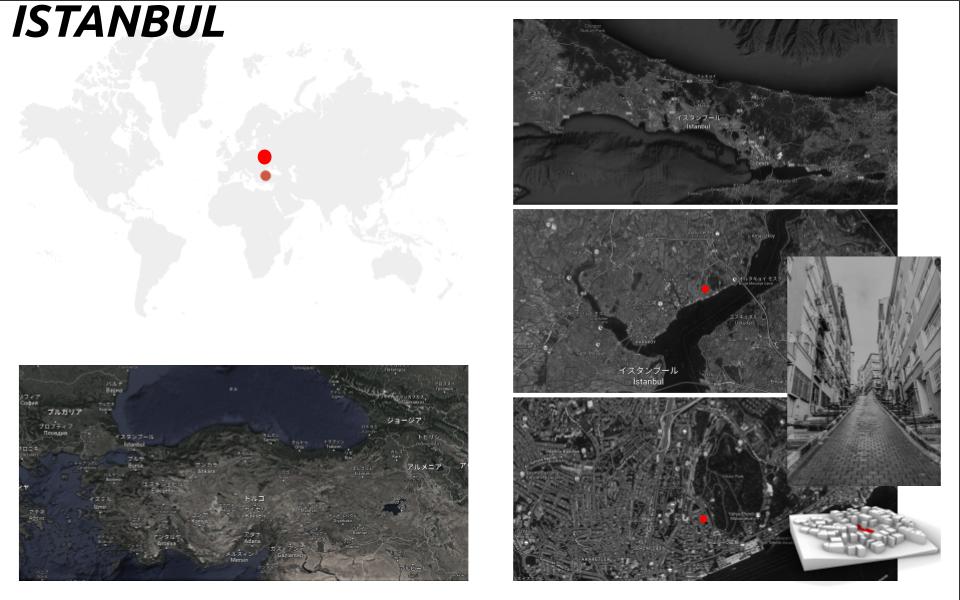
The project is located in Istanbul. It is the city I dream to develop design projects in the near future. I used this chance to practice the basics of an environmentally informed design in a city where the built environment is dense, the buildings always in very close proximity and the topology is hilly. It is located in Besiktas where streets are narrow, the buildings are adjacent to each other.
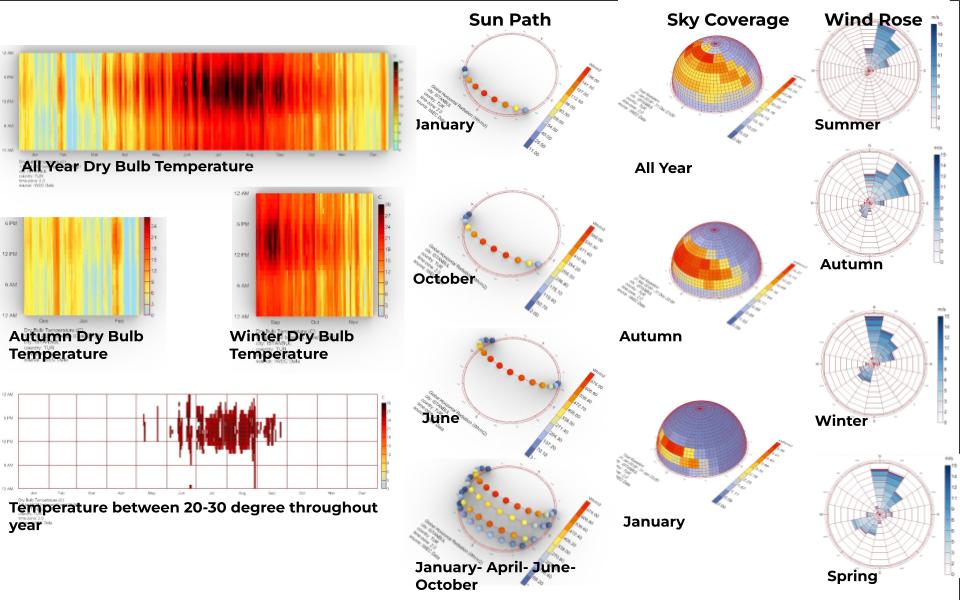
Istanbul has a borderline Mediterranean climate, it has four distinct seasons. The winters are not harsh but the urban heat island effect creates a huge difference in summer in case of feeling the heat between concrete blocks. Looking at the climate analysis, being able to divide and filter the information according to hours was the biggest takeaway for me. September still carries the summer like temperature, the city receives plenty of sunlight all year long. The predominant wind direction is North, Northeast but also before, during and after winter because of the temperature movement of the air wind from the southwest which is called Lodos is observed. It is a nightmare for fishermen.
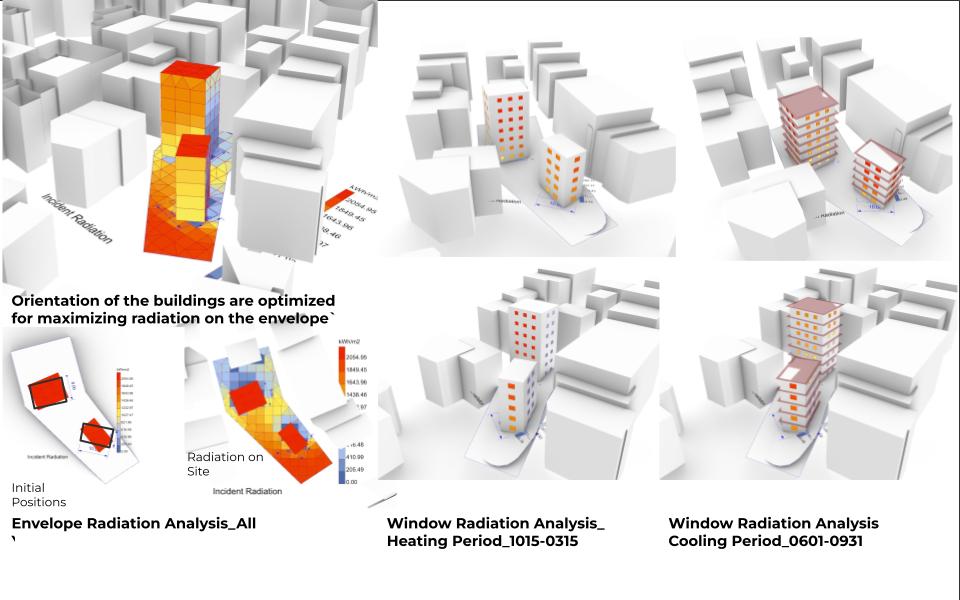
Orientation of the buildings are individually optimized for maximizing radiation on the envelope in the all year long period. The more distance between the buildings causes less shadow in each other. The building behind higher, the building front lower is a good combination for the building behind to get more sunlight. Division of the information helps to create a scenario for optimization.
Size and amount of the windows are optimized for maximizing radiation on the windows for the heating period. Building behind has more windows, the building front has fewer but bigger windows. Building behind gains much more radiation on the higher levels.
Offset of the shadings are optimized for minimizing radiation on the window for cooling period. Building behind has a bigger offset of 80 cm than the Building front 60 cm according to the amount of radiation each building receives in this specified period.
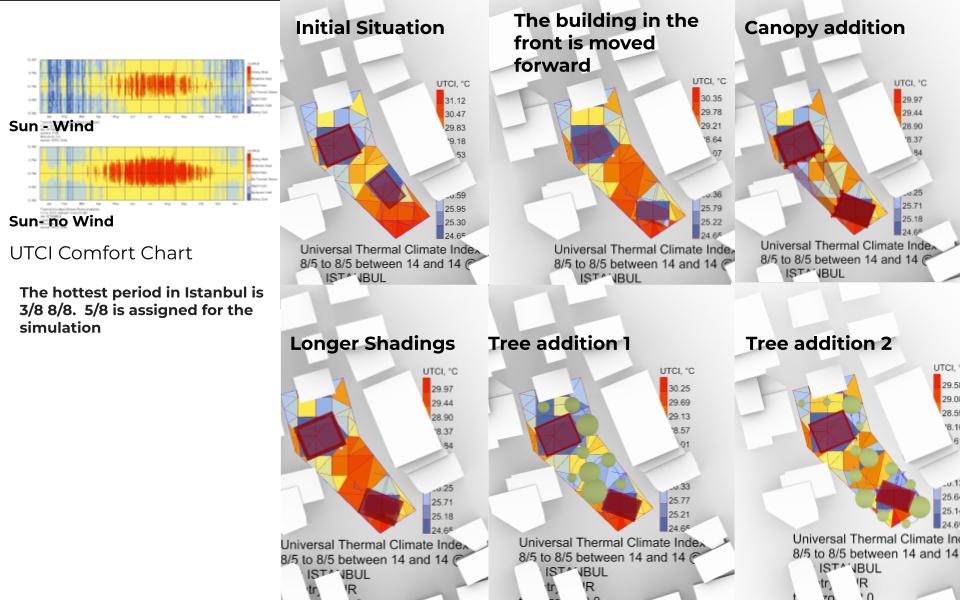
The outdoor thermal; comfort is analyzed for the public space in between the buildings on the hottest period in Istanbul which is the first week of August. First the already built in relations of the area are examined, the building in the front is moved forward to cast more shadow on the site than the building behind, also longer shadings are applied. Later a canopy is added between two buildings where the shadows of the buildings are less effective. Lastly, different plantation scenarios are added on the site.
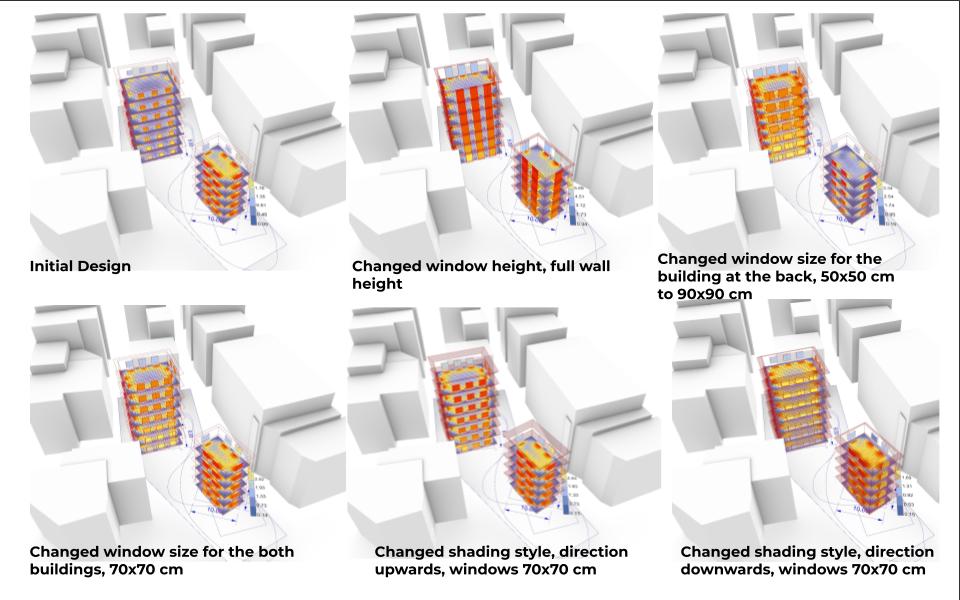
One of the biggest problems in Istanbul is receiving daylighting to the interior. From the generic initial design, the window heights are changed as longer at the bottom, full wall height, building at the back from 50×50 cm to 90×90 cm. Also the shading style is examined as direction upwards, windows 70×70 cm, Changed shading style, direction downwards and so on.