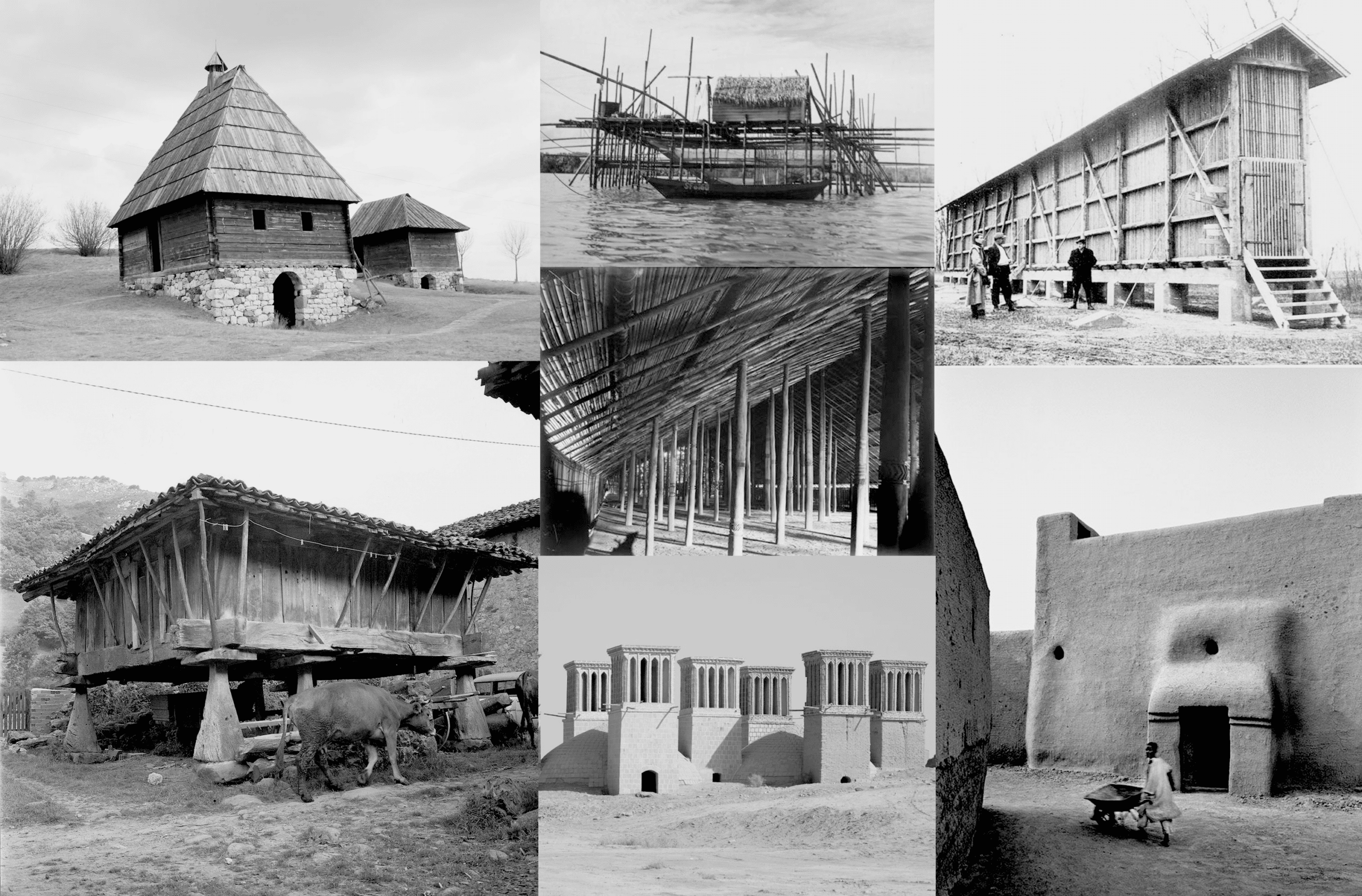
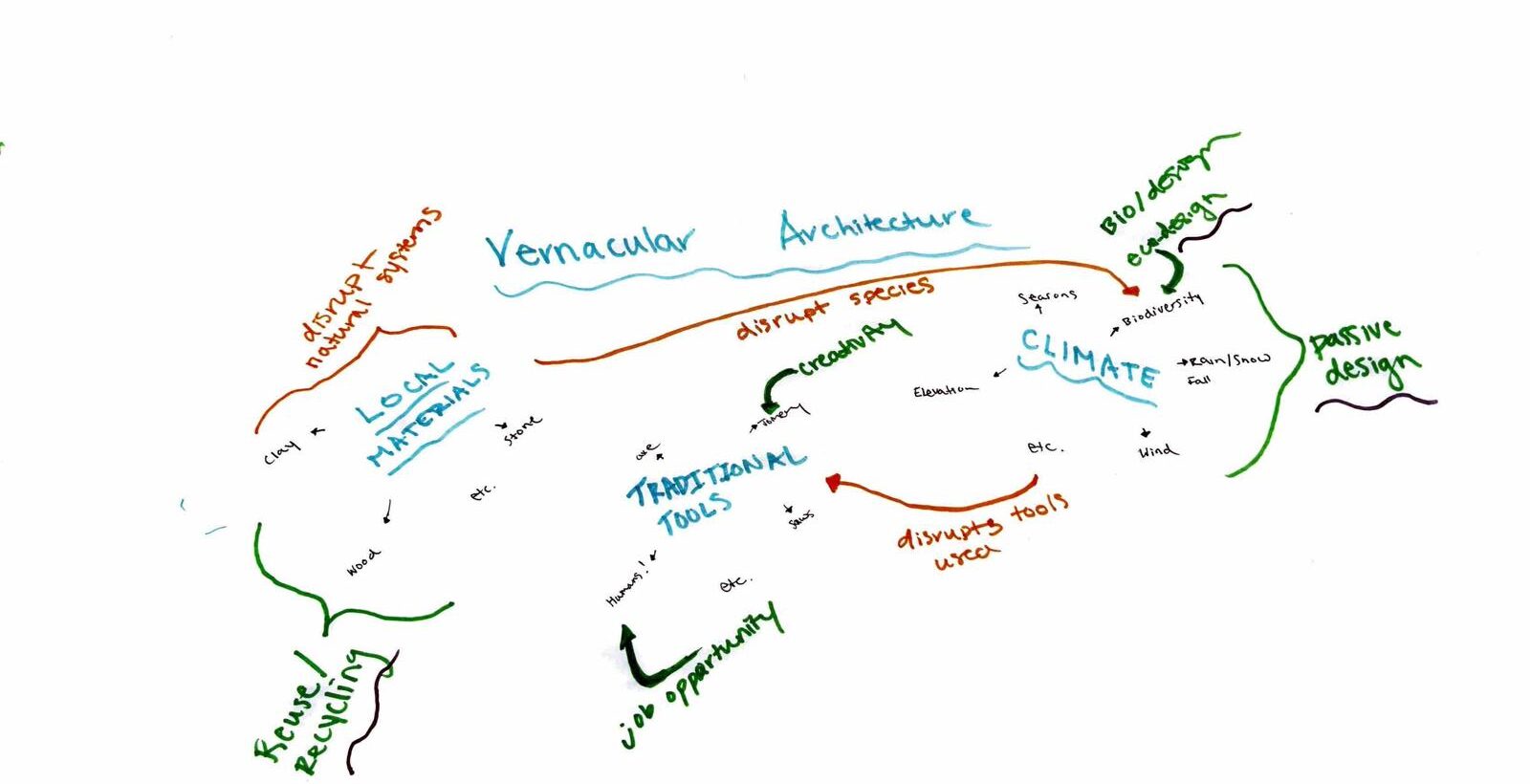
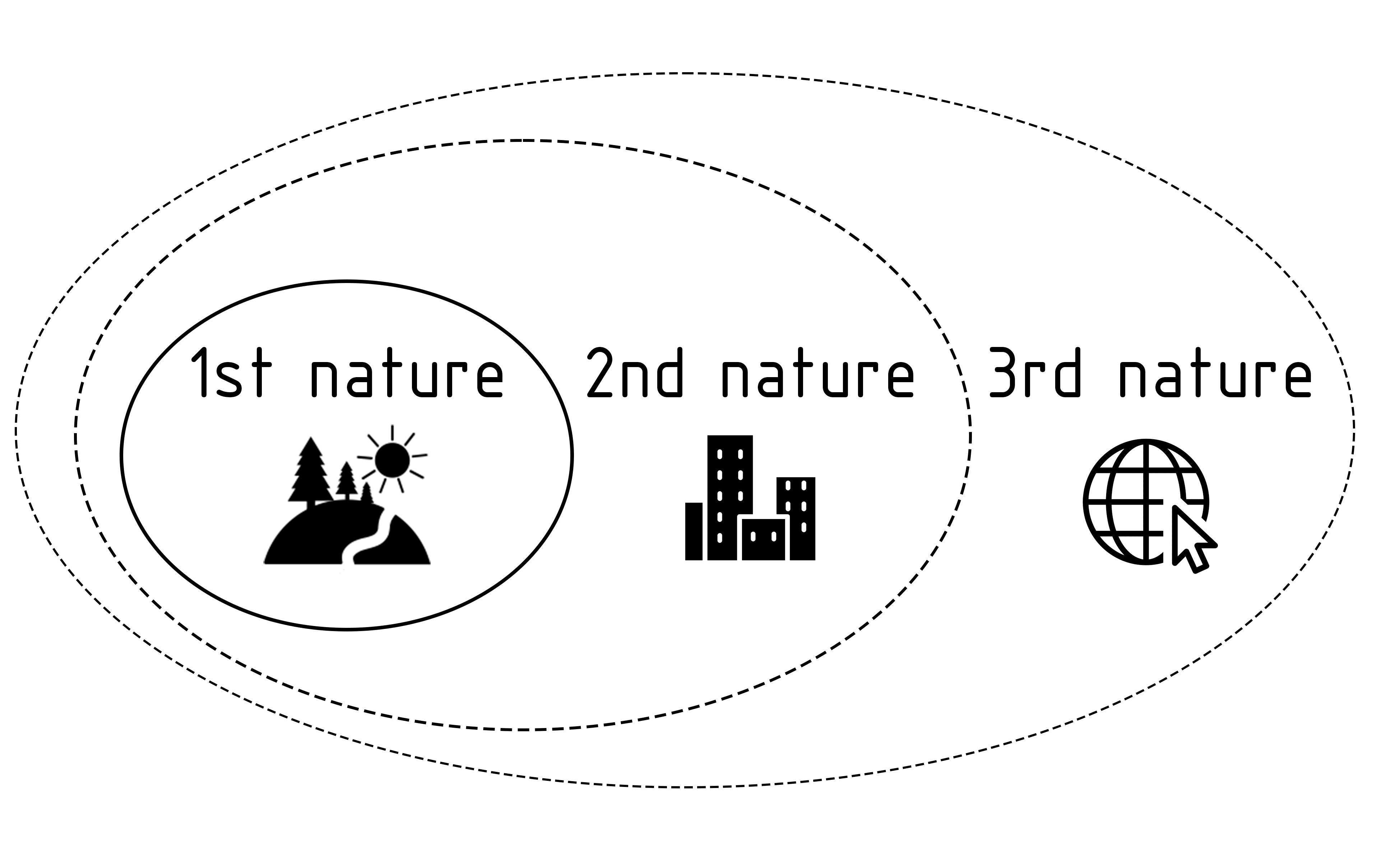
The goal of the Masters in Advanced Ecological Buildings and Biocities is to encourage students to adopt a more ecological approach, but this ideal notion of ecology needs to be individually considered. In fact, the definition of ecological design, sustainable design, or green design needs to be regularly contested and debated by architects and designers. The design of human ecosystems has immense consequences for the environments we operate in, and the advent of climate change has forced modern culture to acknowledge this fact. As architects and designers, we assume responsibility for understanding what actions our designs have on their context.
Through a process of ecological thinking, we seek to connect different worlds and scales into a conception of what it means to design ecologically. Ecology is defined as the relation between organisms and their environment, but there is no necessarily positive or negative connotation associated with acting ecologically. The power of ecological intelligence lies in its ability to transcend scale or species and understand a broader network of actors, entanglements, and relationships. Recent trends in architecture and urban design have introduced radical simplification driven by mechanical infrastructures inspired by the industrial revolution. Since then, complex webs of nature have been increasingly subjugated by the forces of industrial growth and development, leaving behind immense waste and destruction. By thinking ecologically, we can make meaningful connections between decisions made by architects and designers and the effects they have on the externalized environment.