Incorporating the principles of Industry 4.0, our architectural project redefines urban living by seamlessly integrating sustainable design strategies with advanced manufacturing techniques. With a focus on promoting bicycle culture and health, our industry manufactures bikes.
We present a visionary housing project that integrates thermodynamic principles to ensure the comfort and well-being of its residents while optimising energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. By strategically orienting buildings to maximise natural ventilation and solar exposure and by incorporating high-efficiency insulation materials and shading devices, we create an environment that minimises energy consumption while maximising comfort for residents.
Concept
Our industry being bikes, we used the aerodynamics of biking as a inspiration to wrap our building with an organic envelope. A continuous bike lane goes from the street level to every floor of the building. Every space is can be accessed by bike. The bike ramp and organic slab is hung from the trusses using tensors which resemble a cycle wheel. The facade also behaves as a water filtration system while incorporating passive design techniques.
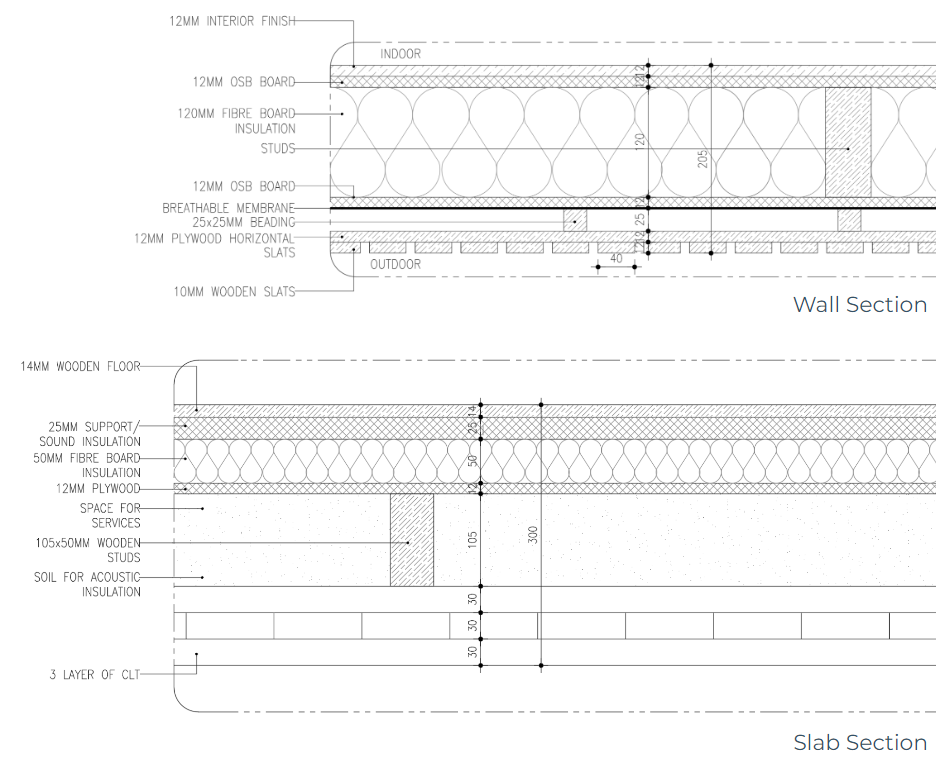
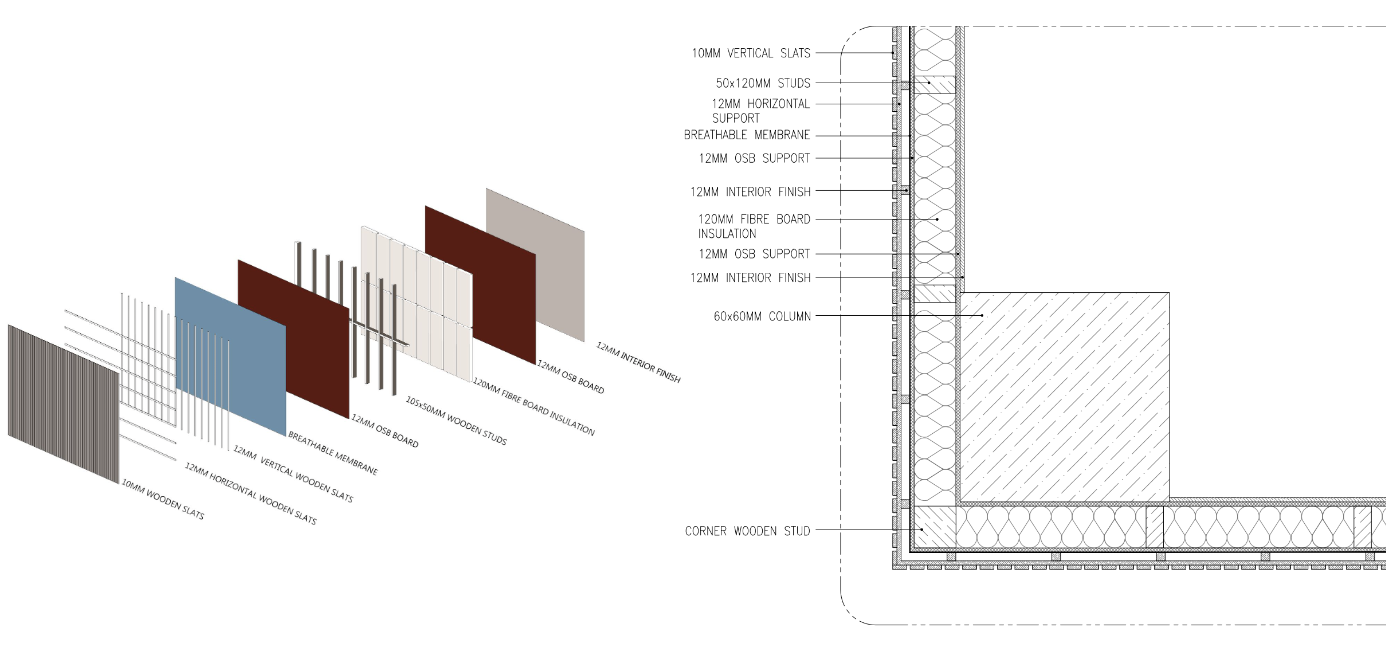
Wall and Slab Details
The details show the layers and materials used in the walls and slabs of the building. The materials were chosen based on thermodynamic data. The idea would be to keep the structure rather lightweight, while adding enough insulation to avoid overheating in summer or a big heatloss in winter.
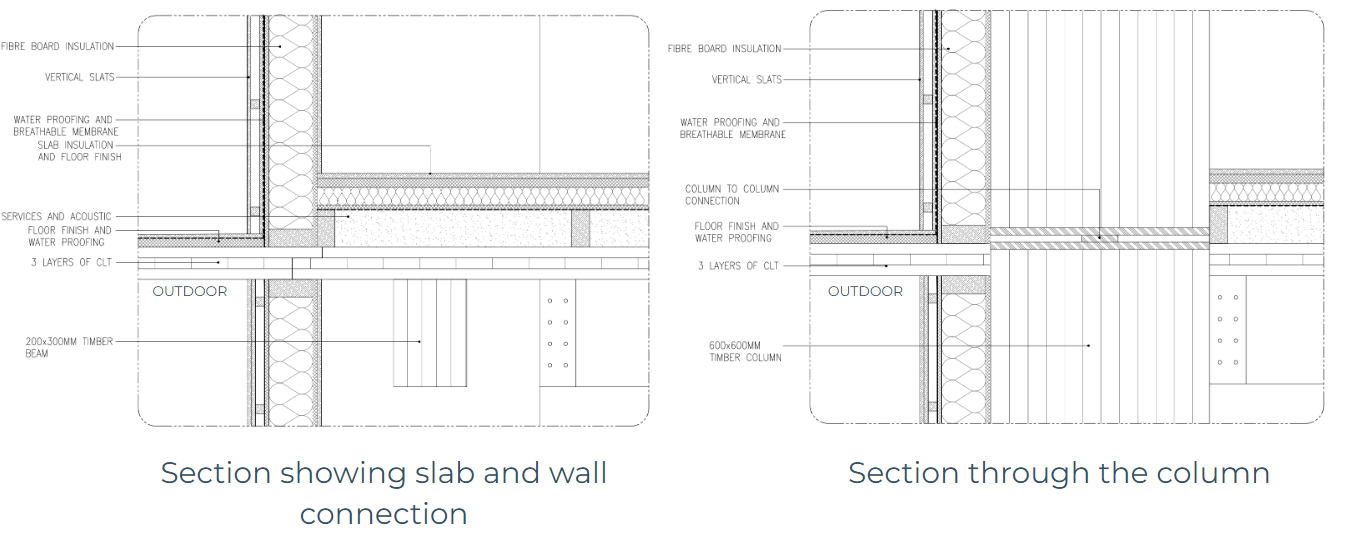
The details of wall and slab joinery show the connection between the wall and slab. To avoid thermal bridges, the insulation (and consequently the exterior facade finishing) was placed in front of the columns which form the bearing structure of the project. However, some critical points were still identified. The slab, which should be a continuous element, introduces a thermal brigde at the connection of the terrace and interior wall. However, after discussion, it was considered wood can be considered as thermal resistant.
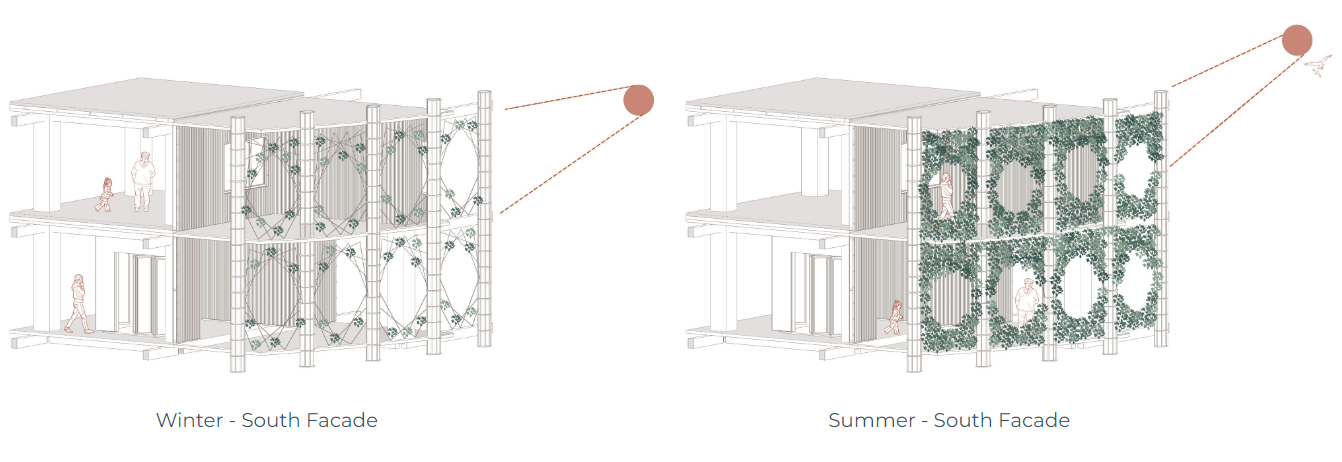
Passive Design Strategies
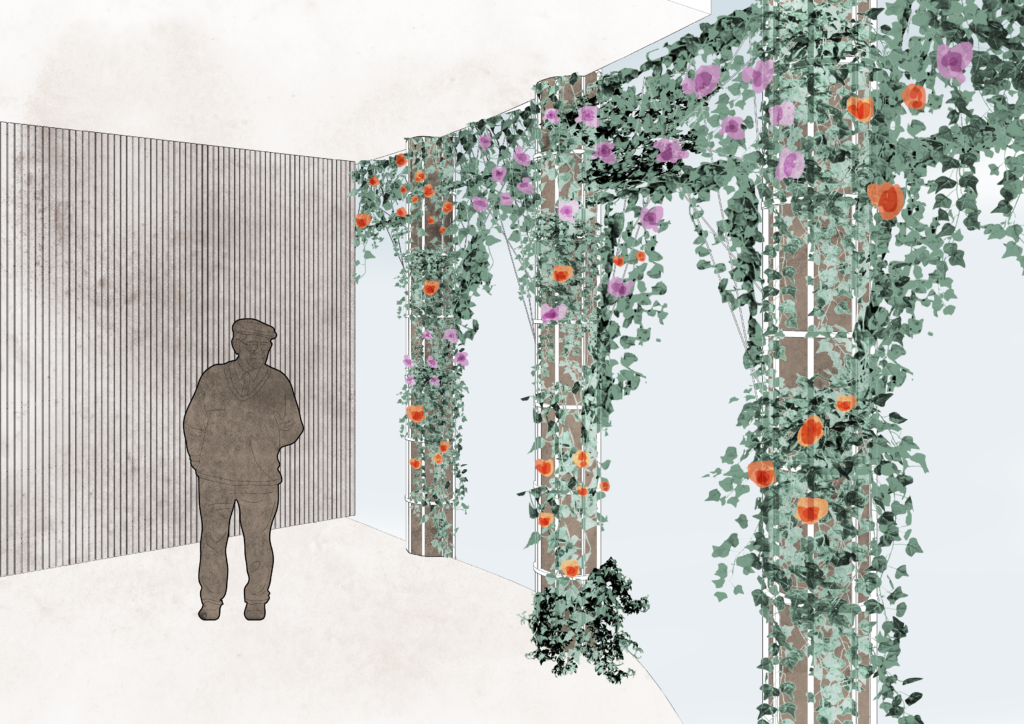
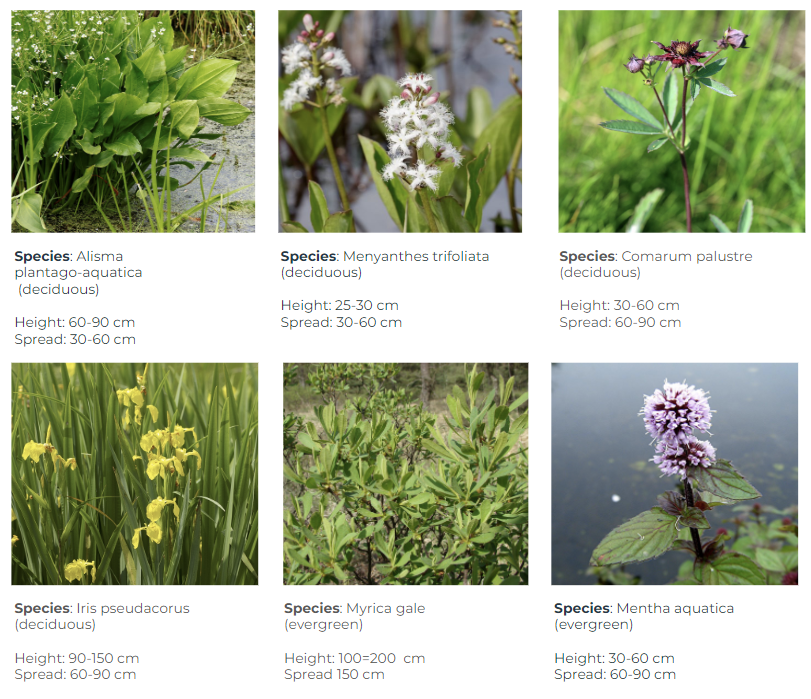
The facade has vertical soil membranes which grow plants. these plants use the tensors as a support system to grow. The deciduous plants have a wide spread in the summer which provides shading and air filtration; in the winter, they allow more sunlight into the building.
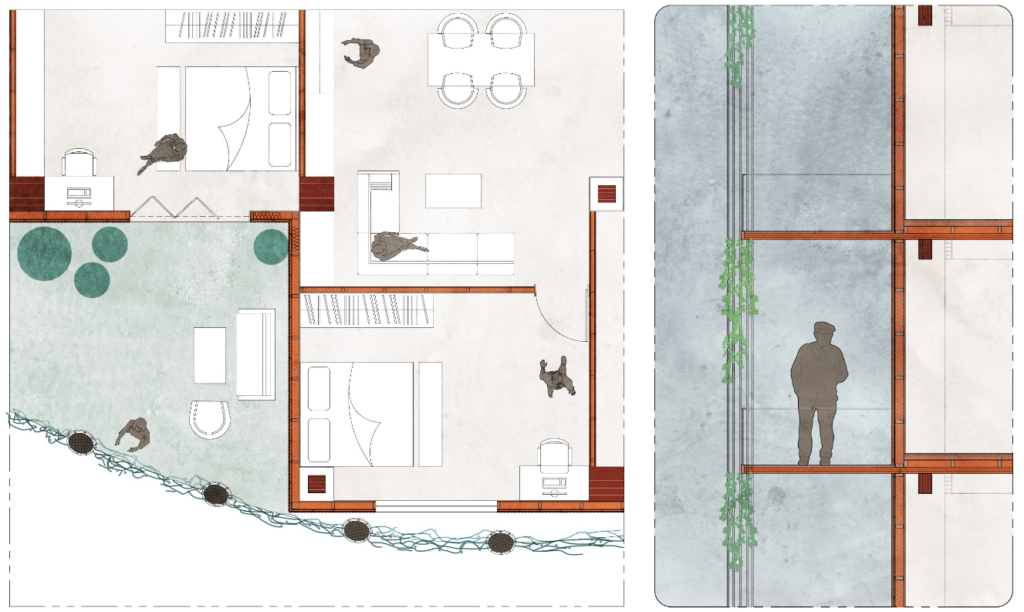
Envelope Details
The diagrams show the interaction between the interior spaces and the facade. The green facade creates a buffer between the interior and exterior.
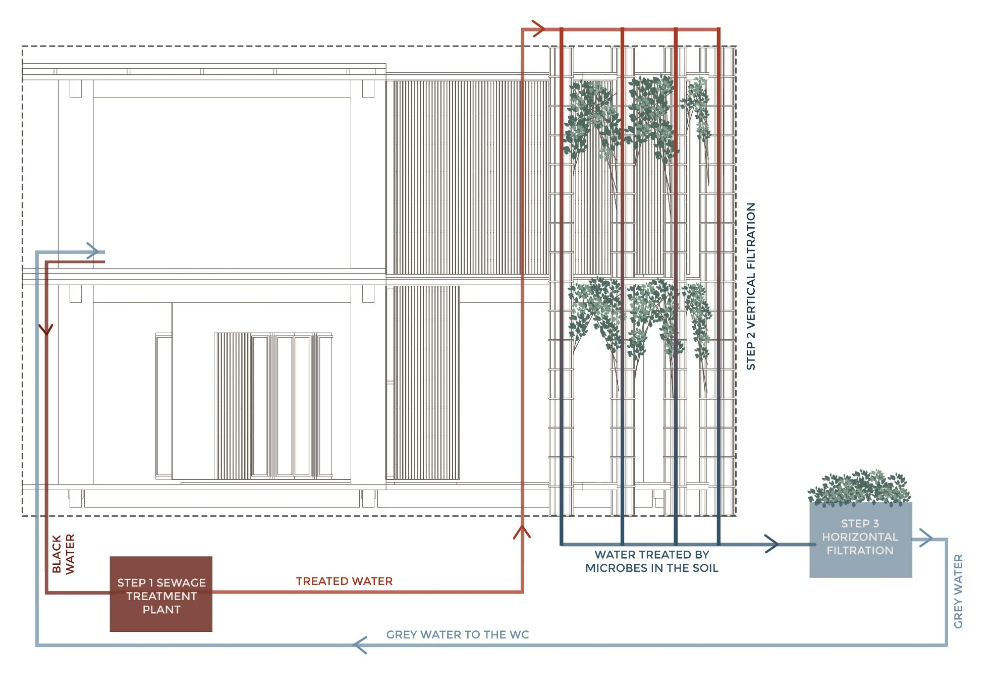
Vertical Water Filtration
Not only is the envelope used for thermodynamic purposes, but the vertical columns out of which the plants for our shading grow, double as a water filtration system. As the second step of the water filtration system, bacteria are taken out of the water by the plant roots and serve as growing agents for the latter.
Vegetation
Deciduous plants are grown in the southern facade and evergreen plants in the northern facade.