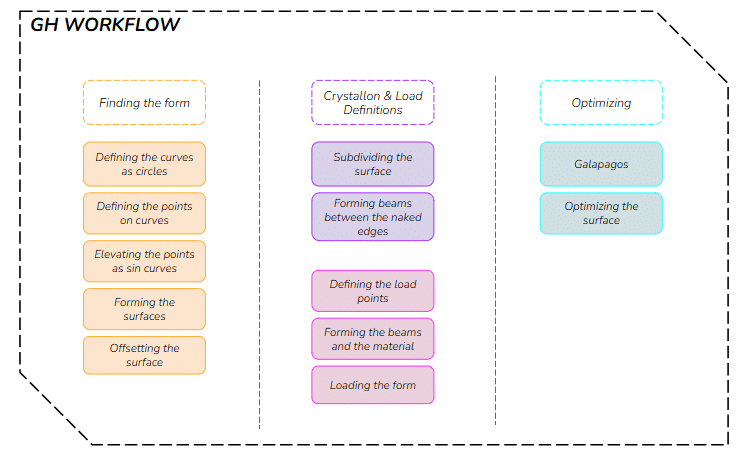
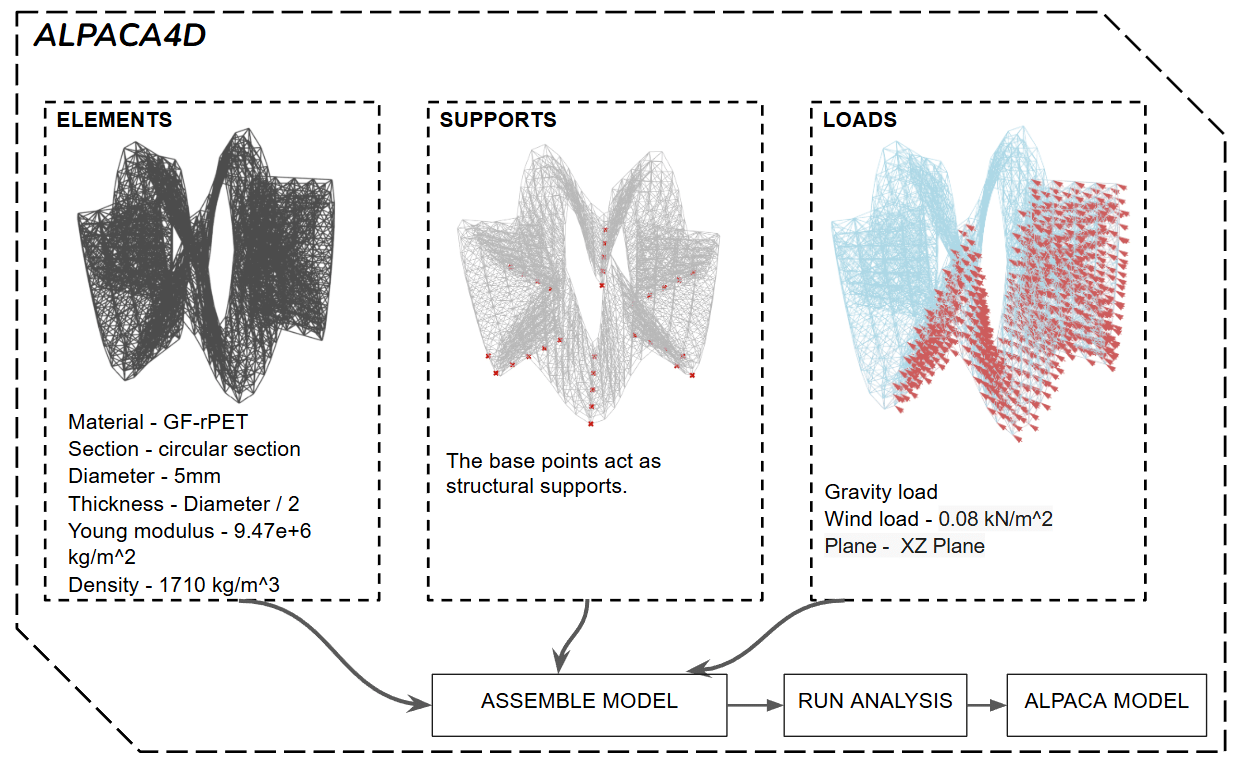
The Sine Tide aims to analyse the design of a PET pavilion from a lattice structure that fits within an 8x8x6m bounding box. The pavilion was designed using the sine function. Later on, the lattice structure was formed using Crystallon. After the design, the loads and materials were defined using Alpaca4d. Finally, it was optimised using Galapagos. The design was visualised using Twinmotion.
Work Flow
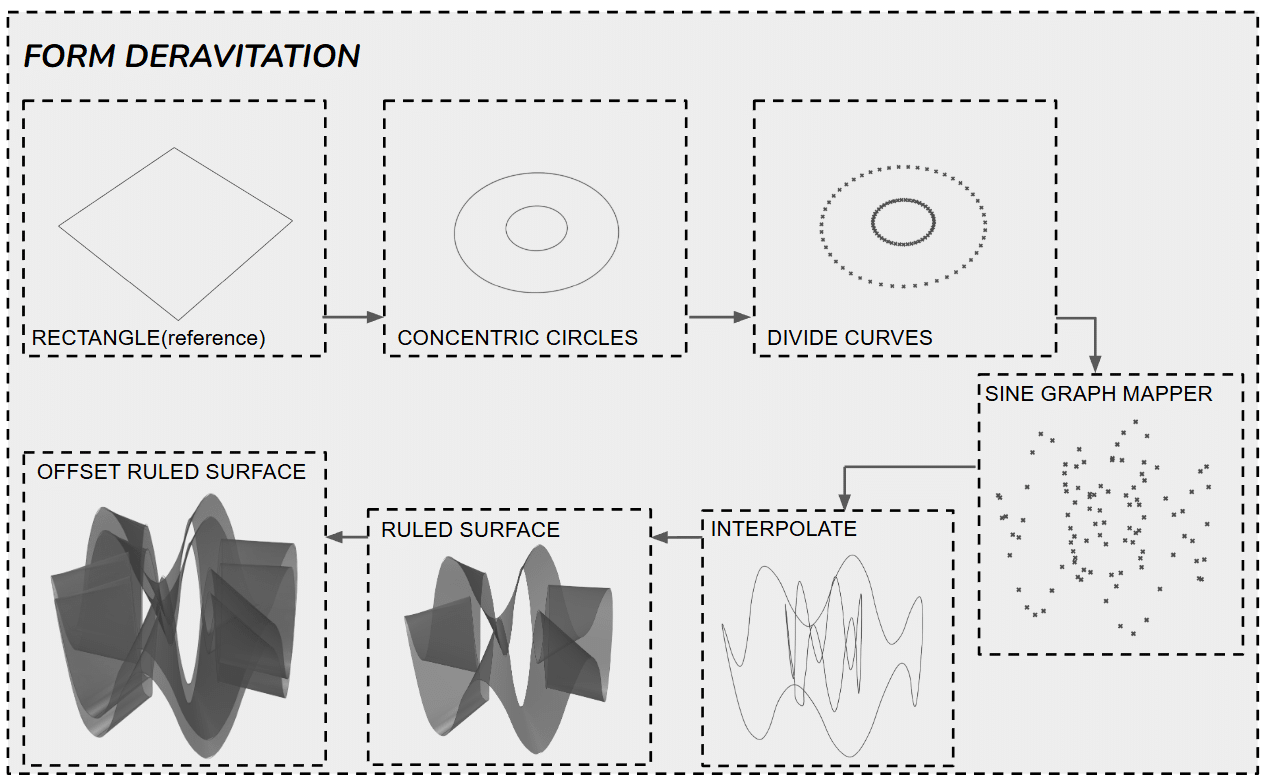
Form Derivation
The form generation begins with a rectangular bounding plane used as a reference. This base geometry is transformed into concentric circles; these circles are divided into discrete points, and a sine graph mapper is applied to introduce controlled vertical variation along the z-axis. The modified points are interpolated to generate continuous curves, which are then connected using a ruled surface to generate the surface, which is finally offset to achieve the final volumetric form.
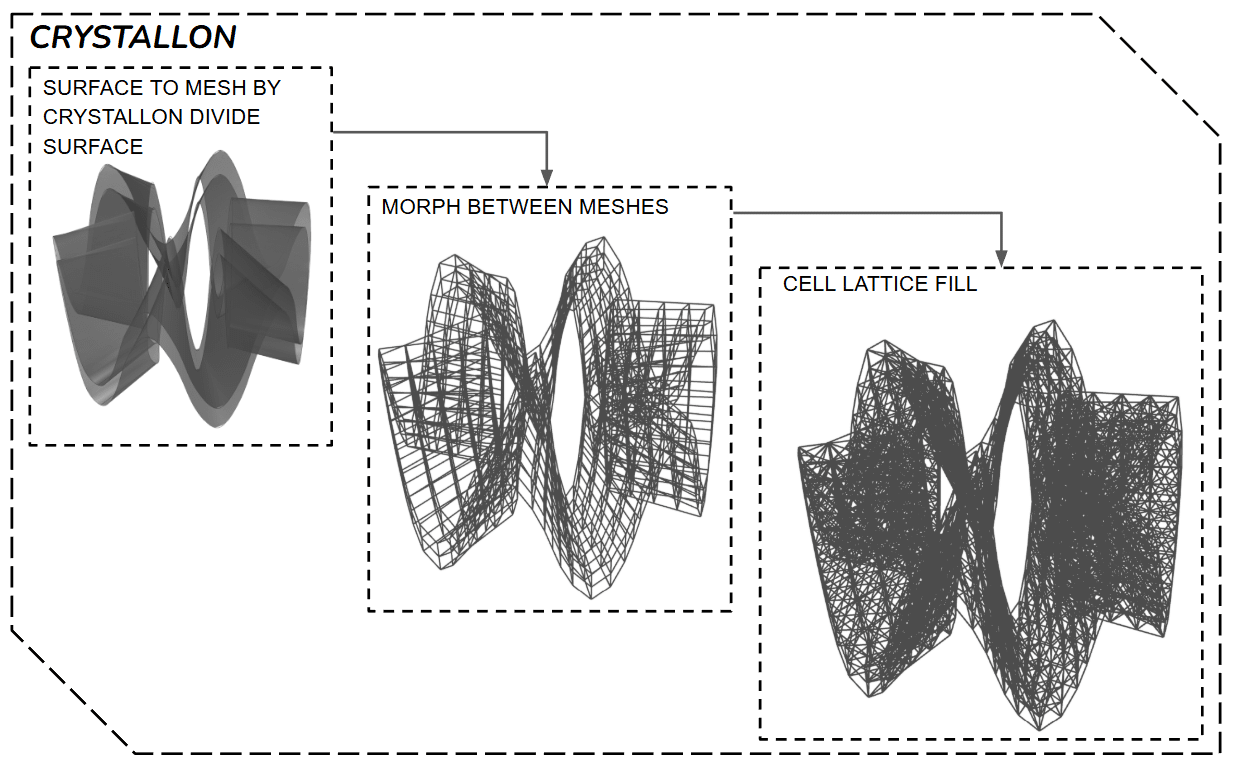
CRYSTALLON
The final surface is converted into a mesh using Crystallon Divide Surface and morphed between different mesh states to control density and continuity. The resulting mesh is filled with a cellular lattice, generating a lightweight and structurally expressive framework.
ALPACA4D
The lattice geometry is defined as structural elements with a circular cross-section, using Glass reinforcement RECYCLED PET material with a 5 mm diameter, a thickness equal to half the diameter, and assigned Young’s modulus and density.
The base points of the structure are defined as fixed supports to establish boundary conditions.
A gravity load and wind load of 0.08 kN/m² is applied in the XZ plane to simulate environmental forces.
All structural elements, supports, and loads are assembled into a single analytical model.
Structural analysis is carried out in Alpaca4D to evaluate axial forces, deflection, and overall structural behaviour with its mass.

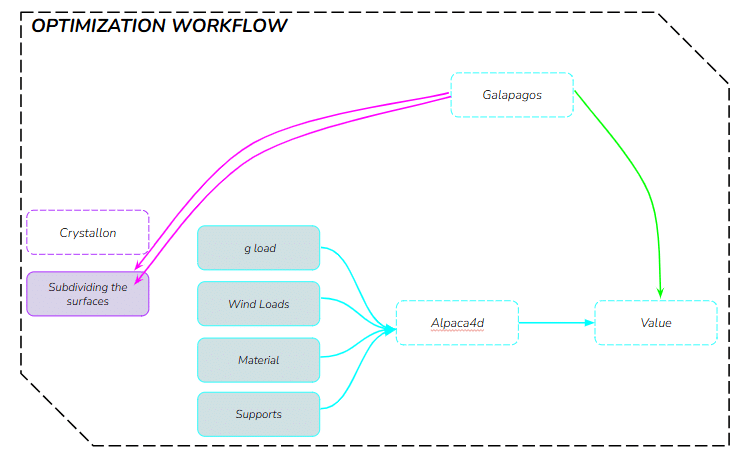
OPTIMIZATION
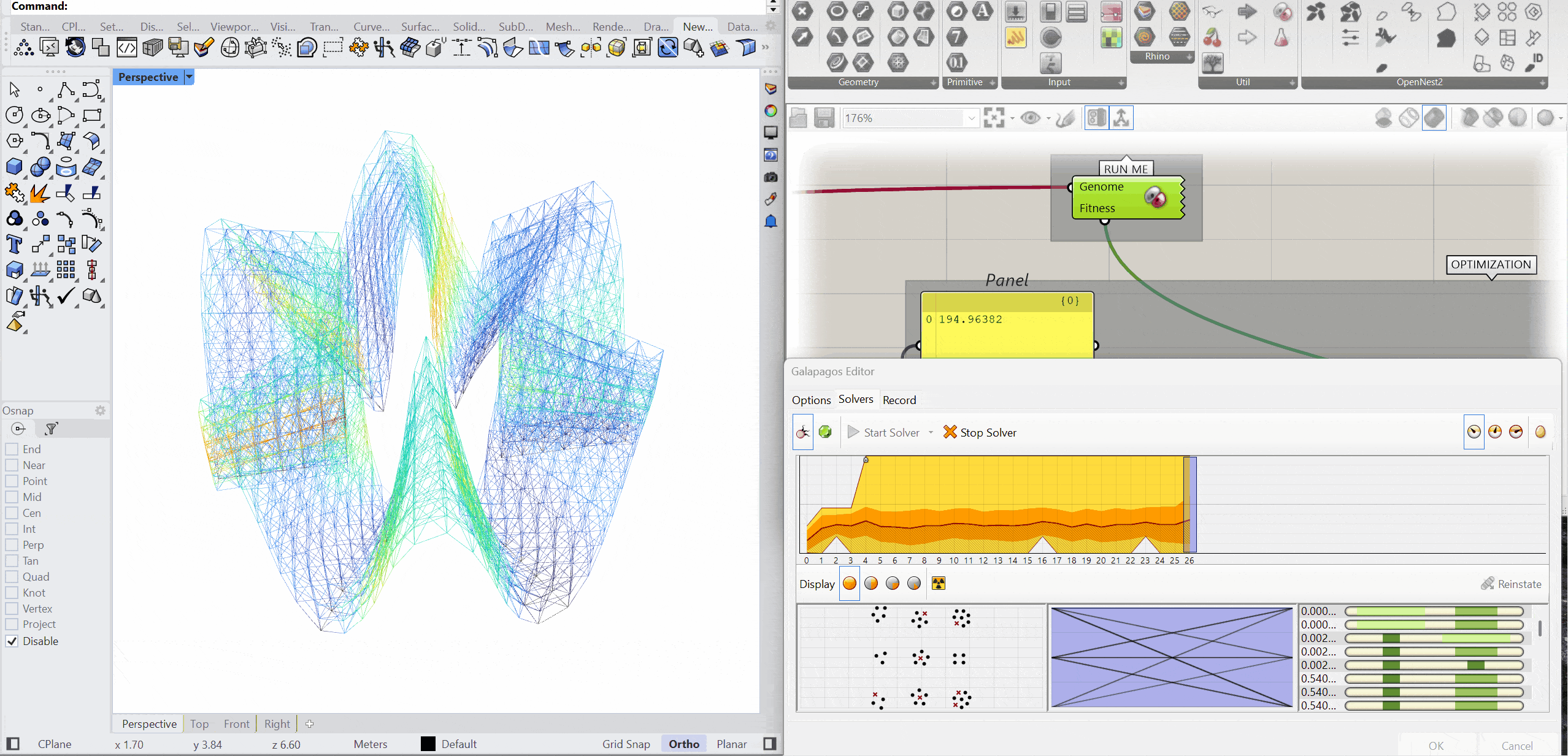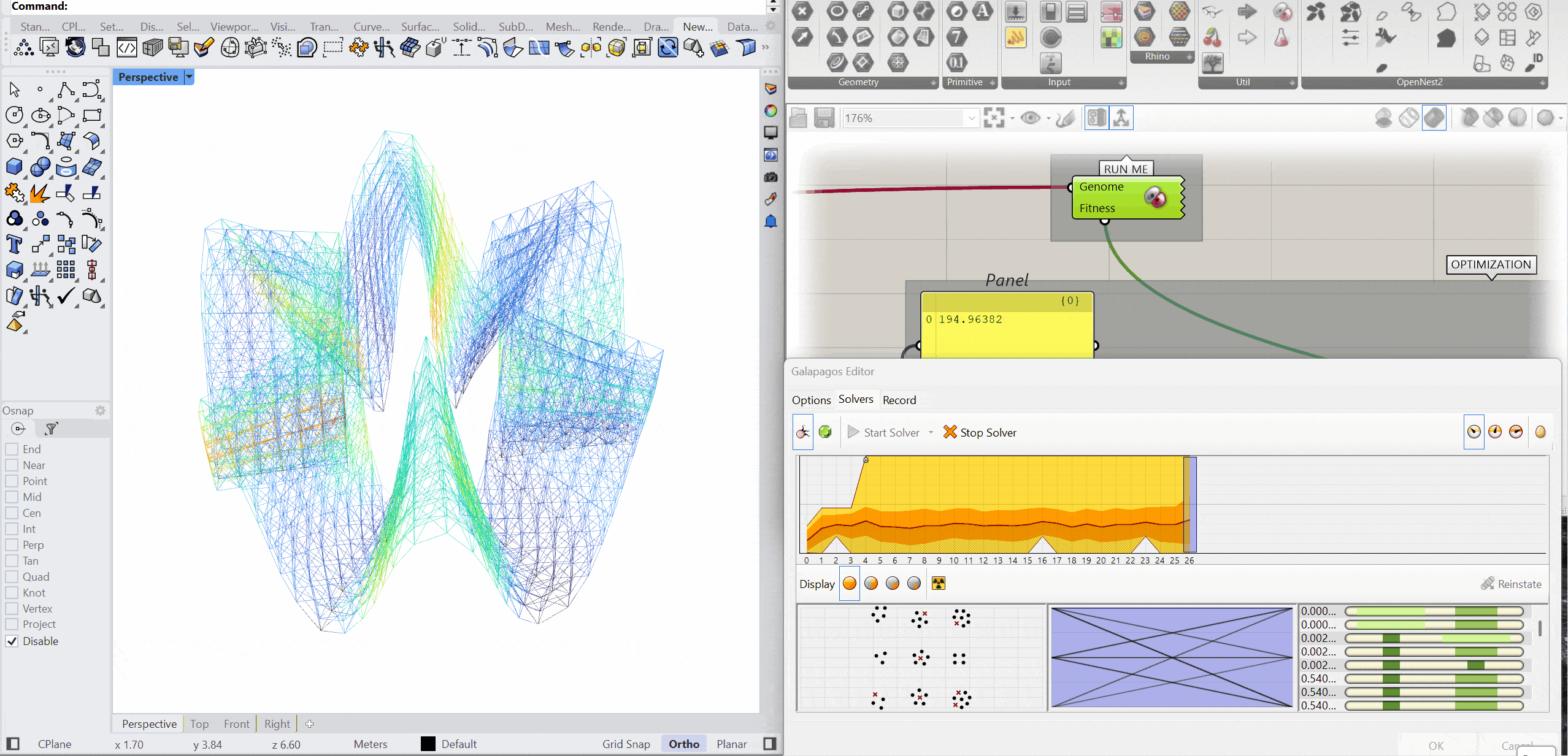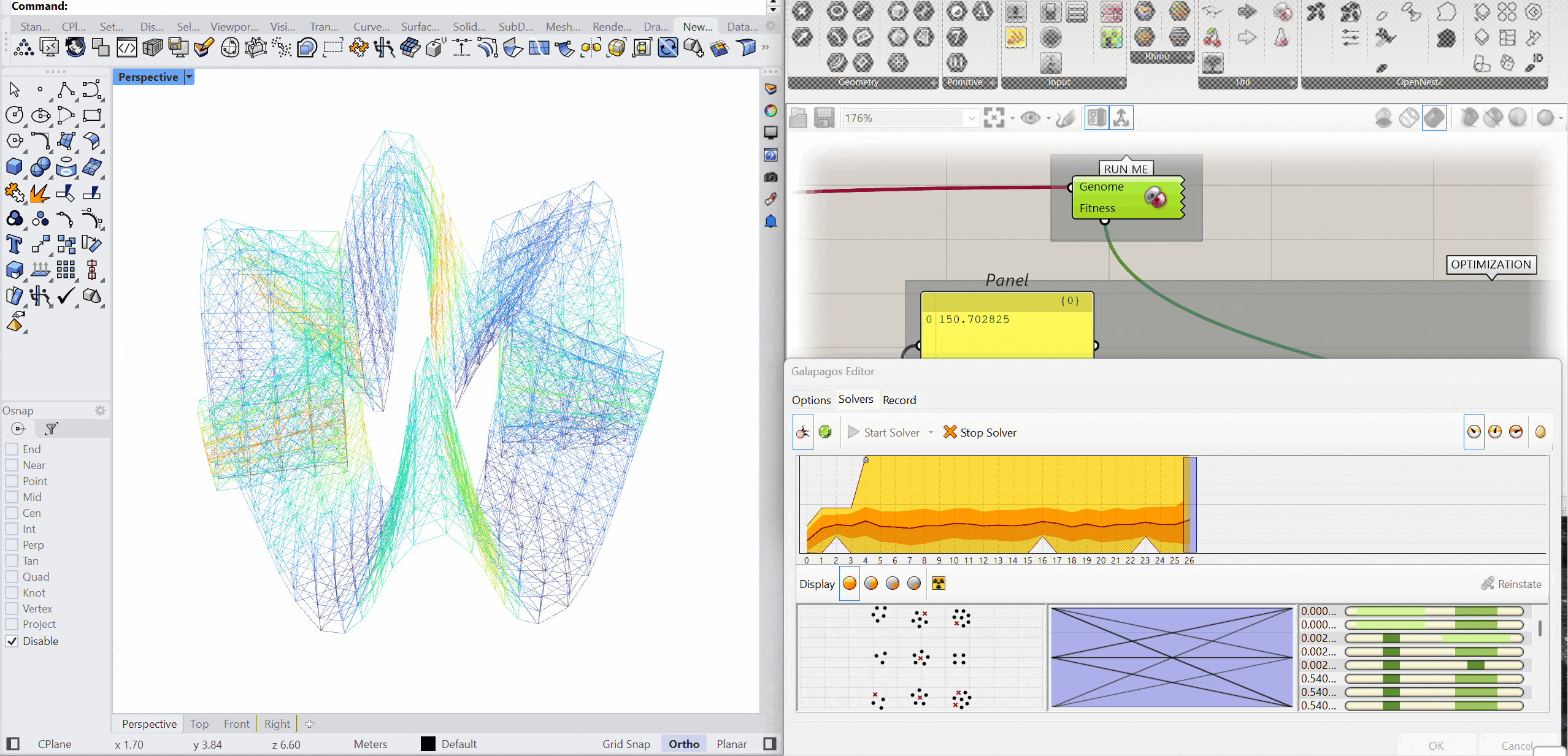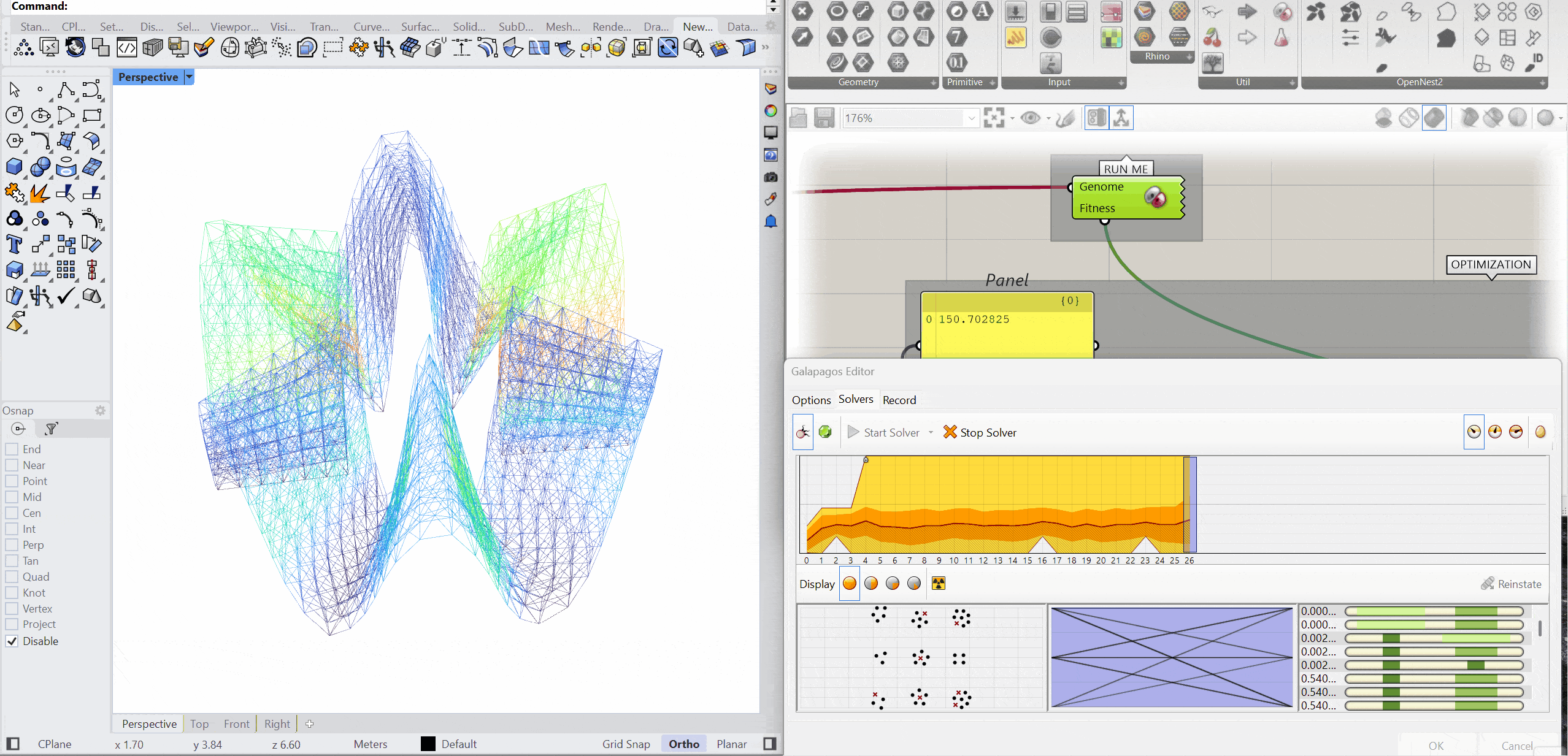
The structure was optimised using Galapagos by varying the initial boost parameter to evaluate its impact on structural performance. Increasing the initial boost from 2 to 5 reduced the overall mass and significantly decreased deflection while maintaining comparable axial force levels. The optimised configuration demonstrates improved structural efficiency with lower deformation and material usage.

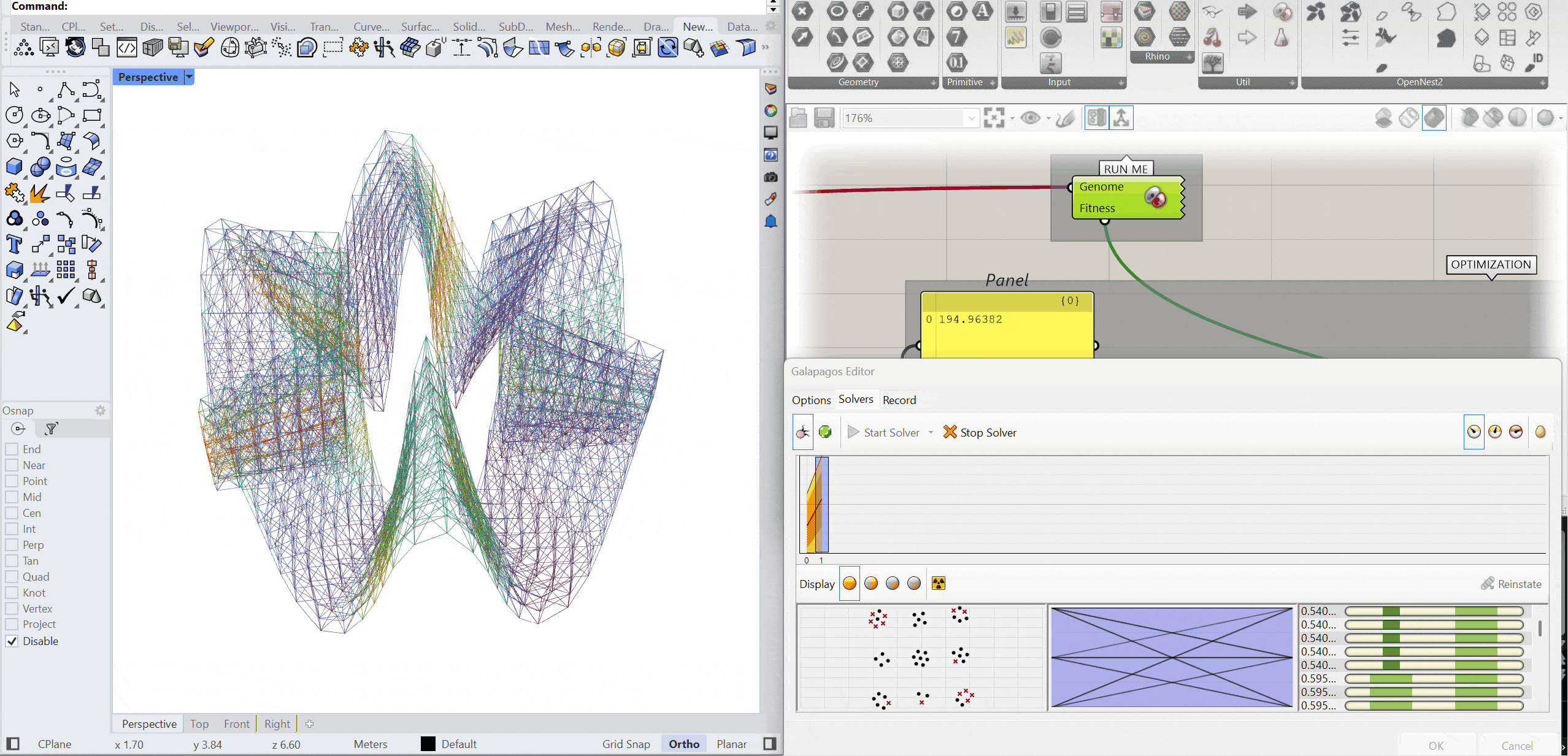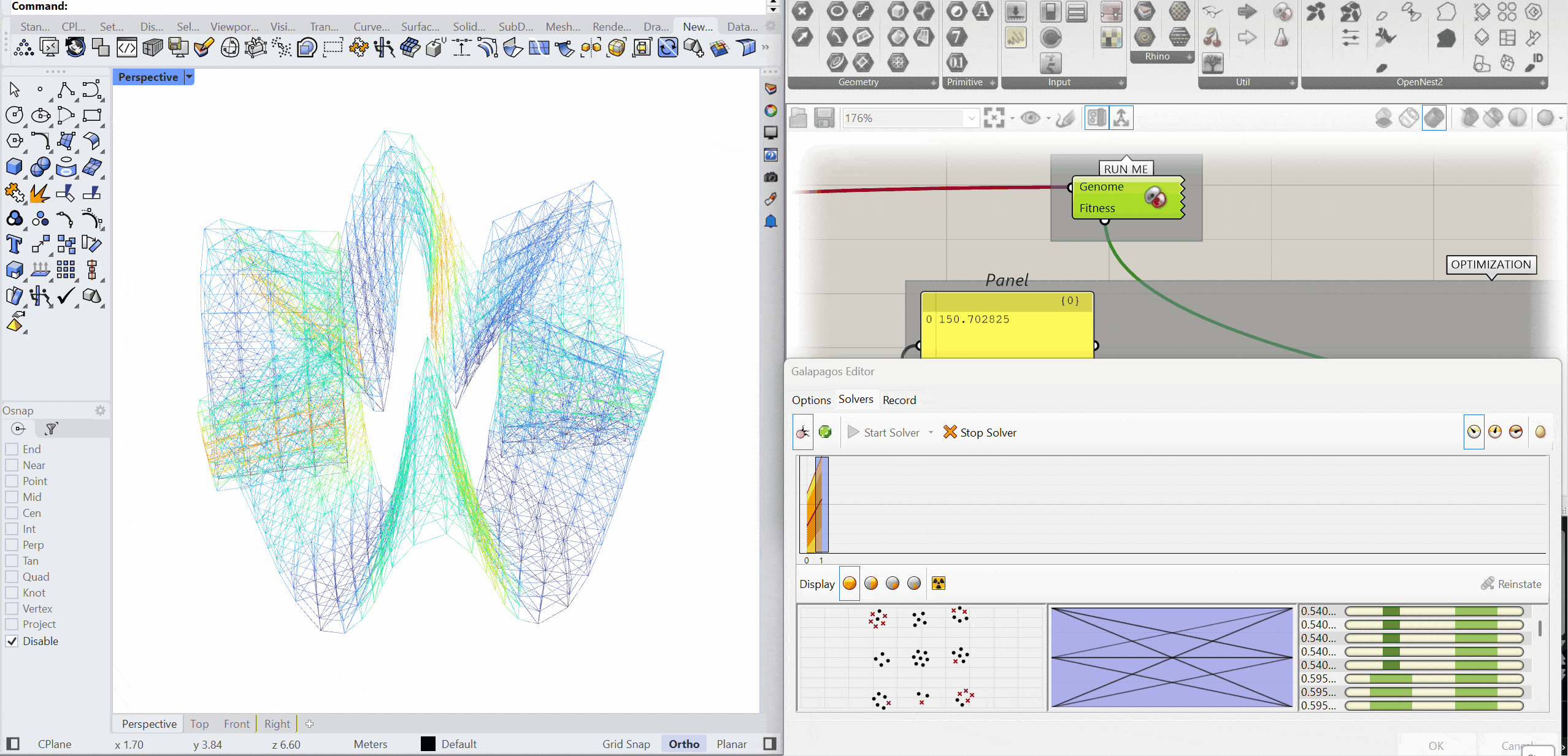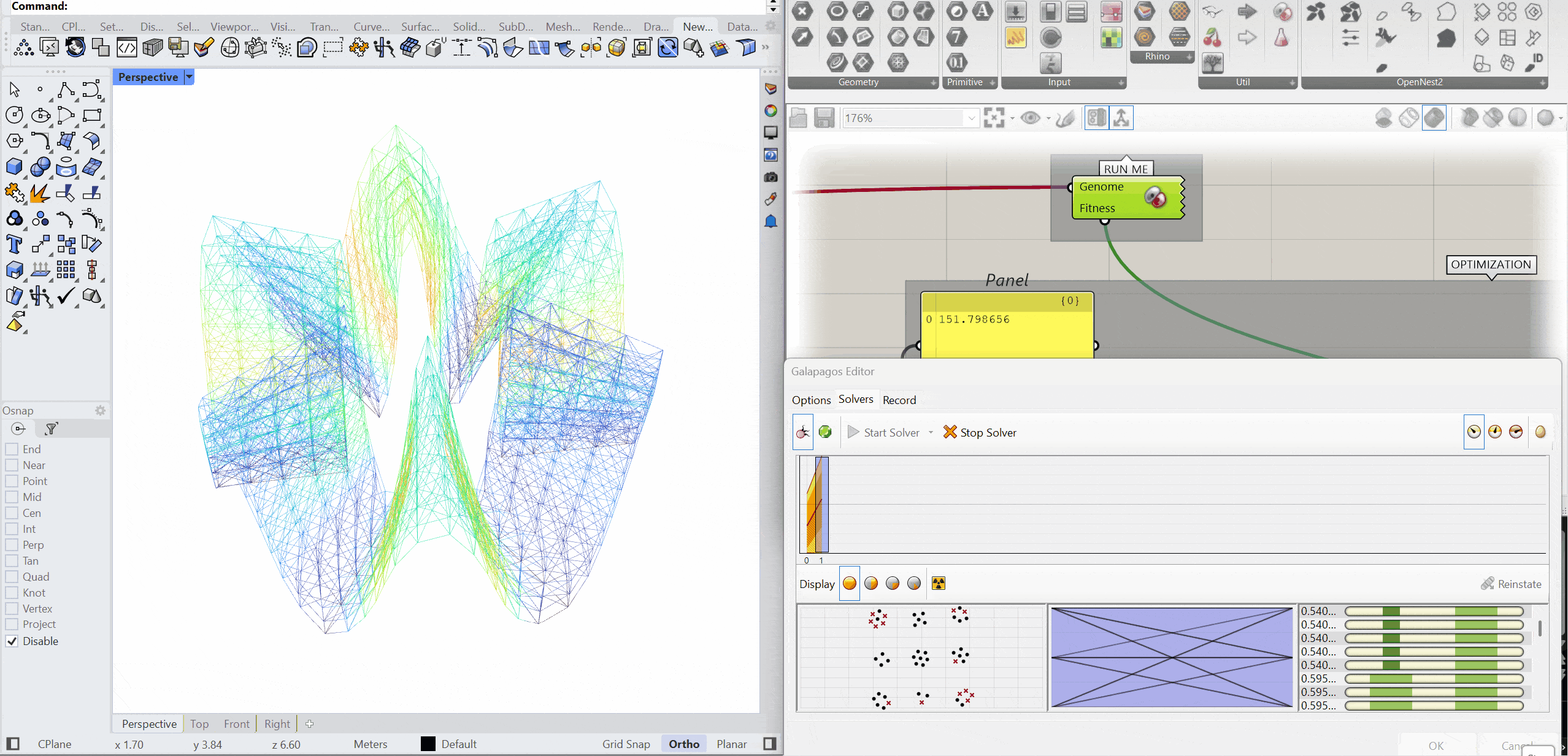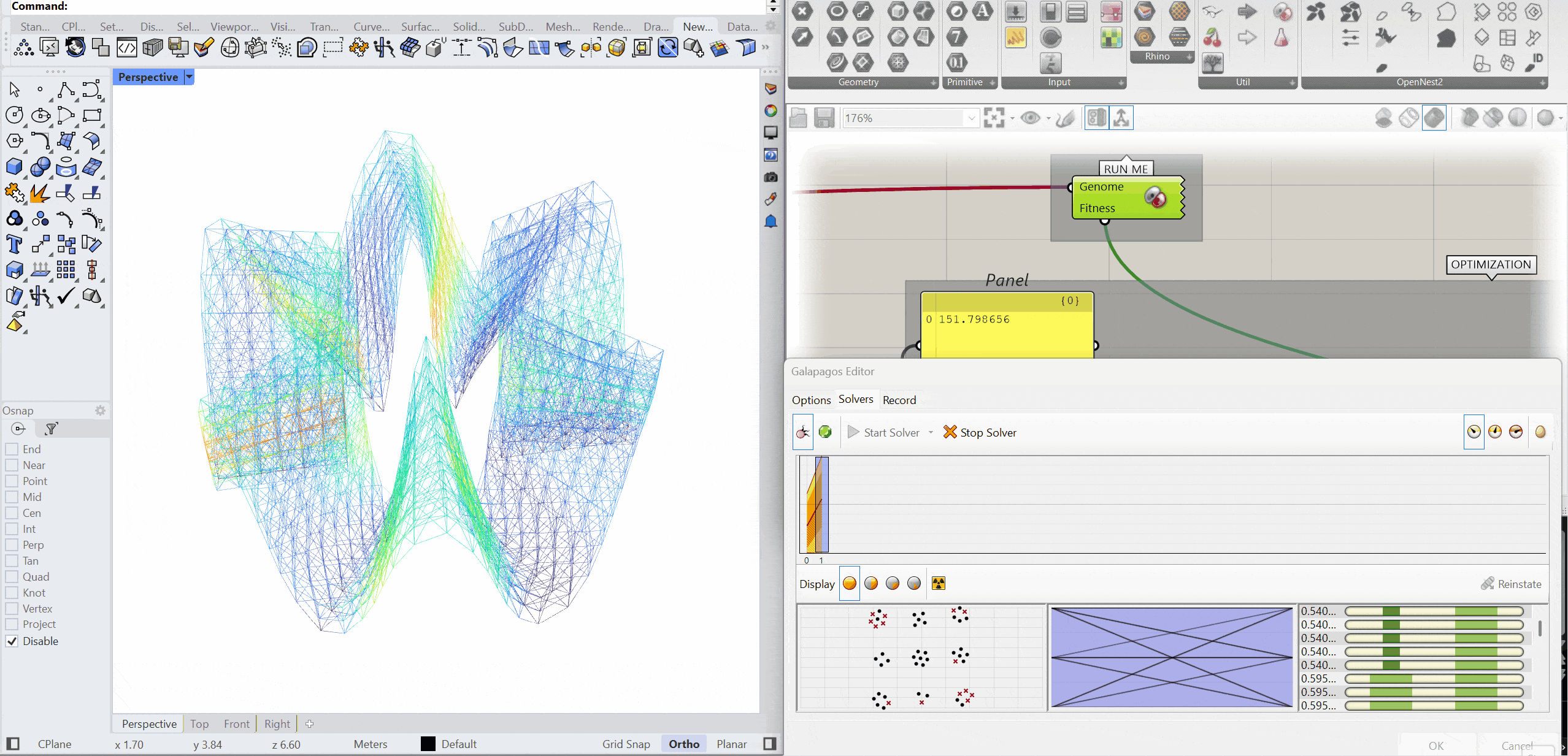
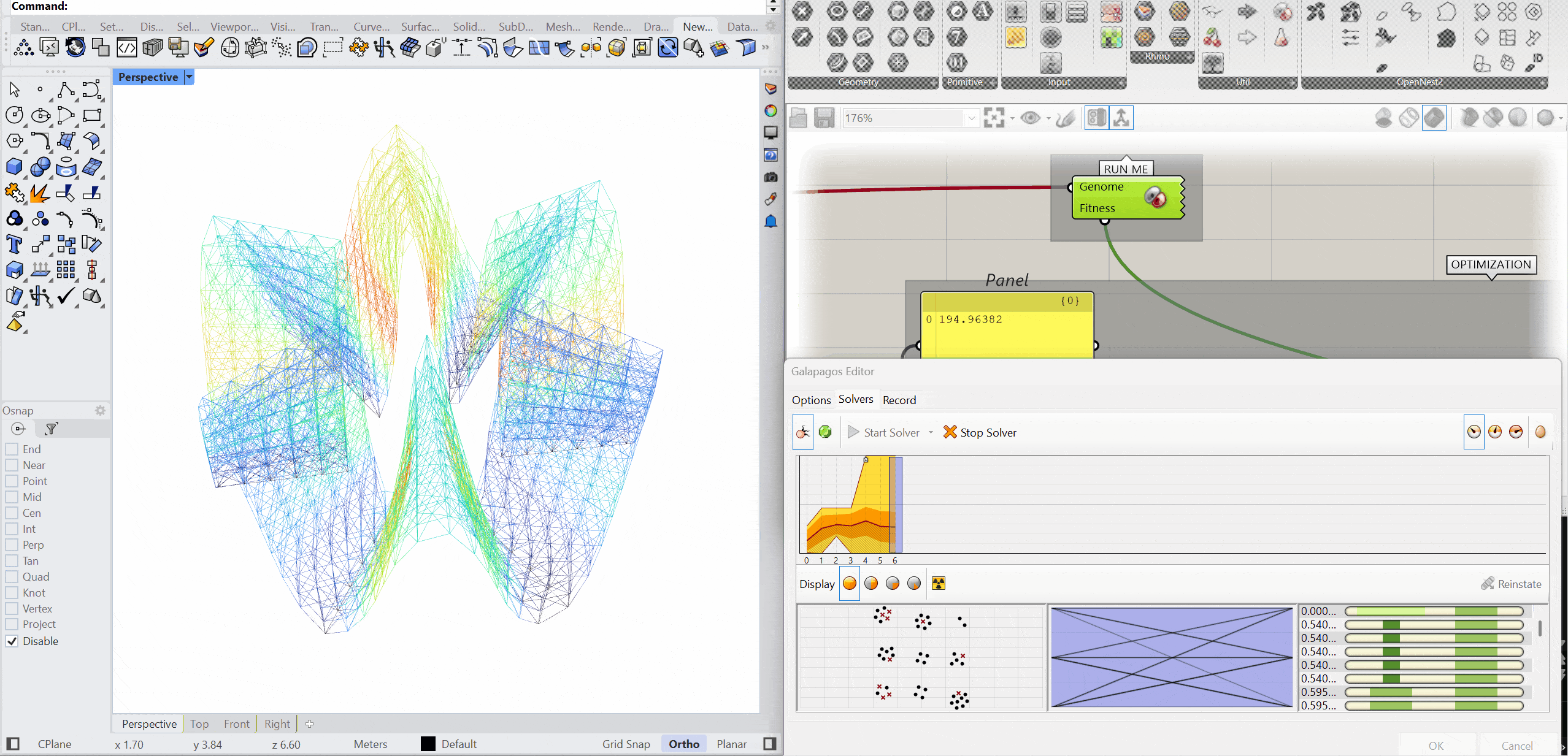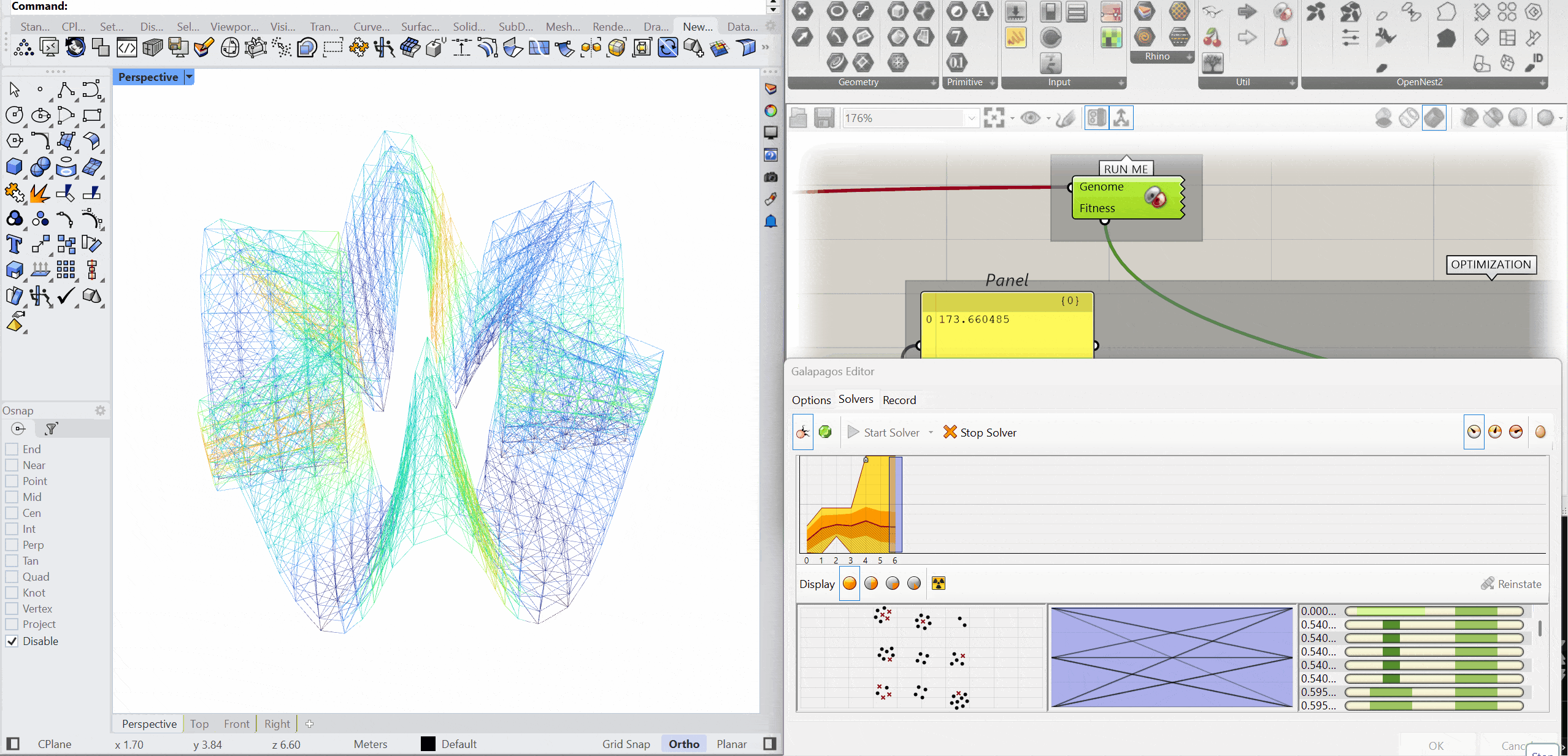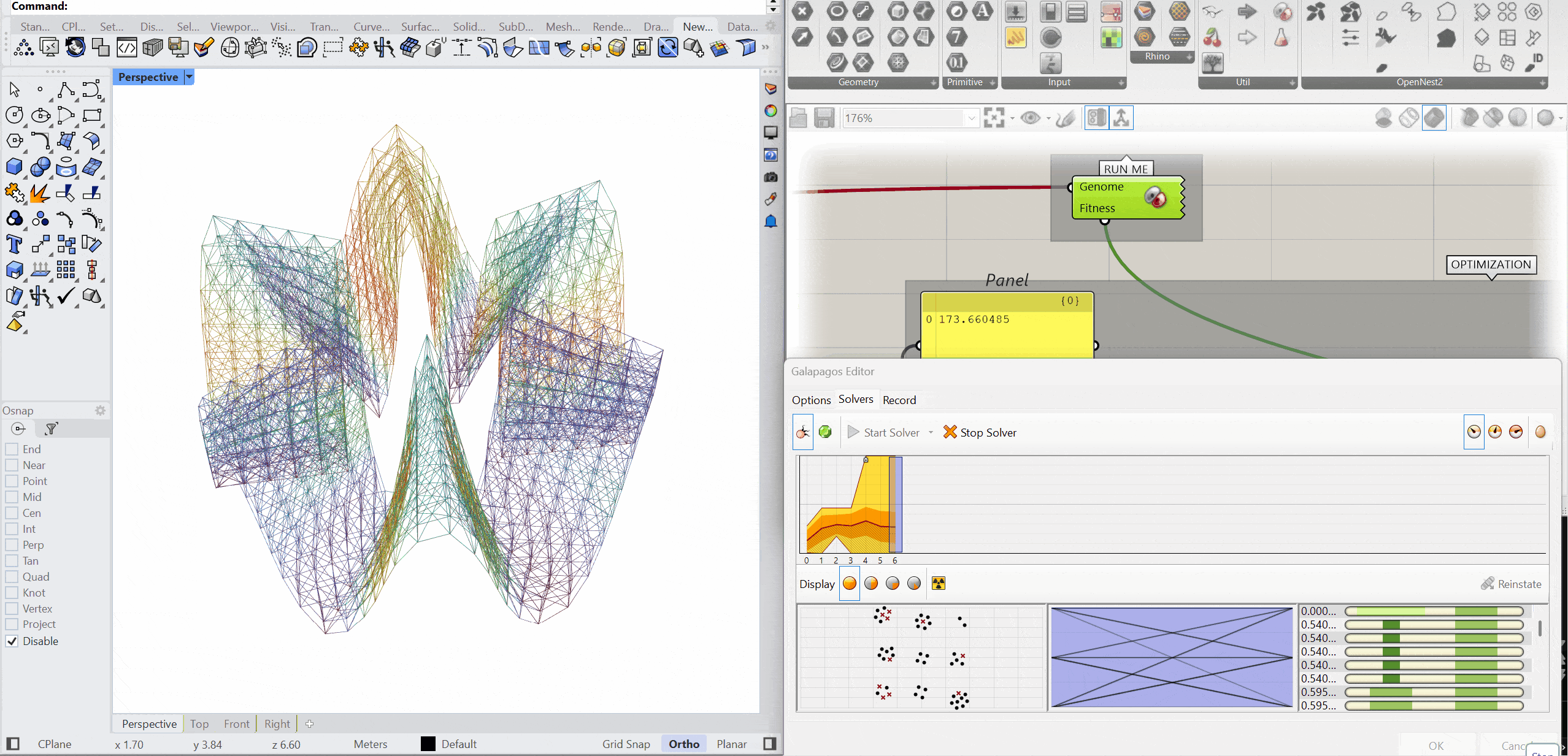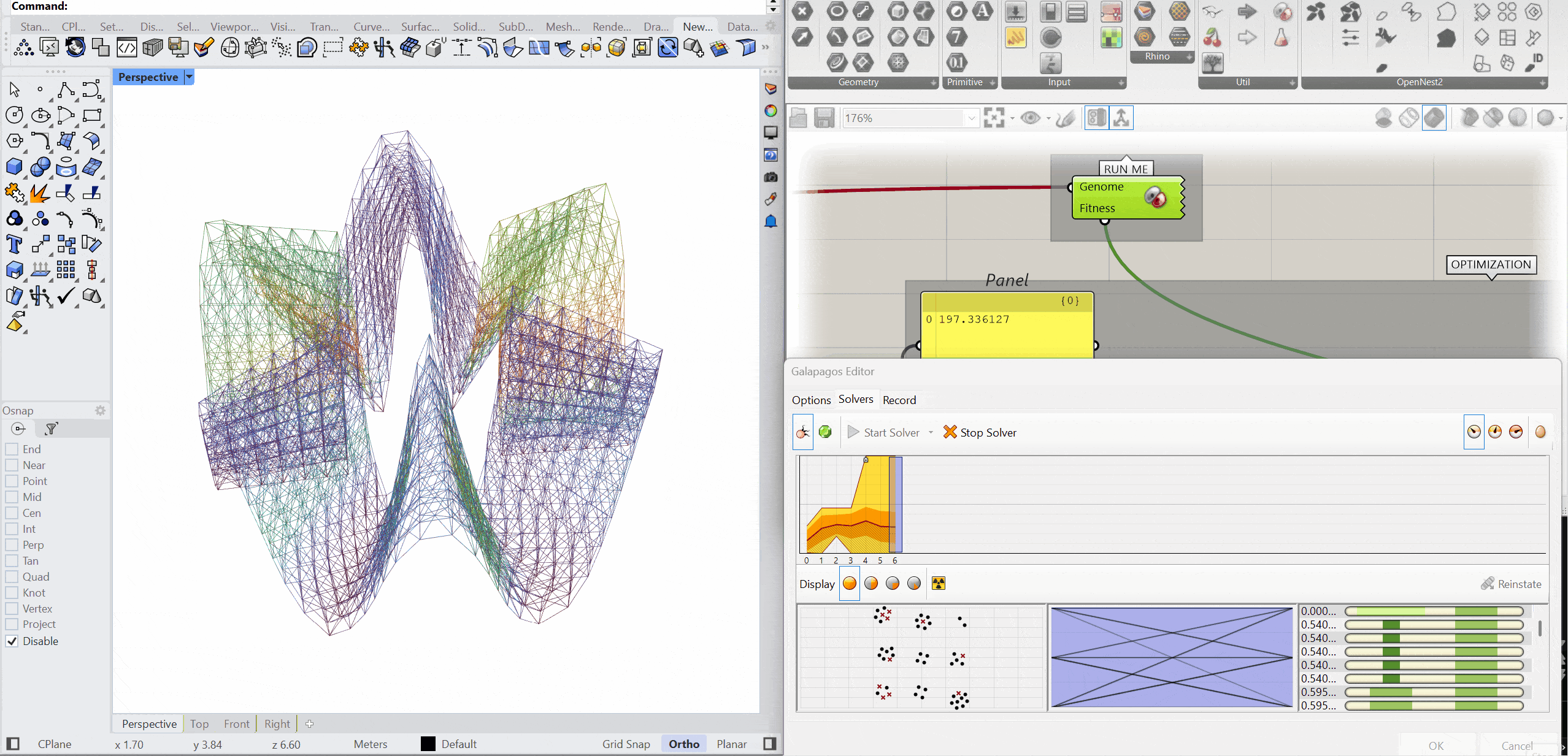
INITIAL BOOST = 2
MASS – 152.76 kg
DEFLECTION – 0.246 mm
AXIAL FORCES – 2.83 kN
INITIAL BOOST = 5
MASS – 151.79kg
DEFLECTION – 0.104 mm
AXIAL FORCES – 2.58 kN
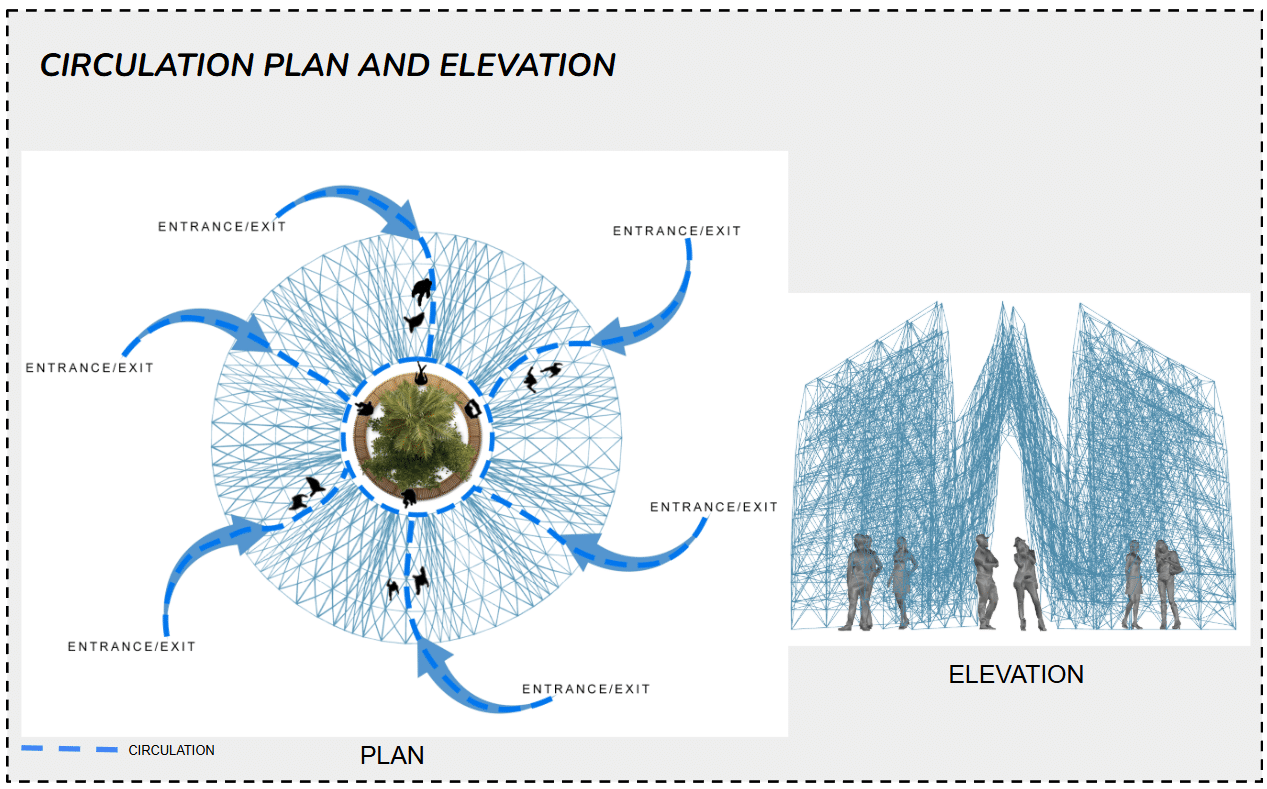
CIRCULATION PLAN
The circulation plan organises movement through multiple entry and exit points that converge toward a central gathering space, ensuring smooth pedestrian flow and visual connectivity throughout the structure. And this is the elevation view of the structure.
VIEWS
These views illustrate the pavilion placed in diverse contexts, such as beaches and open waterfront landscape parks, generated in Twinmotion and refined using an AI-visualisation tool.


