The Zona Franca in Barcelona is an area that receives thousands of workers everyday and, having The Port, is one of the main points of contact of the city with the rest of the world. Through a quick analysis based on an understanding of the site, questions and issues within Barcelona’s ‘Free-Trade’ zone are tackled in order to understand how can it be better integrated into the city fabric and represent a better space for the people that inhabit it.
What is a ‘Zona Franca’ (Free-Trade Zone)?
A Zona Franca is a designate zone in which companies are taxed very lightly or not at all to encourage economic activity. The impacts of having goods not subject to import duties or trade policy measures include:
- Increased International Commercial Activity
- Foreign Investment
- Industrial and commercial development
Key Places in the Zona Franca
The Zona Franca is characterized by big industries and by the presence of Barcelona’s Port. Please see below for a description of the key places.

Main Industries
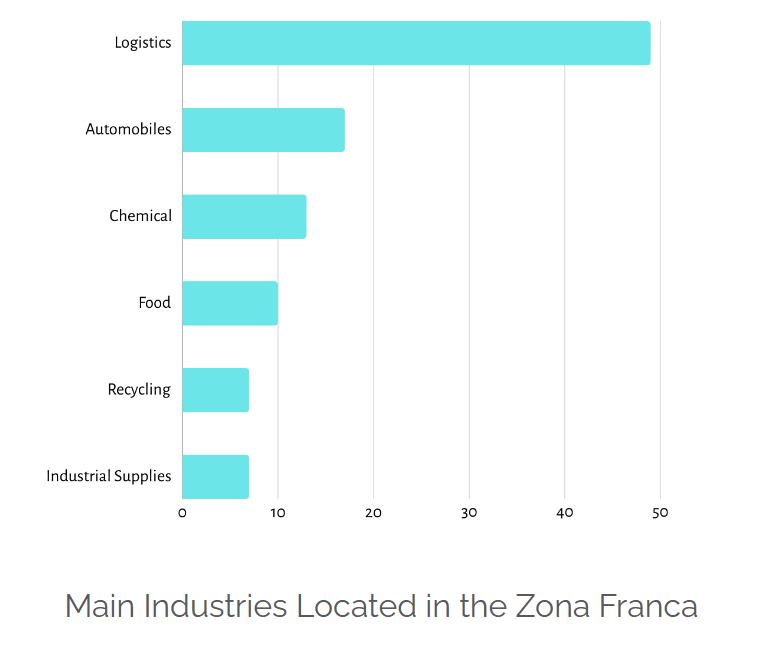
The Zona Franca Barcelona is known for hosting a variety of industries, and some of the prominent industry types in this area include:
- Logistics and Distribution: Given its strategic location and emphasis on trade, the Zona Franca is a hub for logistics and distribution centers. Many companies use this area as a base for importing, exporting, and distributing goods.
- Automotive Industry: The Zona Franca Barcelona has been historically associated with the automotive industry. It hosts manufacturing and assembly plants for automotive companies, making it a key area for the production and export of vehicles and components.
- Technology and Innovation: Over the years, there has been a growing focus on technology and innovation in the Zona Franca. Some companies in the information technology and innovation sectors have established a presence in this area.
- Trade and Commerce: The Zona Franca serves as a center for international trade and commerce, attracting businesses engaged in import and export activities.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Various industrial manufacturing activities take place in the Zona Franca, ranging from machinery and equipment manufacturing to other heavy industries.
Land Use in the Site
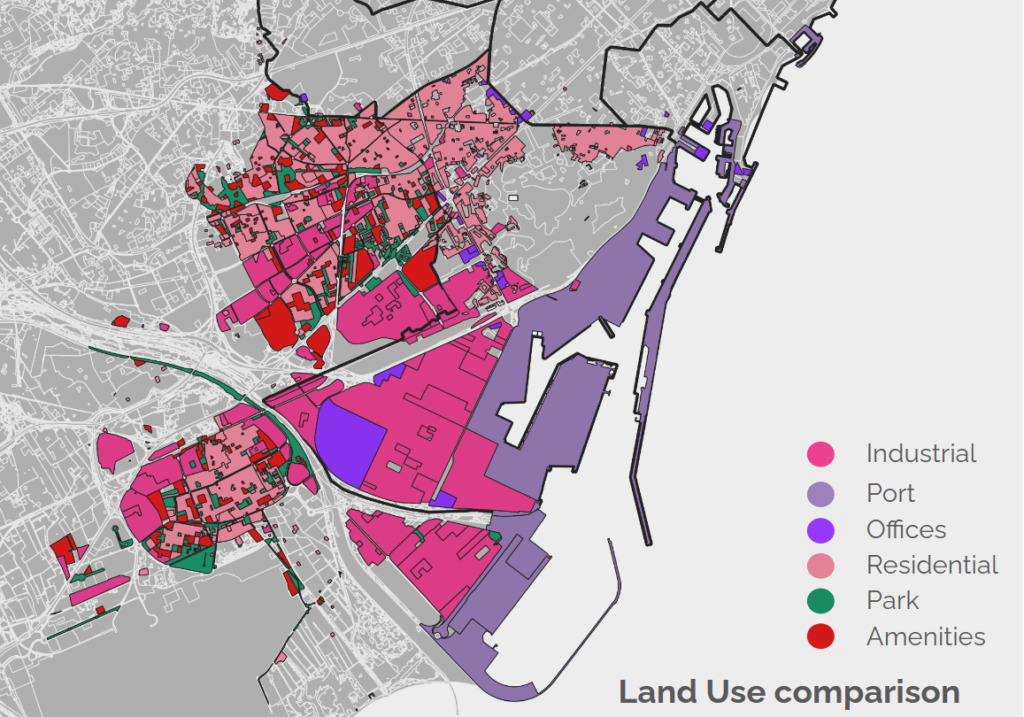
When compared to the surrounding areas, it can be clearly noticed that the land use in the Zona Franca is very homogeneous (it only includes only offices, industrial and the port), which is associated with a lack of amenities.
Projected Trends
In order to understand how the Zona Franca is going to develop in the future, it is essential to analyze the current economic trends that might affect it. The most relevant identified trends include:
A. Tourism Tendencies: The tourism industry is going to be mostly impacted by the continuous growth of cruise ships, as they are going to bring more people to the city through the port.
B. Changes within the industry: During the most recent years, the Automobile industry has been experienced a clear transition into electric cars, as the demand for fuel cars has decreased due to a rise in climate change awareness. This might shape the Zona Franca as a lot of Automobile factories are located there.
Additionally, since the 2020 pandemic, e-commerce has consistently increased. This is going to have an impact on the port dynamic and in logistic industries located on the site as Amazon.
C. Technology: New technology is being developed every day, especially in locations like the Zona Franca where there is development of 3D Printing, AI and IoT sensors and applications.
Opportunities and Constraints
By compiling the previous analysis, the following strengths and weaknesses were identified in the area:
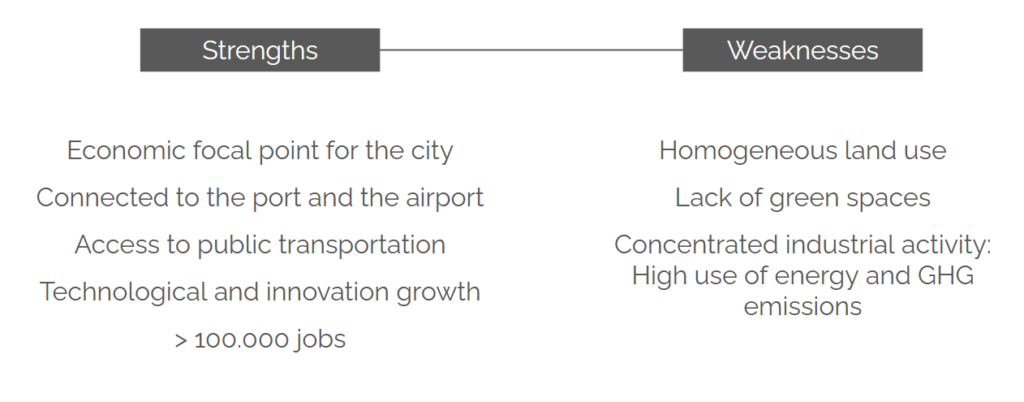
Through the analysis, it became clear that the Zona Franca is a site populated by thousands of tourists and workers on a daily basis, that is connected to the city by public transportation. It represents a concentration of technological growth and a focal economical point in Barcelona. However, this area does not address many of the necessities of the people, as there is a clear lack of amenity spaces and green areas. Finally, there is a missed opportunity on addressing the energy consumption and pollution in the area, considering that it is a leader in innovation.
Knowing that the Zona Franca receives thousands of workers and tourists daily , how could it be better improved to accommodate their needs?
Taking into account the previous weaknesses and opportunities, the following strategies are proposed to transform the Zona Franca into a healthier ecosystem for people and create a more balanced work-life environment:
A. Repurposing industrial buildings to accommodate community-building spaces and amenities.
This exercise has been implemented in other areas of the city. One good example is Can Batllo, which is a Self-managed Community and Neighborhood Space is a social and cultural facility located in different buildings, in the old textile factory of Can Batlló, in the Bordeta neighborhood.1
Although no empty buildings were identified in the Zona Franca, regulations can be applied so the land use is required to be diversified. This would benefit specially the workers in the area as they would be able to engage in different activities, improving their work-life balance.
B. Intervening empty spaces to create recreational facilities and parks.
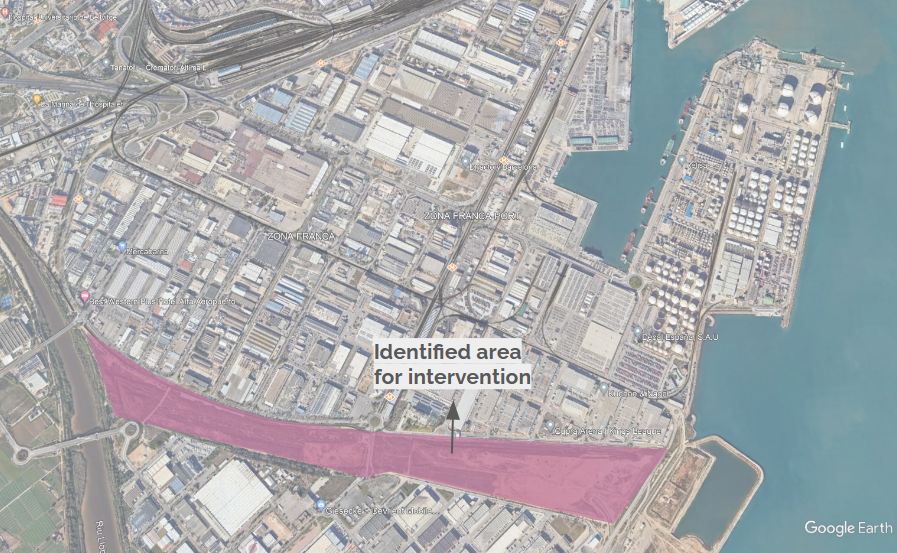
There is currently an area adjacent to the Zona Franca that represents an opportunity for intervention, as there is no infrastructure or a clear use on it.
This area is a potential park where commercial spaces could be incorporated, so they can benefit workers, nearby residents and tourists.
Creating a public green space in the area (around 700 m^2) would help tackle the lack of amenities and green spaces. Having such a big area for intervention is a big opportunity for the site.

C. Policy-making that address green-energy production:
According to Barcelona’s Energy Observatory, only 1% of the energy consumed in the city comes from renewable sources. As a site for innovation, the Polygon should be a leader in sustainable production and transition from fossil fuels.
References:
- Can Batllo (2023) Espai comunitari i veïnal autogestionat de La Bordeta Obtained from: Can Batlló | Espai comunitari i veïnal autogestionat de La Bordeta (canbatllo.org) ↩︎


