A critical map of the industry, its shortcomings and pathways for technological innovation.
Syllabus


The Master in Robotics and Advanced Construction prepares a new generation of interdisciplinary professionals who are capable of facing our growing need for a more sustainable and optimised construction eco-system, with a focus on the emerging design and market opportunities arising from novel robotic and advanced manufacturing systems. While the Digitalization in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) sector is slow due to significant challenges in technology adoption 1, a number of advanced technological applications have emerged in recent years, within the research realm with a few making their way onto the market. This comes in an effort to respond to increasing housing demands, the need for an increased speed in construction, the adoption of a more complex architectural design language and unstandardized applications, all while aiming for an (EU) economy with net-zero greenhouse gas emissions.2
To date, the built environment requires vast amounts of resources and accounts for about 50% of all extracted material. The construction sector is responsible for over 35% of the EU’s total waste generation. Greenhouse gas emissions from material extraction, manufacturing of construction products, as well as construction and renovation of buildings are estimated at 5-12% of total national GHG emissions, and the building sector remains a major contributor to energy consumption and CO2 emissions in the European Union (EU), accounting for 40% of energy consumption and 36% of energy-related emissions.3
The Applied Theory course hence aims to develop a critical reflection on the role of technology in the sector, it’s more relevant applications, while giving the MRAC students access to the front runners of this multidisciplinary field, who, through a master class format, share the challenges and learnings of their professional engagements in real case applications. Applied theory is therefore a platform where the students have direct contact with professionals from diverse areas of expertise, furthering their formation and knowledge towards their own personal development in research, the industry and the professional realm in general.
Learning Objectives
The course is furthermore oriented towards the development of students´ critical thinking capacities, engaging the students in a series of debates, questioning diverse approaches and possible outcomes, as well as the development of conclusive outputs. Through a dynamic mapping of construction technologies, processes and their diverse applications in the construction sector, students will gain insights into industry needs and the utilisation of the knowledge gained throughout the MRAC, building towards propositive and innovative visions for practice along the three central topics of the Master Programme: Materialising with Machines, Scanning and Learning Machines, Human-Machine collaboration.
- Develop students’ critical thinking capacity by engaging them in a series of master class lectures with robotic experts.
- Learn to extract key concepts from a discussion and elaborate it in writing a manifesto highlighting technology use in today’s built environment.
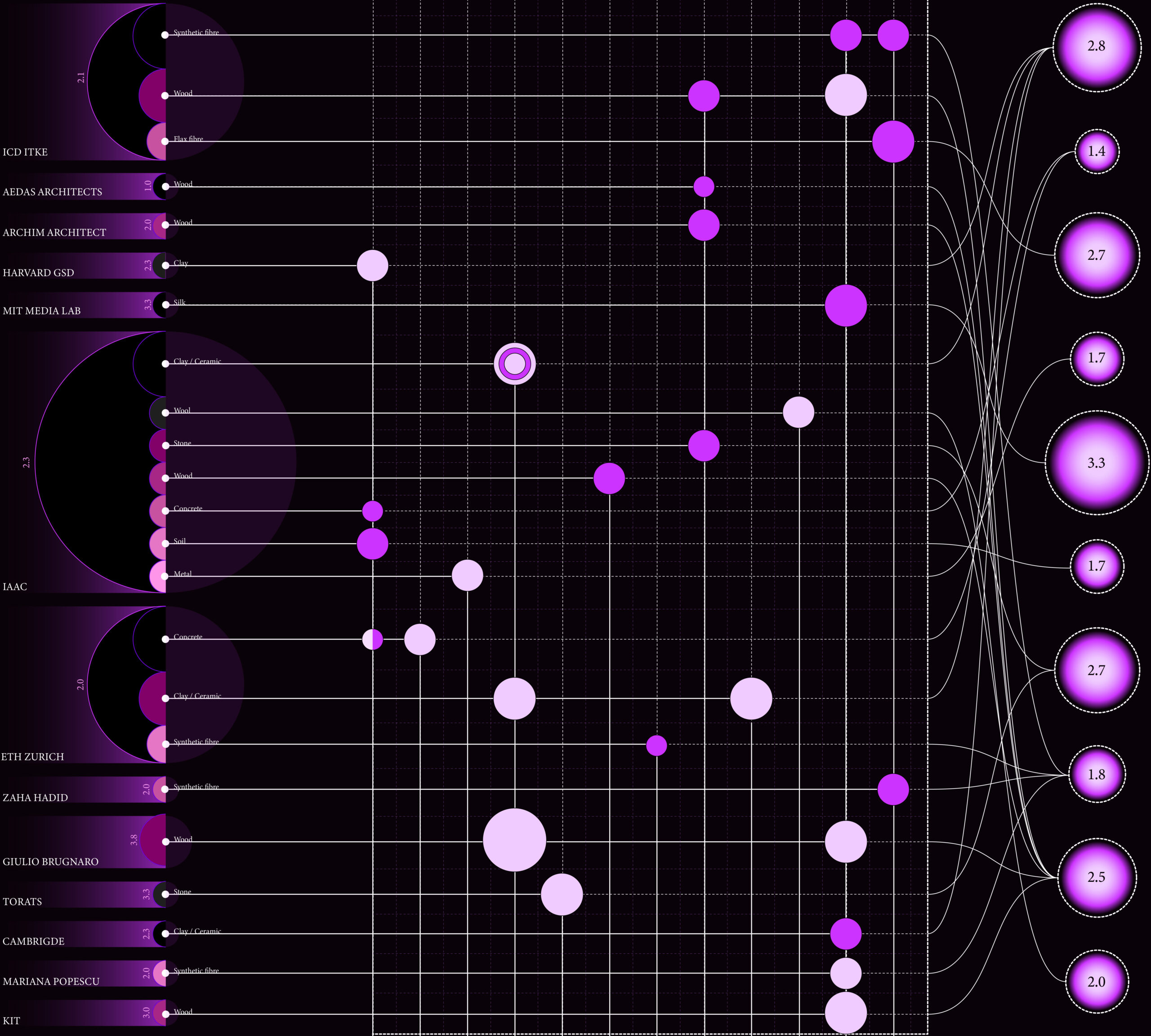
- Enable students to categorise and map state-of-the-art projects based on defined criteria (research lines, operations, materials etc) and feed this information into an interactive mapping platform.

Faculty
Projects from this course
Advanced Fabrication for Circular Materials
The construction industry has long been a major contributor to global resource consumption and waste production. In response to these challenges, circularity in construction has emerged as a transformative approach aimed at reducing environmental impacts, conserving resources, and promoting sustainability. This blog explores the core parameters of circularity in construction—materials, design, and energy consumption—and provides … Read more
Robotic Craft Interaction
An Intersectional Investigation Robotics is the field of study focused on the research and application of robotic systems. This definition, however, doesn’t provide much insight. So, what is a robot? Robots are machines that can operate autonomously or through programmed input to perform specific tasks, often replacing human effort. These tasks are typically complex and … Read more
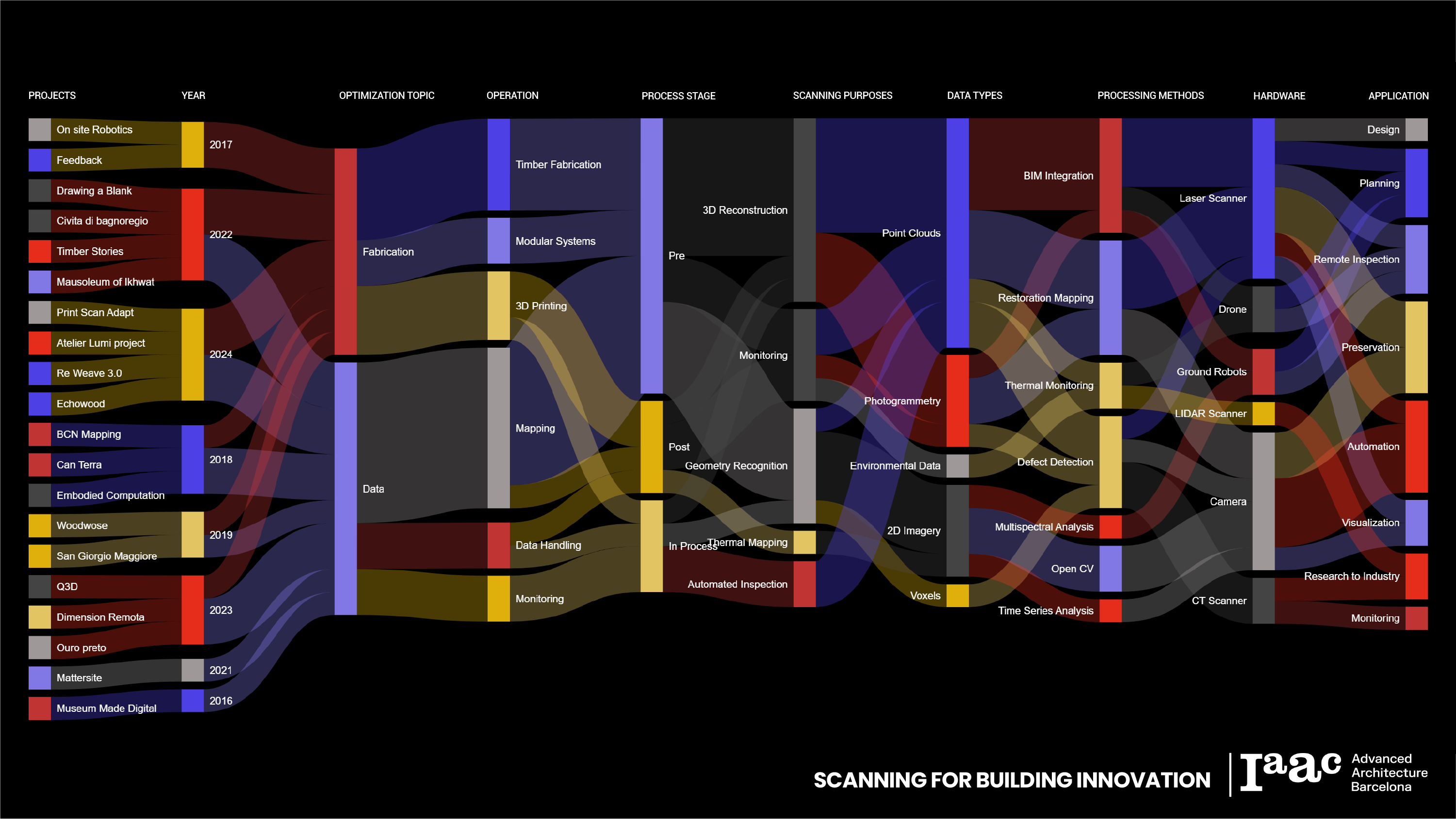
Scanning for Building Innovation
From capturing intricate geometries to enhancing processes, our research emphasizes in innovation in construction and data optimization, showcasing the transformative potential of advanced scanning tools. These technologies not only enhance our ability to capture the intricacies of physical structures but also provide actionable insights for a variety of applications. Research Topics 1. Fabrication OptimizationWe leveraged … Read more