This seminar will serve as an introduction as to how subtractive manufacturing methods, such as 3-axis CNC machines and 6-axis industrial robots, equipped with various wood cutting, and computational design tools can be used to translate digital designs to physical prototypes.
CNC milling is widely applied in manufacturing for precision parts, furniture production, prototyping, and standardized workflows where speed and accuracy are prioritized.
Similarly, robotic milling offers higher precision, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex geometries that would be time-intensive or impossible by hand. However, it lacks the intuitive, adaptive knowledge of a craftsperson and requires upfront digital planning.
It is most effective for large-scale components, non-standard geometries, and processes requiring flexibility in tool orientation. Designing for robotic milling involves anticipating material behavior, tool accessibility, and integrating robotic constraints into the design from the start.
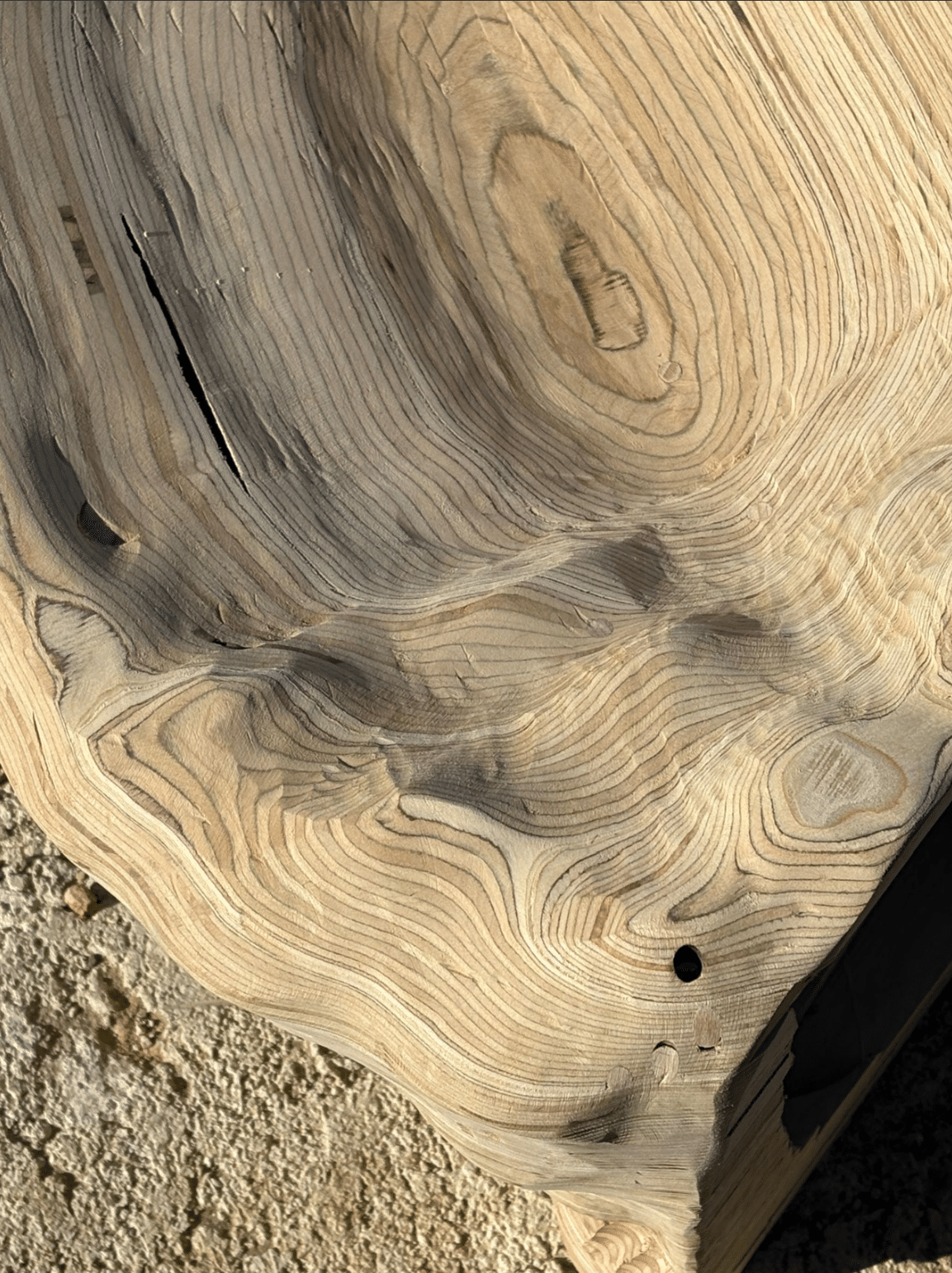
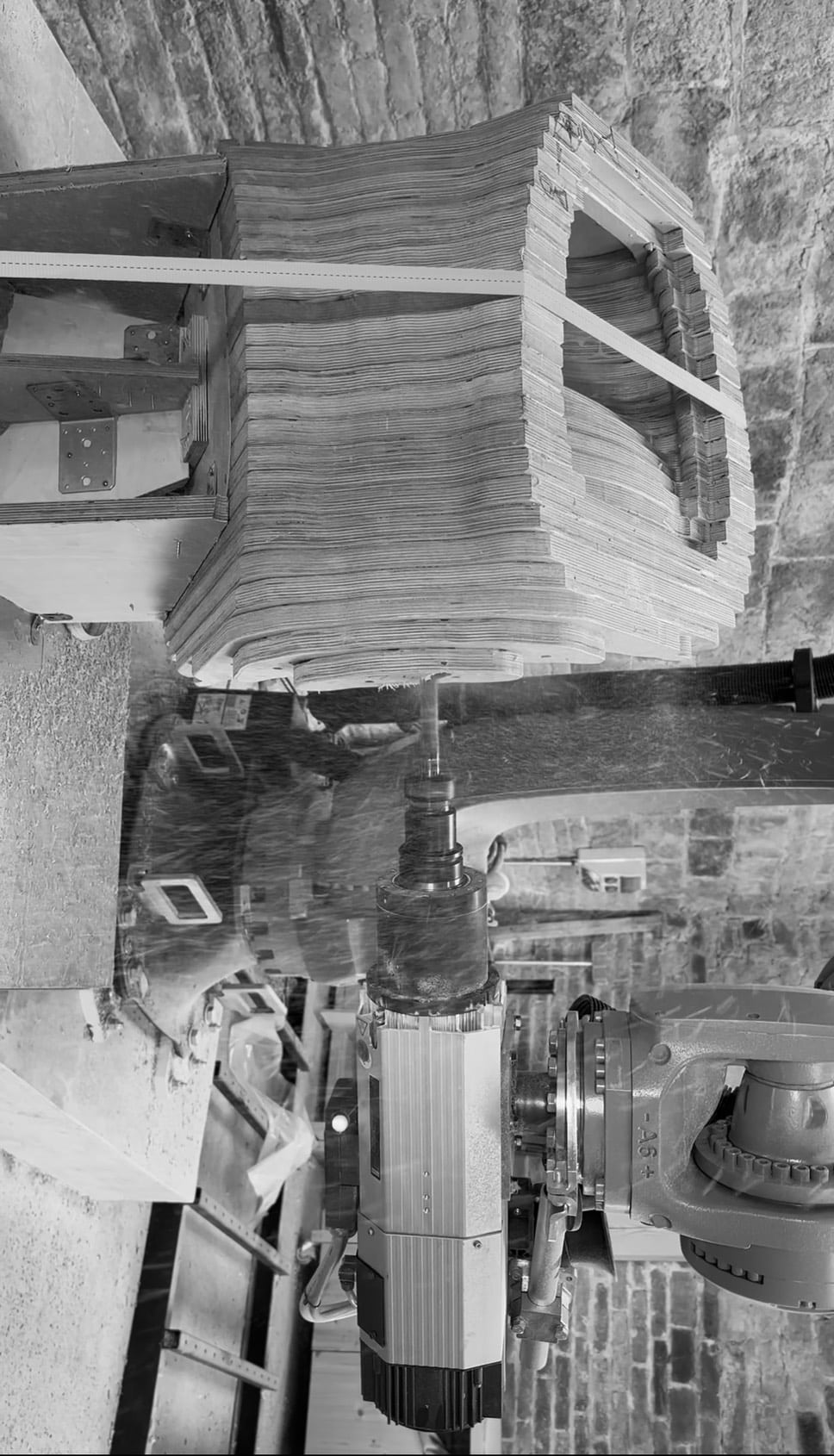
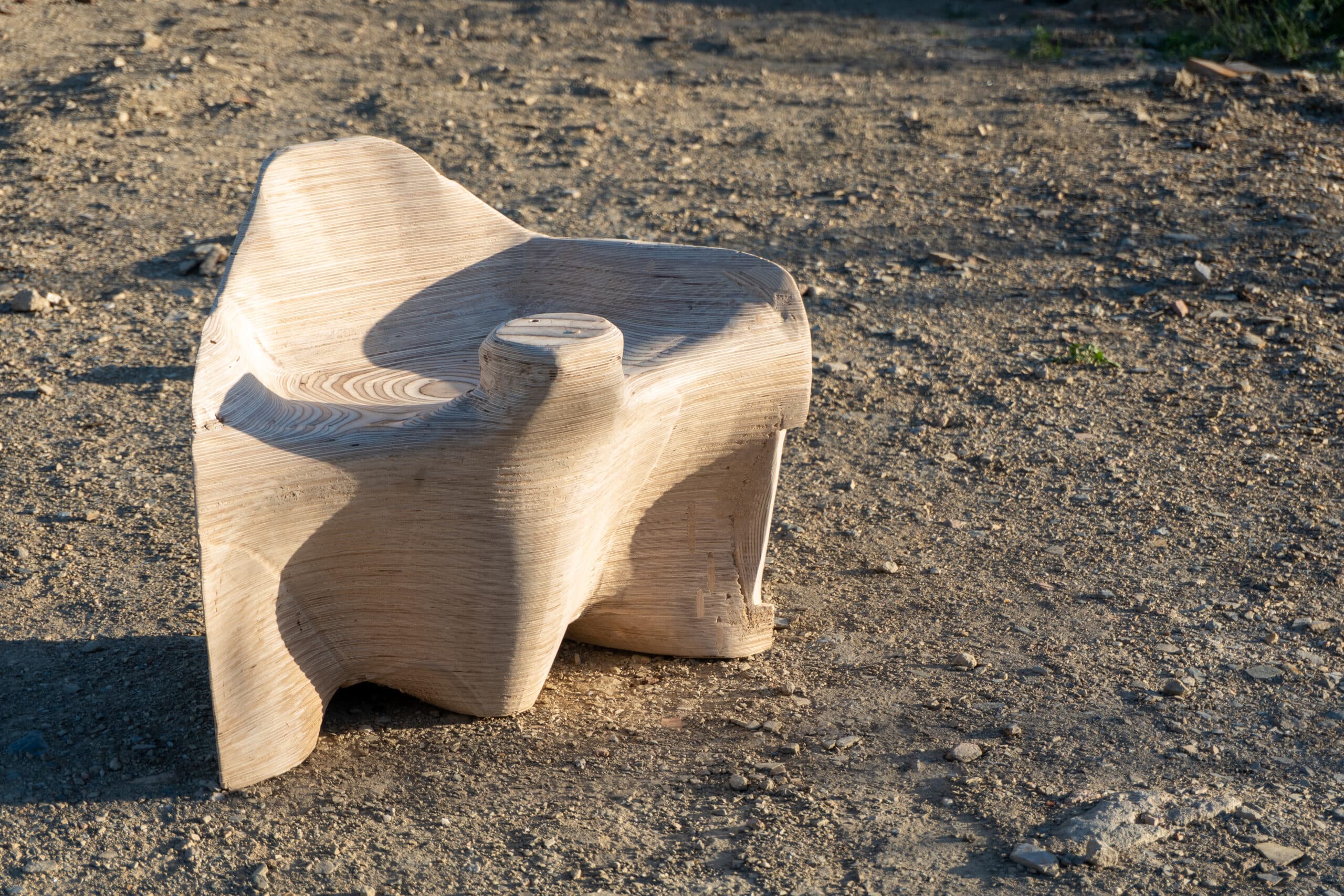
To address these challenges and opportunities, this workshop will explore a hybrid workflow combining 3-axis CNC milling and 6-axis robotic milling. Participants will first employ a 3-axis CNC machine to produce the rough contours of a geometry through the stacking of plywood layers, approximating the desired form. This stage focuses on understanding toolpath generation, material efficiency, and geometric translation from digital to physical form.
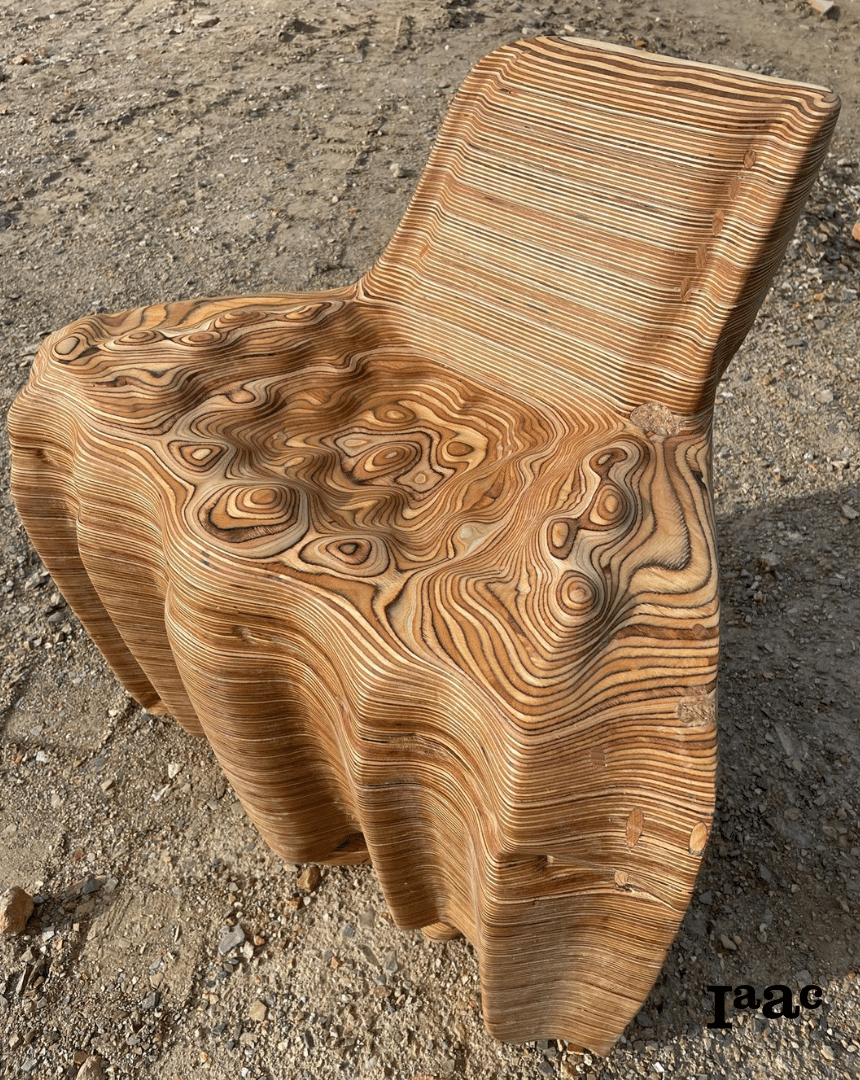
In the second phase, the 6-axis robotic milling process will be used to perform finishing operations on the assembled piece. By taking advantage of the robot’s full kinematic range, including its external rotary axis, participants will refine the surface geometry and achieve smooth, continuous forms that would be difficult to produce with conventional methods. This phase will emphasize robotic toolpath planning, calibration, and adaptive machining strategies.
Through this two-step workflow, students will gain an understanding of how different subtractive manufacturing processes can be combined to balance speed, precision, and material expression in digital fabrication.