Syllabus
Photo Credit: City Intelligence Lab, Austrian Institute of Technology
Syllabus
Artificial intelligence (AI) has permeated almost all facets of our digital and physical world. By now, it
is a rarity to find an aspect of our day?to?day lives that has not been somehow influenced by an AI?
driven technology. Even within the built environment, an industry that is known for its sluggish uptake
of new technology, AI has been applied towards detecting anomalies in city?wide datasets, generating
and optimizing urban morphologies, increasing the speed of onerous urban?scale microclimate
simulations.
AI in the Built Environment focuses on practical applications of AI within urban planning and design.
Through method?driven pedagogies, this module is aimed at taking students with a basic
understanding of machine learning, to applying deep learning algorithmsto urban issues. Students will
learn to identify problems amenable for AI?driven intervention, use and fine?tune AI models to gain
hands?on intuitions about hyperparameter tuning, and build micro apps to deploy AI models in the
cloud. Throughout the course we will cover a range of different machine learning modelsranging from
clustering, object detection to image generation and present different pathways on how to integrate
existing models into practical workflows.
Learning Objectives
The course starts with a brief introduction to machine learning and an overview on major
breakthroughs in the field throughout the last few years. Next, we give a dense input of selected deep
learning models including examples of their application in practice.
In the following sessions, we will highlight three different approaches to access and use ML models,
along with each approach we will introduce one ML model in more detail and use it as an example
case.
Finally, the students will be able to deploy their own micro?ml?app online using Hugingface Spaces.
Faculty
Projects from this course
rAImagine
Designing spaces made easy Context In an era where visualizing changes in interior spaces is crucial, whether it’s for purchasing a new home or renovating an existing room, the challenge lies in accurately envisioning the end result. The process often requires specialized skills, time, and significant financial investment. However, with the development of an innovative … Read more
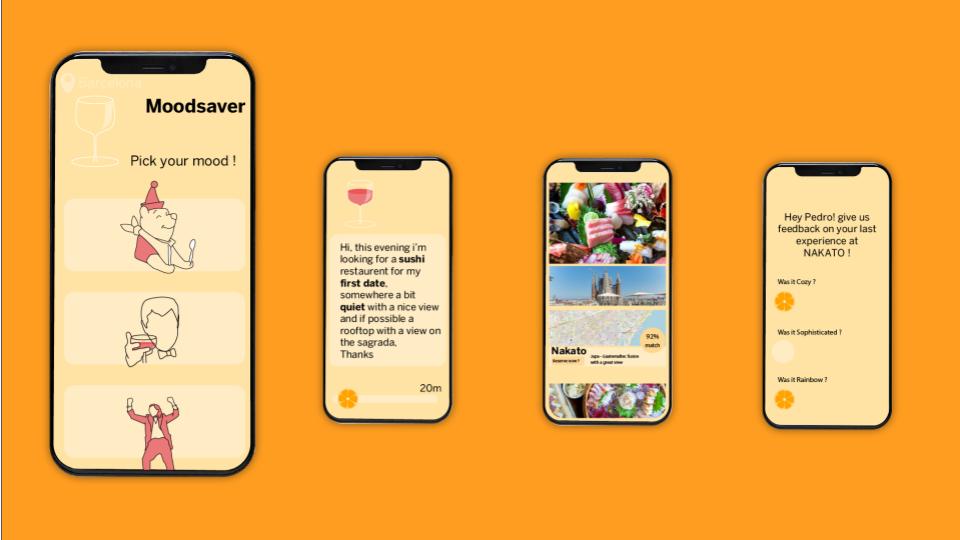
MoodSavor
CONTEXT When looking for a restaurant, current search methods are based on filters of factors like cost, rating, cuisine, etc. and limited to those. Natalia wants to find a zany and artistic place somewhere in the city for a raucous Friday night with her friends. But she doesn’t know how to search in google map, … Read more
Style_Designer
Github Methodology example file: https://github.com/jamesalcock1309/Style_Designer.git
ThermoVision
ThermoVision is a predictive tool that leverages machine learning to gauge thermal comfort in urban landscapes, allowing us to understand the correlation between our built environment and the thermal comfort. There is inconsistent outdoor thermal comfort due to varied building topologies, building materials and vegetation. Understanding the thermal landscapes is challenging due to their complexity. … Read more
Strata – Green
Context 1 (2022) Europe’s air quality status 2022 [Preprint]. European Environment Agency. Available at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/status-of-air-quality-in-Europe-2022/europes-air-quality-status-2022 2 WHO global air quality guidelines. Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. Licence: CC?BYNCSA?3.0?IGO Problem Statement Urban designers and city planners are not able to predict the impact … Read more
Reinforcement Learning
Group 5 How can apartment typologies be designed to create communities within buildings, addressing social exclusion and isolation caused by modernist architecture? Can reinforcement learning be used to optimize the distribution of public and private spaces, such as apartments, balconies, patios, and courtyards, to create sub-communities within the building.
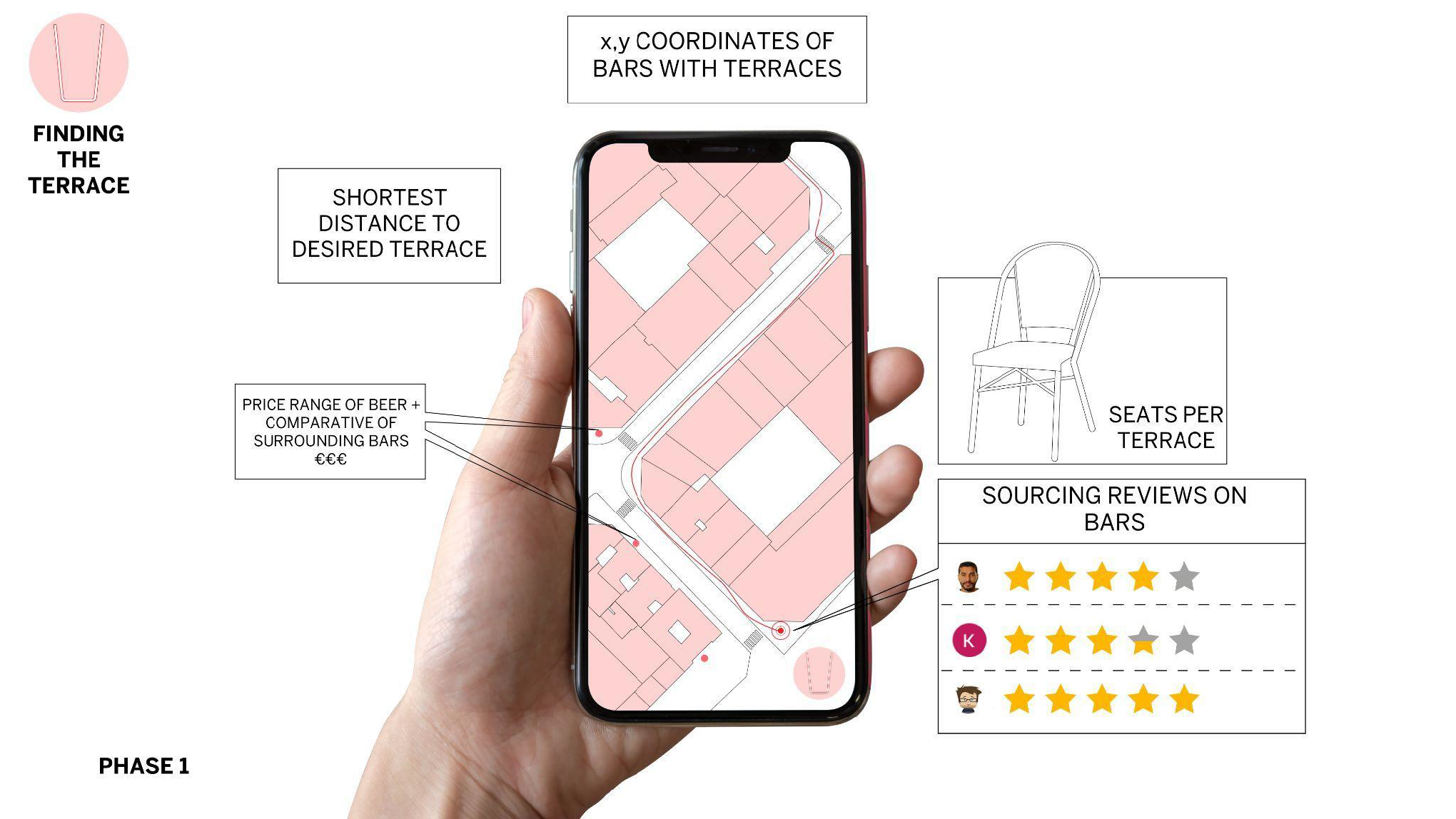
Terrace Hunter
CONTEXT: Pedro always has visitors and enjoys exploring the city while finding new patios to have a drink in the city of Barcelona. Often with larger groups of people, the patio size can’t always accommodate. Before choosing a spot, he wants to know how big the patios are and where within the city they are … Read more
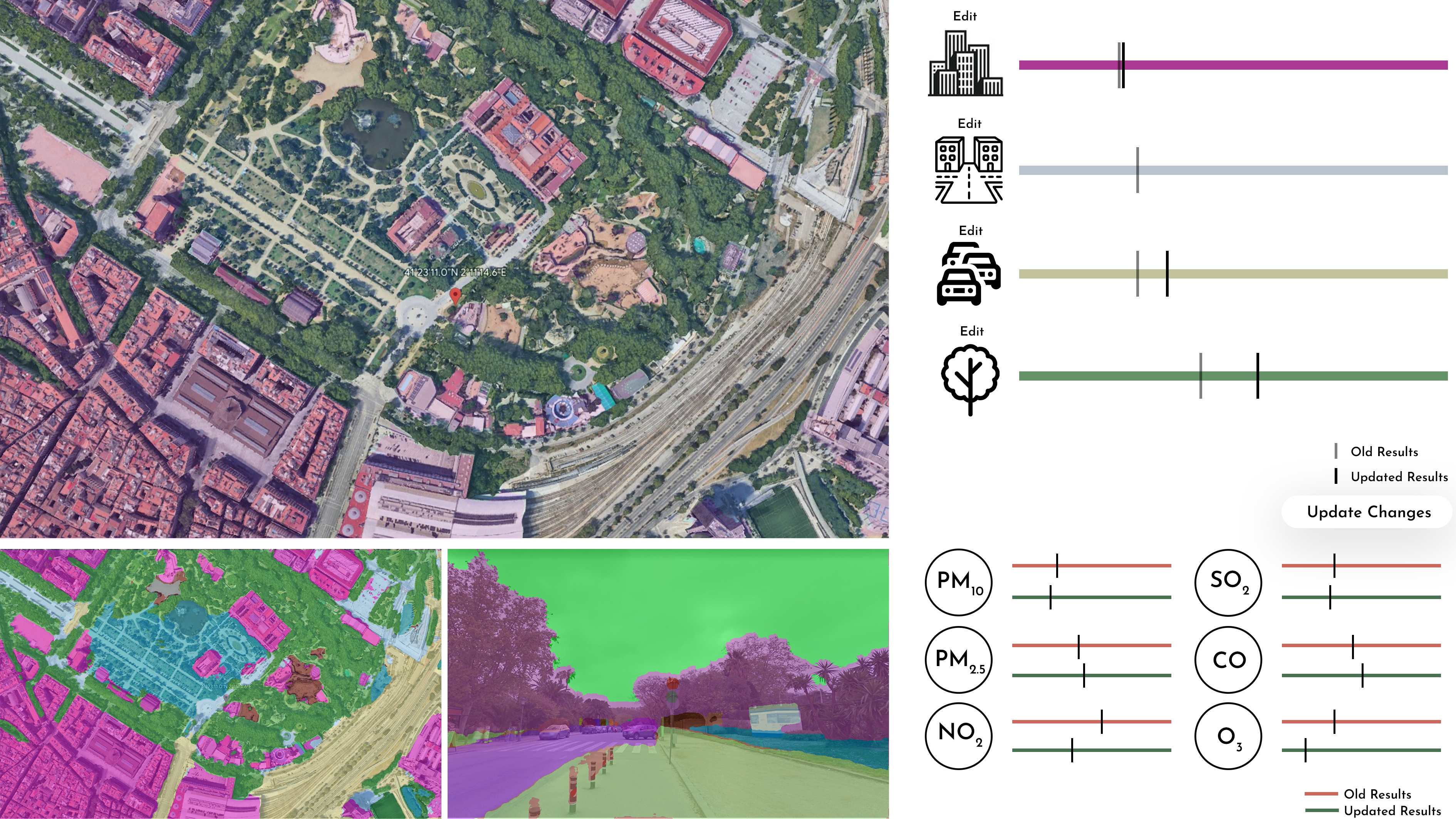
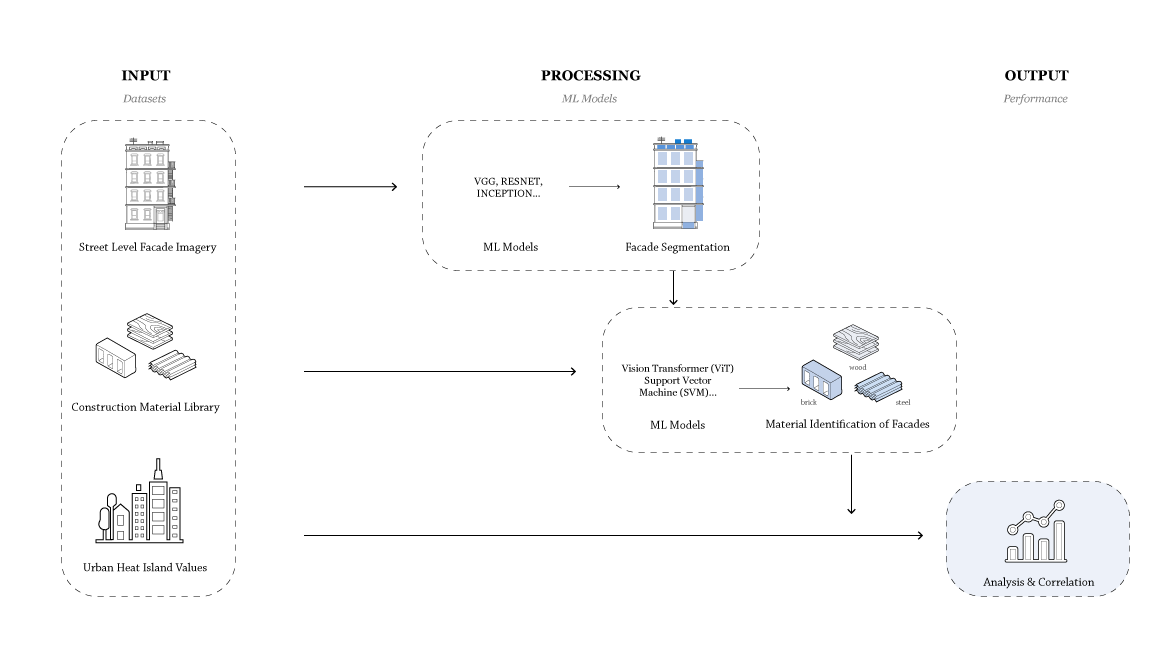
Impact of Facade Materials on UHI Values
Introduction This project aims to investigate the extent to which different facade material choices can influence the urban heat island effect in the surrounding area. Urban Heat Island There are many factors that affect urban heat island and the three main branches are urban morphology, meteorology and surfaces. Out of all the factors three were … Read more
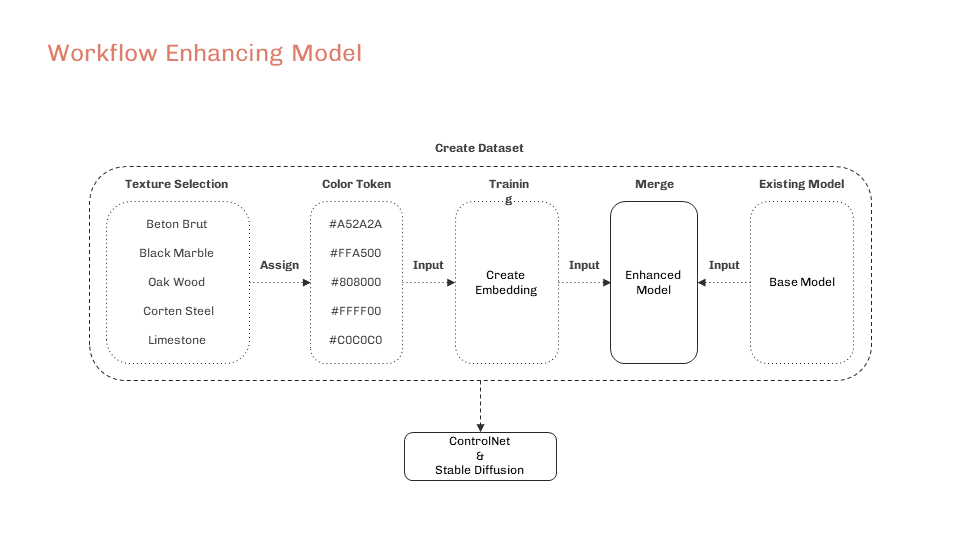
Proposal for Enhancement of Semantic Segmentation Model for Architectural Purposes
The current semantic segmentation model for ControlNet provides a list of usable materials, but they are not specific enough for architectural purposes. By generating new tokens (colours) that extend the existing model with new material types, we aim to improve the process by which stable diffusion operates and make it more suitable for architecture applications.
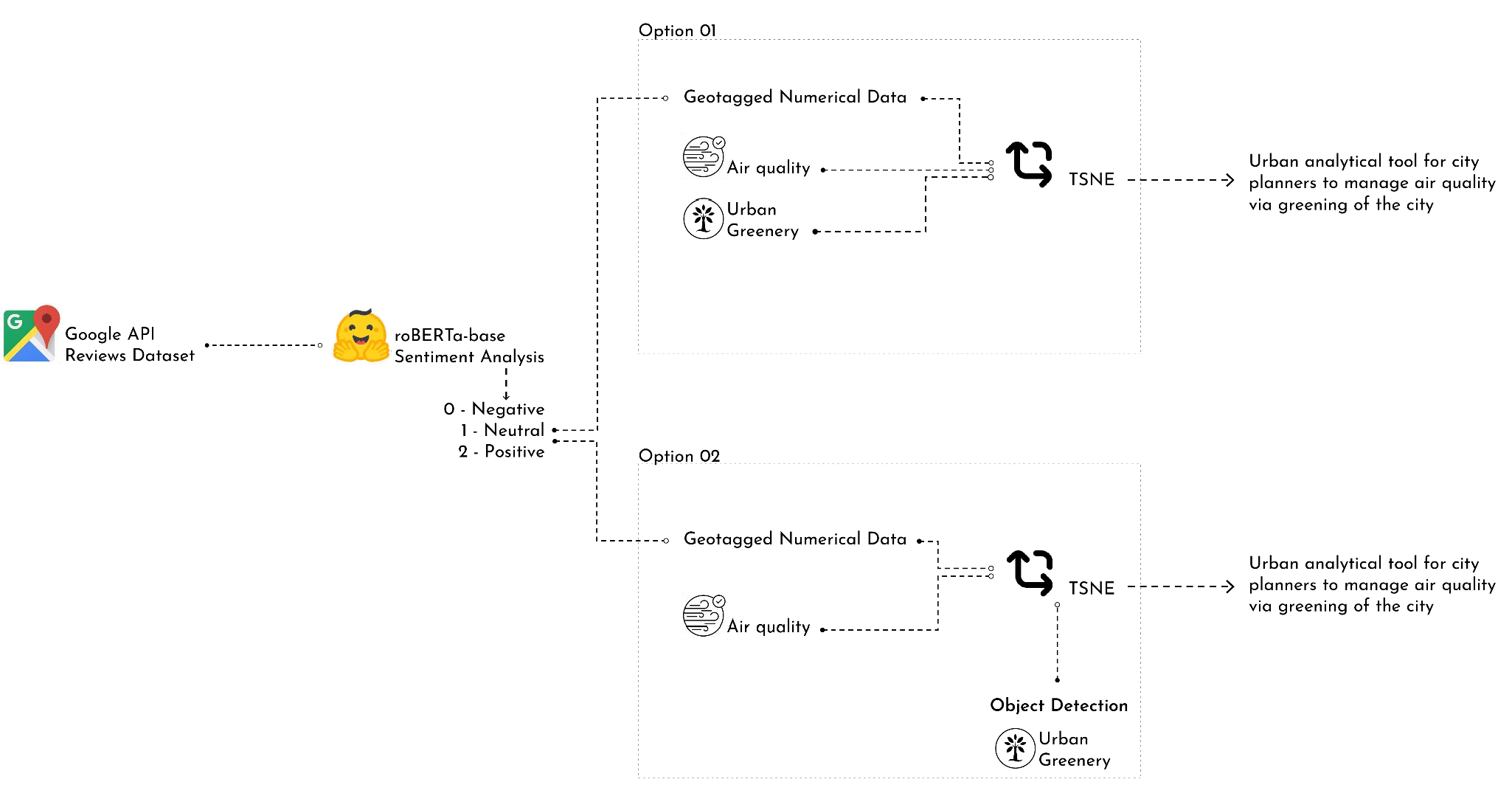
AI in the Built Environment | Urban Analytical Tool for Greening the City
Juan is a young professional living in a narrow street in Barcelona and he describes the street he lives in as a concrete hell. How air quality and greenery impact the experience, how a citizen feels, about a public space? The result will be an urban analytical tool for the city planners to manage air … Read more