DIGITAL TOOLS FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ANALYSIS
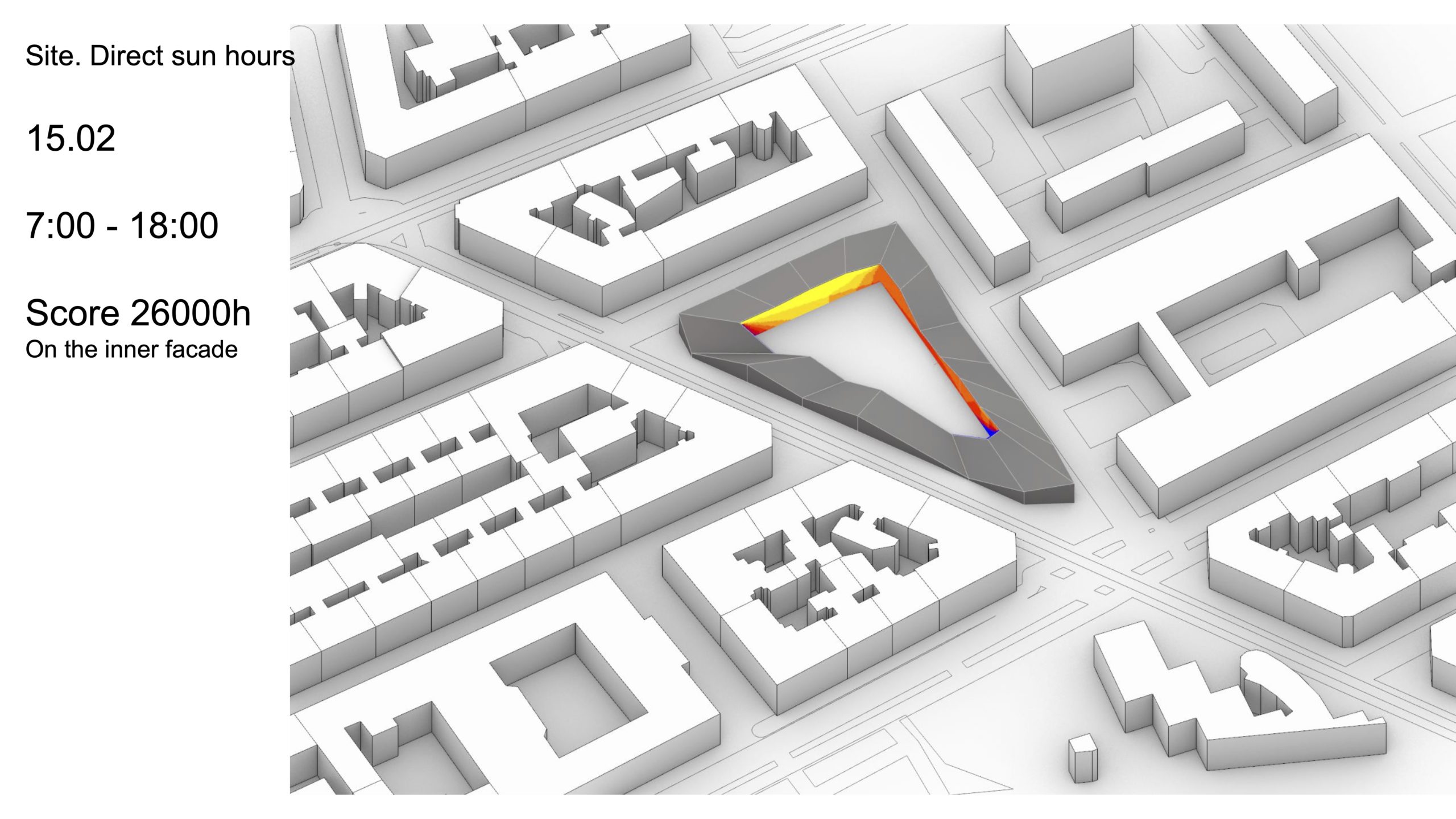
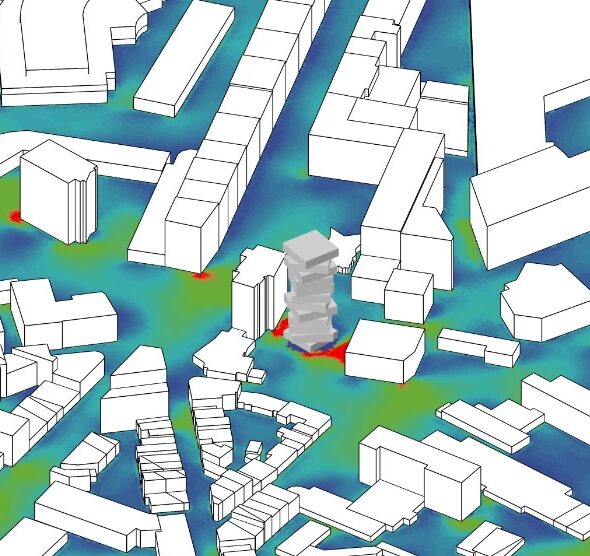
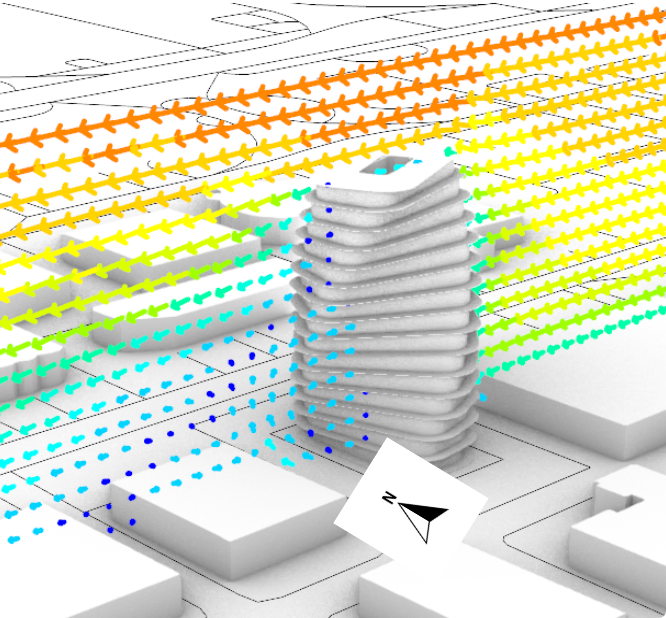
Source: MaCAD22-23 Environmental Analysis seminar by student Anton Klyshnia.
The undoubtedly significant contribution of buildings’ performance to the devastating effects of climate change has in the past decades driven research and development efforts in the architecture, engineering and construction industry. To enable the shift towards more performance-aware design, environmental simulation tools have become more readily available through the constant development of new interfaces that incorporate state of the art simulation engines in mainstream CAD frameworks. Architects and urban designers have at their disposal today, as part of their design workflows, a wide range of analytical tools that allow them to assess the environmental performance of their designs, in order to make informed and sustainable design decisions. Further to the incorporation of simulation tools the recent developments in optimization and generative design methods are fundamentally changing the computational design workflow and enable the exploration of vast design spaces, unconceivable by manual processes.
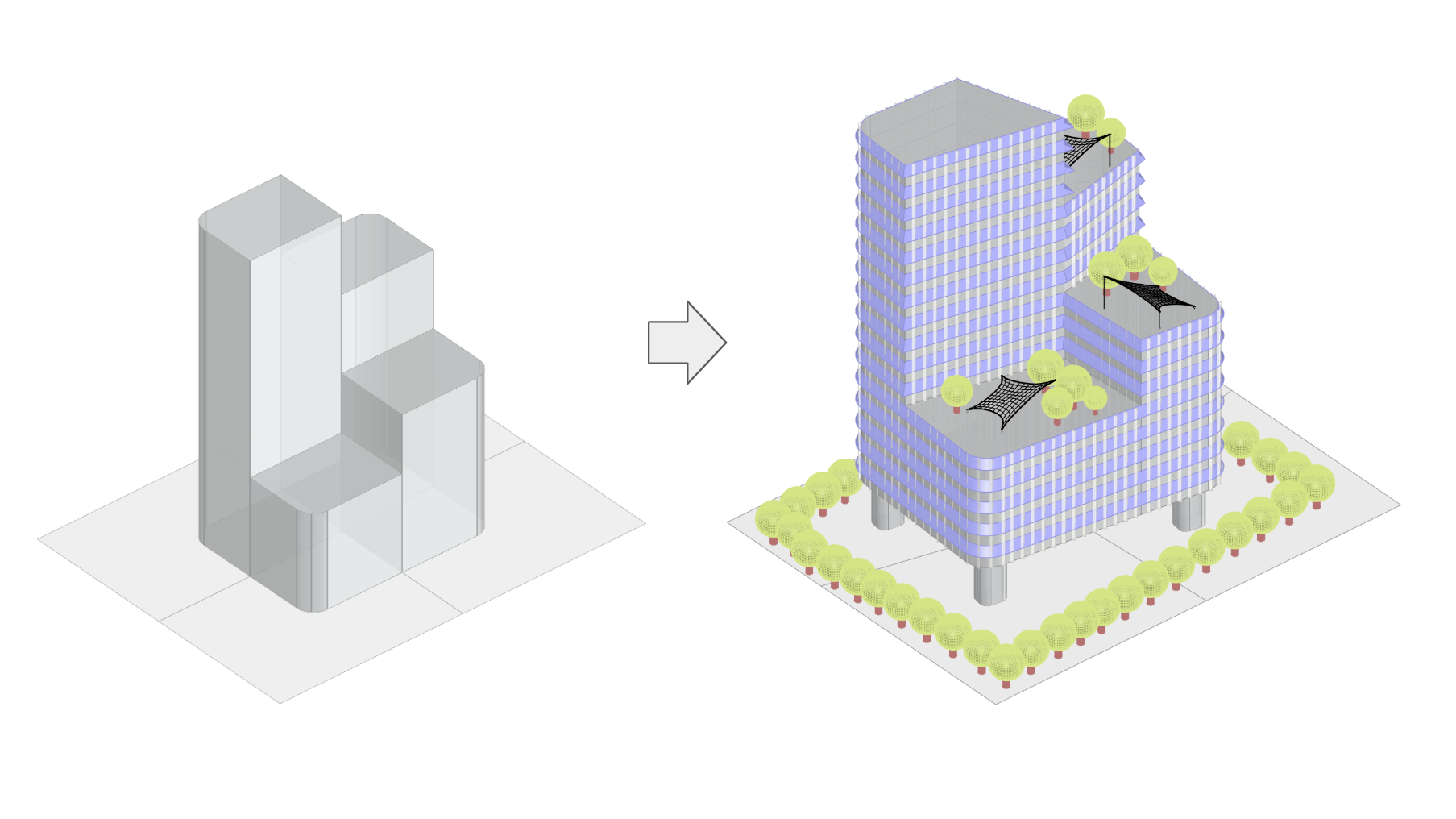
This seminar aims to empower students with the theoretical background and the technical expertise to inform architectural design in an urban case study site using environmental simulations. Either on empty unused land plots or the rehabilitation of existing infrastructures, the projects will have synergy with the rest of the digital tools seminars, allowing the students to apply the knowledge received into a practical and speculative design proposal. This hands-on investigation will enable students to apply evidence-based solutions to complex environmental design problems using state-of-the art software and analytical techniques.
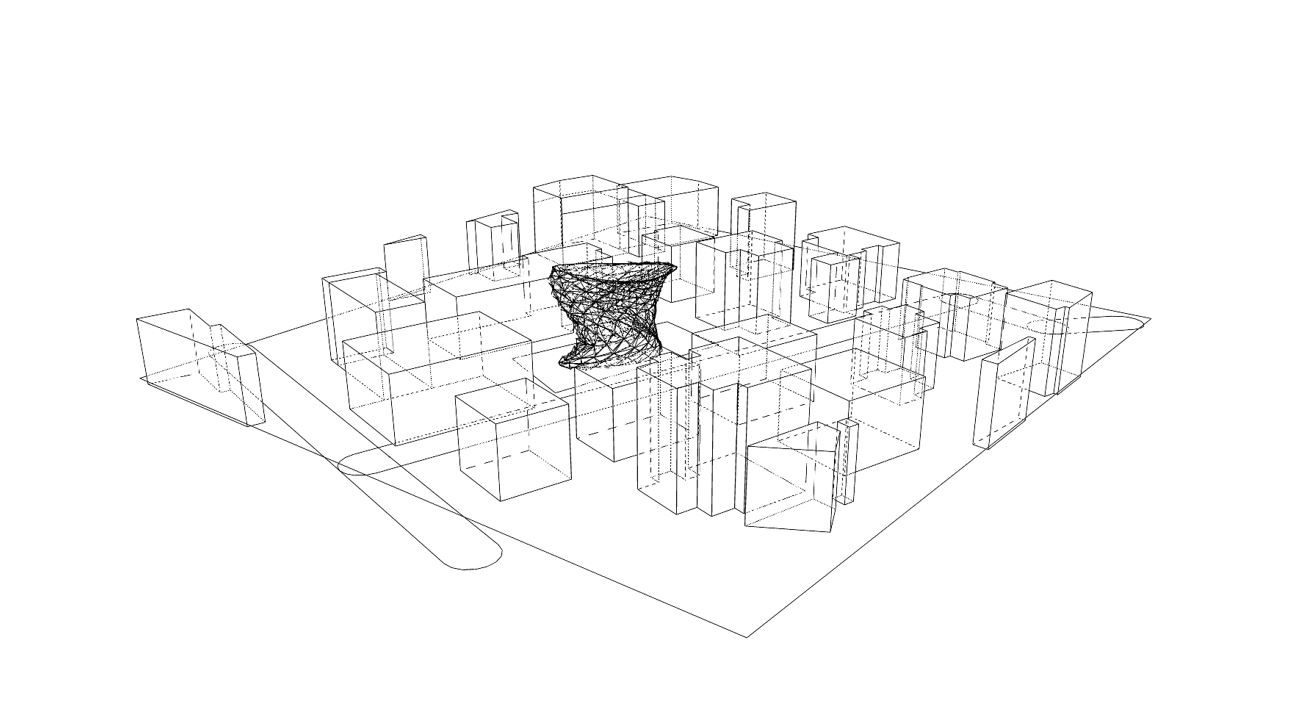
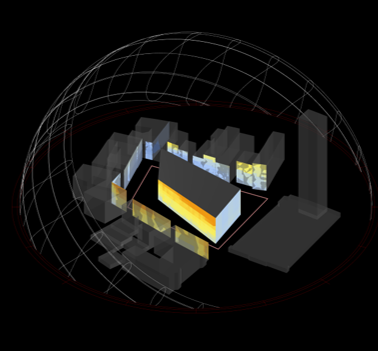
Source: Angelos Chronis
Learning Objectives
At course completion the student will:
- Understand Environmental Simulation principles for Architecture and Urban Design.
- Be able to set out a simulation strategy for a given problem.
- Be familiar with the fundamental simulation engines and integrated tools in Rhino
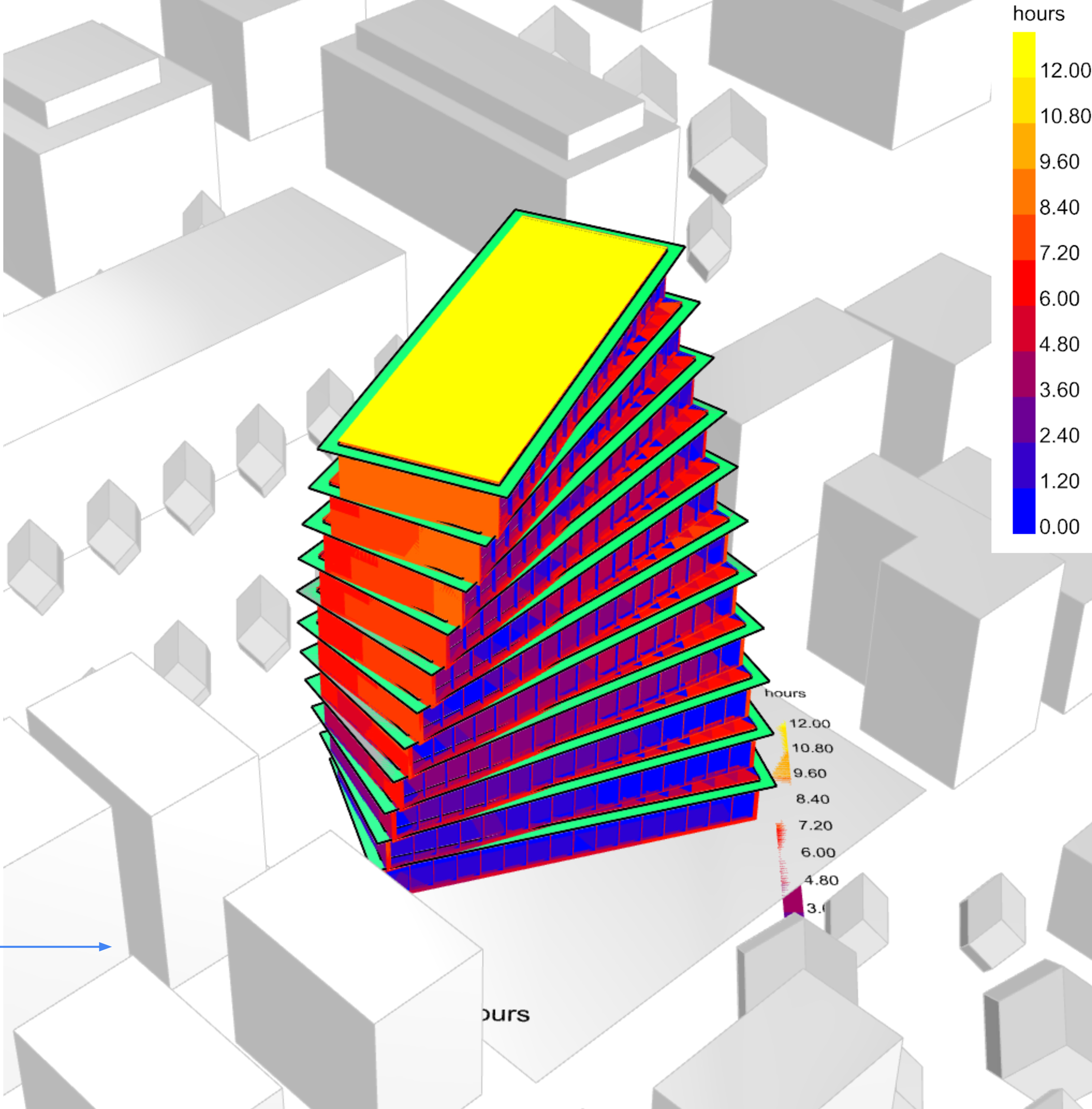
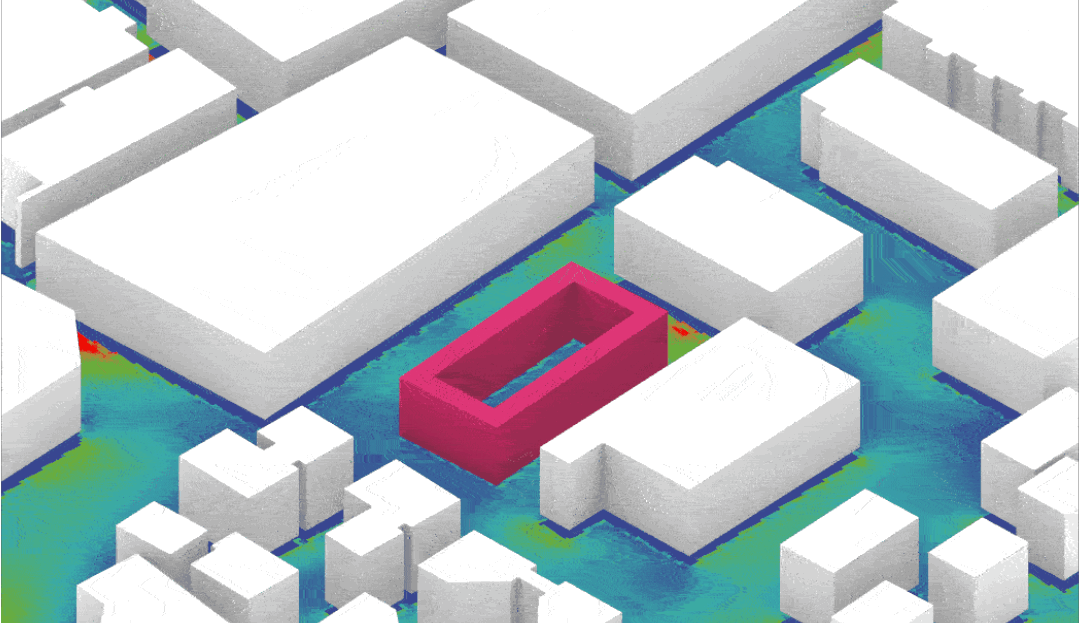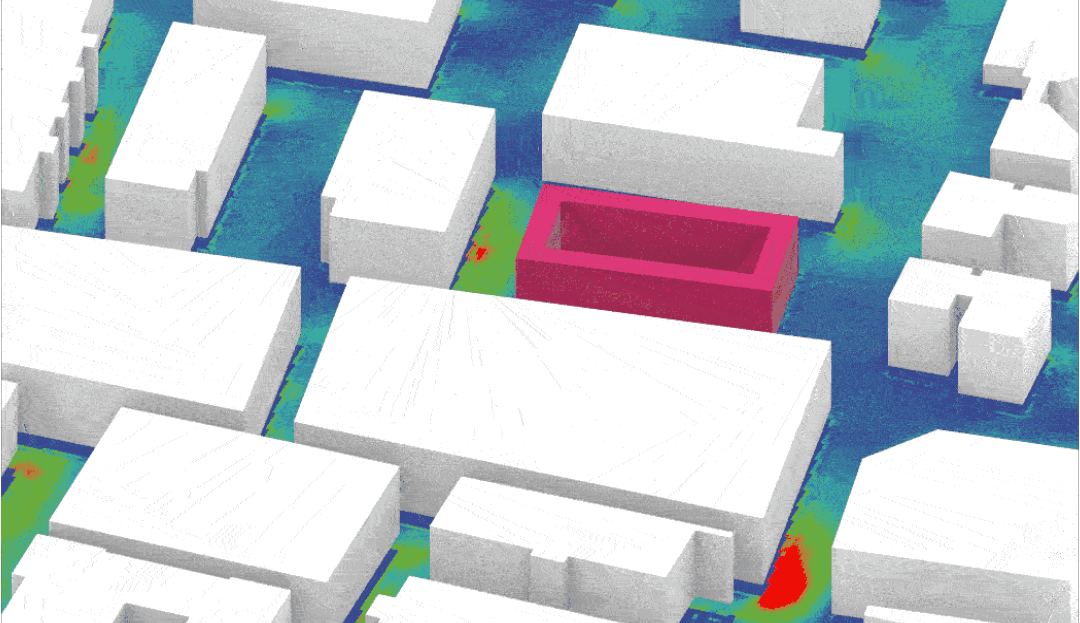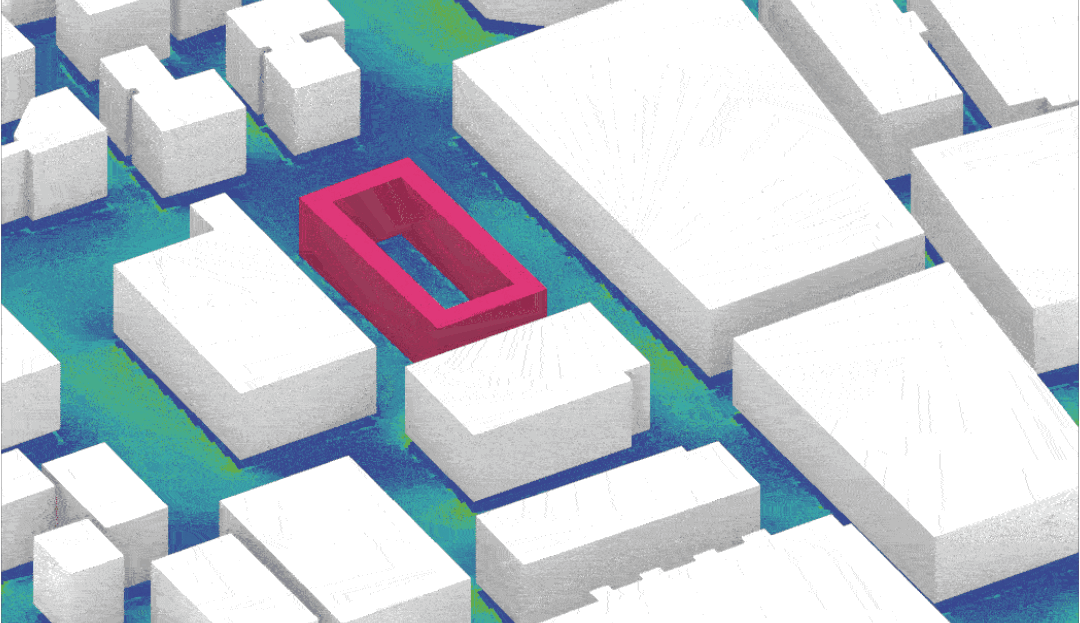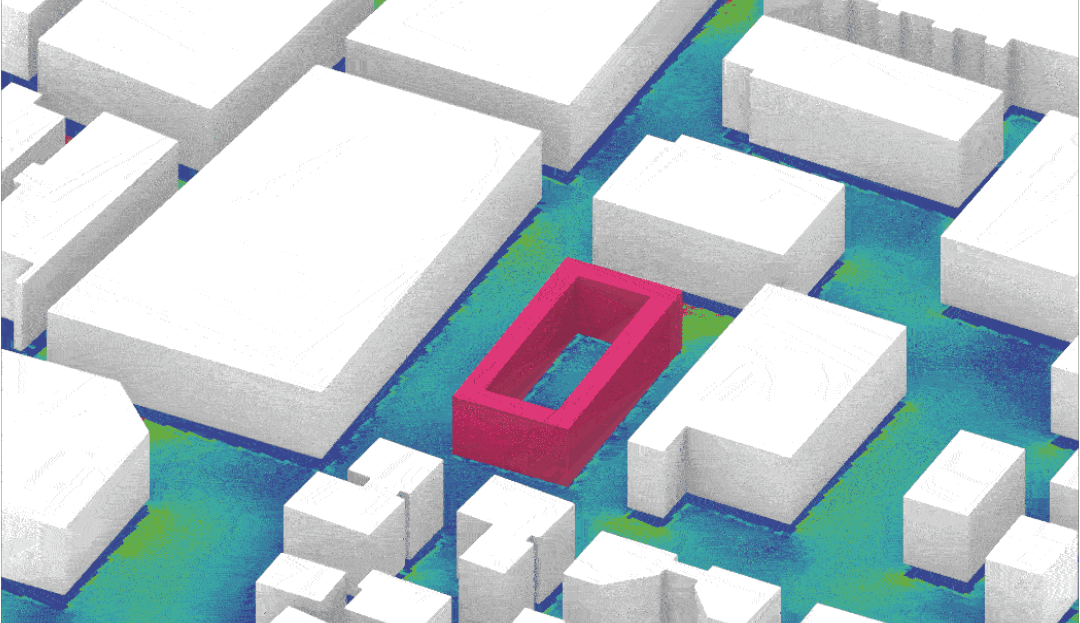
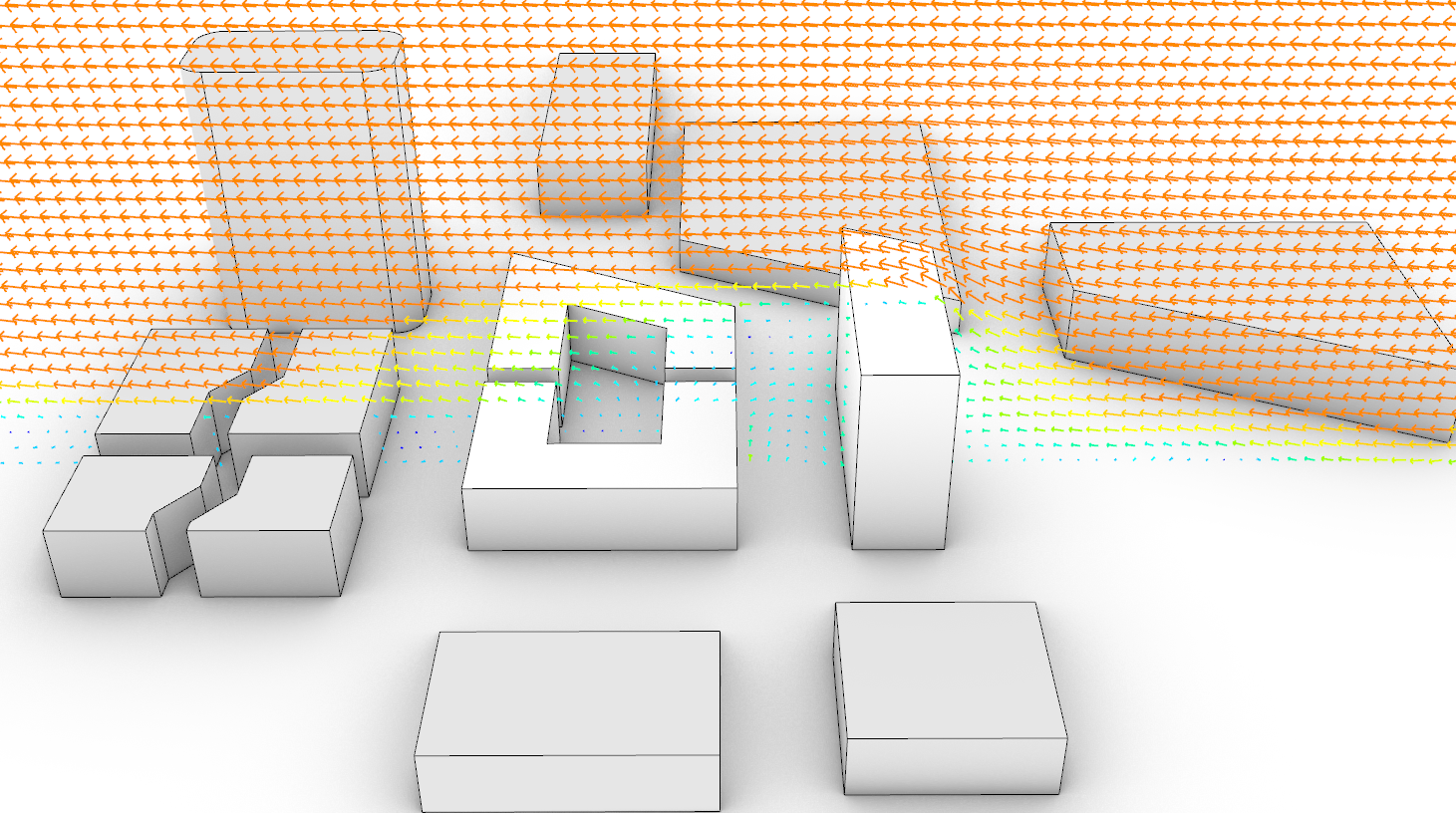
- Set up and run fundamental simulation studies – Solar Radiation, Daylight and CFD
- Visualise, understand and meaningfully interpret the results of simulations
- Be able to make informed decisions based on the simulation results