Description
Making the intangible tangible is essential for communicating and representing a project.
Digital Fabrication has enabled the leap from industrial manufacturing, which is hard to access, to affordable and accessible personal fabrication to allow for rapid prototyping in the development of projects.
The accessibility to rapid prototyping is the opportunity to transmit information in an engaging way.
At first, the relation between design and digital fabrication has been focused on the production of non-standard parts / components and on the speculation of forms as an end itself. Instead we will focus on shapes and machines as a means to develop performance based design with efficient fabrication methods.
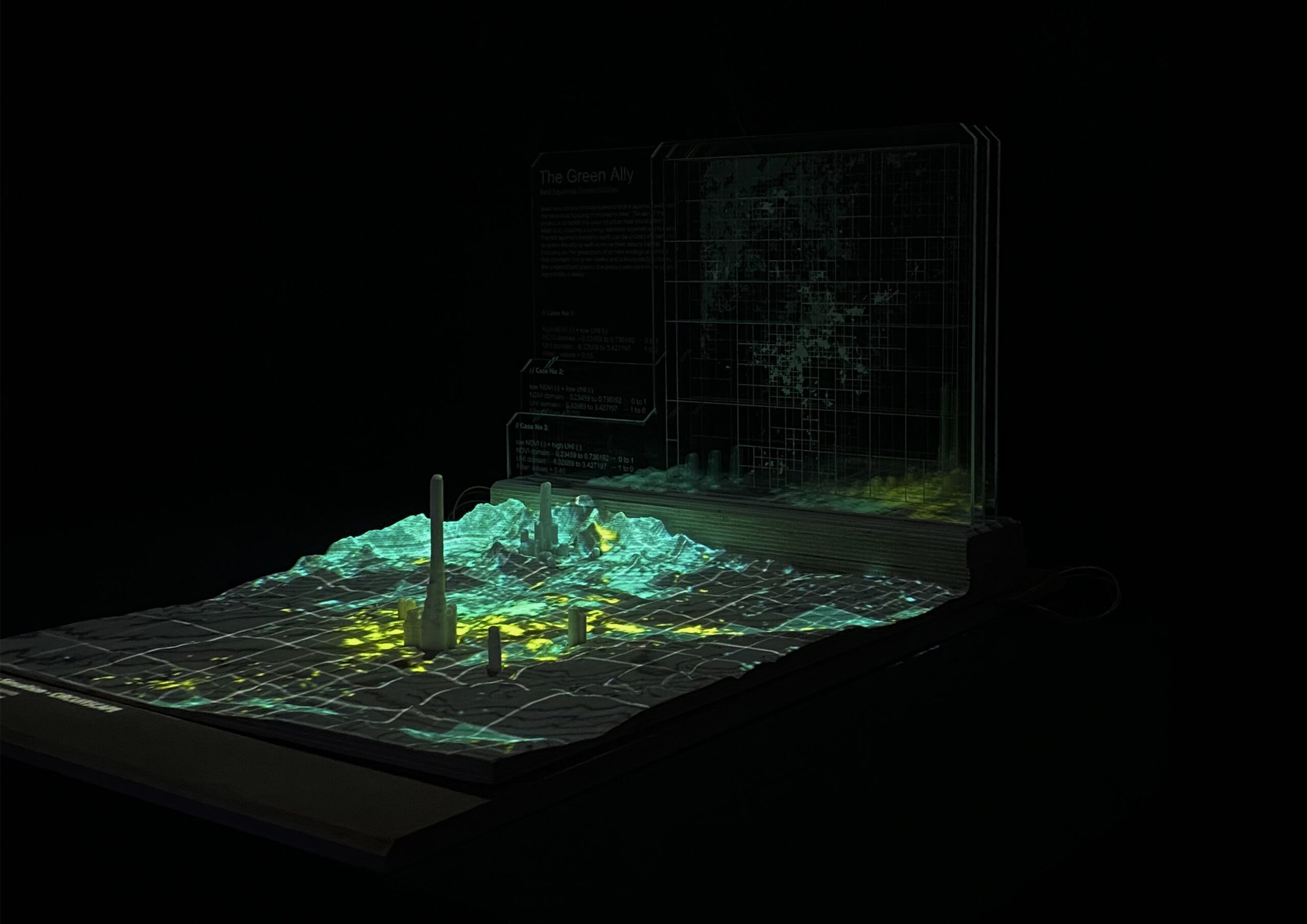
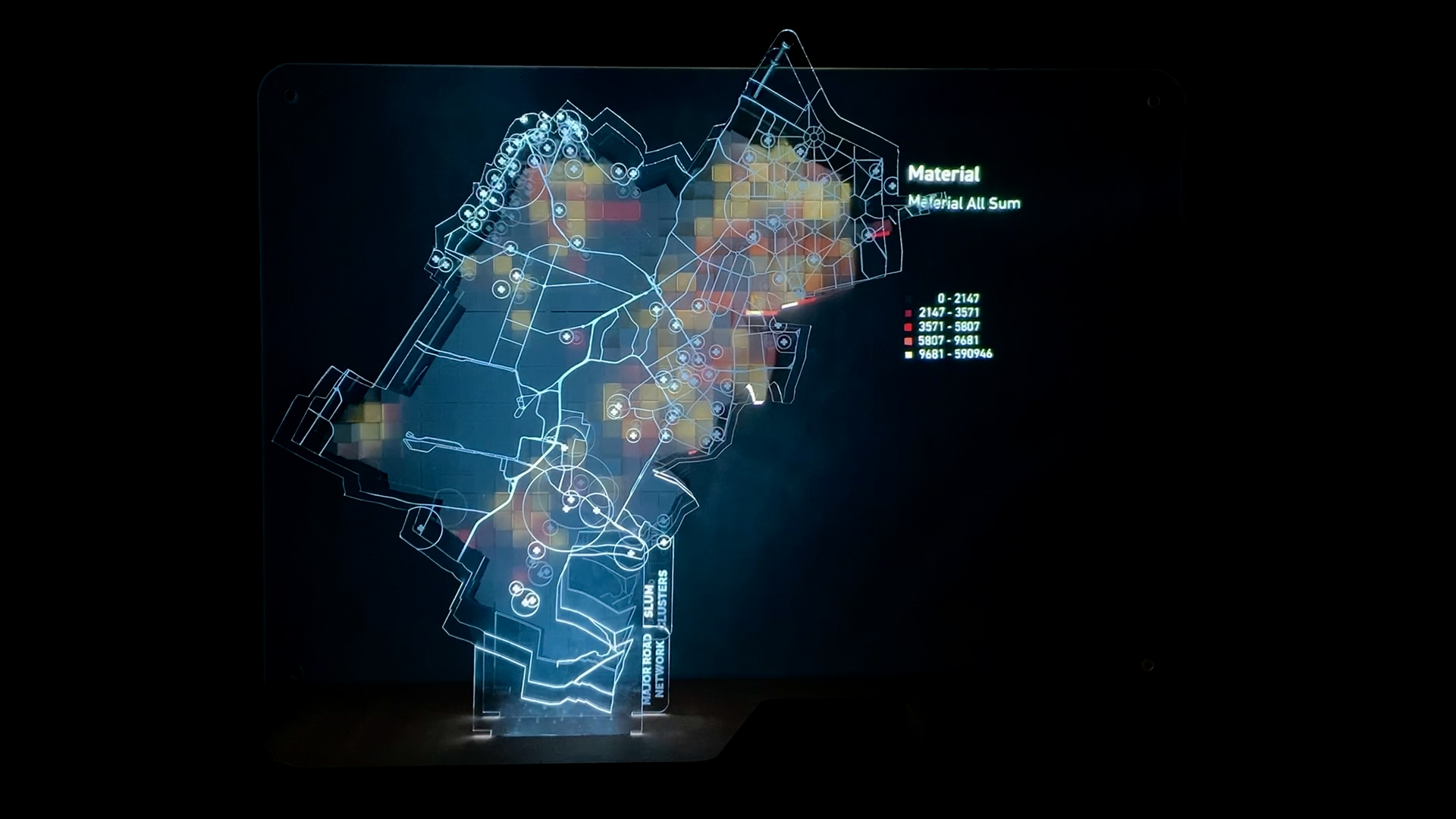
Digital Fabrication techniques through the relation between computer data and machine oriented fabrication, can translate concepts in the most diverse and creative ways. With the use of a wide range of materials and processes, it is possible to create objects rich in details that are the physical and accurate representation of digital design.
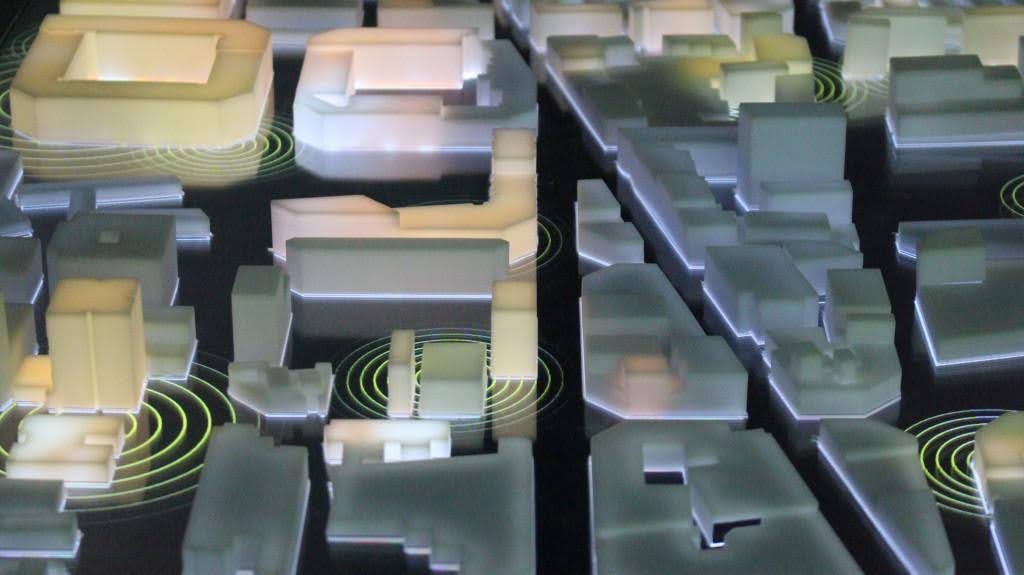
To be communicative, design will be responsive, interactive and equipped with connectivity, following those steps: integration of electronics in the design, programming electronics, mechanical outputs and interaction between your projects and their environment.
Learning Objectives
The aim of the course is to explore the design opportunities arising from three common digital fabrication processes: Laser Cutting, CNC milling and 3D Printing. Assignments will be supported by an interactive exploration of each technology and material, going through a conceptual and prototyping process of design each week.
By the end of the course, every student should be familiar with digital modelling, fabricating, documenting and assembly. Students should be able to invent strategies to translate geometry into an articulated constructible solution, produce the CAD-CAM file for production and use the machines by themselves.
During the course, students will also learn to handle a digital workflow, in both the design and prototyping stages, learning to design projects efficiently and quickly; understand manufacturing processes and contemporary rapid prototyping, confer to the projects the ability to interact and respond to the environment around them.