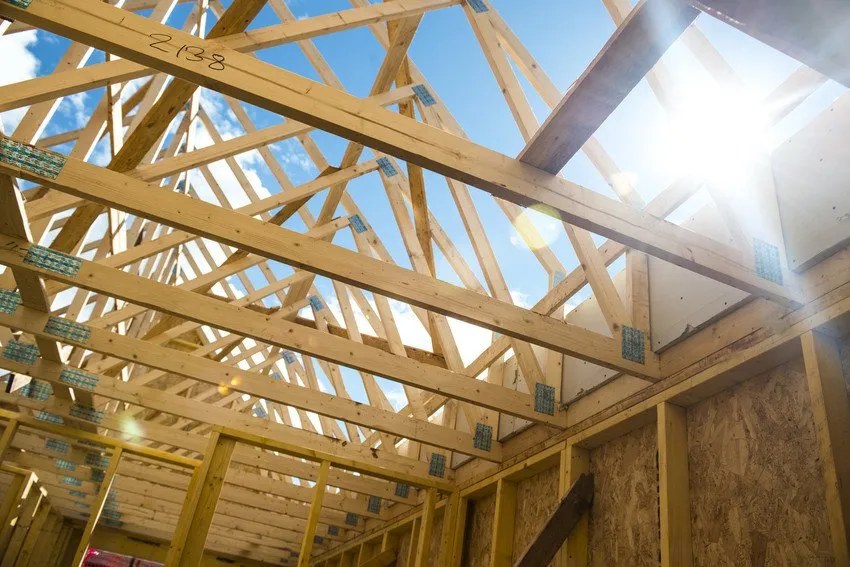
The seminar focuses on performative data informed structures for extreme contexts. Being a two-term seminar, it links structural design and fabrication techniques, by means of feedback between digital and physical. While using structural engineering plugins for Rhino and Grasshopper, students gain knowledge on how to design based on concepts and typologies of structural optimisation. This culminates in off-site construction methodologies, testing 1:1 connections and/or assembly methods.
Syllabus
Credits: STORE STORE BUILD
THE PROJECT
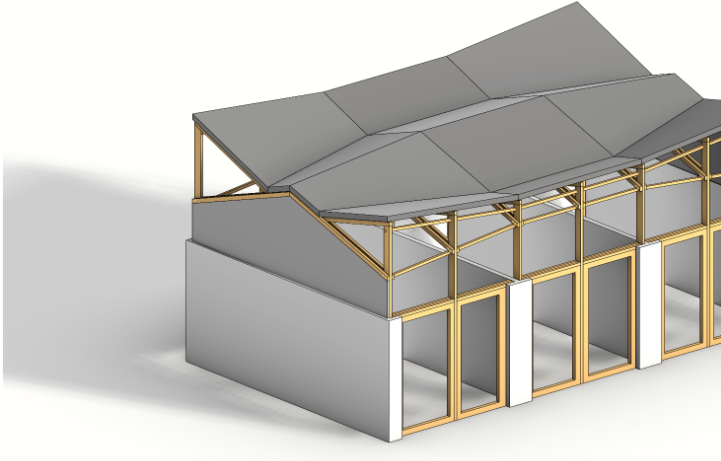
This year Data informed Structures will collaborate on an exciting brief defined by STORE STORE in London: The design of a timber roof for existing garages which would bring light into the space and transform the garage into a workshop.
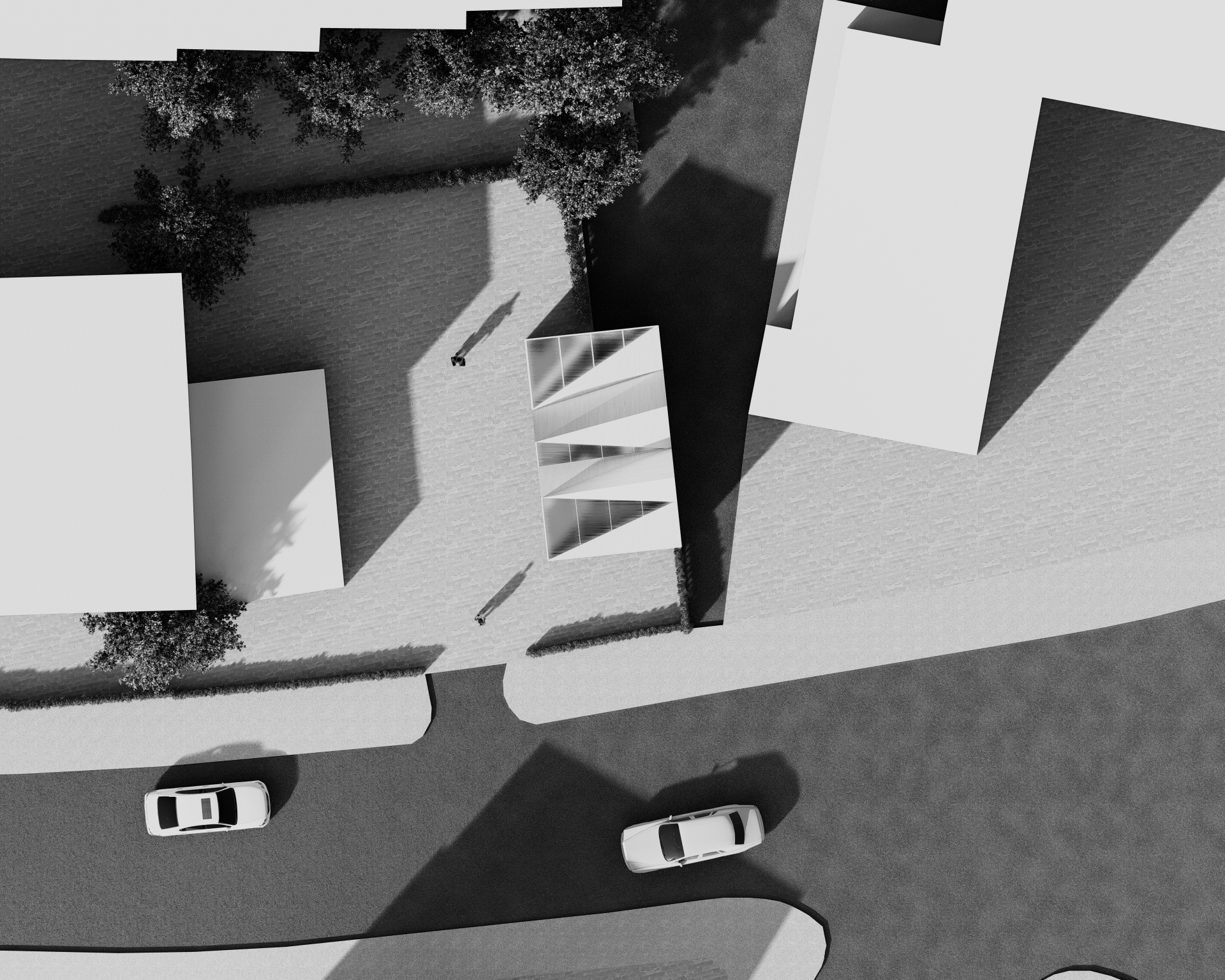
STORE have identified a garage site on Clissold Crescent, Hackney.
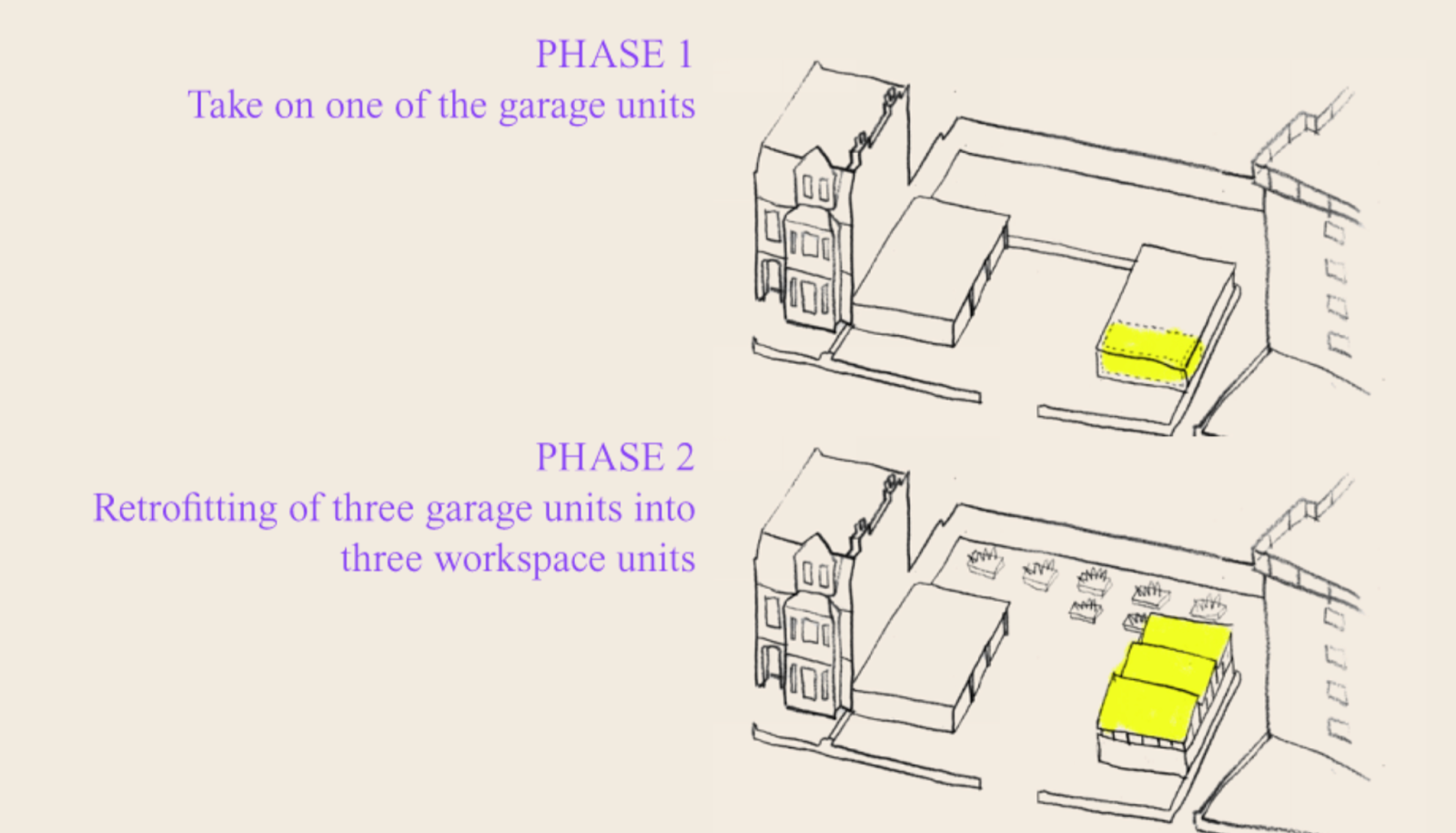
The project proposes the transformation of the garage site into an affordable workspace. During phase 1, the existing roofs will be removed and a new roof will be designed to let light in and increase head height. The first phase of the regeneration of the project is to transform one garage, remove the roof, and with the new roof can become profitable for the local community as a workspace. In the 2nd phase the new timber roofs will be dis-assembled, and transformed into new garages, with different sizes on different sites to start the same regeneration process.
Students in London and IAAC students will team up to develop the structure and detailing for this new roof, based on design for dis and reassembly.
IAAC will specifically focus on the adaptation, how we can retrofit the roof designed for Phase 1 site, to adapt to another site, addressing its performance in terms of letting light in, harnessing solar energy and water, as well as how it can be constructed by laymen.
STORE STORE BUILD
STORE STORE Build London is a small-scale building project run as an educational program, where the students taught have an active role in the delivery of the architectural project – from the planning and design phases to the actual construction of a building. This is a project that looks to upskill a generation of young people (13 to 19 years old) in London about their built environment, giving them a voice in how their communities are designed and built. The construction site becomes a living classroom, raising awareness of green building technologies and the circular economy.
This roof transformation project tests radical ways of learning, allowing students to be involved in every aspect of a building, from site surveys, design development and construction. This will be taught as a series of After School Clubs, Summer Schools and One Day Workshops in local state schools.
The actual transformation of the existing garages in London will take place in winter 2024 and done by STORE STORE London and the local community and volunteers. Our seminar will assist in the development of the concept as part of the planning application, aim to be completed mid May, 2024.
Syllabus: Adaptation + performance
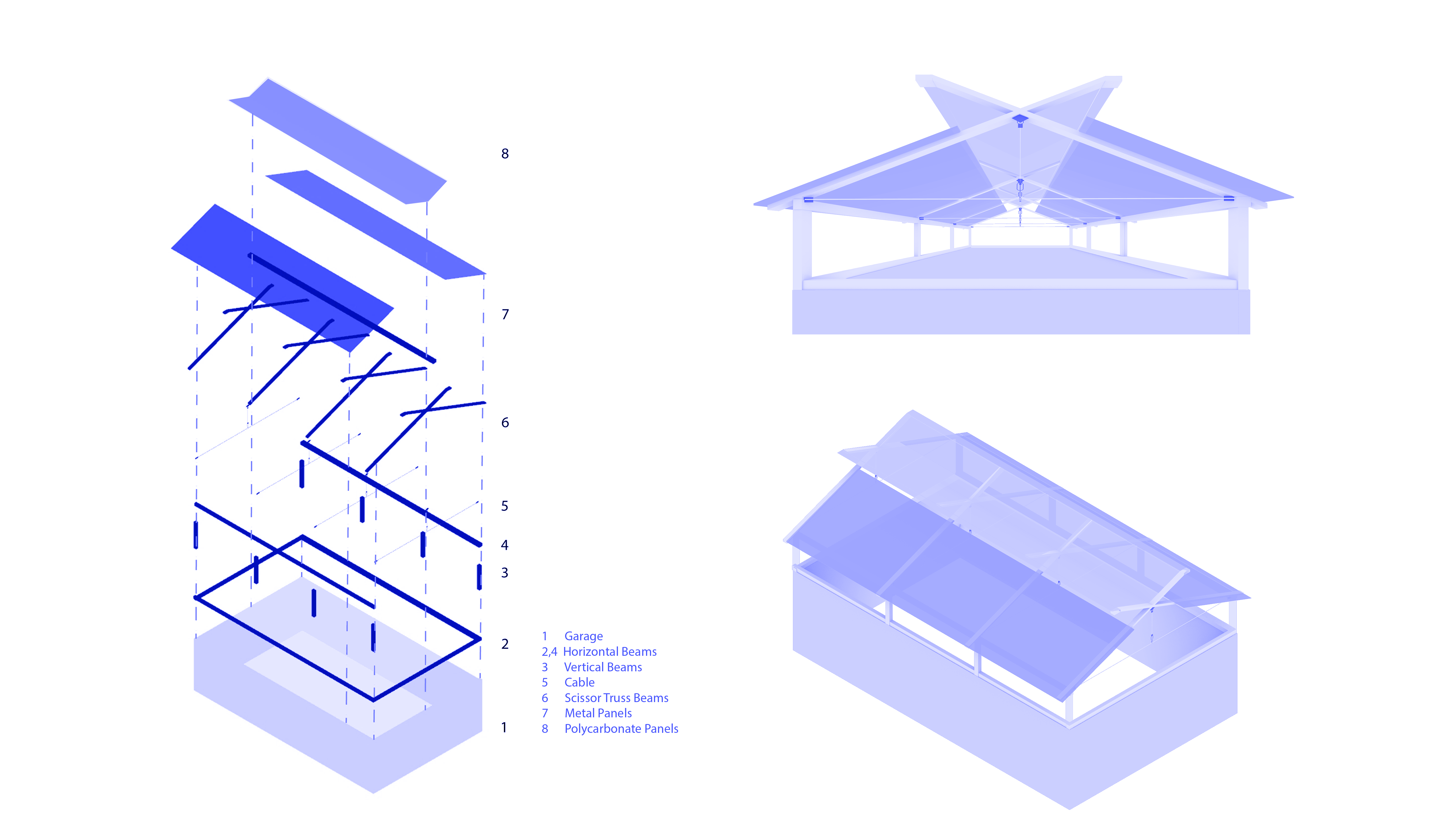
We will design a timber roof structure which brings light to the space of the garage, but moreover can be dis-assembled and relocated onto another garage, focussing on the adaptation of the timber roof structure to different sizes of garages and site.
We will work with:
- Structural design for adaptation, incorporating design for dis and reassembly, focussing on design and analysis of the key structural elements and details which we will also test structurally physically at IAAC;
- Design the roof performance linked to its geometry (solar panels, water collection, incorporating habitation of other species, etc.);
- Develop a construction methodologies which allows for engagement with the local community.
Collaboration with STORE STORE BUILD
For STORE STORE students (13 – 19 year olds), it will be great to experience how more advanced tools can aid to develop an adaptive system as well as the ability to put data (structural and environmental) to the performance of the roof. It is almost like a taster of working with professionals. We will take design inspiration from the younger learners, and assist them in how their developments can become reality. For example: London students can collaborate in the development of roof forms, which could inspire us to explore forms and systems created without a performance aspect in mind.
FINAL BUILD – 5 day workshop (part 2)
The outcome of the seminar can be 2-fold, and we will engage the team to decide what’s best:
- Develop one design collectively mixing the developments during the seminar sessions of PART 1, build it at 1:1 scale, prove dis-assembly and showcase how it can respond to a different site, size of garage, connection to the brickwork, including structural testing and verification of the elements making up the design;
- Develop parts of some key adaptive aspects of the developed design(s) in PART 1 at 1:1 scale, providing an array of systems able to adapt to different sites.
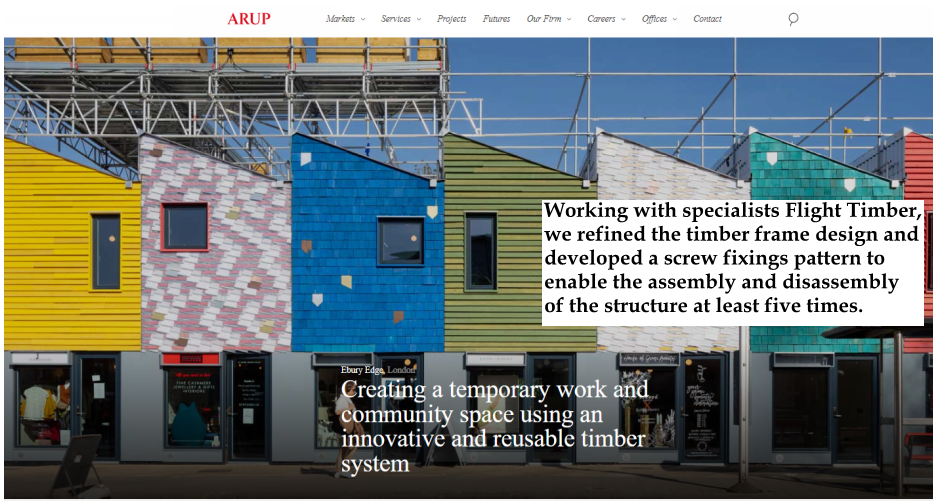
Credits: Arup Ebury Edge, London Jan Kattein Architects
Topics and Themes
The following topics will be researched for the design of the adaptable roof structure:
- Structural design of adaptive system;
- Integrating environmental performance (as well as structure) into geometry;
- Design for dis and re-assembly;
- Construction done by unskilled workers, embedding information into elements, and working with minimal drawings;
- Lifecycle, future use circularity.
Learning Objectives
At course completion the student will:
- Understand the fundamentals of structural design through physical testing and computational structural analysis with Karamba;
- Understand how to set up an analysis, strategically change parameters and understand and respond to structural analysis results. i.e. apply feedback loops;
- Relate structural design to construction and fabrication impacts. Translate digital analysis and structural performance to material design constructs;
- Relate structural principles with 1:1 construction methods to existing site conditions, both in terms of the physical building performance, as well as the climate aspects;
- Understand the relations between architectural potential and structural aspects in a holistic way.
- Develop an integrated design workflow that incorporates fabrication / material / logistics constraints into the architectural proposal;
- Understand the limitations and potentials of digital fabrication as part of the design language.
Faculty
Projects from this course
Very Many
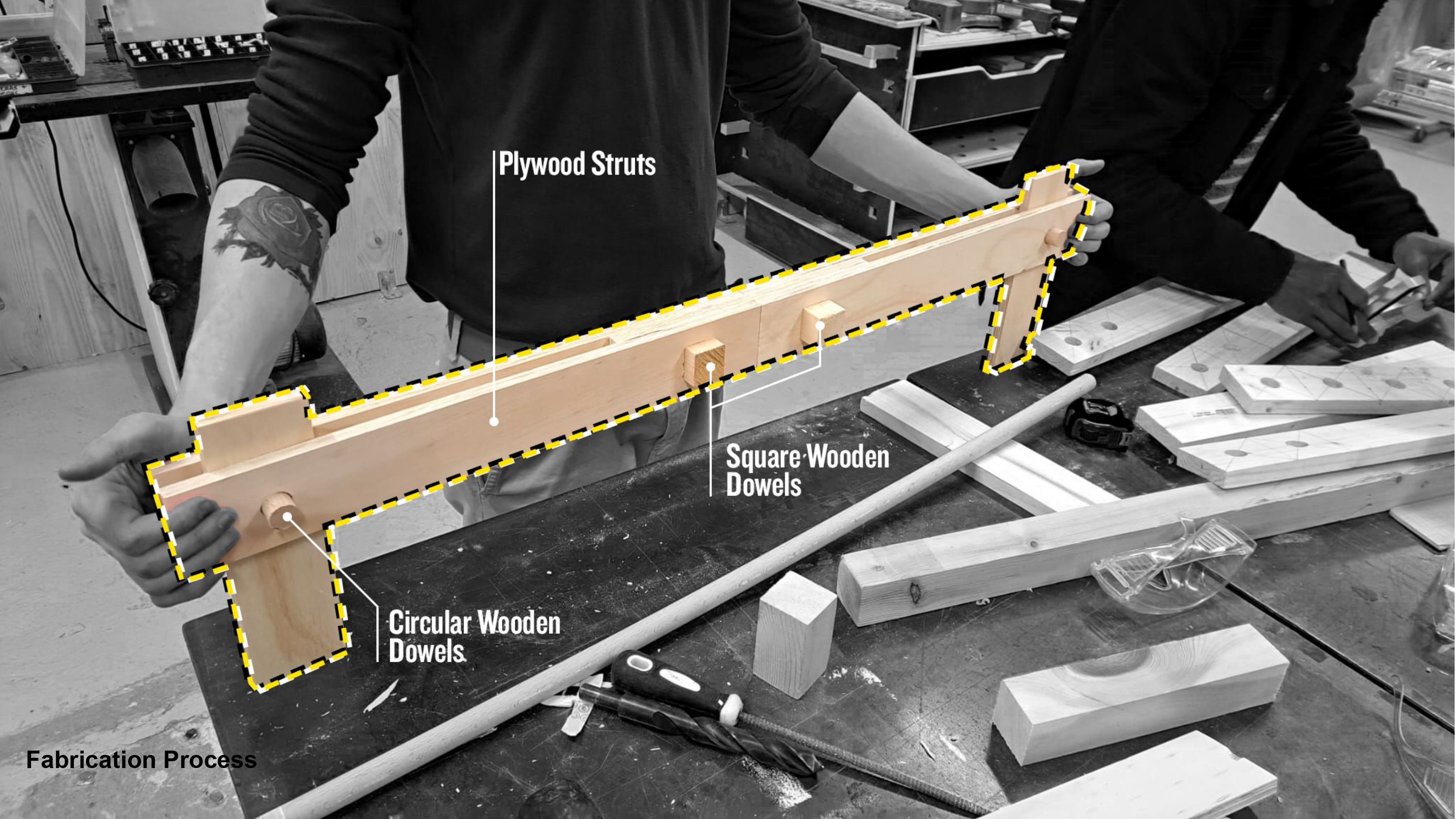
Design References Design Simulations Cladding Composition The Sandwich Panel is a combination of a top 6mm Polycarbonate Sheet with Dry Insulation and Cork forming our inner layers and to finish it off with a 6mm thk Polycarbonate Sheet at the bottom. Fabrication Process Using plywood as a base for dowels, which would serve as lateral … Read more
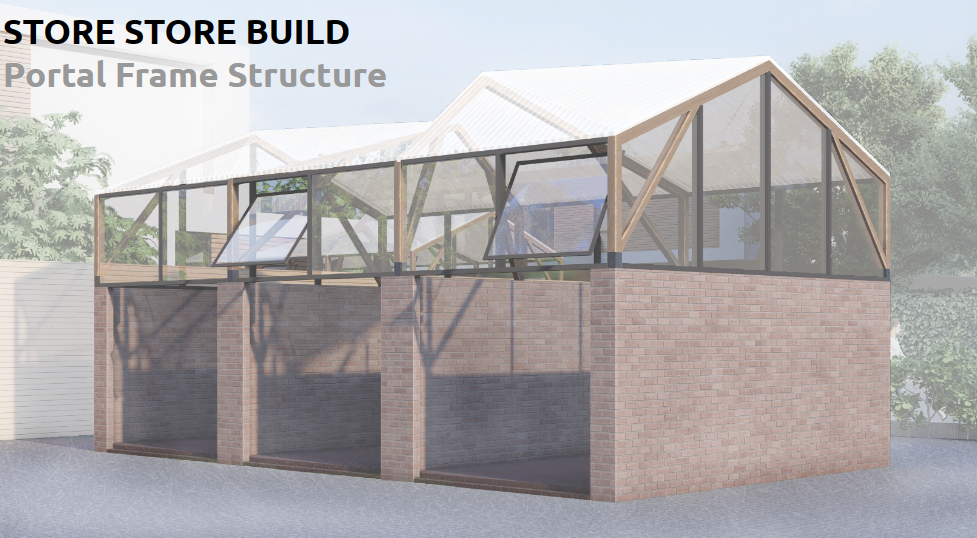
Portal Frame Structure
The Portal Frame structure represents a modular roofing solution characterized by the integration of various portal frames along a longitudinal series. This design facilitates efficient assembly, disassembly, and reassembly processes, enhancing adaptability to diverse environmental conditions and functional requirements. Notably, the frames are engineered to optimize natural lighting and shading within the structure. Furthermore, their … Read more
Inverted Layered Truss
Case Study The Inverted Truss Retail. Taipei City, Taiwan B+P Architects Martha’s Vineyard Airport Terminal West Tisbury, MA Fennick McCredie Architecture Design Proposal Perspective View – Frame Only Perspective View – With Roofing Maintenance Roof Load: 270 kgf Frame Mass Weight: 635 kgf Wind Load: 1 kN/m2 Front View Section Axonometric View
Folded Structures
Plan Grid of Triangulation COMPARISON CONCLUSION OPTION 01 self weight: 1146 kg max displacement: 0.107cm max utilization: 0.230 mean utilization: 0.035 min utilization: 0 Pro: Overall the performs well with minimal displacement and utilization Con: There is a small space for failure in terms of the structure’s capability to carry loads compared to Option 03 … Read more
TimberTech
Our journey to craft a thoughtfully designed structure for the STORE x STORE garage transformation began with two distinct timber frameworks, each built around a trio of trusses. Structure A started as a straightforward, three-truss framework, embodying simplicity. In contrast, Structure B ventured into more complex territory, presenting a three-dimensional, intricate timber assembly. Throughout this … Read more
Scissor: Adaptive to Different Roof Spans and Orientations
The performance of a structure is judged by its ability to support applied loads with a minimum of material and a balanced stress distribution that avoids excessive overloads and underloads.playing with different materials, tension, and rotation of elements. OUR GOALS DESIGN STRATEGY STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS 2D utilization comparison Utilization provides measurement of the performance of a … Read more
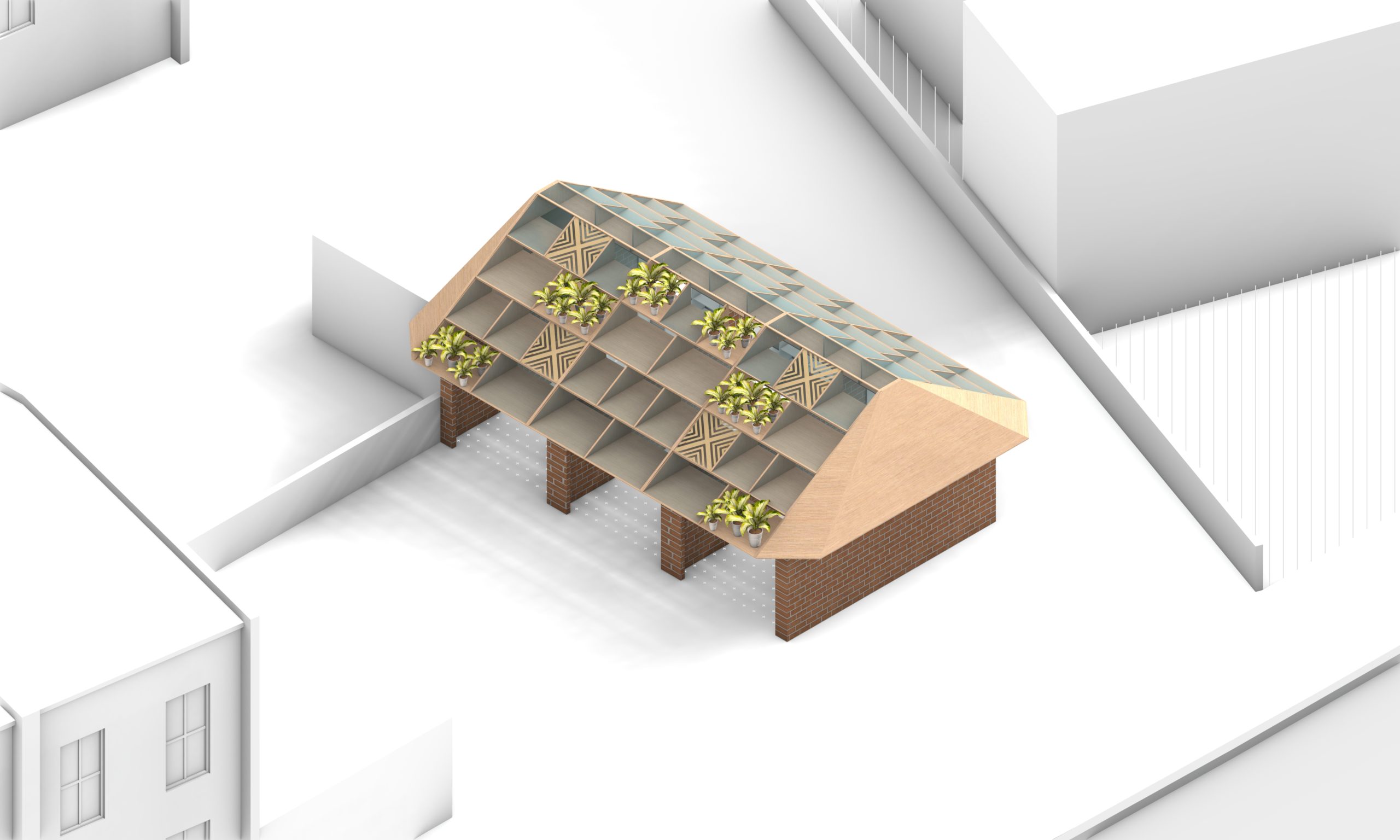
Shelves as Structure
The objective of this presentation was to explore the shelves as structure in order to transform an existing garage in London (Clissold Crescent, Hackney) into a workshop space. Through this seminar we understood the various opportunities and the potential of adapting shelves into roof structures. We made various grids by moving the positions of shelves … Read more
Platefold Prefab
Design Approach Folded Structure System Folded plate surfaces, architectural marvels with interconnected planar elements, gain further dynamism through linear additions. These straight elements seamlessly integrate with the folded structure, enhancing both aesthetics and structural efficiency. The result is a visually striking and functionally optimized design, showcasing the harmonious blend of form and function in contemporary … Read more
Shelf-Scape
At the request of STORE STORE in London, we developed a proposal for a timber structure roof for an existing garage located specifically in Clissold Crescent, Hackney. The objective is to transform the space into a workshop. The project presented a unique challenge as it is planned in phases, necessitating a demountable design that can … Read more