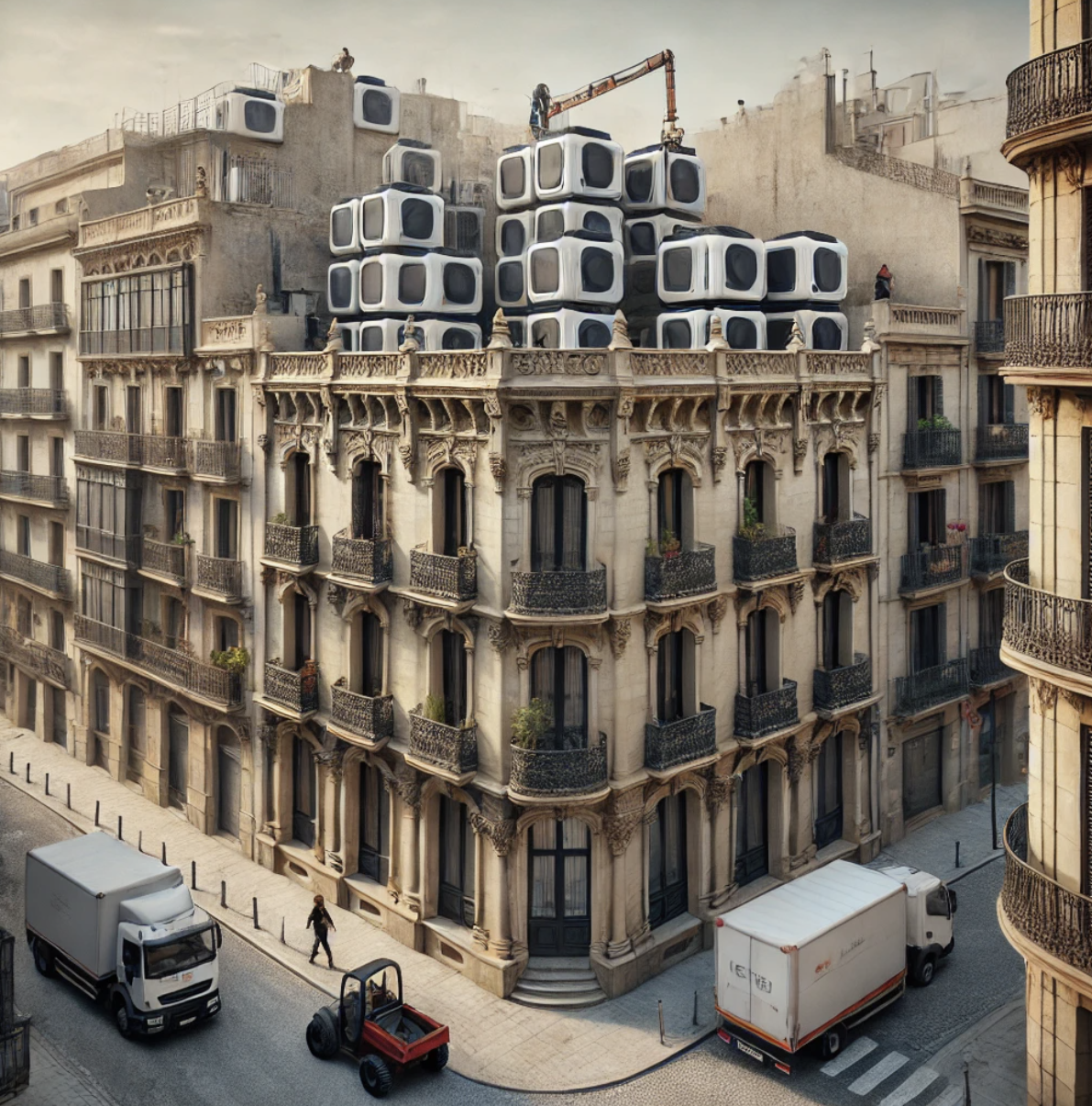
The implications of advanced manufacturing in the AEC sector go beyond the physical act of construction. It introduces a new paradigm in how professionals approach design and fabrication, problem-solving, and collaboration between agents and technology. As these technologies profoundly influence design capabilities, they also challenge traditional roles within the industry, prompting architects, engineers, and builders to embrace more interdisciplinary roles.
With the increasing adoption of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems, architects, engineers, and builders can transition from design to production seamlessly. This enables now the realisation of complex geometries, innovative material formulations, and structures that were previously challenging to construct. The integration of these technologies with the current architecture and construction reality will remain a fundamental aspect of the construction industry’s future, and an important aspect of the cluster.
MAA02 marks the first time students are faced with the challenge of research with their own agendas, besides the required knowledge of the state-of-the-art that frames their individual research projects and common practices in research studios, students of the advanced manufacturing cluster will be required to gain knowledge and expertise in the following areas:
- Fundamentals of the research frame: Gain knowledge of the principles and methodologies of advanced manufacturing and its relevance to contemporary architectural practice, linking and agglutinating them in a coherent framework.
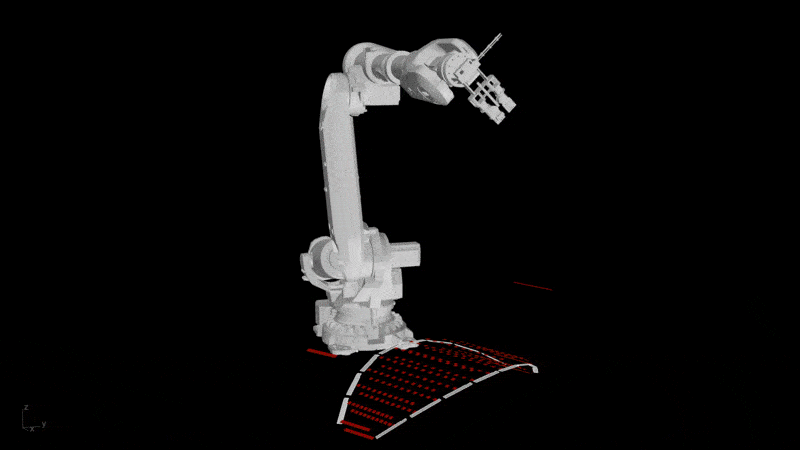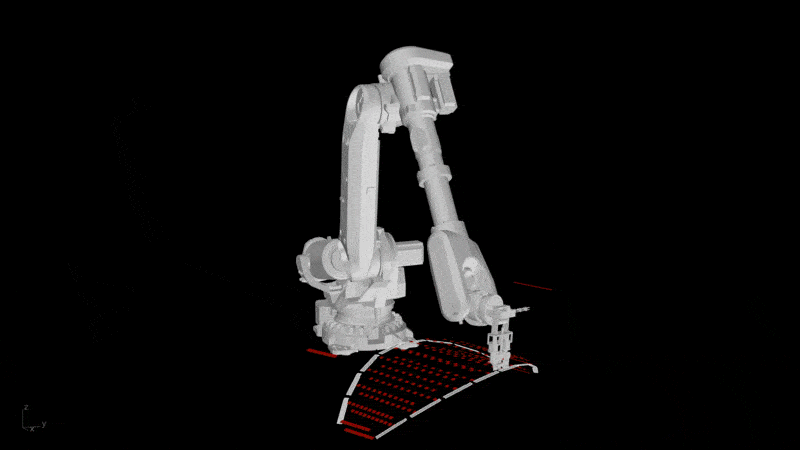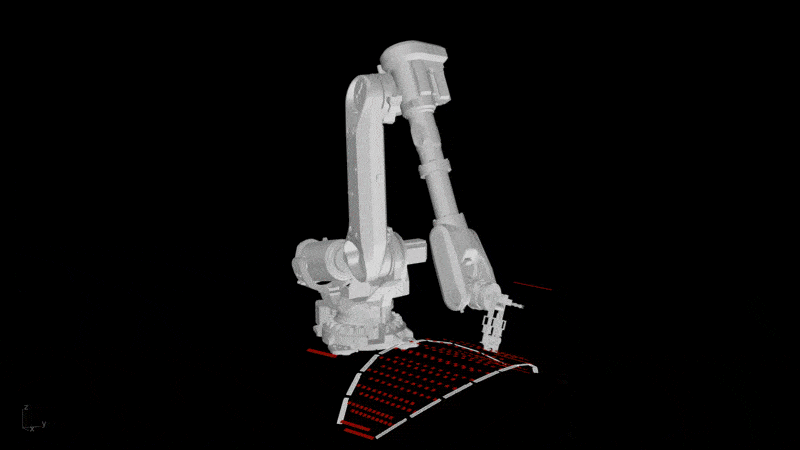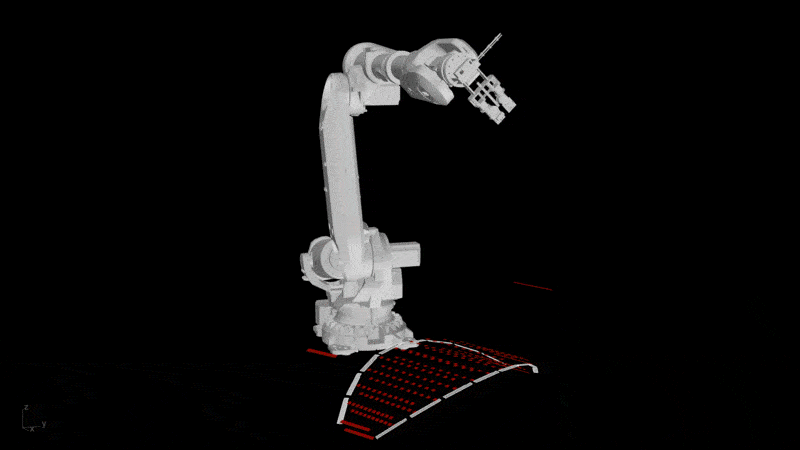
- Digital Proficiency: Expand previous knowledge in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) tools for developing digital workflows and simulations and a general understanding of their role in the design-to-fabrication workflows.
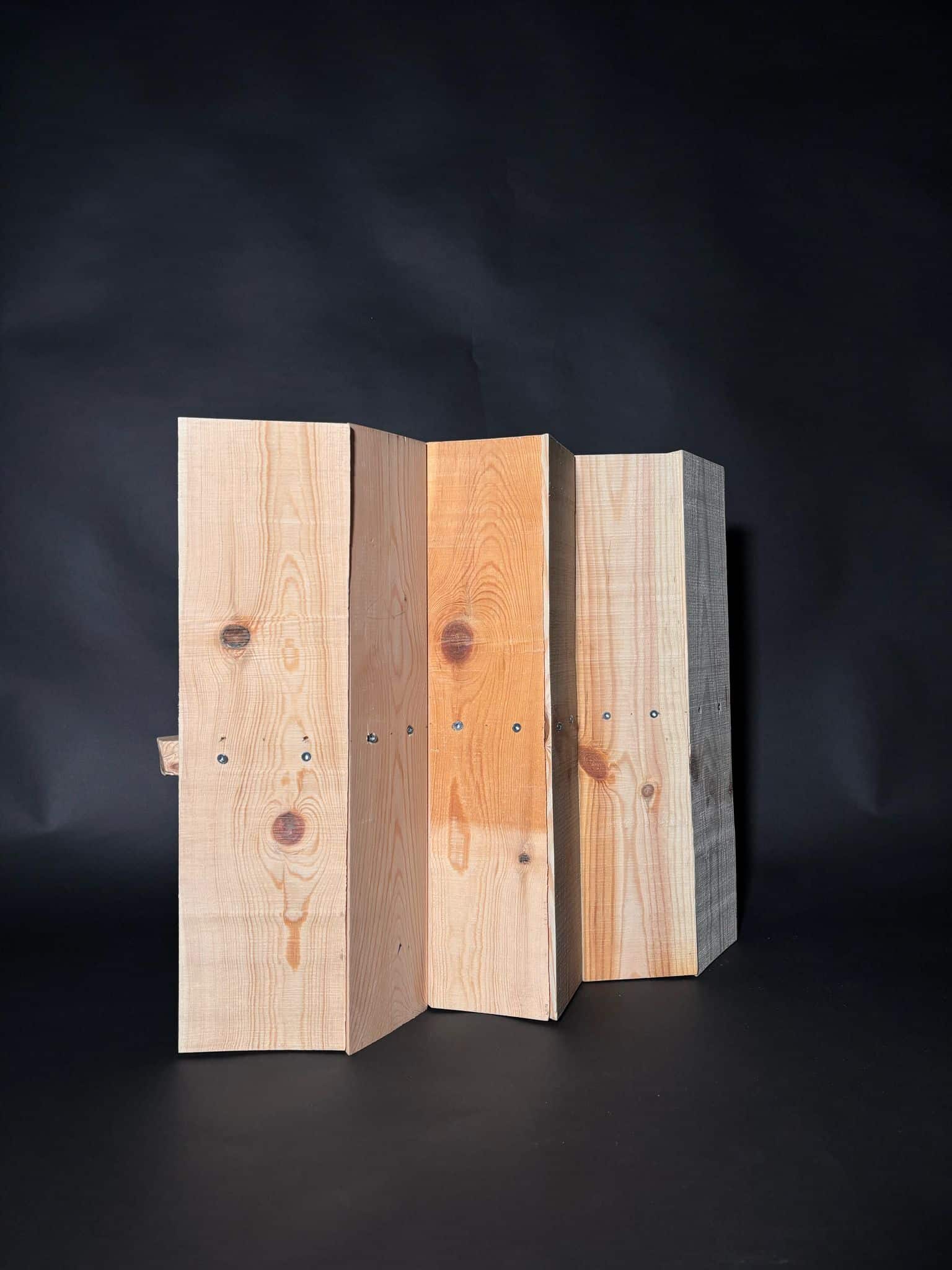
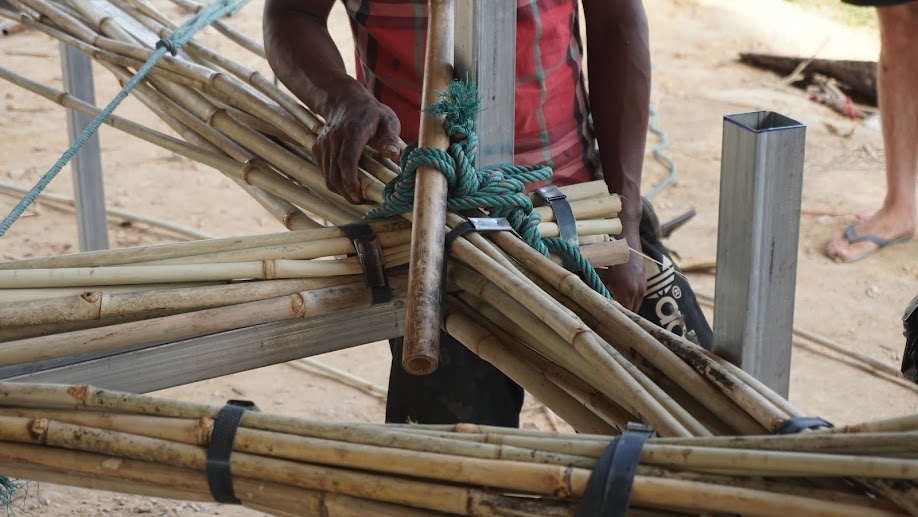
- Material Exploration: Investigate and understand the properties, potentials, and limitations of the materials that will be used in their research projects.
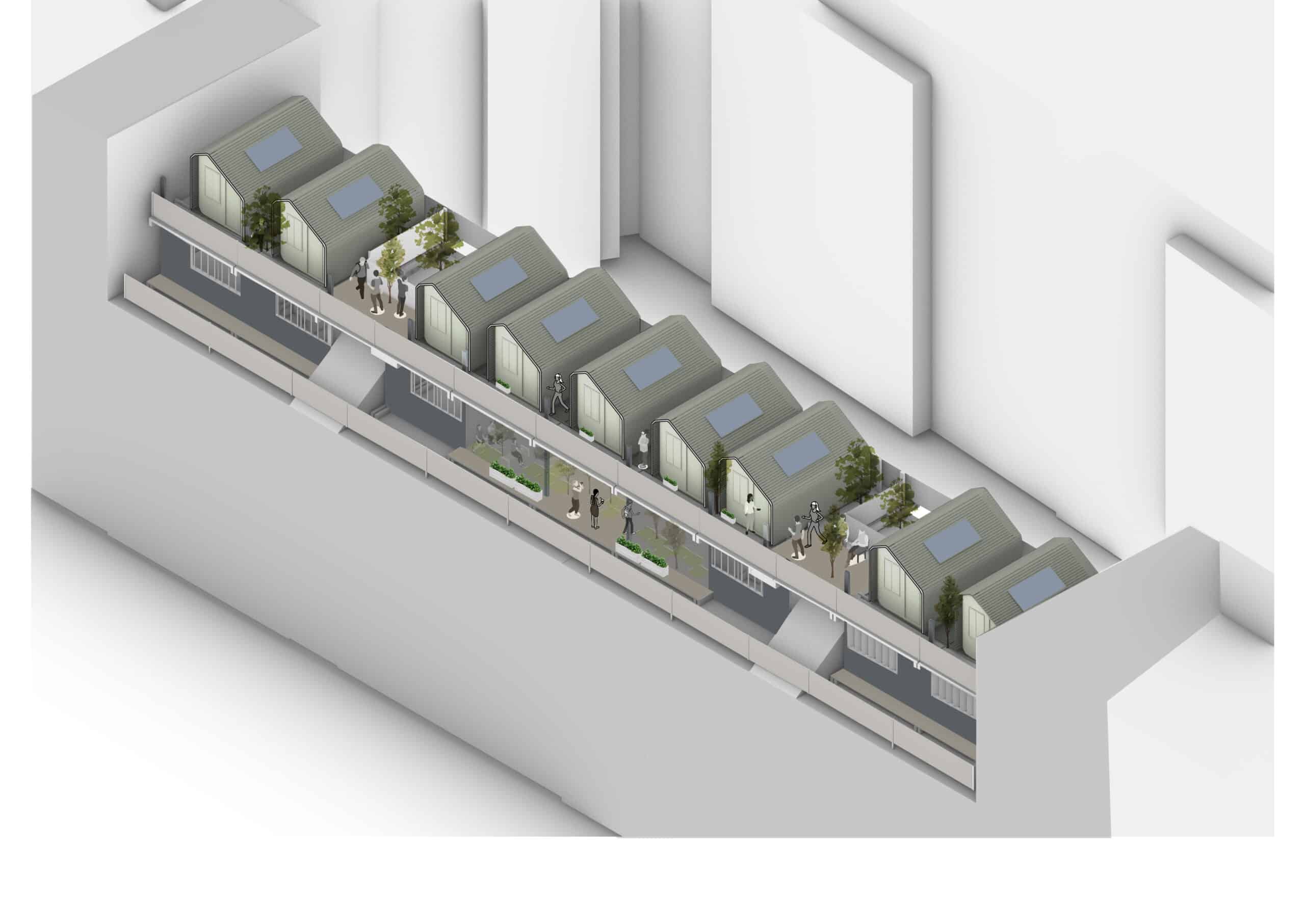
- Design for Manufacturability: Learn to design architectural components with manufacturability in mind, considering factors like material constraints, fabrication methods, and assembly logistics and transport.
- Sustainability and Efficiency: Recognize the potential of advanced manufacturing for sustainable architectural practices, including waste reduction, efficient use of resources and recycling and repurposing of architectural components.
- Fabrication Problem-Solving: Develop the ability to leverage fabrication techniques to address complex challenges posed by the design and manufacturing of components.
- Future Trends and Research: Create a research framework that will have the ability to evolve and expand according to present and future research.