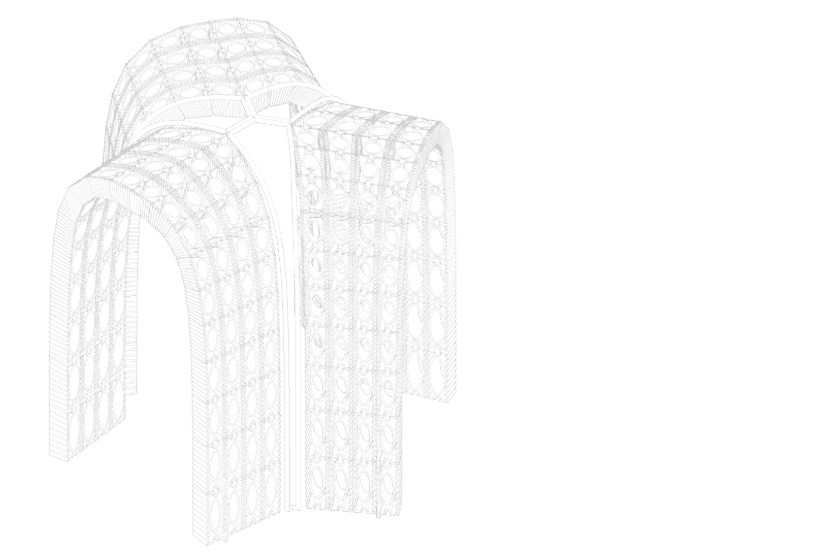
This seminar introduces students to computational design strategies for digital and robotic fabrication, focusing on the software aspects that drive these processes. As architectural designs become increasingly complex, the ability to translate intricate digital models into buildable forms through precise toolpath development and simulation is crucial. Robotic fabrication technologies play a pivotal role in this process by enabling the creation of detailed, case specific forms that would be challenging or costly to materialise with traditional methods.
Through a series of lectures and exercises, students will learn the end-to-end process from conceptual design to the generation of fabrication files for robotic systems and CNC machines, using Rhino and Grasshopper for geometry processing, toolpath development, and process simulation
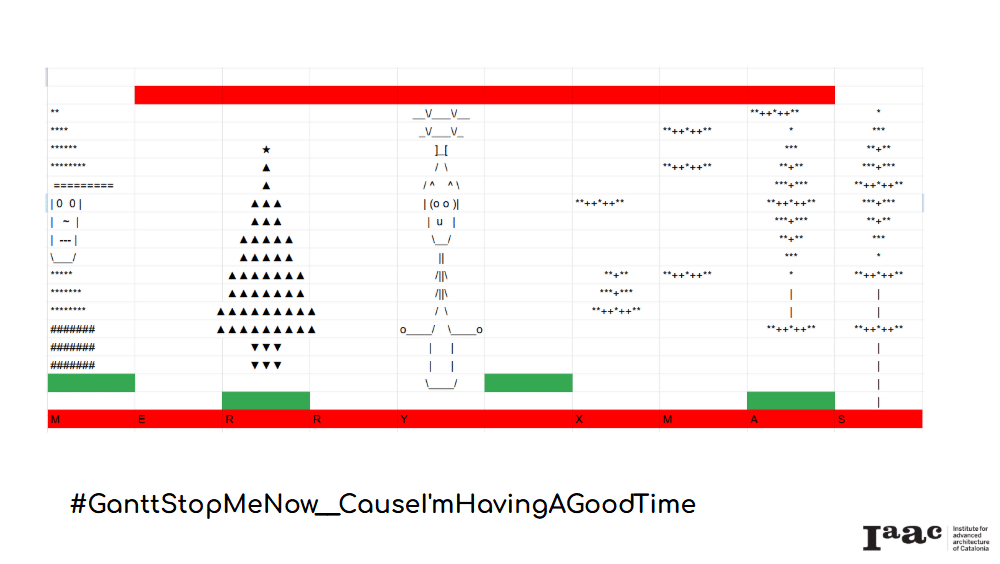
The seminar develops into the following 5 modules:
- Motion control of robotic arms through grasshopper and sketching devices (brushes) 07.10.2025
- Manipulation and Part-to-Tool Processes with Robots (kapla) 14.10.2025
- Computer Numerical Control of Machines and g-code development 28.10.2025
- Large Format Additive Manufacturing (LFAD) with Robots (Clay 3d printing) 04.11.2025
- Feasibility and cost estimations in digital fabrication (fabrication estimations) 11.11.2025
Each module comprises an introduction to the fabrication technology, analysis of case studies, hands-on exercise tutorials, and a group assignment.
Learning Objectives
At course completion the student will:
- Understand computational and parametric design strategies for CNC and robotic fabrication.
- Develop proficiency in Rhino and Grasshopper for geometry processing, toolpath design, and robotic simulation.
- Analyse and optimise designs for digital fabrication, considering material, time, and cost constraints.
- Gain hands-on experience in robot programming and motion planning for various manufacturing processes, including additive and subtractive manufacturing, as well as robotic manipulation.