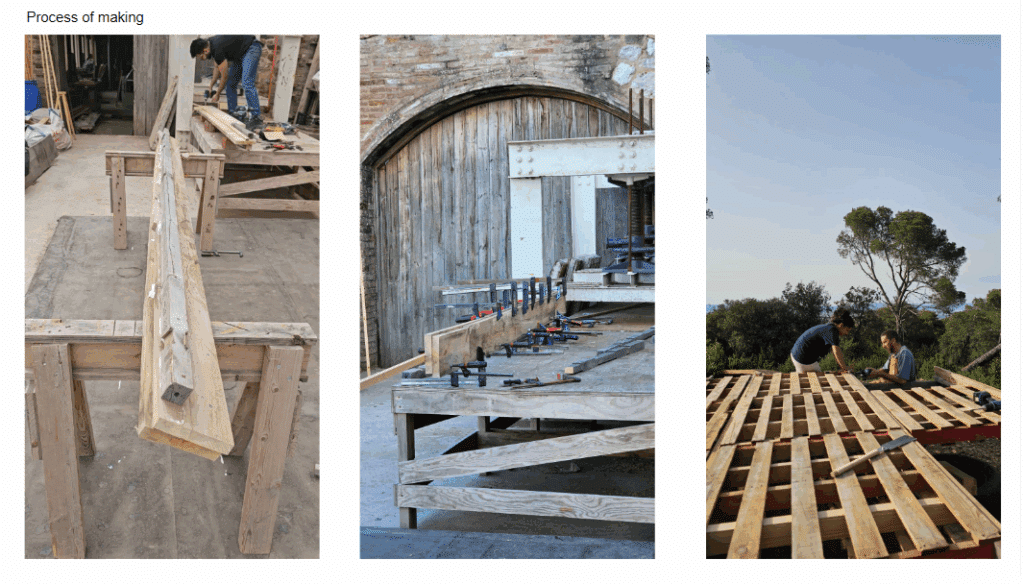
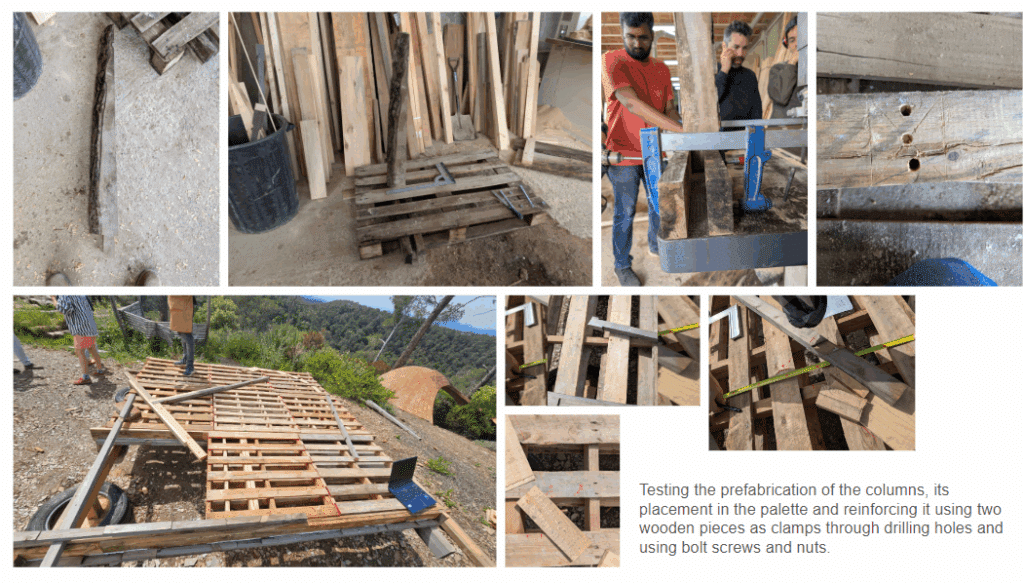
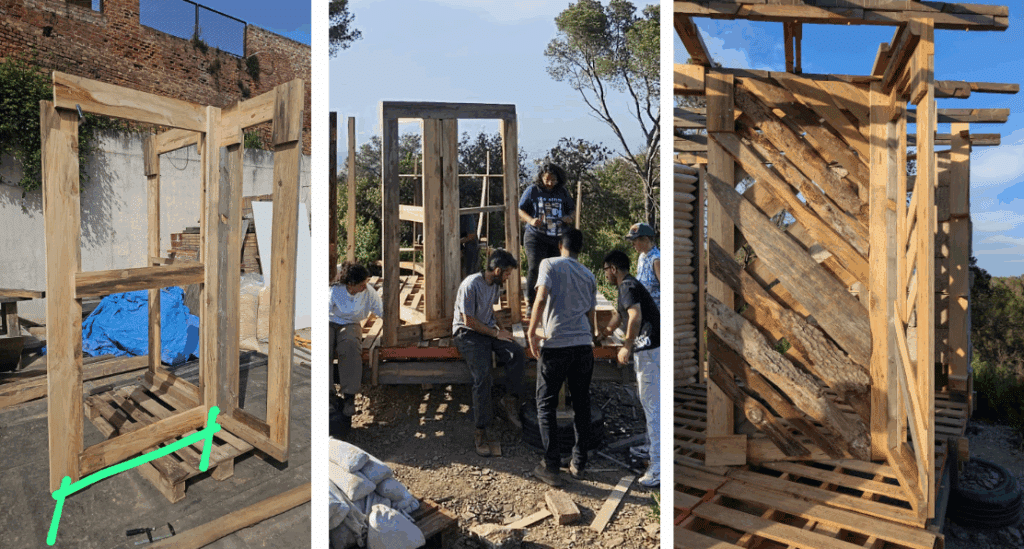
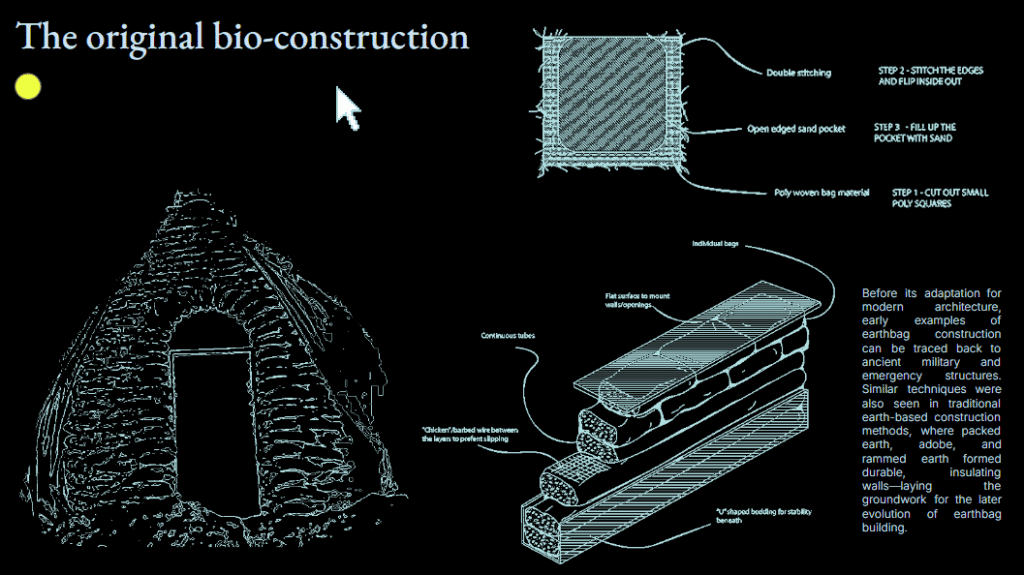
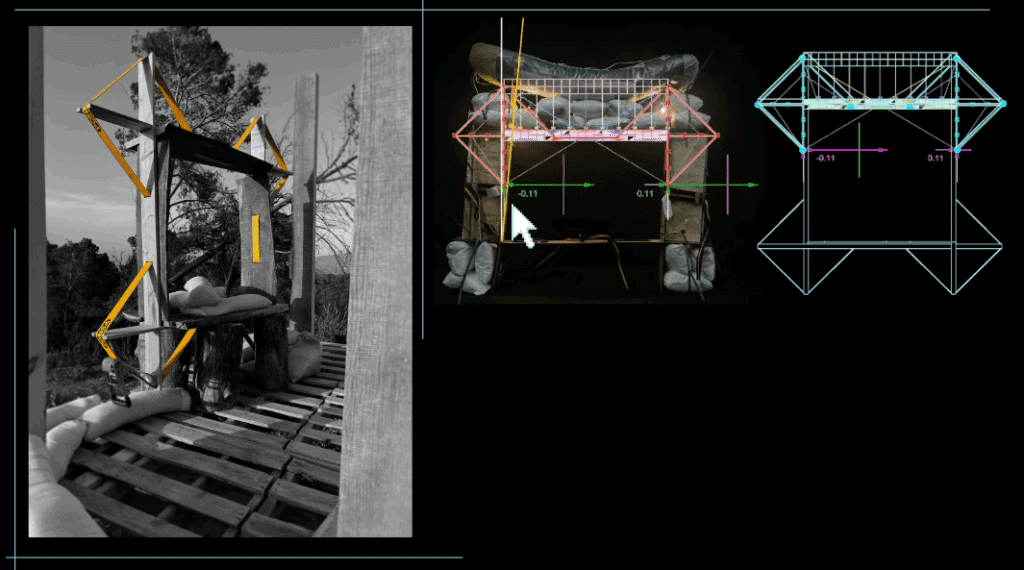
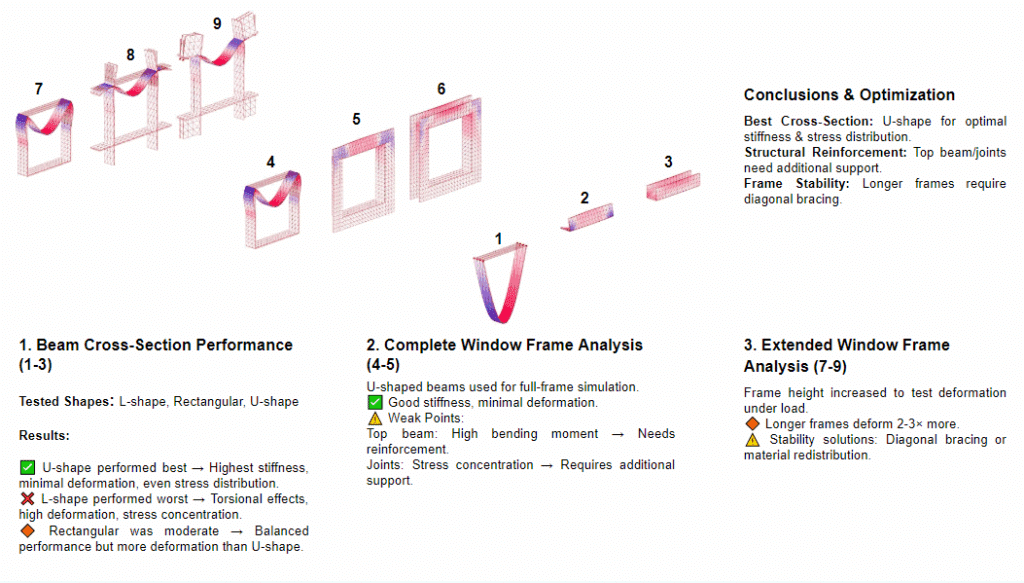
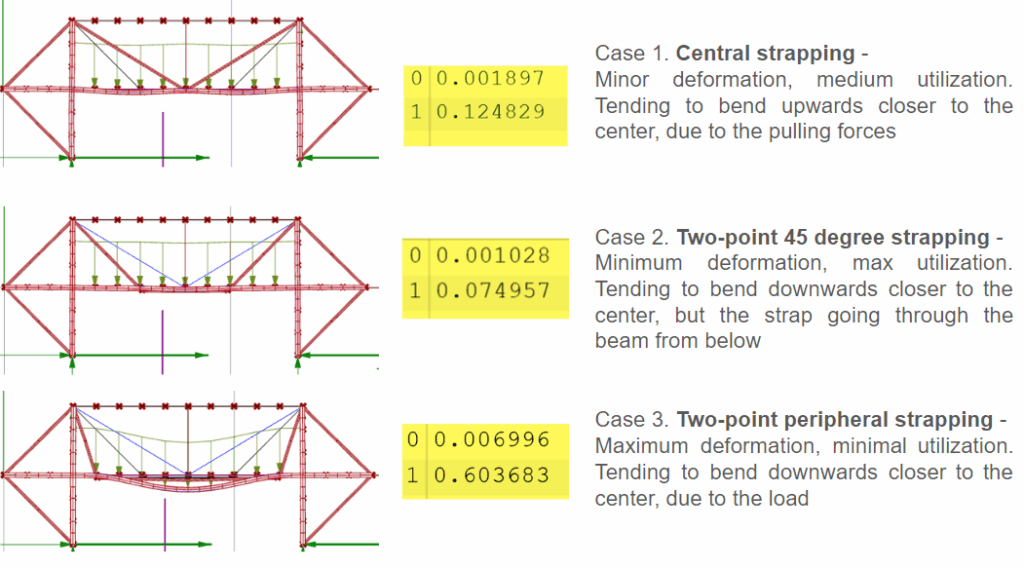
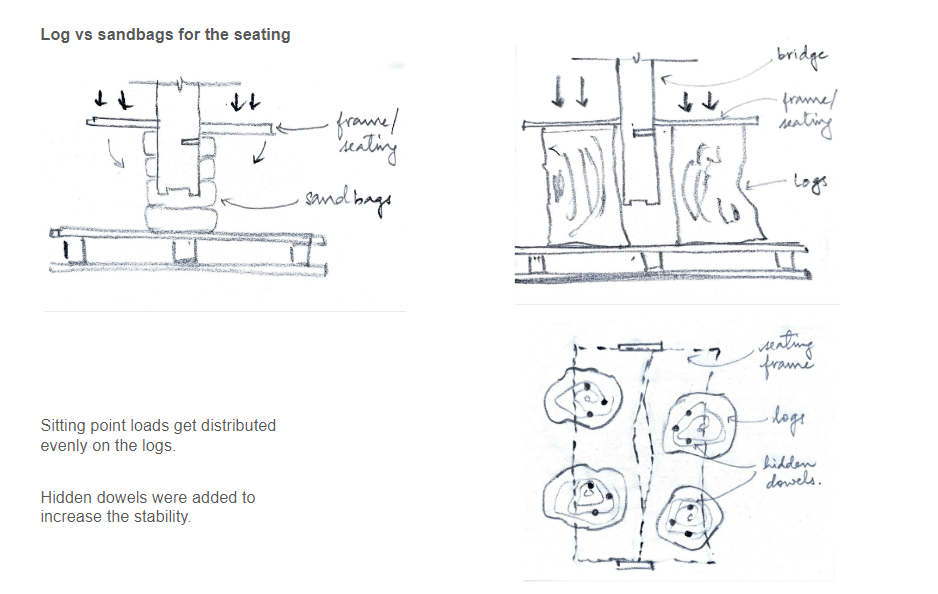
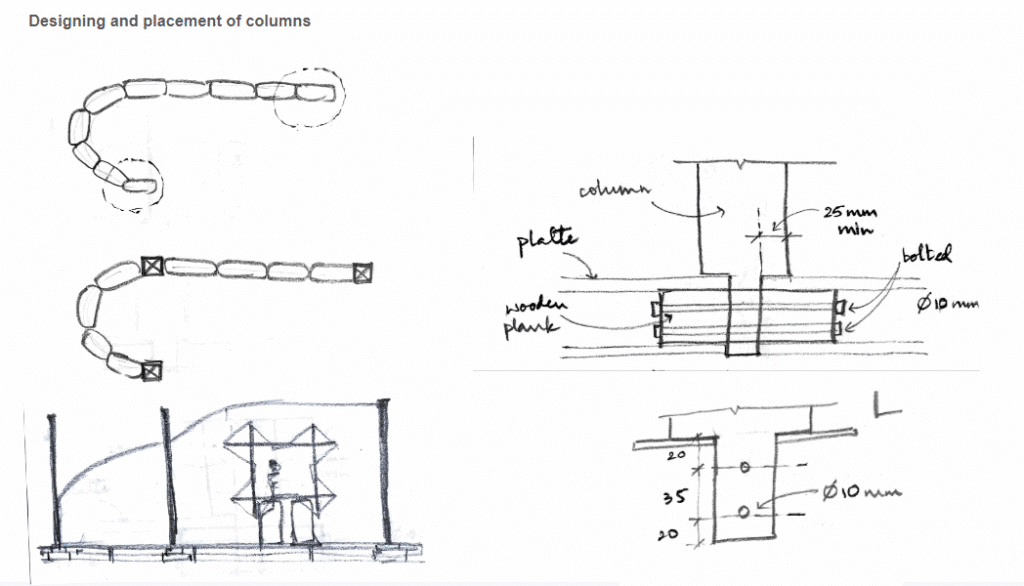
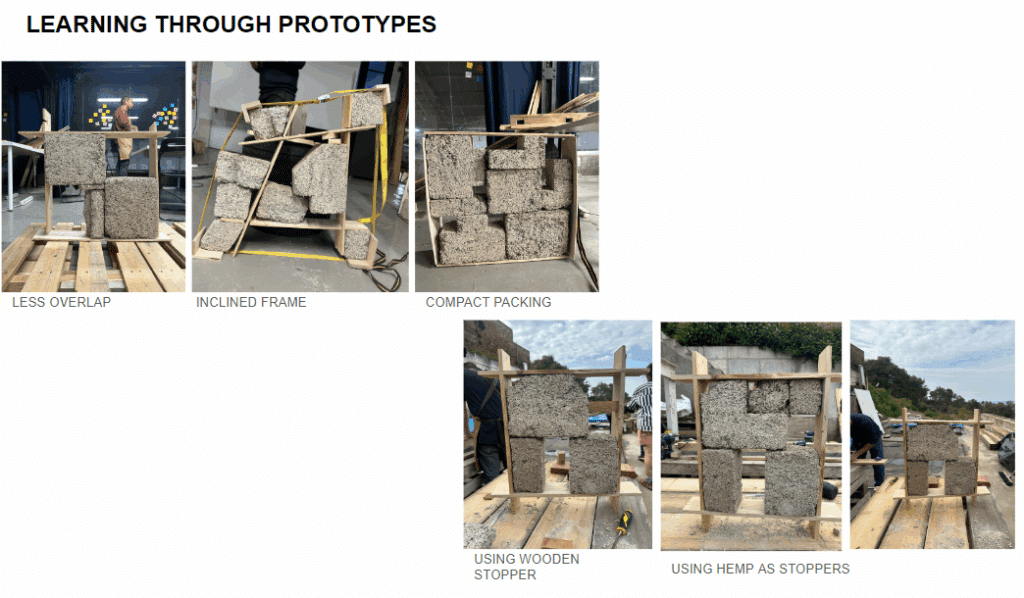
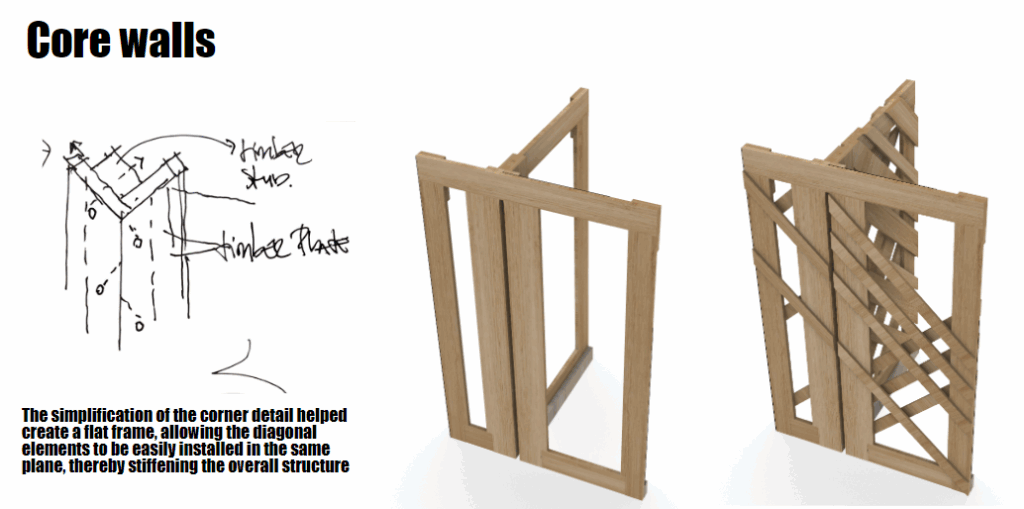
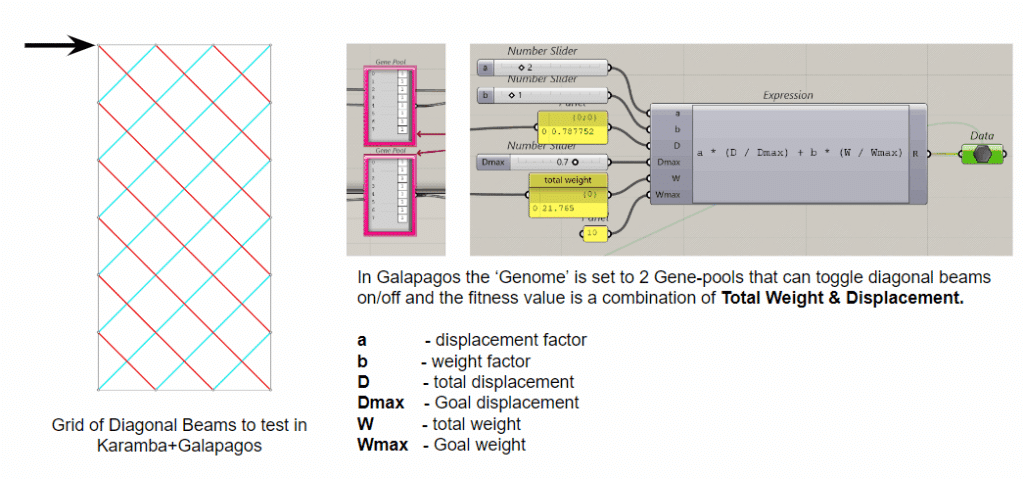
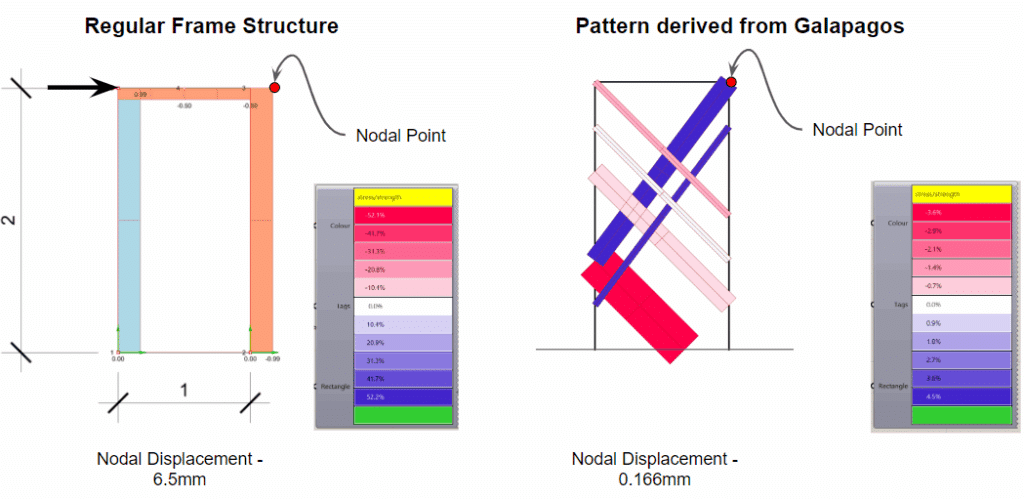
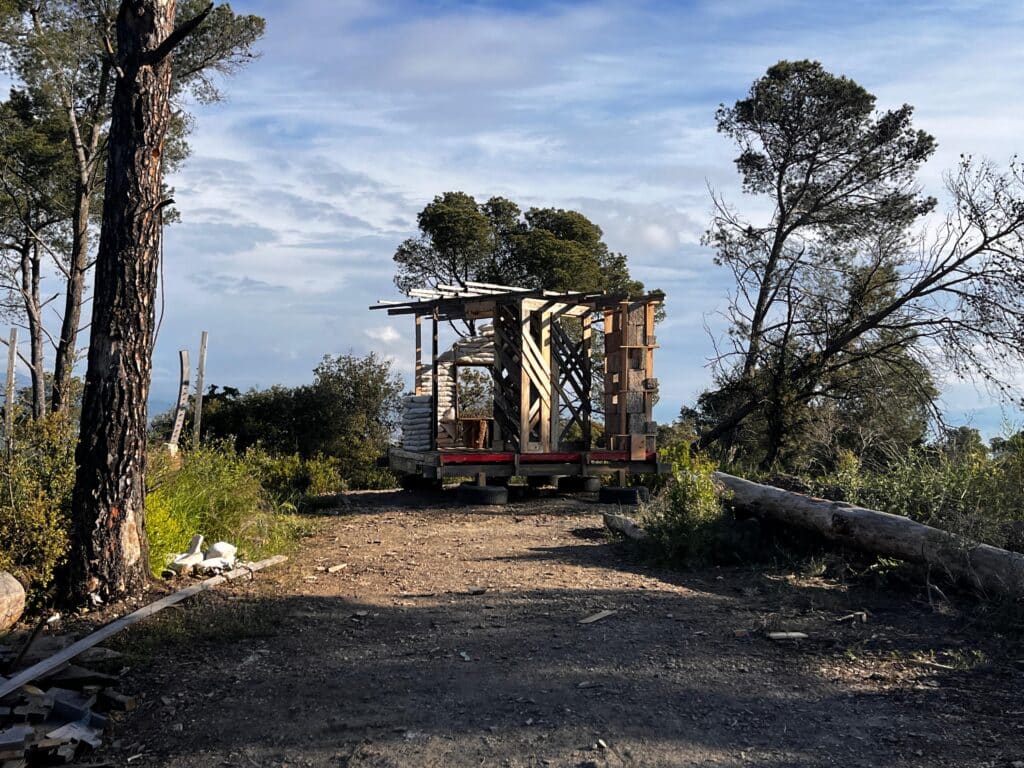
This off-grid microstructure is a low-impact, self-built shelter that combines reclaimed and natural materials to create a compact, modular space embedded in nature. Raised on a foundation of reused tires filled with earth, the floor is made from wooden pallets, allowing air circulation and minimizing site disturbance. Walls are constructed using hempcrete blocks and stacked sandbags, providing both insulation and thermal mass. A multifunctional wardrobe unit acts as an internal support structure for the angled roof panels above. Designed with simplicity and sustainability in mind, the structure integrates with its forest surroundings while showcasing a raw, honest aesthetic rooted in material reuse and hands-on construction.
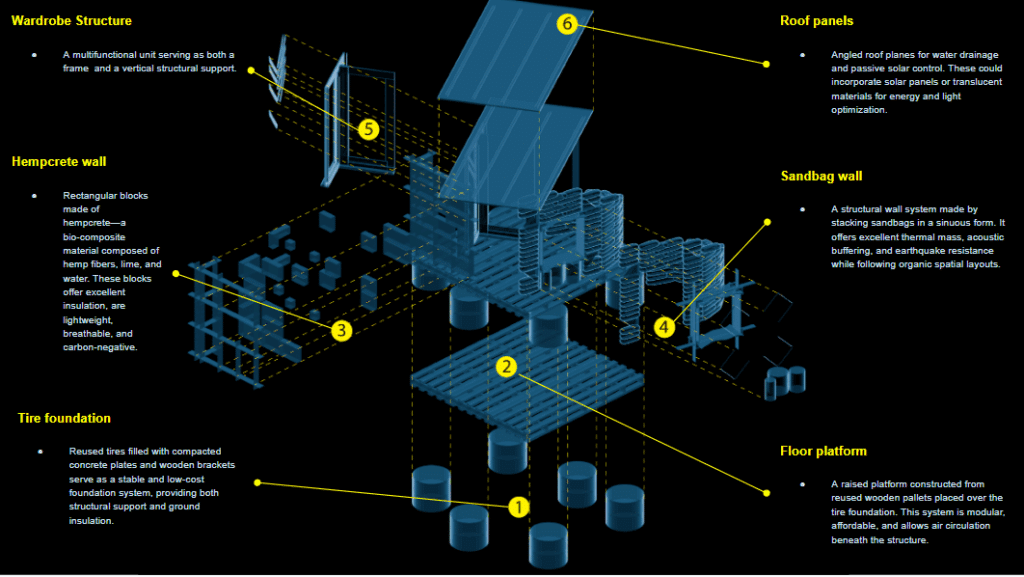
- Tire Foundation (Cylinders)
Reused tires filled with compacted earth or concrete provide a stable, cost-effective, and sustainable base for the structure, with strong load distribution and moisture resistance. - Floor Platform (Wooden Pallets)
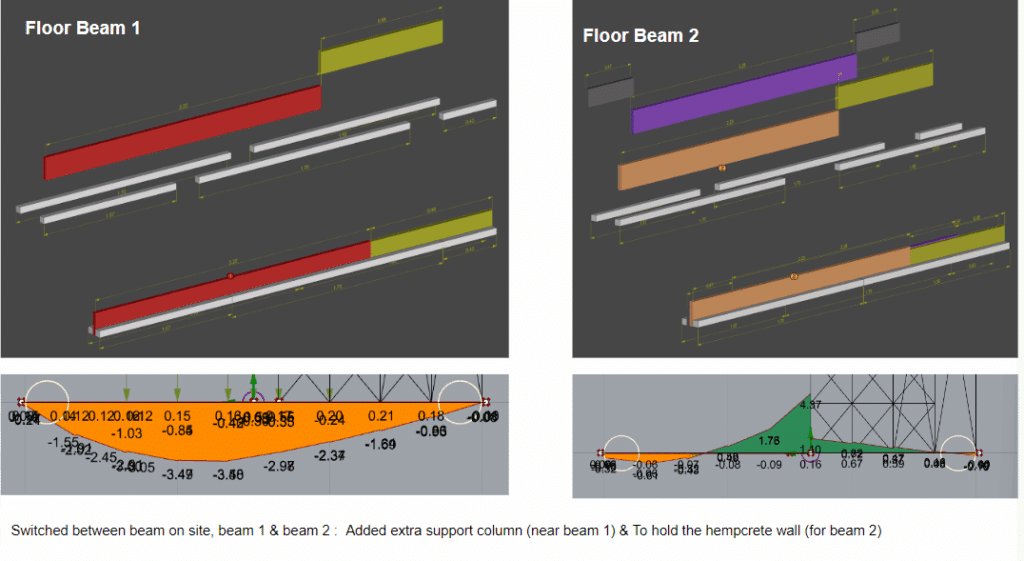
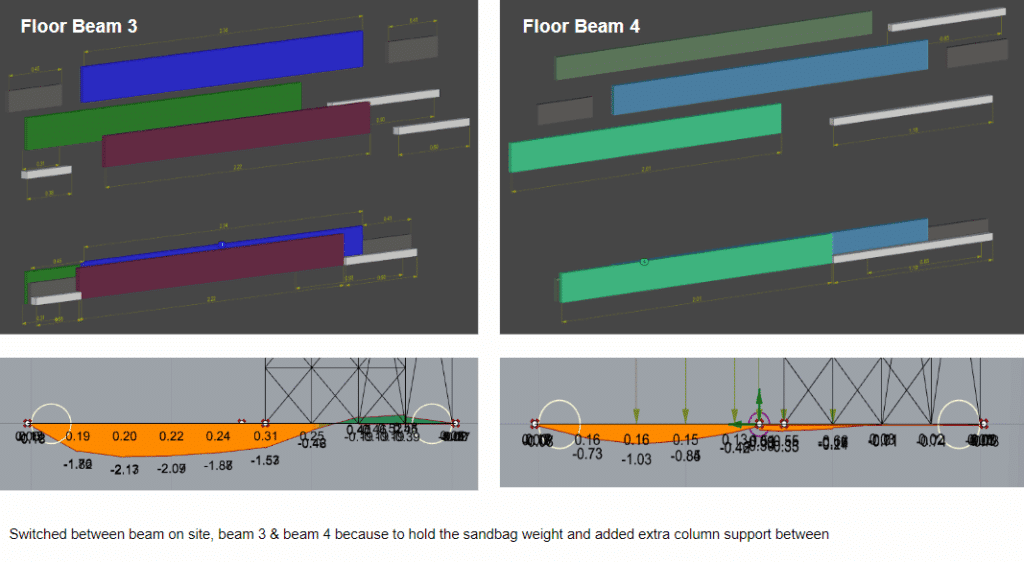
A raised modular floor made from reclaimed wooden pallets. This system is quick to assemble, promotes underfloor ventilation, and reuses widely available materials. - Wall Blocks (Hempcrete)
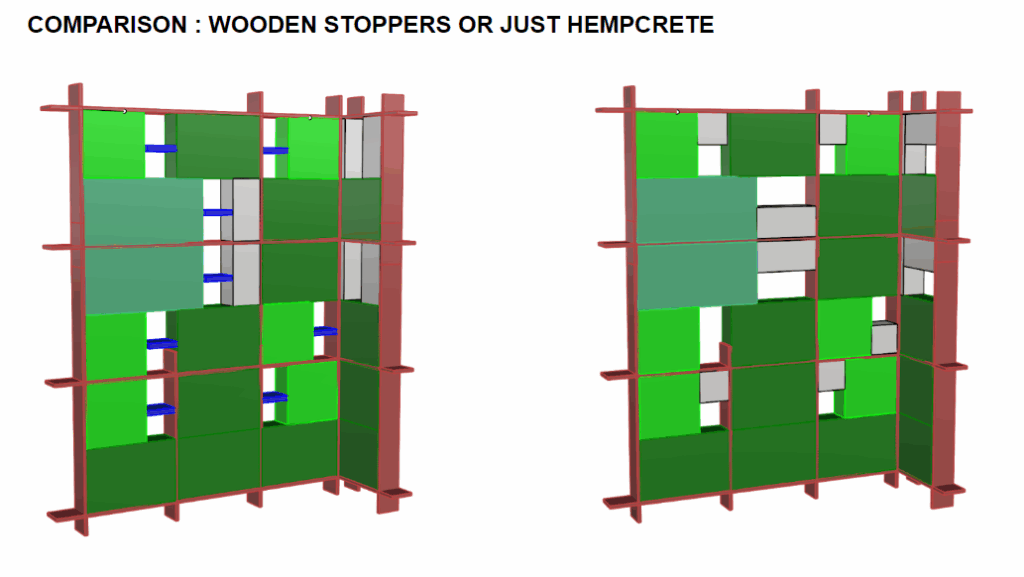
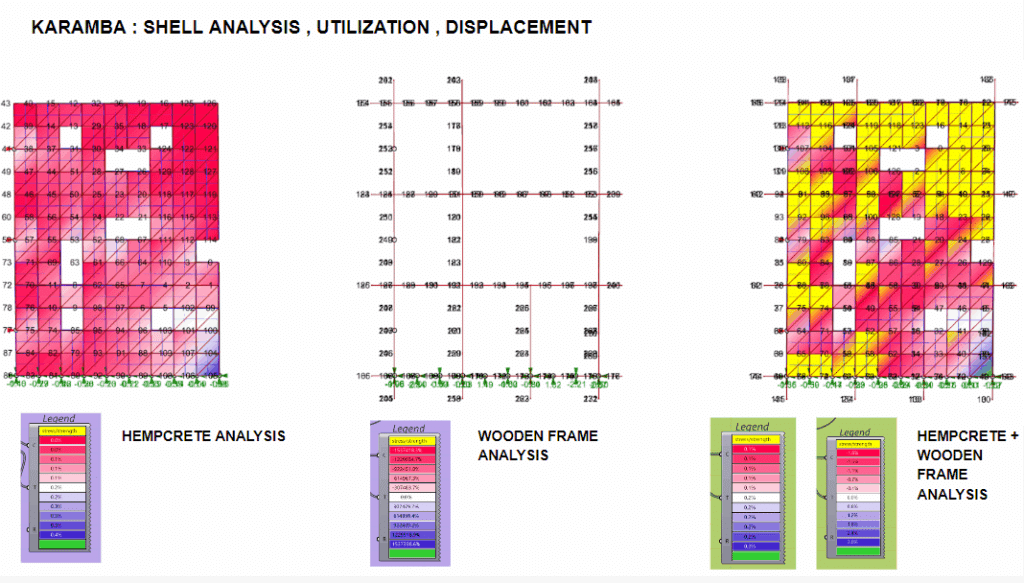
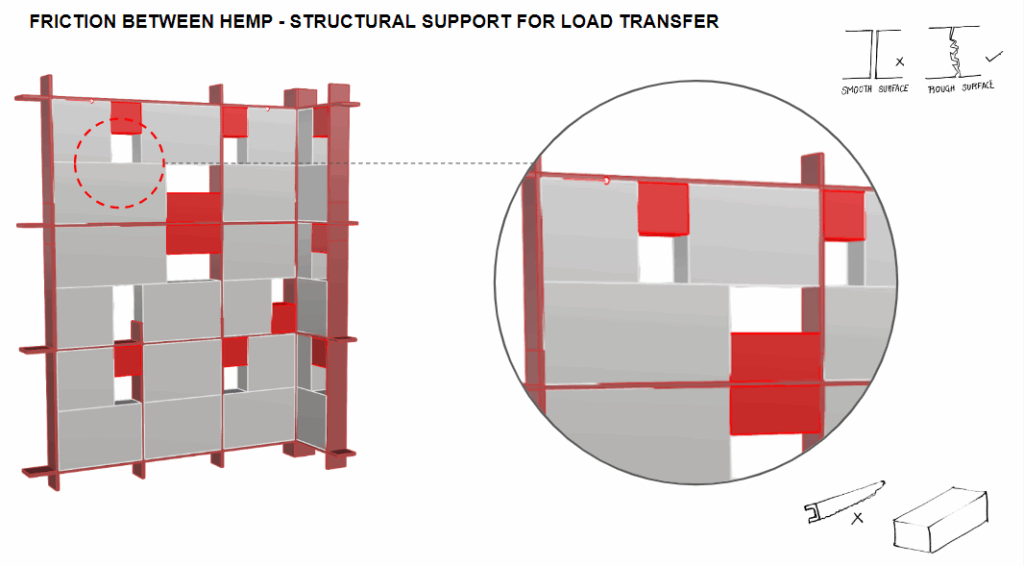
Rectangular blocks formed from hempcrete—a breathable, insulating, and sustainable bio-composite of hemp fibers and lime. They offer lightweight thermal and acoustic performance. - Curved Wall (Sandbag Wall)
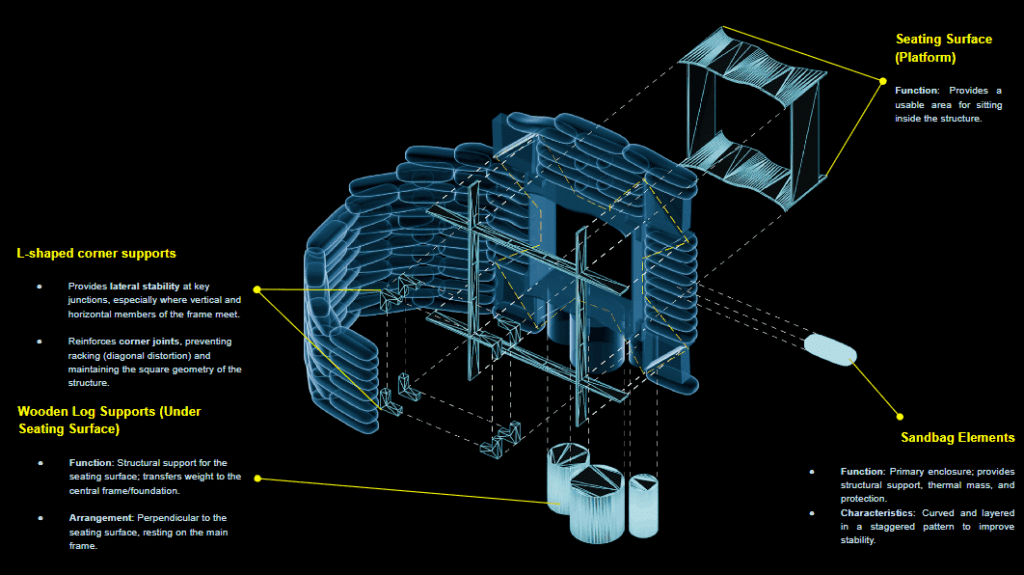
Organic-shaped walls constructed with stacked sandbags. These earth-based components provide strong thermal mass, structural resilience, and natural aesthetics. - Wardrobe Structure (Roof Support)
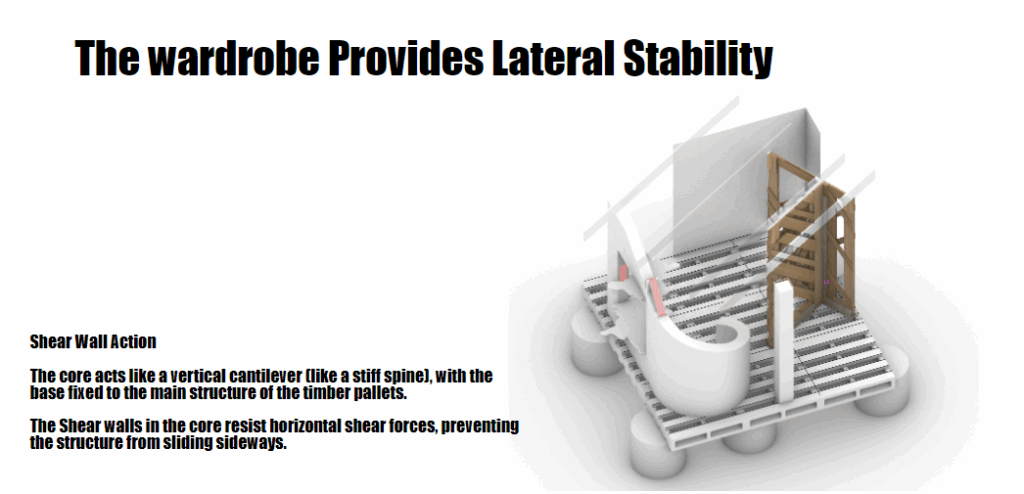
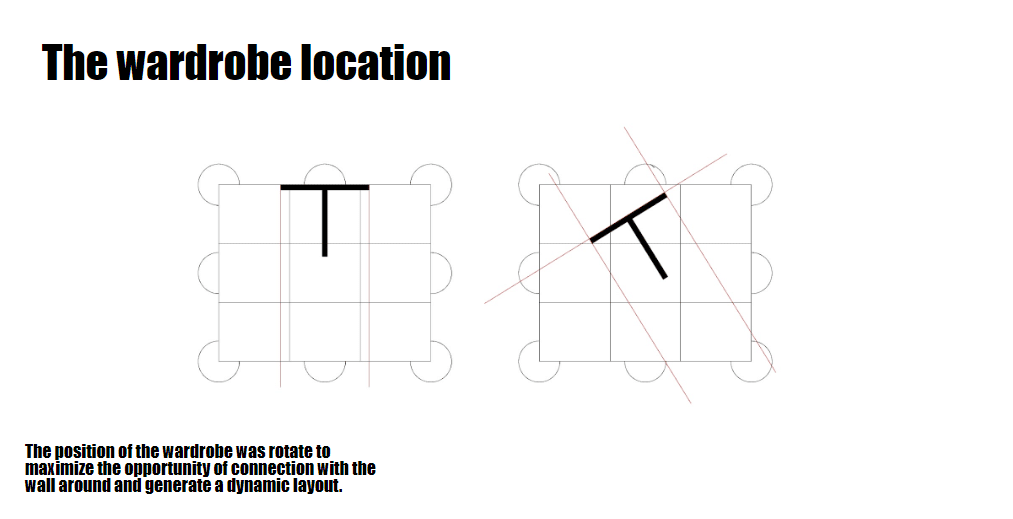
A multifunctional interior unit serving as both a wardrobe and a vertical structural frame. It plays a dual role: organizing interior storage and supporting the roof load above. - Roof Panels
Angled roof elements designed for water drainage and passive solar strategies. Potentially made with translucent or solar-integrated materials to enhance lighting and energy use.

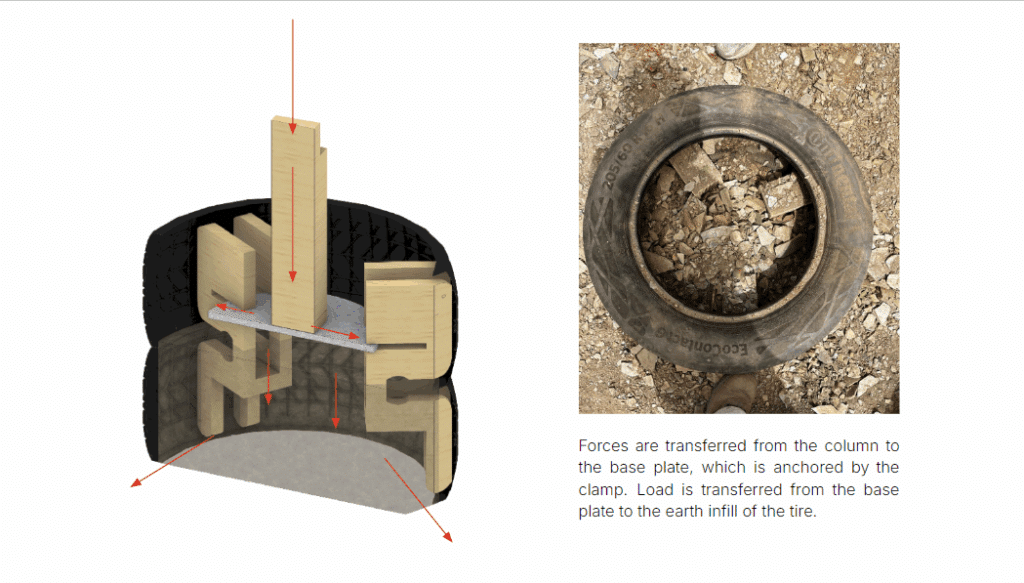
Two tires are stacked, with only the bottom tire buried in the soil. The bottom tire distributes load, while the top tire provides stability, resists lateral wind loads, prevents uplift, and secures the base plate in place.
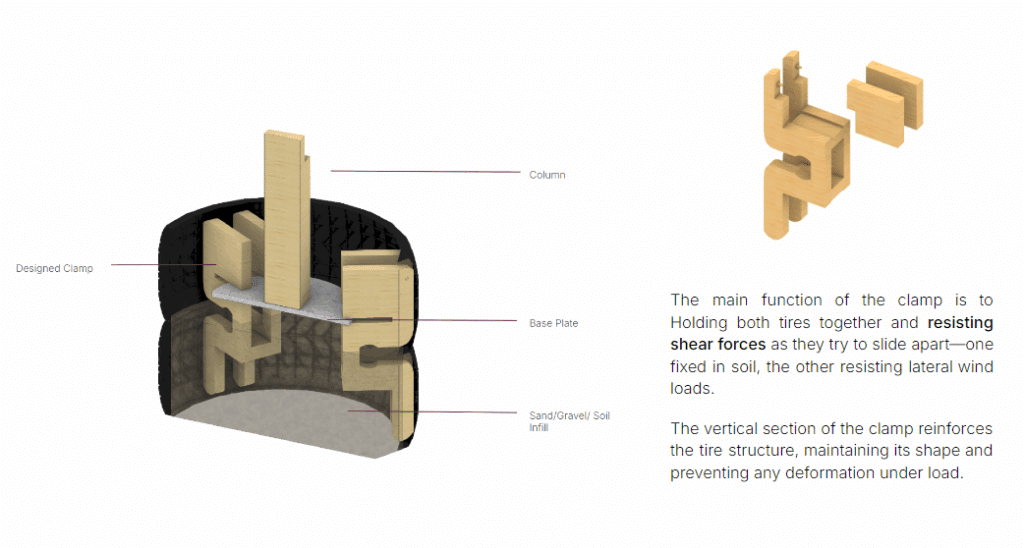
The main function of the clamp is to Holding both tires together and resisting shear forces as they try to slide apart—one fixed in soil, the other resisting lateral wind loads.
The vertical section of the clamp reinforces the tire structure, maintaining its shape and preventing any deformation under load.