Introduction
Urban areas are increasingly becoming impermeable, exacerbating environmental challenges such as elevated temperatures, flooding, and pollution. EcoNodes is designed to empower policymakers with a sophisticated tool for dynamically assessing and adapting urban environments towards increased sustainability by pinpointing and prioritizing areas for green interventions.
Impervious Surfaces and Urban Heat Islands
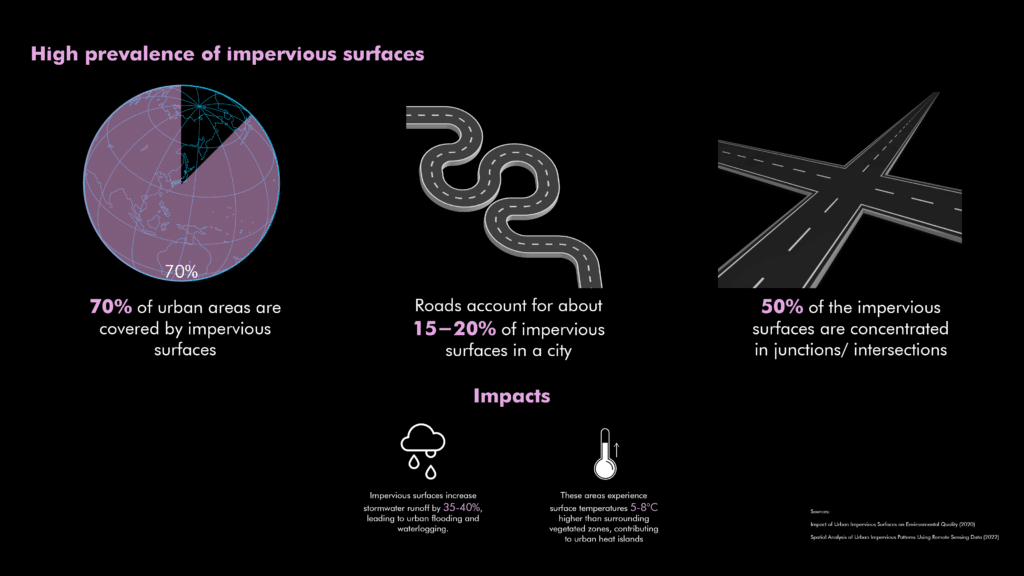
Cities today face the challenge of having approximately 70% of their surfaces covered by impermeable materials such as concrete and asphalt. These surfaces significantly raise local temperatures by 5-8°C, creating urban heat islands. Additionally, they cause a dramatic 35-40% increase in stormwater runoff, leading to frequent flooding and pollution. Imperviousness is particularly severe at road junctions, accounting for roughly 50% of these problematic surfaces.
Importance of Intersections
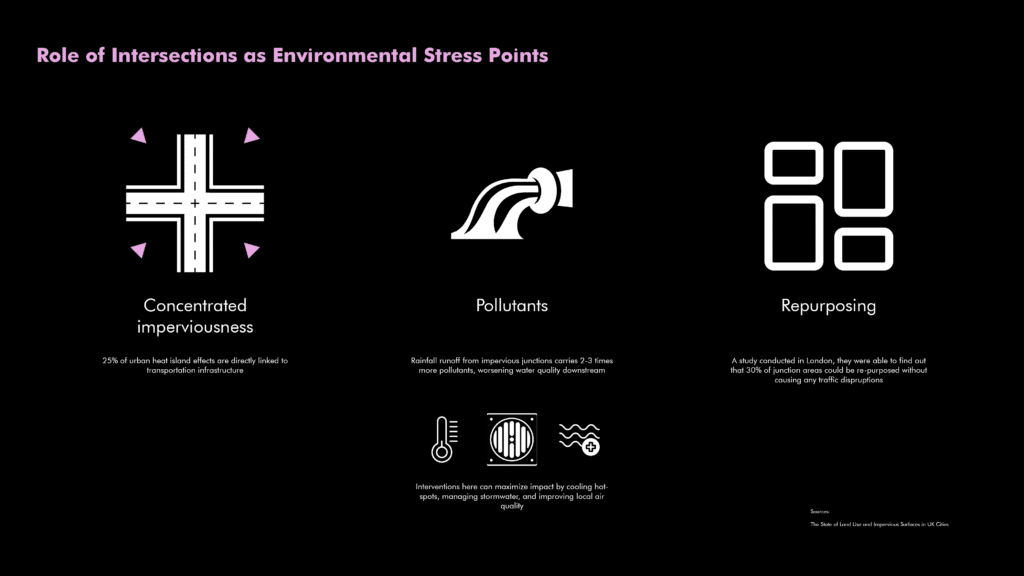
Urban intersections emerge as critical environmental stress points. Approximately 25% of urban heat island effects originate directly from transportation infrastructure at these junctions. Rainwater runoff at intersections contains 2-3 times more pollutants, substantially worsening water quality downstream. Effective intervention at these points can significantly mitigate heat islands, manage stormwater effectively, and enhance local air quality without hindering traffic flows.
Urban Prairie: Learning from Detroit and Chicago

Successful examples from Detroit and Chicago illustrate the concept of urban prairies. Detroit reclaimed just 3% of its impervious land into 500 hectares of prairies, reducing stormwater runoff by 20%. Chicago transformed intersections into partial green spaces, achieving temperature reductions of 3-5°C and enhancing local biodiversity by 30% within three years.
Research Question
"How can AI-driven analysis systematically identify and prioritize urban junctions to optimize green interventions?“
Bridging Technological and Planning Gaps
Current urban planning methods lack integration of key environmental metrics, sustainability objectives, user-centric design principles, and real-time adaptive capabilities. EcoNodes fills these gaps by combining aerial imagery, street view data, walkability scores, heat mapping, and vegetation indices to provide an interactive, holistic platform for urban planners.
Methodological Framework
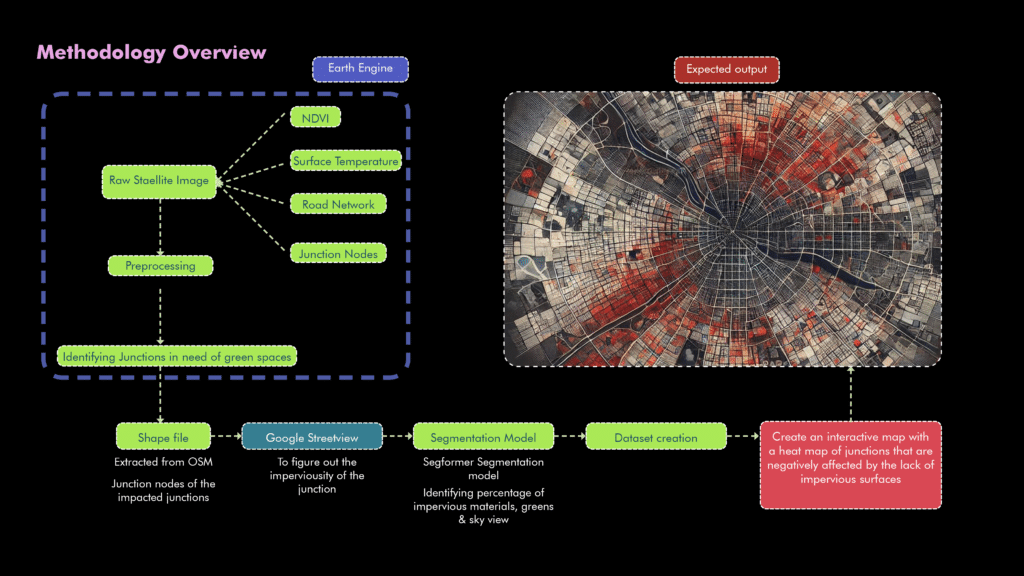
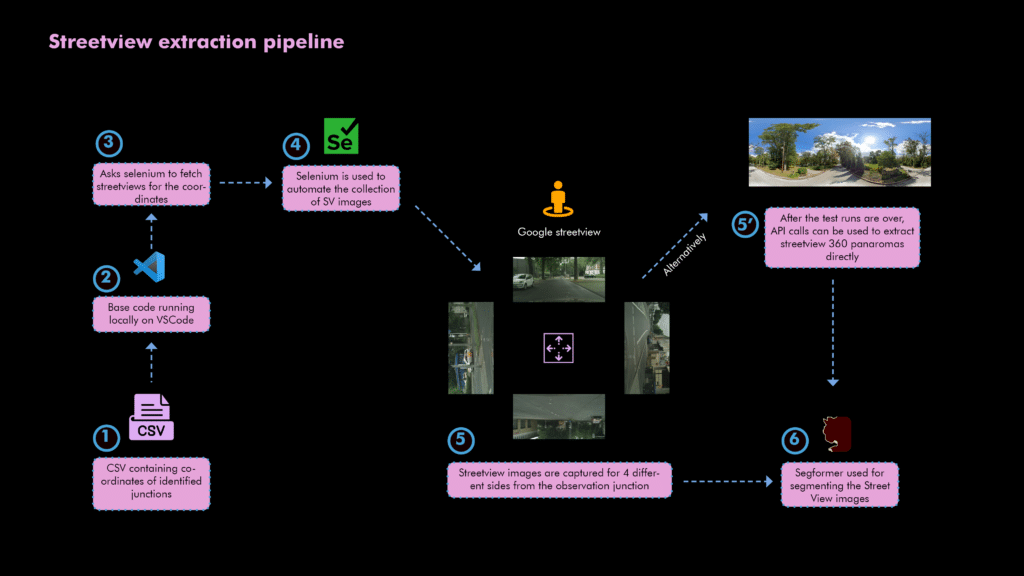
EcoNodes employs comprehensive datasets including Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 satellite imagery, OpenStreetMap (OSM) data, and Google Street View images. These datasets facilitate detailed and precise identification of priority junctions requiring immediate environmental attention.
Street View Segmentation

Street-level images from Google Street View are segmented using advanced AI techniques to precisely categorize impervious surfaces, vegetation, and sky visibility. This ground-level analysis validates satellite-derived data and provides accurate, detailed environmental insights.
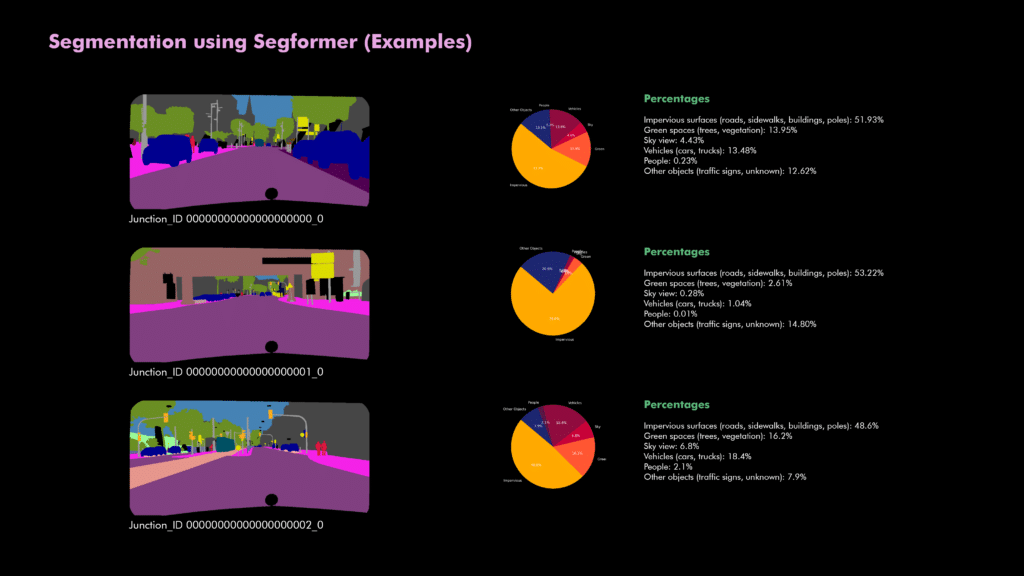
Segmentation categorizes urban surfaces into clear metrics, including impervious surface coverage, green space proportions, and sky visibility. This quantification provides actionable insights essential for planning urban sustainability interventions.
Dynamic Scoring and Neighborhood Influence
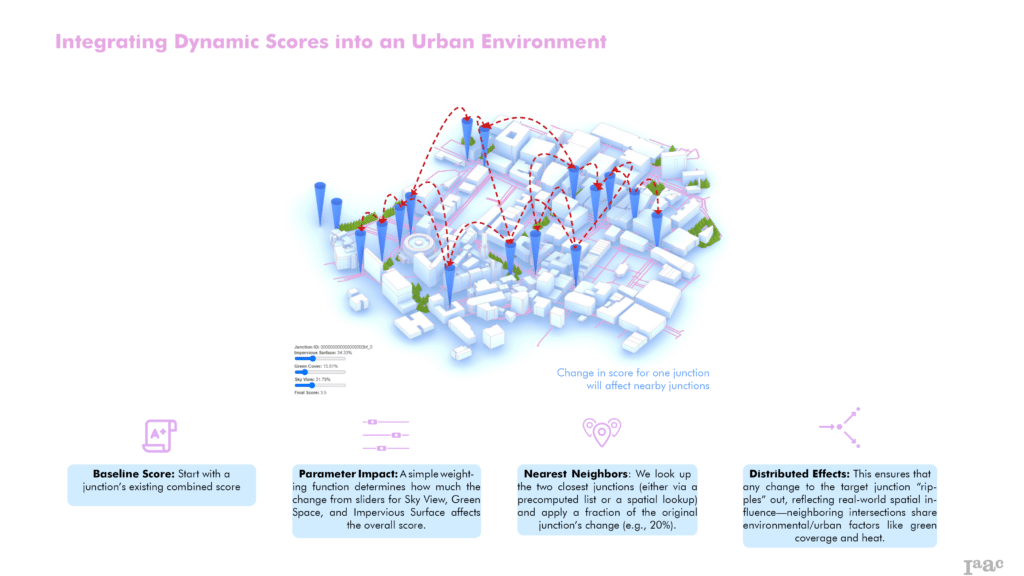
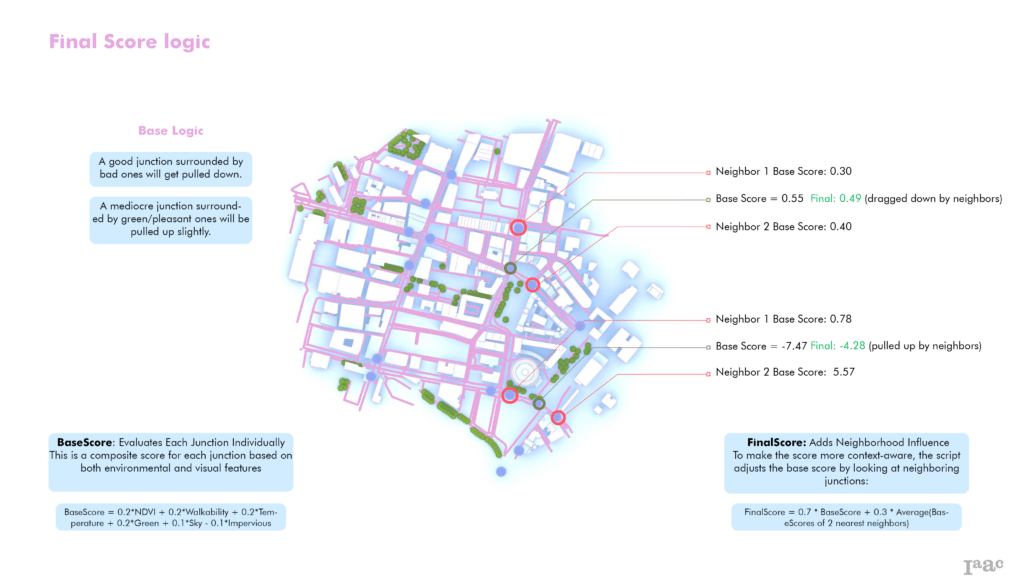
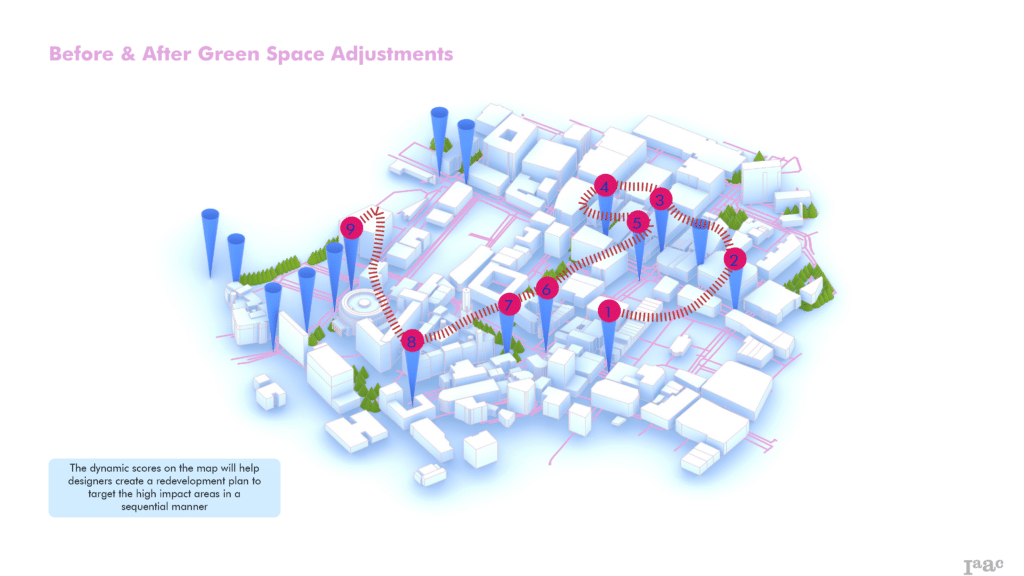
EcoNodes implements dynamic scoring that incorporates spatial relationships, accounting for neighboring junction conditions. Changes in one area automatically reflect adjustments in adjacent junctions, modeling real-world environmental interactions.
Interactive Heatmap for Decision Making

EcoNodes provides an intuitive interactive heatmap, visually depicting junction scores. This visualization assists planners in rapidly identifying and prioritizing interventions, clearly highlighting hotspots requiring immediate environmental action.
Implementation and Next Steps
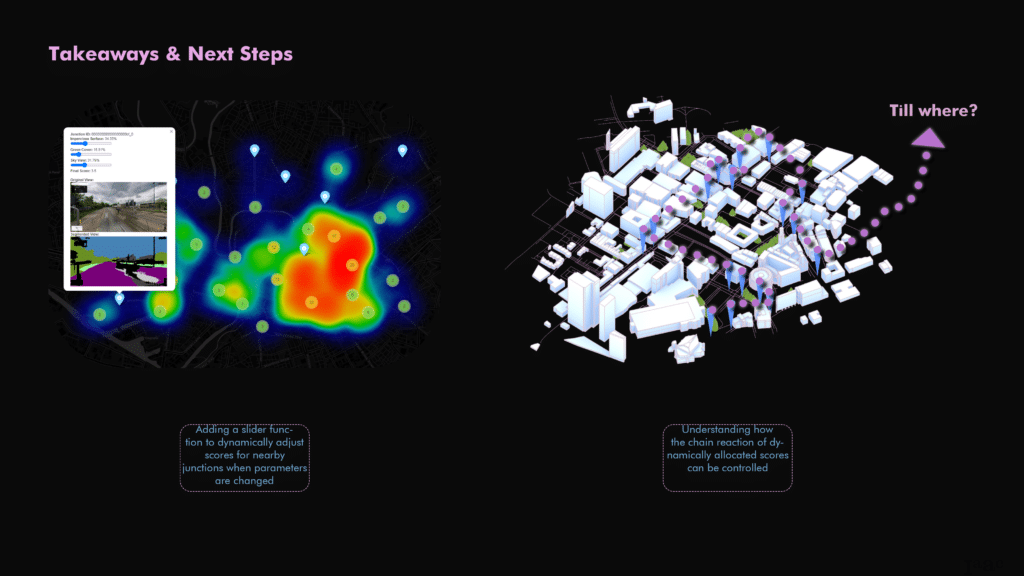
Future enhancements include introducing dynamic adjustment sliders, allowing planners to visualize how interventions at specific junctions influence broader urban areas in real-time, enabling informed, strategic decision-making.
Conclusion
EcoNodes serves as an advanced, practical tool that integrates diverse data streams into actionable insights, equipping policymakers and urban planners to foster sustainable, resilient, and livable cities effectively.

