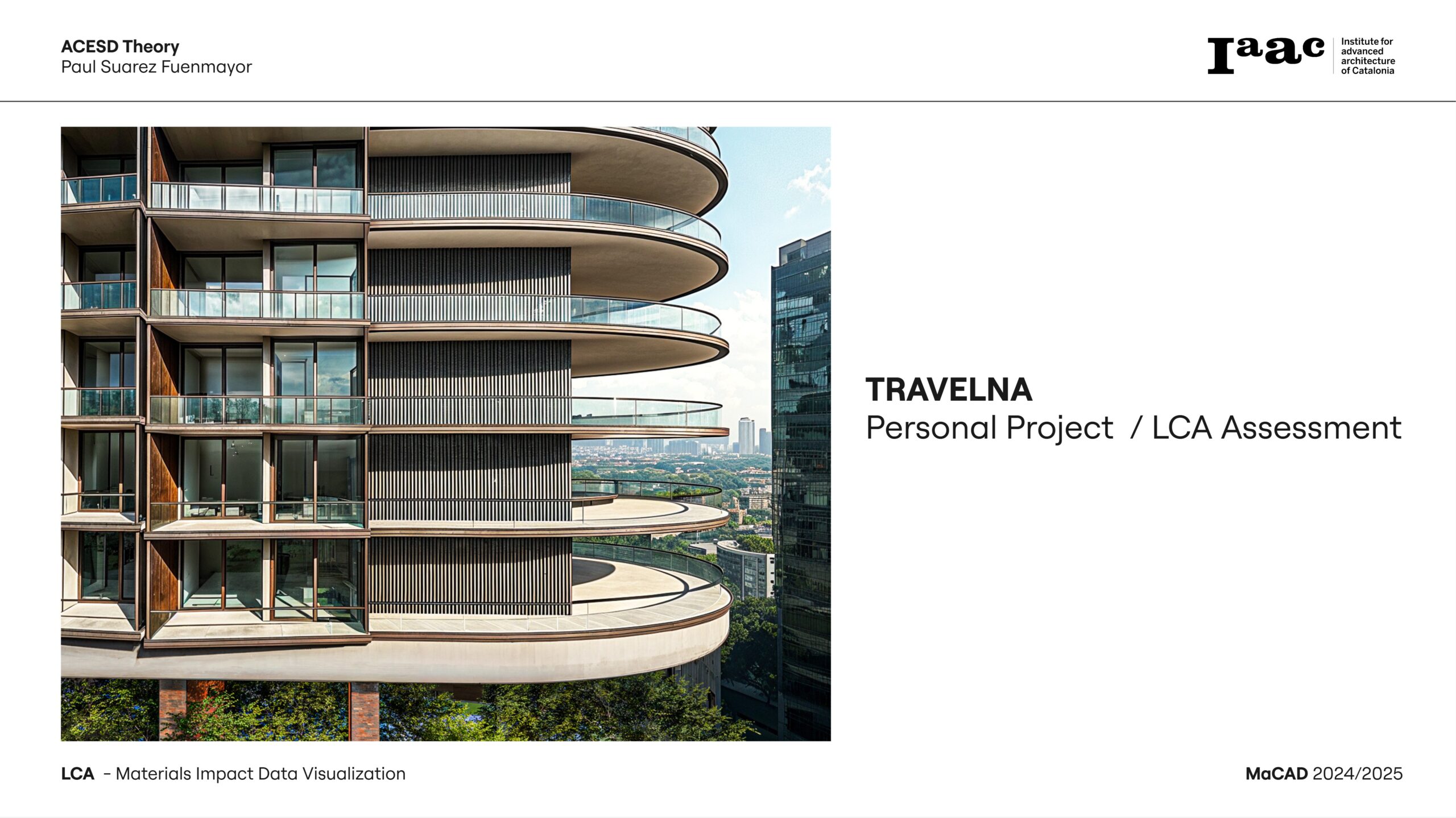
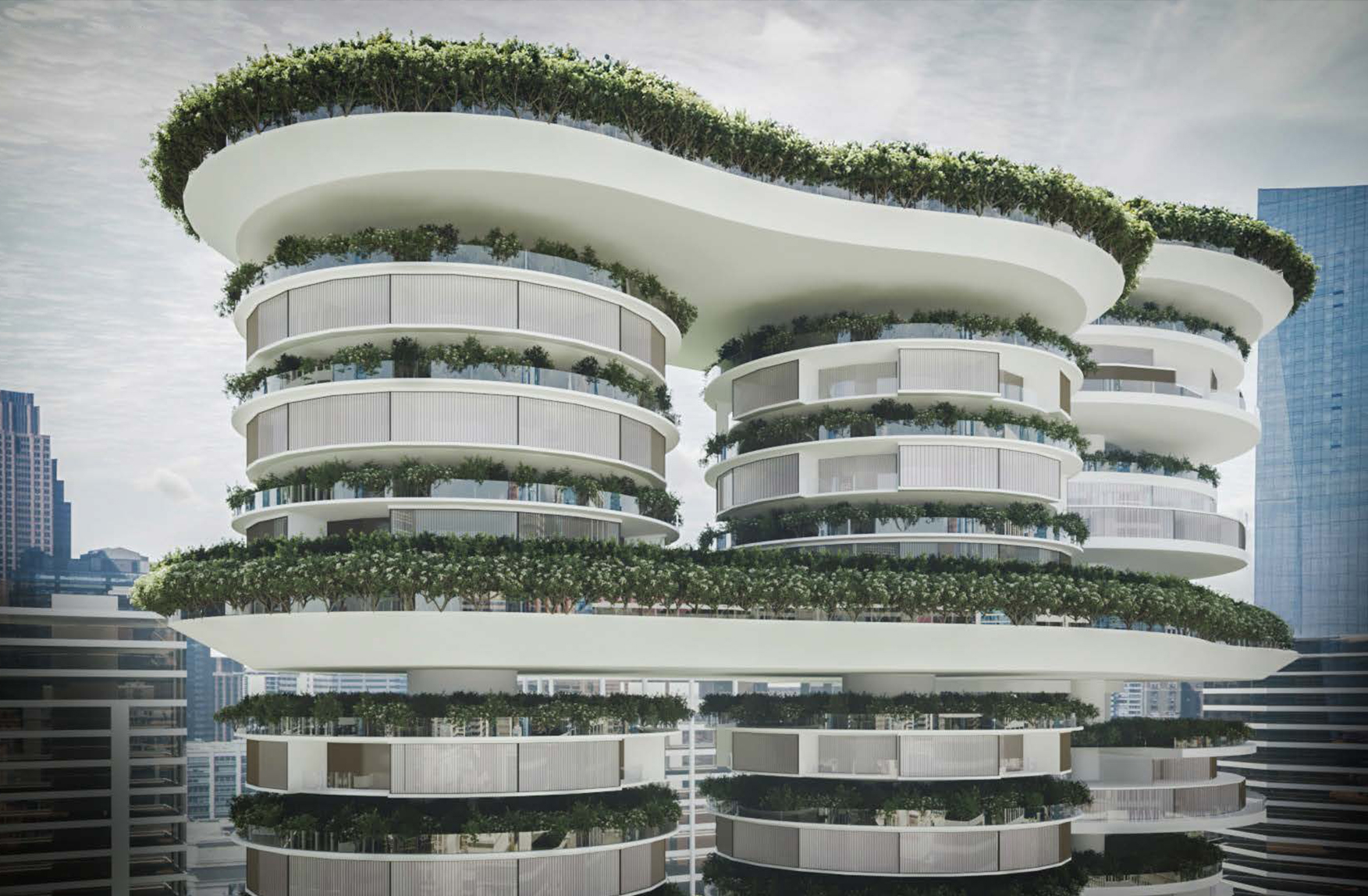
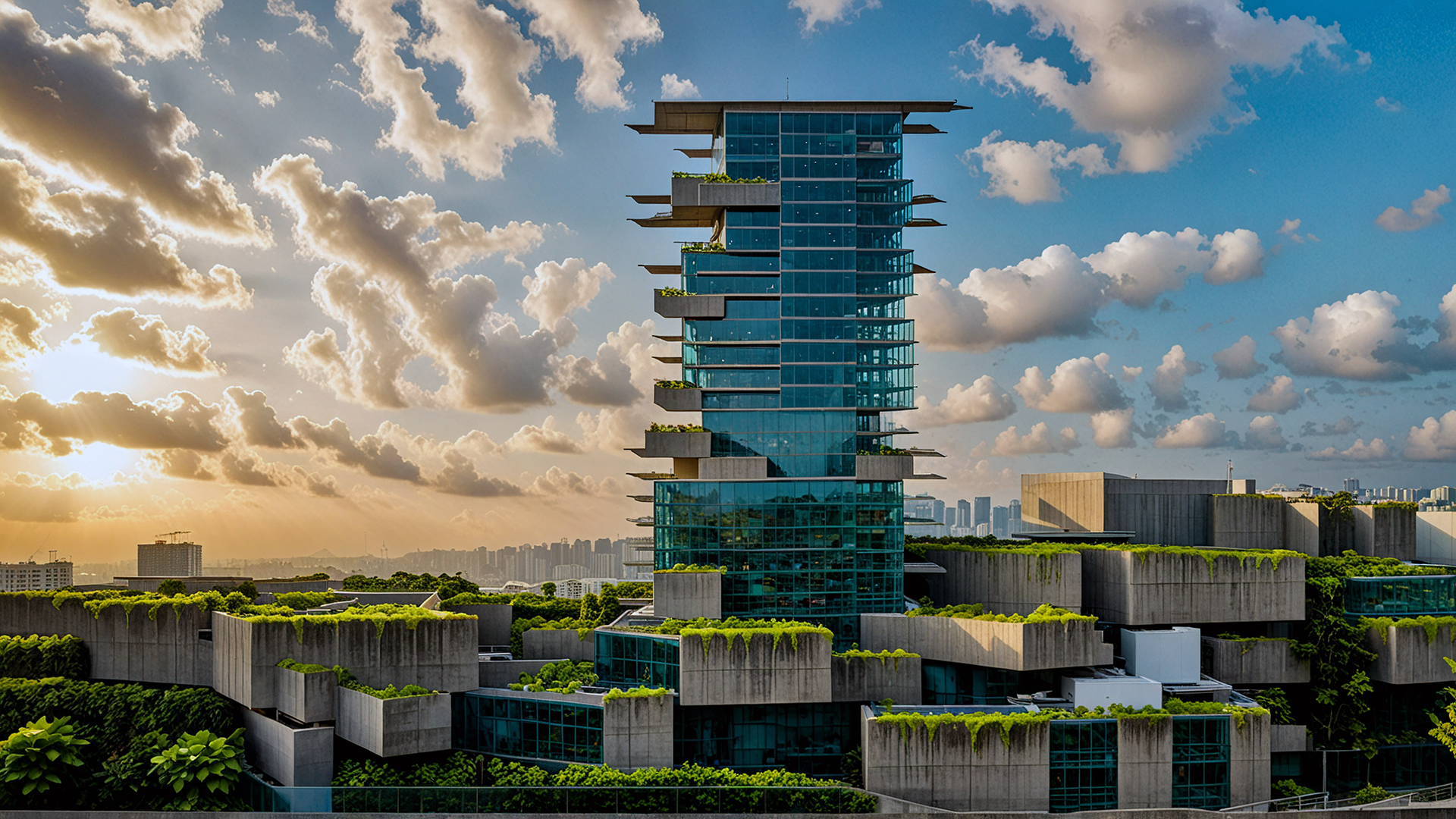
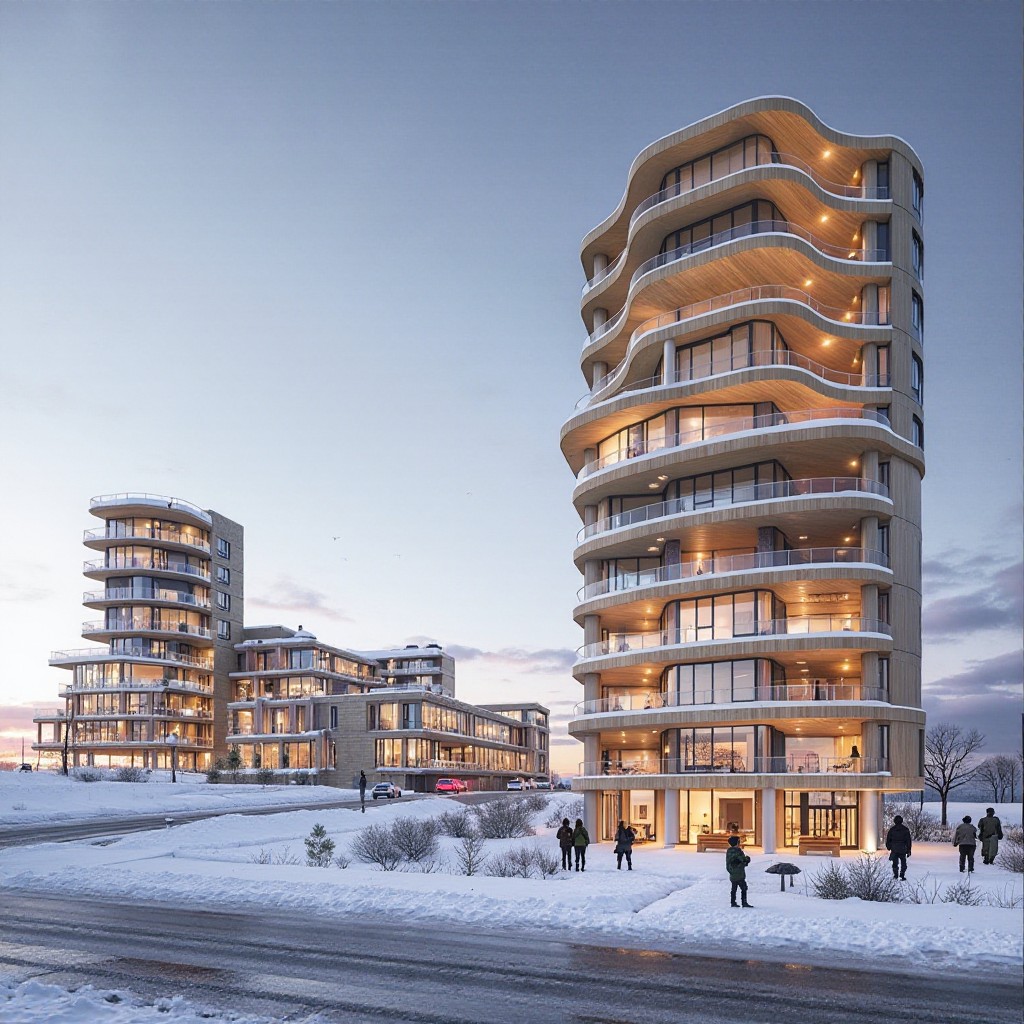
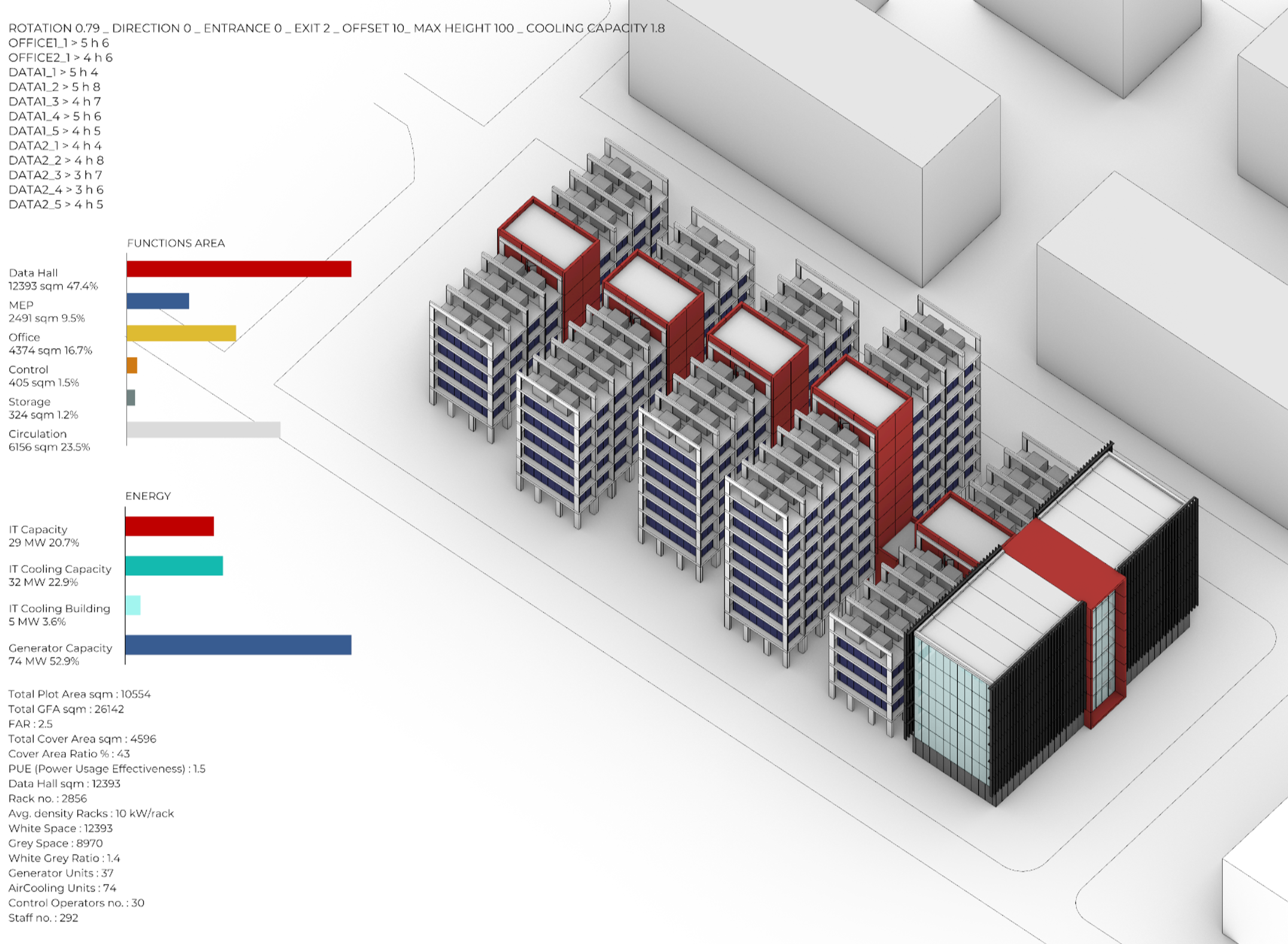
Advanced Manufacturing Transfers: from environmental impacts to industrial implementation
MaCAD ACESD THEORY SEMINAR
Source: XtreeE
The ACESD Theory seminar aims to provide students with means of assessing the environmental impact of their design practice, with a focus on the role of advanced manufacturing tools in such impacts. The Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA) method is introduced relying on standard European regulations. The changes brought about in the construction industry by the resort to advanced manufacturing technologies is tackled relying on five case studies. Each case study focuses on a specific environmental impact, illustrating the notion of impact transfer core to digital practices environmental evaluation.
The course guides students through these issues by means of a theoretical course combined with a series of exercises in which the conditions of industrial implementation of cutting edge advanced manufacturing techniques are interrogated.
The seminar sessions will present lectures, case studies, discussions and associated readings to support the students learning process and formulation of their own new design practices.
Learning Objectives
The course aims to offer the following learning objectives:
- Memorise the fundamental notions of life-cycle assessment for the built environment.
- Explain the particulars of life-cycle assessment for advanced manufacturing.
- Identify specific relevant impacts for advanced manufacturing LCA case studies.
- Apply to a personal design project.