.
A spectre is haunting the world — the spectre of the divide between imperial and metric measurement systems.
Where is an architect that hasn’t faced the effect of these conflicting measurements? Where is the building design that hasn’t been critiqued for using the “wrong” system, whether by rivals, clients, or critics?
Two things result from this fact:
I. This crisis is already acknowledged by all architects as a fundamental challenge.
II. It is high time that architects, innovators, and designers should openly, in the face of the whole world, publish a solution and meet this age-old tale of divide with an ultimate tool that solves it, one centimeter at a time.
.
.
Future Development Ideas
- Give it more personality — make it scream in pain when someone makes a horrendous guess and sigh in relief when they finally get it right.
- Mass-produce the device and flood online marketplaces. With well thought-out marketing strategies plus over-the-top luxury packaging, a limited edition version might just take the market by storm.
- And the final goal, to set up giant public installations in major cities that still cling to the imperial system.
.
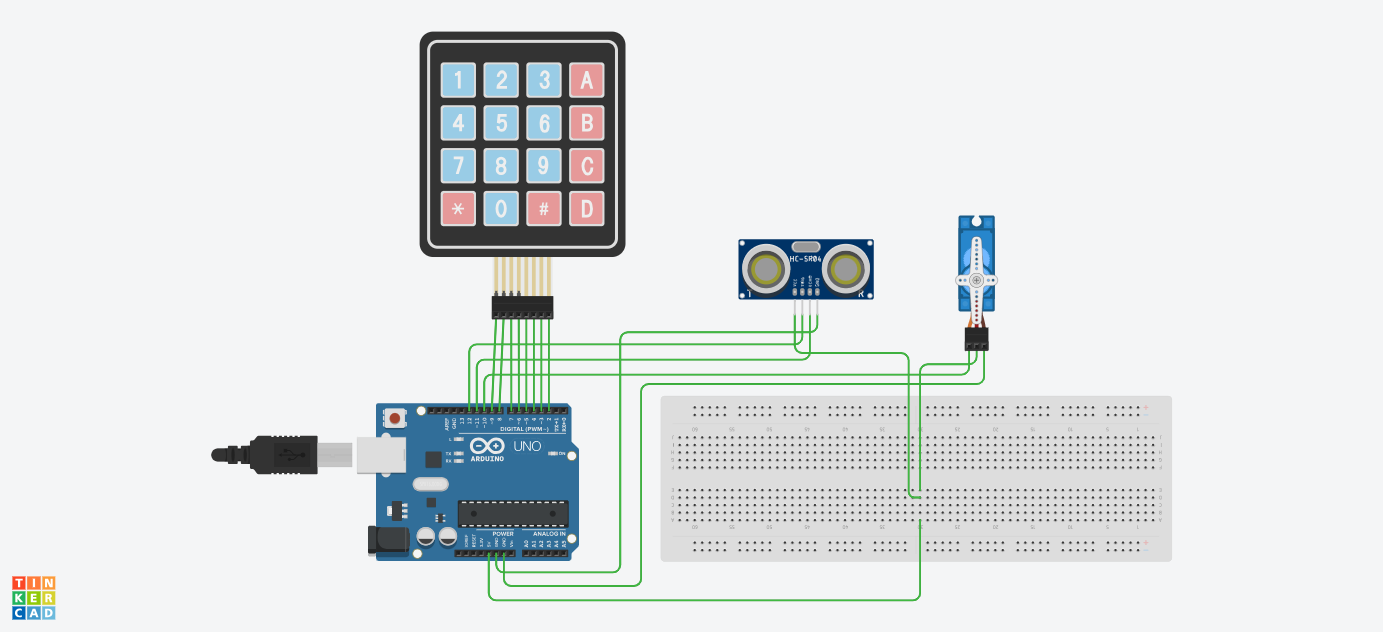
Bill of Materials
- Arduino
- Servo Motor
- Ultrasonic Sensor (HC-SR04)
- Wires and Jumper Cables
- Breadboard
- 4×4 Matrix Keypad
.
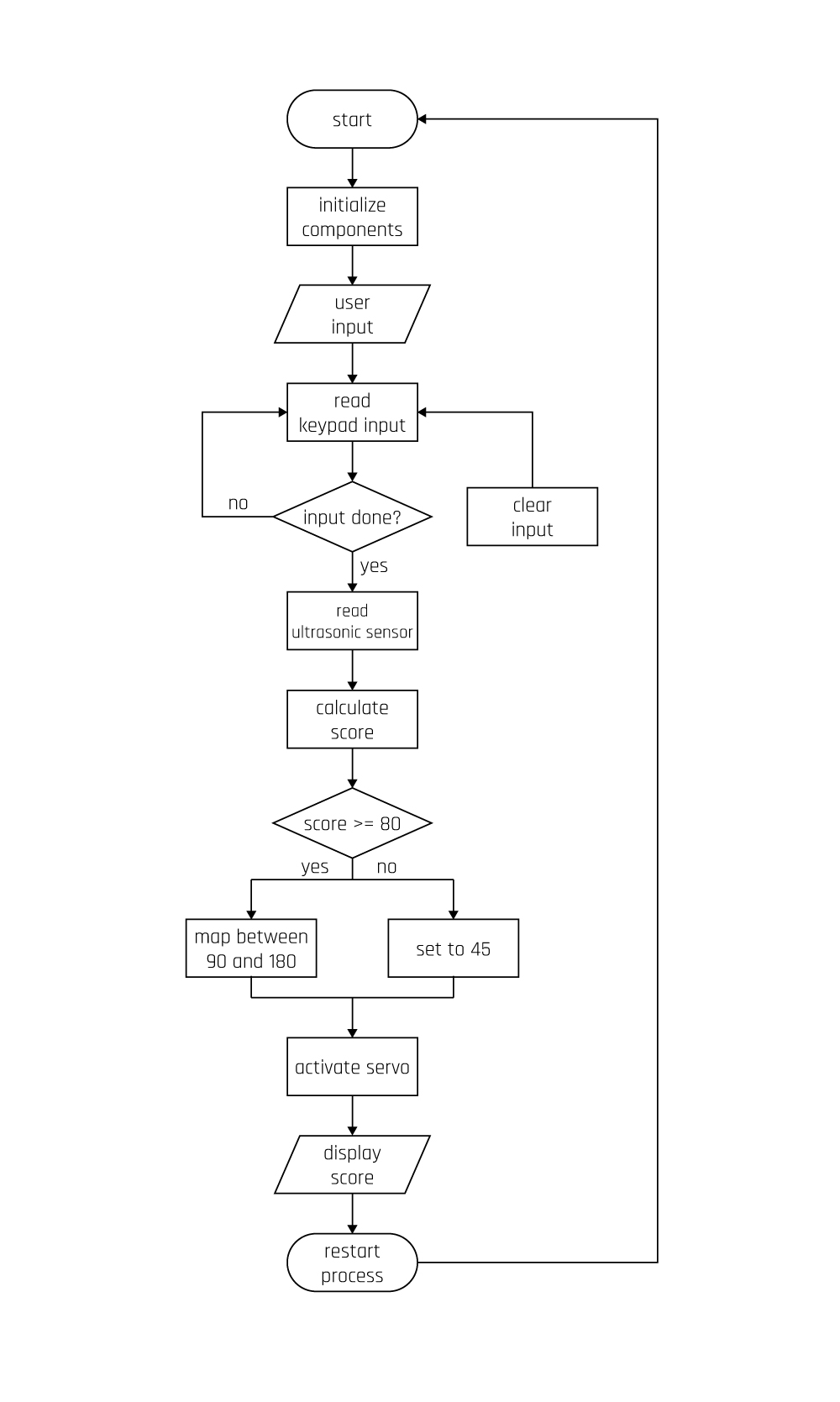
Source Code
#include <Keypad.h>
#include <NewPing.h>
#include <Servo.h>
#define TRIGGER_PIN 12
#define ECHO_PIN 11
#define MAX_DISTANCE 200
// Keypad settings
const byte ROWS = 4;
const byte COLS = 4;
char keys[ROWS][COLS] = {
{‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘A’},
{‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘B’},
{‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’, ‘C’},
{‘*’, ‘0’, ‘#’, ‘D’}
};
byte rowPins[ROWS] = {9, 8, 7, 6};
byte colPins[COLS] = {5, 4, 3, 2};
Keypad keypad = Keypad(makeKeymap(keys), rowPins, colPins, ROWS, COLS);
NewPing sonar(TRIGGER_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE);
Servo myServo;
String inputNumber = “”;
bool readyToMeasure = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(“Enter a target distance (in cm):”);
myServo.attach(10);
myServo.write(0);
}
void loop() {
char key = keypad.getKey();
if (key) {
if (key == ‘#’) {
if (inputNumber != “”) {
Serial.print(“Target distance set to: “);
Serial.print(inputNumber);
Serial.println(” cm”);
readyToMeasure = true;
} else {
Serial.println(“No input detected. Please try again.”);
}
} else if (key == ‘*’) {
inputNumber = “”;
readyToMeasure = false;
Serial.println(“Input cleared. Enter a new target distance:”);
} else {
inputNumber += key;
Serial.print(“Current input: “);
Serial.println(inputNumber);
}
}
if (readyToMeasure) {
delay(500);
int distance = sonar.ping_cm();
Serial.print(“Measured distance: “);
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(” cm”);
int targetDistance = inputNumber.toInt();
int difference = abs(targetDistance – distance);
Serial.print(“Difference: “);
Serial.print(difference);
Serial.println(” cm”);
float percentage = 100.0 * (1.0 – (float)difference / (float)targetDistance);
percentage = constrain(percentage, 0, 100);
Serial.print(“Percentage: “);
Serial.print(percentage);
Serial.println(“%”);
sweepServo();
// below 80, 45°.
if (percentage < 80) {
myServo.write(45); // Move servo to 45 degrees for scores below 80%
Serial.println(“Servo at 45° (score below 80%)”);
}
// between 80 and 100, between 90° and 180°.
else {
int targetAngle = map(percentage, 80, 100, 90, 180); // Map 80%-100% to 90°-180°
targetAngle = constrain(targetAngle, 90, 180); // Ensure the angle stays between 90° and 180°
myServo.write(targetAngle);
Serial.print(“Servo at “);
Serial.print(targetAngle);
Serial.println(“°”);
}
Serial.print(“Final Score: “);
Serial.print(percentage);
Serial.println(“%”);
inputNumber = “”;
readyToMeasure = false;
Serial.println(“Enter a new target distance:”);
}
}
void sweepServo() {
for (int angle = 0; angle <= 180; angle++) {
myServo.write(angle);
delay(15);
}
for (int angle = 180; angle >= 0; angle–) {
myServo.write(angle);
delay(15);
}
}

