STATEMENT
Today, almost 39% of CO2 emissions are attributed to current construction processes. Architectural design implementations have the potential to address these environmental challenges through active and passive strategies. Elements such as facades, walls, or interior components among others play a role in the carbon cycles by capturing, storing and emitting carbon. Biochar, as a material, stands out for its ability to adsorb and sequester carbon, making it a viable resource contributing to efforts of carbon reduction through sequestration, minimizing carbon footprints, and ultimately reducing embodied carbon.
Biochar and clay composites can be programmed to satisfy a range of architecture applications. Through additive manufacturing these composites can be strategically designed to achieve variable thermal conductivity and structural performances. This thesis aims to explore the potentials of this system through design of architectural elements.
OBJECTIVE
This project explores biochar and clay as sustainable material, proposing an alternative to traditional bricks or conventional materials. By integrating biochar and clay, I aim to develop a 3D printable material suitable for additive manufacturing. Through computational tools and digital fabrication, environmental simulations will be used to guide the aggregation of biochar and clay elements, with a focus on solar gain. This approach allows me to propose configurable architectural spaces.
Barcelona serves as a case study to explore the computational logic needed to determine the optimal biochar and clay ratio for building facades. This research aims to develop future facades that not only manage light but also achieve heating and cooling, offering a new sustainable solution for architectural elements.
STARTING FROM DIGITAL MATTER
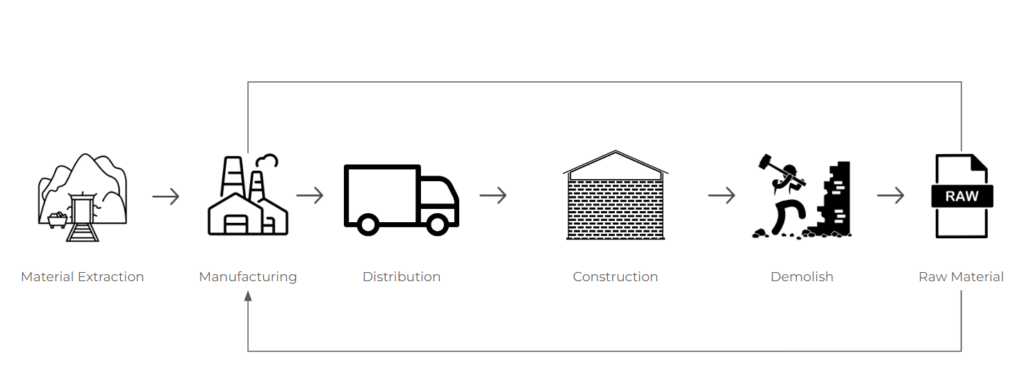
Building on the success of AGROCHAR’s (https://blog.iaac.net/agro-char/) reusable biochar blocks, where biochar and cement composites hold promise, this research explores the potential of biochar and clay mixtures as a degradable material. Degradability, a growing concern in European regulations for waste management and the circular economy is going to be achieved within experimenting various biochar-clay compositions. I aim to unlock the possibilities of this sustainable material.


Can we make compositions of Biochar and Clay?
INTRODUCTION TO MATERIALS:
INTRODUCTION TO MATERIALS – BIOCHAR
- What is biochar?
- How is it achieved?
- Where are the applications now?
Biochar is a form of charcoal that is produced through the pyrolysis of bio-waste in a low-oxygen environment. It is a carbon-rich material that is used for various purposes, particularly in agriculture and environmental applications.
Biochar is known for its ability to enhance soil fertility, improve water retention, and sequester carbon, making it a valuable tool in sustainable farming practices and climate change mitigation.
Biochar is known for:
- Its ability to enhance soil fertility
- Improve water retention
- Sequester carbon (and making it a valuable tool in sustainable farming)
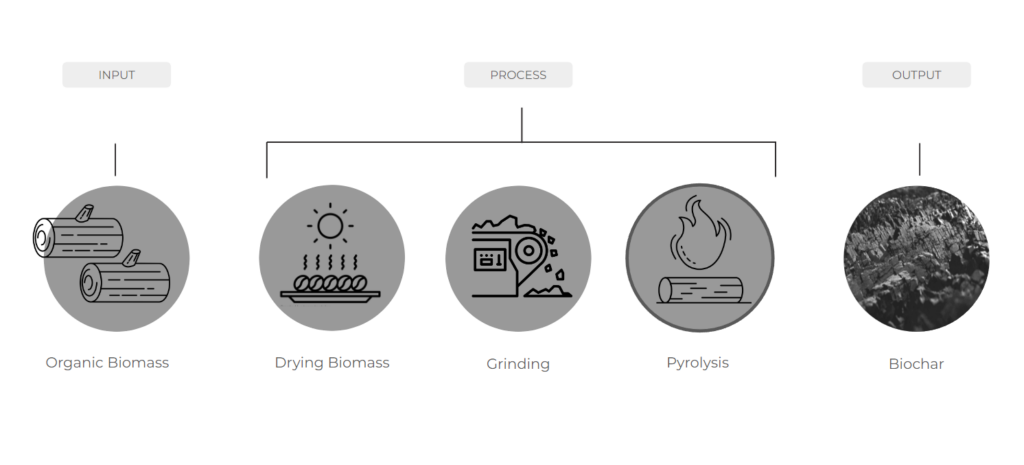
PROPERTIES OF BIOCHAR

APPLICATIONS OF BIOCHAR

INTRODUCTION TO MATERIALS – CLAY
- What is CLAY ?
- How is it achieved?
- Where are the applications now?
Clay is a fine-grained natural material composed of tiny mineral particles.
Ceramics: A major application of clay is in the production of pottery, tiles, bricks, and other ceramic products. When fired at high temperatures, clay transforms into a strong and durable material.
Construction: Clay bricks are a traditional and still widely used building material. Clay can also be used as a component in mortars and plasters.
Industrial Applications: Clay finds use in various industrial processes like refining oil, filtering liquids, etc…
APPLICATIONS OF CLAY

PROPERTIES OF CLAY

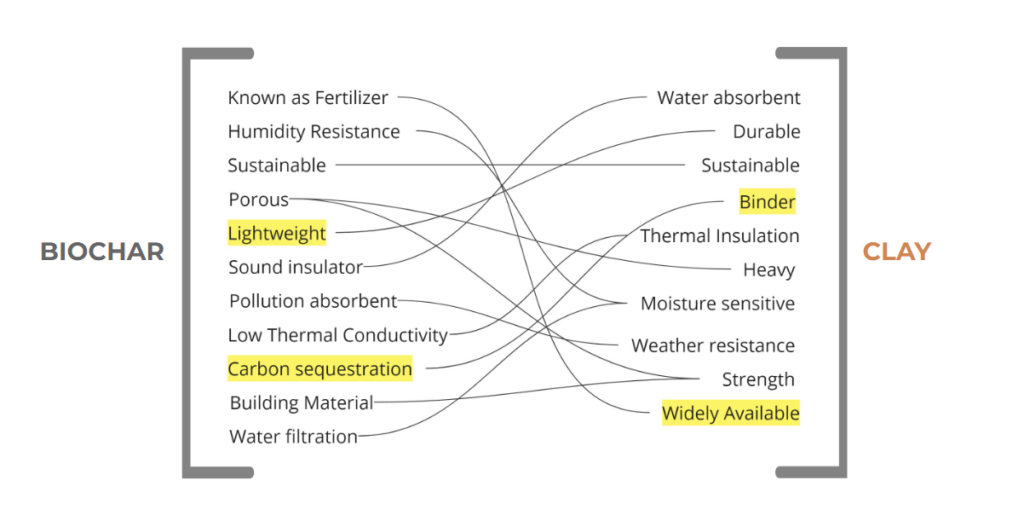
Both biochar and clay are natural materials with potential applications in sustainable construction.
They also possess distinct properties, making them suited for different purposes.
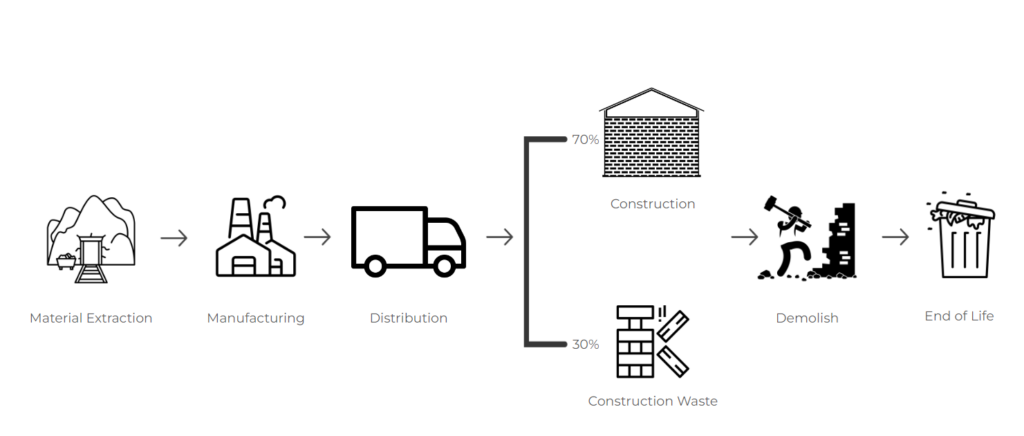
CONVENTIONAL CONSTRUCTON
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
DIGITAL EXPERIMENTS
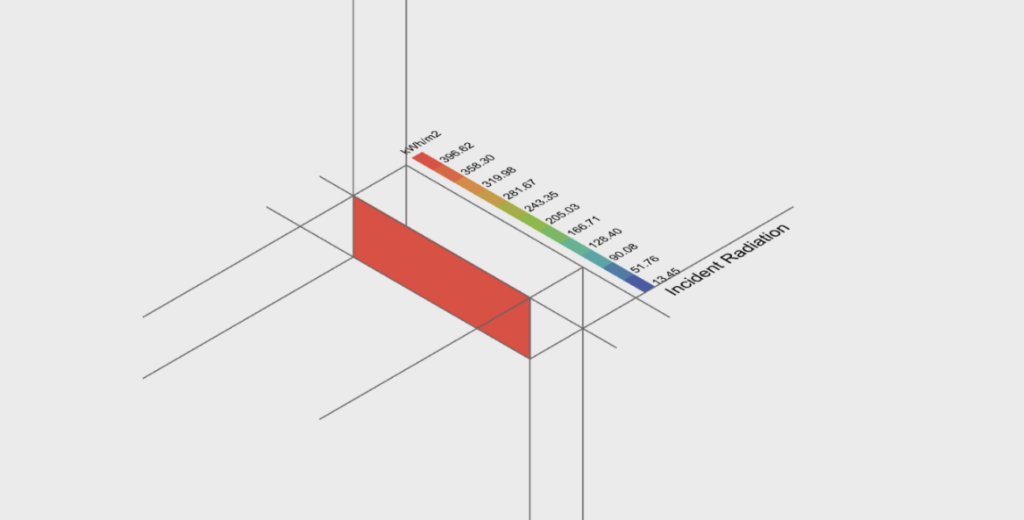
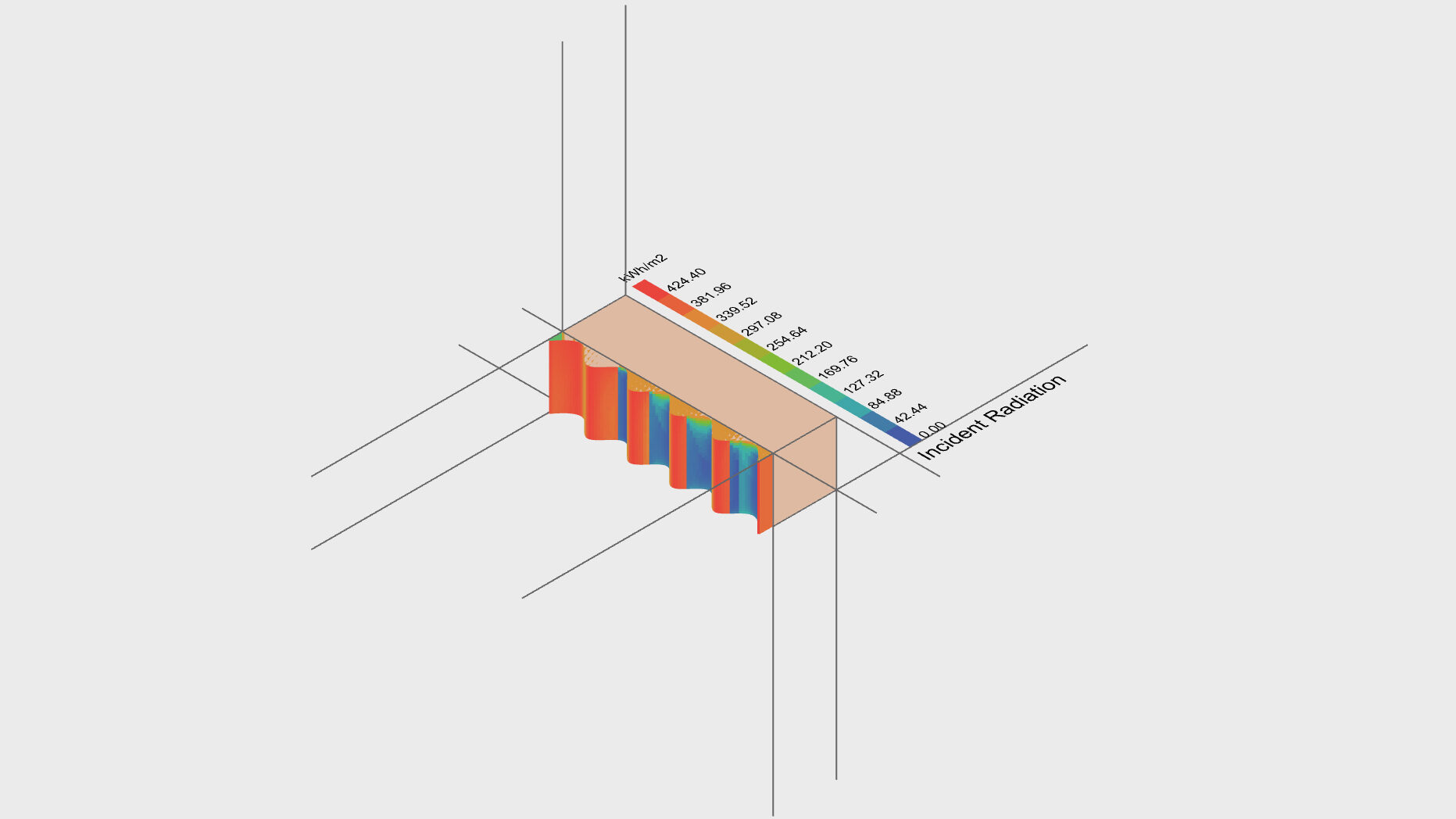
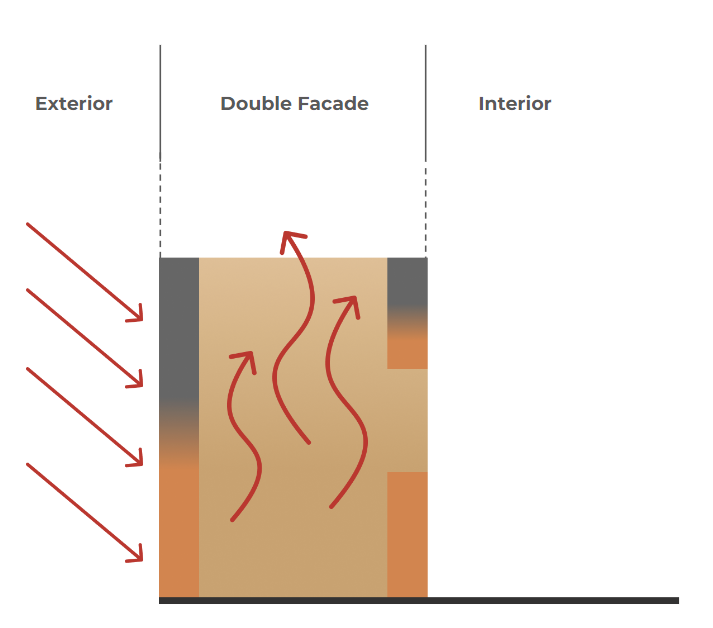
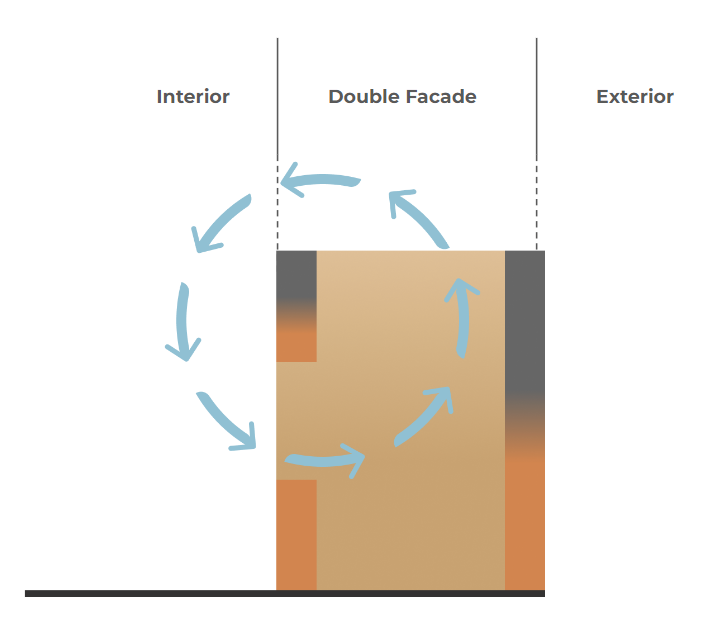
PROCESS DIAGRAMS:
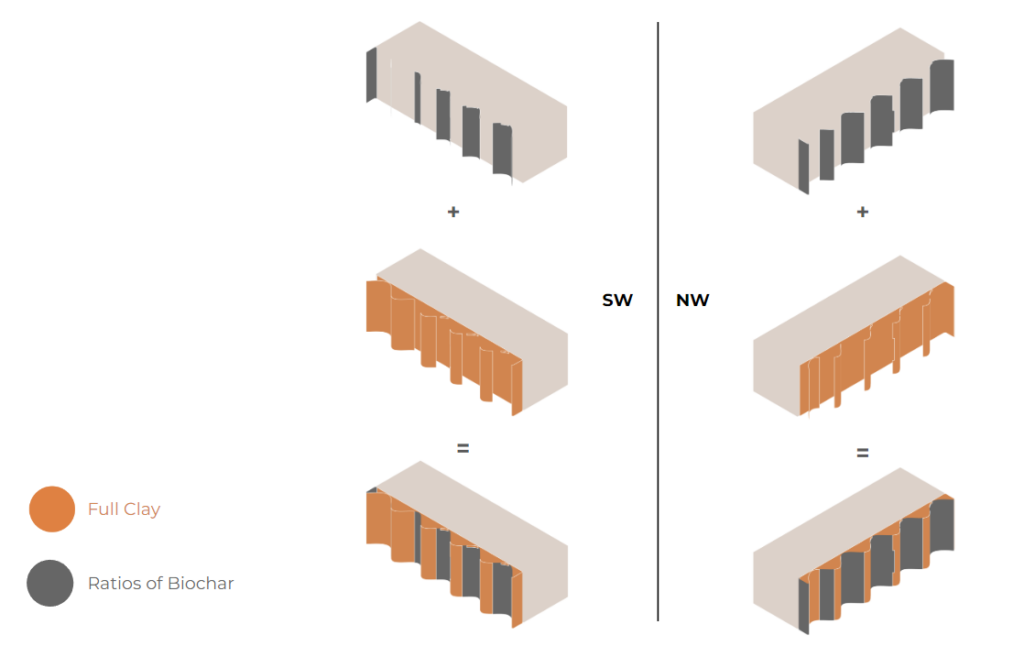
PHYSICAL EXPERIMENTS
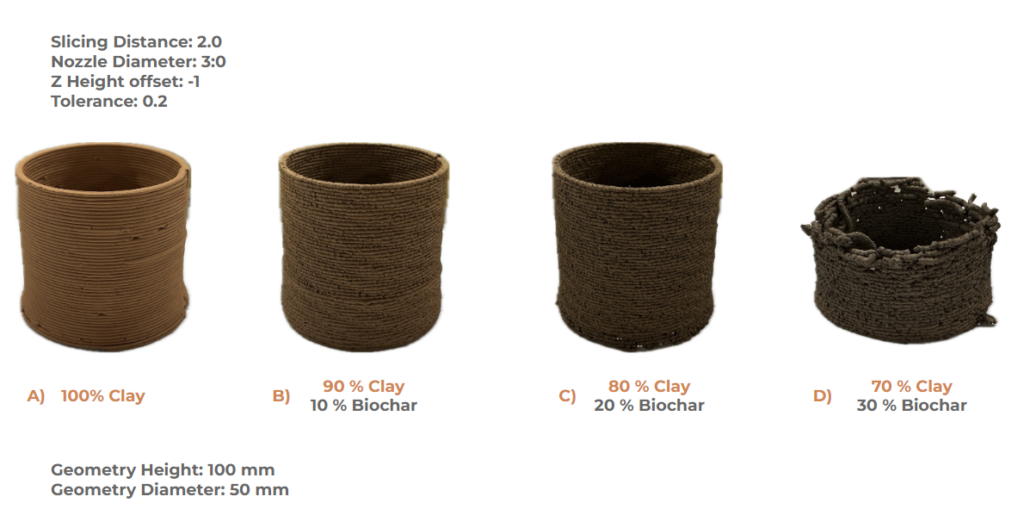
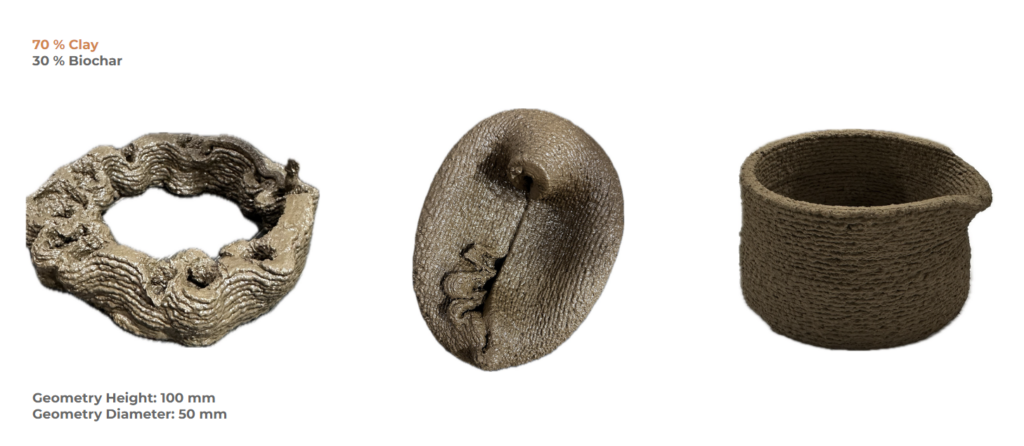



FINAL PHYSICAL EXPERIMENTS
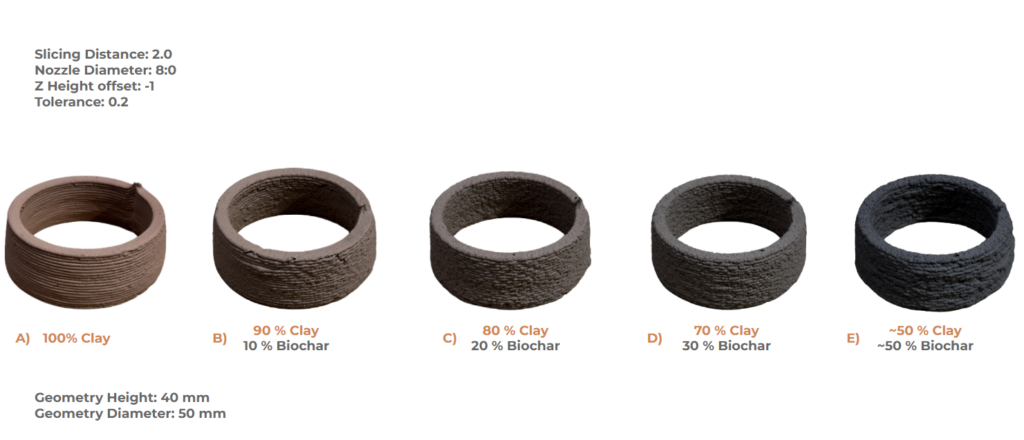

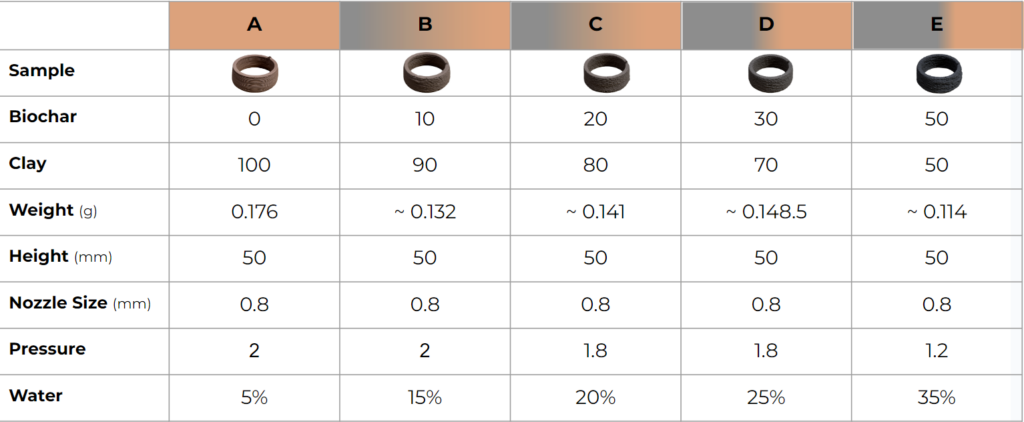
TABLE OF MATERIAL
DESIGN PROPOSAL DERIVED FROM MIDJOURNEY PROMPT:
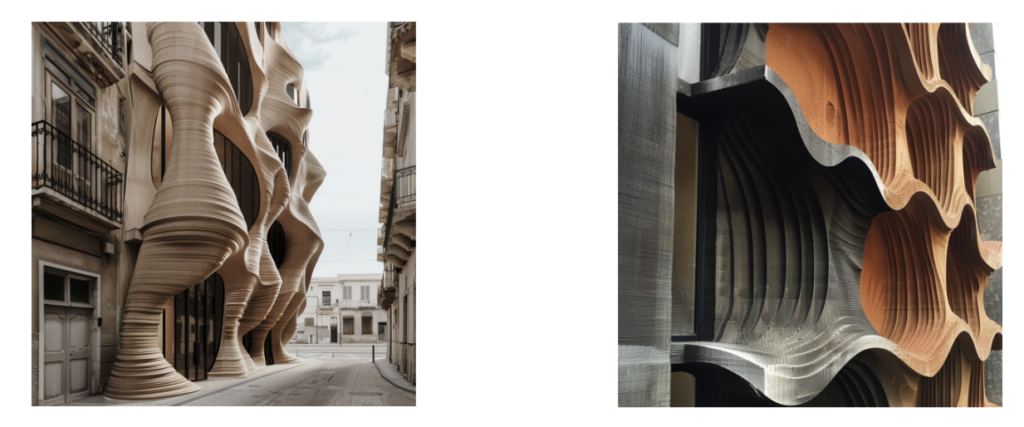


PROMPT: a street view of a building that its facade is printed with ratio of clay and biochar blended together which is designed and constructed with additive manufacturing. the layers of 3D printed material is visible and are in vertical sine shapes.

