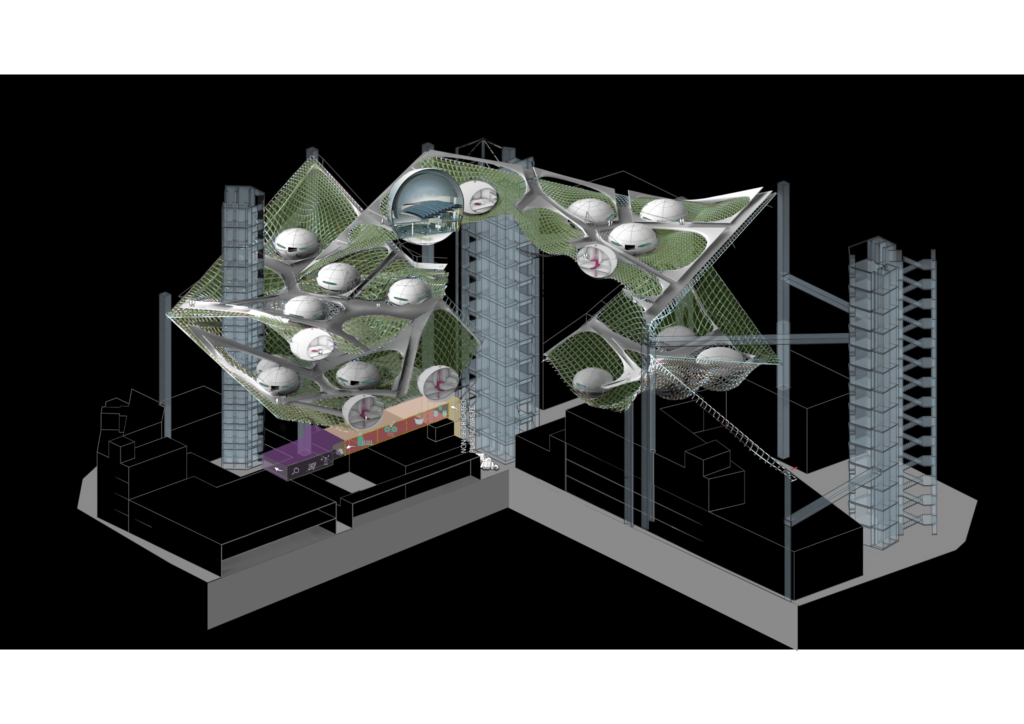
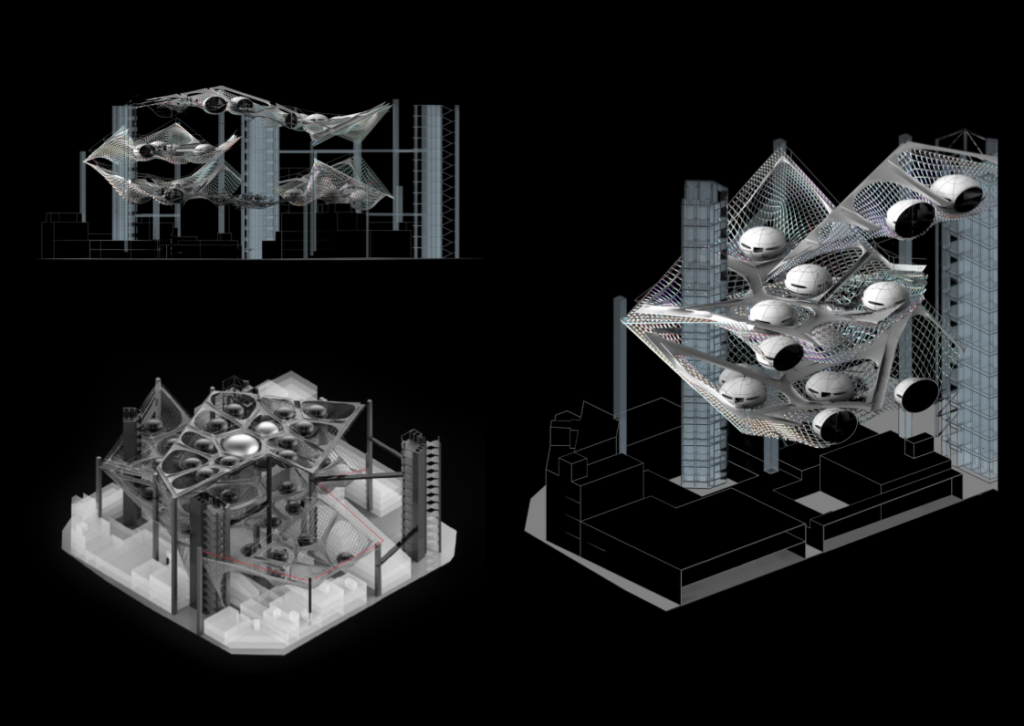
The Urban Re densification project in Barcelona employs a Plastic Waste recycling construction strategy, where buildings gradually grow by consuming the city s plastic waste in a circular loop, creating a lightweight, dynamic, and adaptable architecture that operates in harmony with the existing waste ecosystem to revitalize derelict urban areas.
Site Analysis
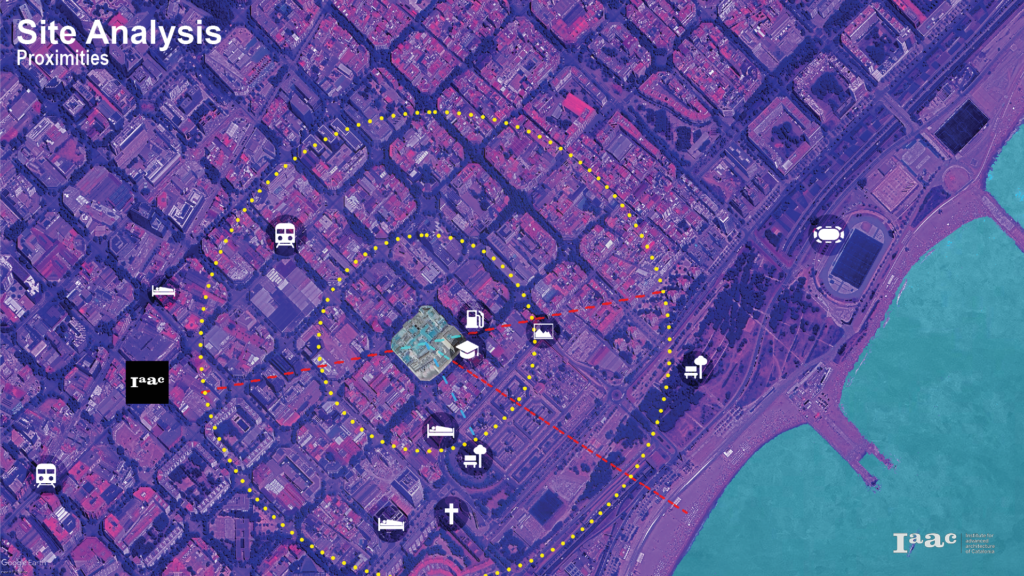
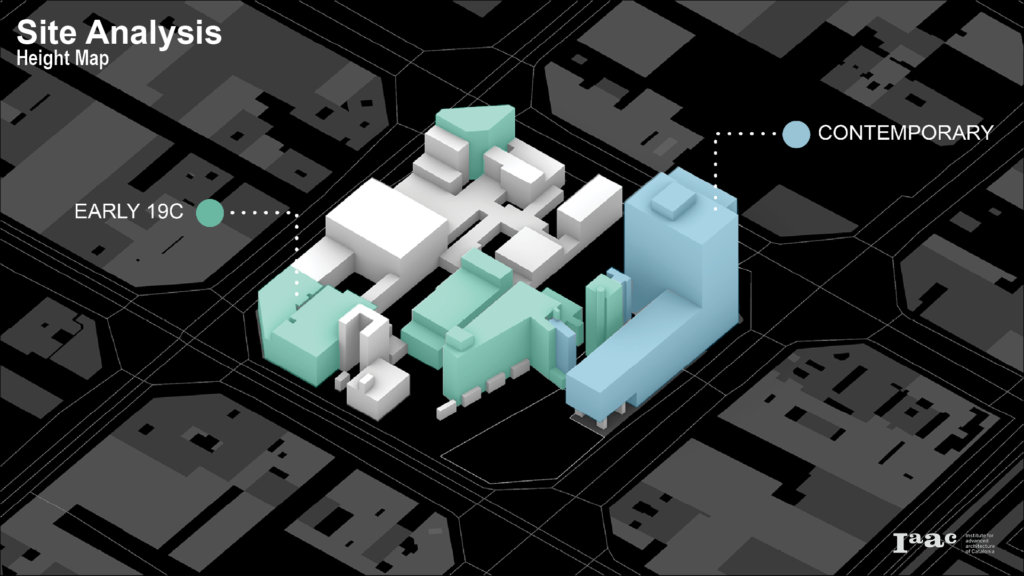
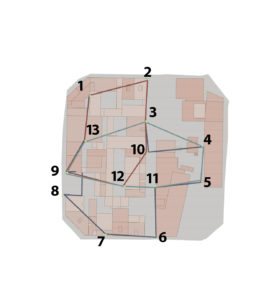
The site is divided into 2 halves by an 8m wide road that includes 2m wide pathways on both sides. These distinct halves exhibit varied spatial arrangements. One portion is predominantly characterized by 1-3 storeyed low-rise residential buildings, complemented by retail spaces and a small-scale industrial unit. In contrast, the other half showcases high-rise office and commercial hotel structures.
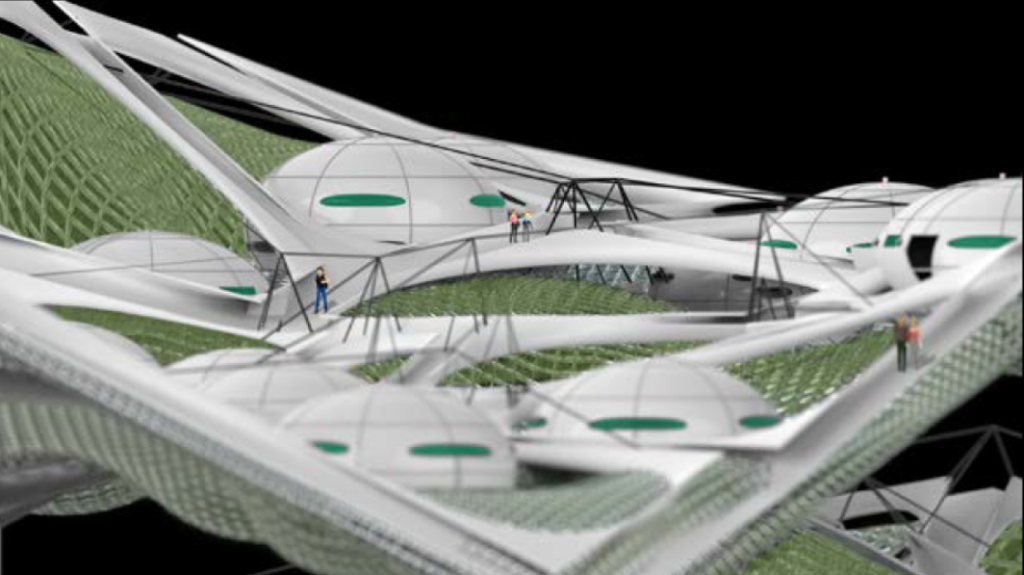
Proposal
This project seeks to convert a city block into a waste management-centered community and integrating waste materials into the buildings to emphasize recycling’s impact on daily life and fostering a sense of community among residents.
Sanky Diagram
Demonstrating the proportions and the process of how the plastic is being used in the project
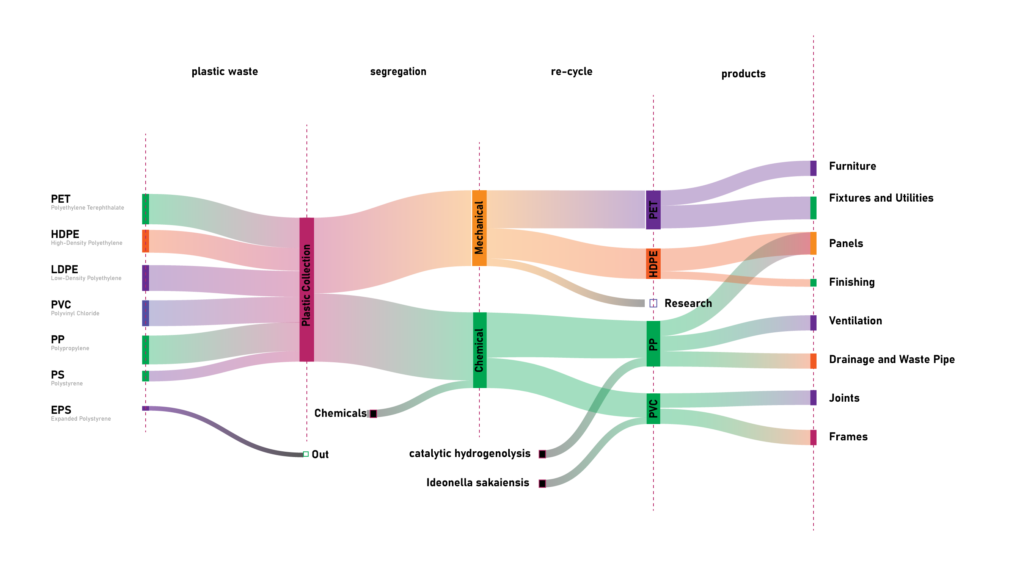
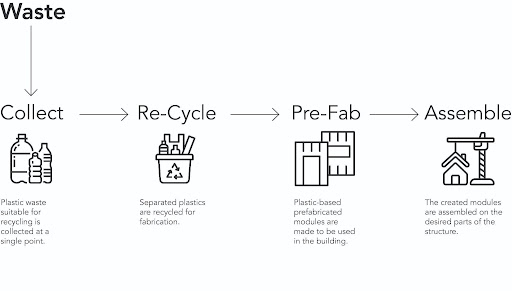
Simplified Cycle:
The cycle starts by collecting the plastics from the inhabitant and ends in the modules fabrication by using the collected plastic. The process has 4 key stages which in between it Re-cycle and Pre-fab to be prepared as a module construction material.
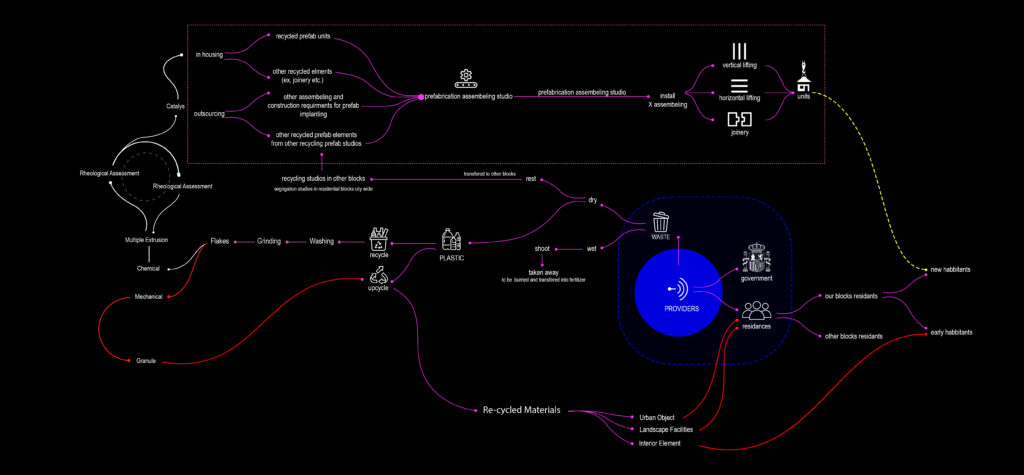
Metabolic Diagram:
Proposal / Methodology Inspiration
Space Time Curvature
study of the relation of mass and the grid (bending)

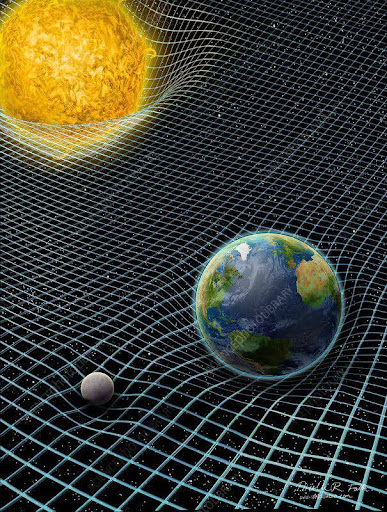
Assuming the mass are the modules and the space time is the project landscape!
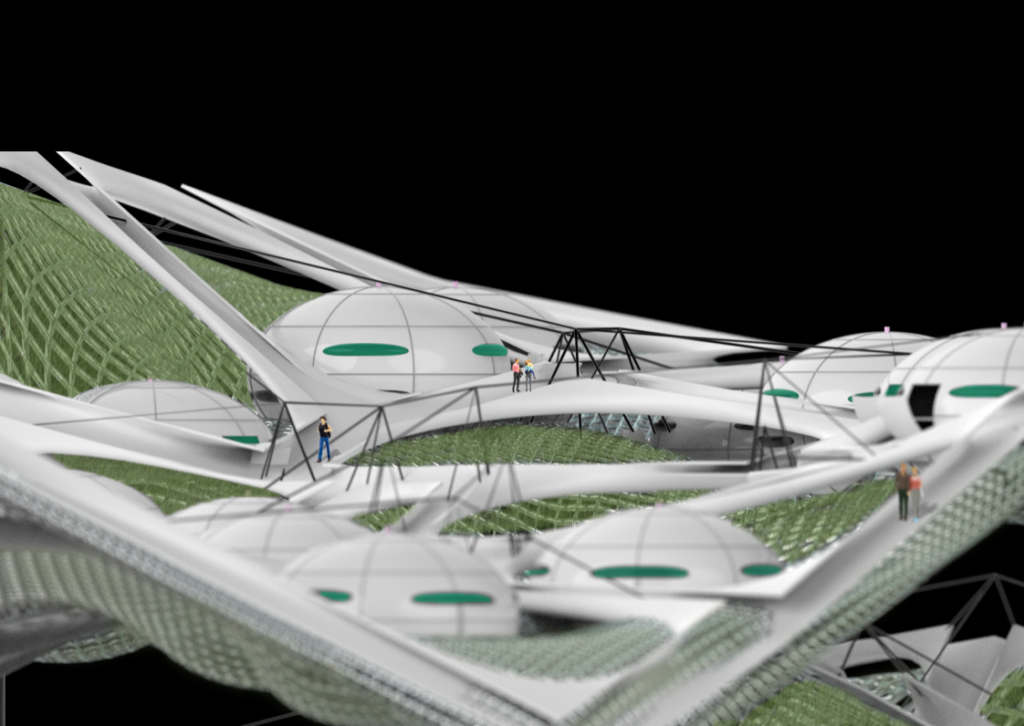
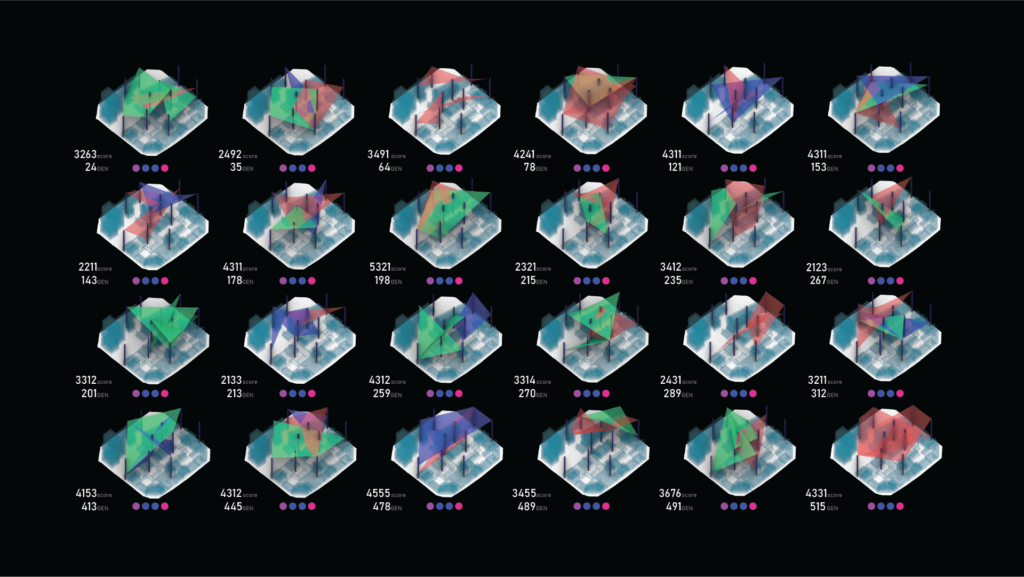
Proposal / Stage01 | Landscape
Landscape design aims to create series surfaces on top of the existing block by the predefined vertical access and construction shafts. As it should maintain a given minimum required area per each surface, Radiation analysis and minimum accessibility.
This exhibition presents a novel application of genetic algorithms in architectural level design. The project features an advanced solver that inputs a set of columns and iteratively connects them to form an optimized layout. The algorithm’s core objective is to balance sky radiation exposure, programmatic distribution, and minimum area requirements. This approach allows for the exploration of a vast design space, harnessing computational power to achieve designs that are not only efficient but also aesthetically compelling and environmentally responsive.
Selected Mutation
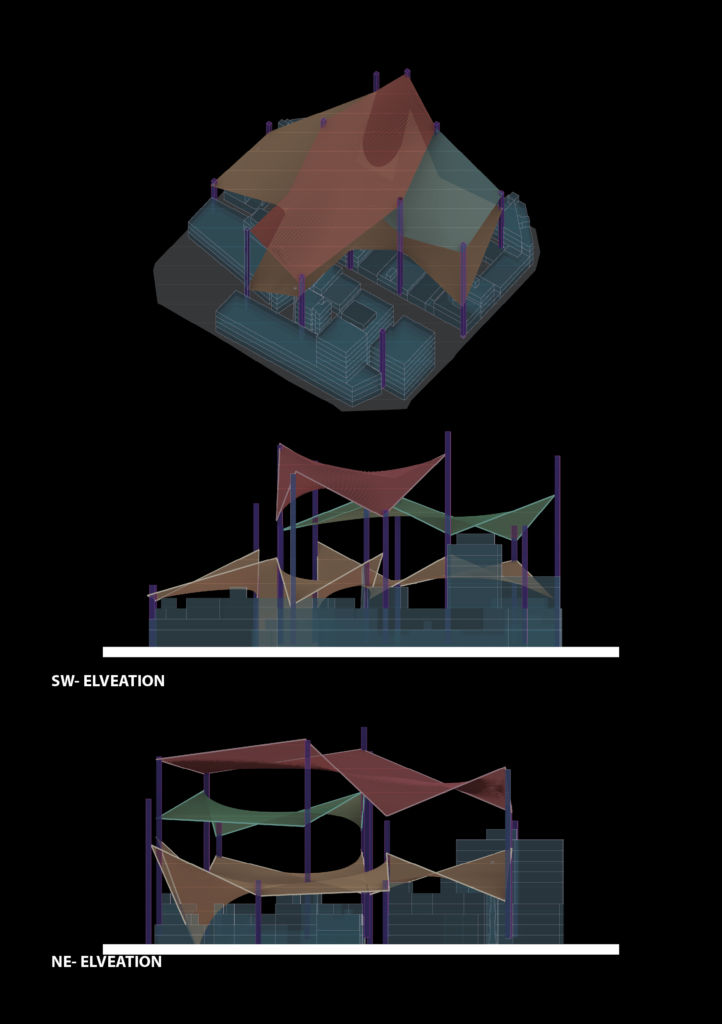
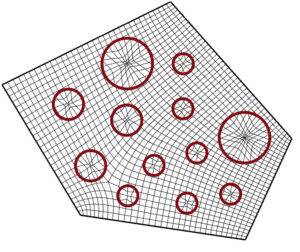
Proposal / Stage02 | Module
This exhibition presents a novel application of genetic algorithms in architectural level design. The project features an advanced solver that inputs a set of columns and iteratively connects them to form an optimized layout. The algorithm’s core objective is to balance sky radiation exposure, programmatic distribution, and minimum area requirements. This approach allows for the exploration of a vast design space, harnessing computational power to achieve designs that are not only efficient but also aesthetically compelling and environmentally responsive.
Process
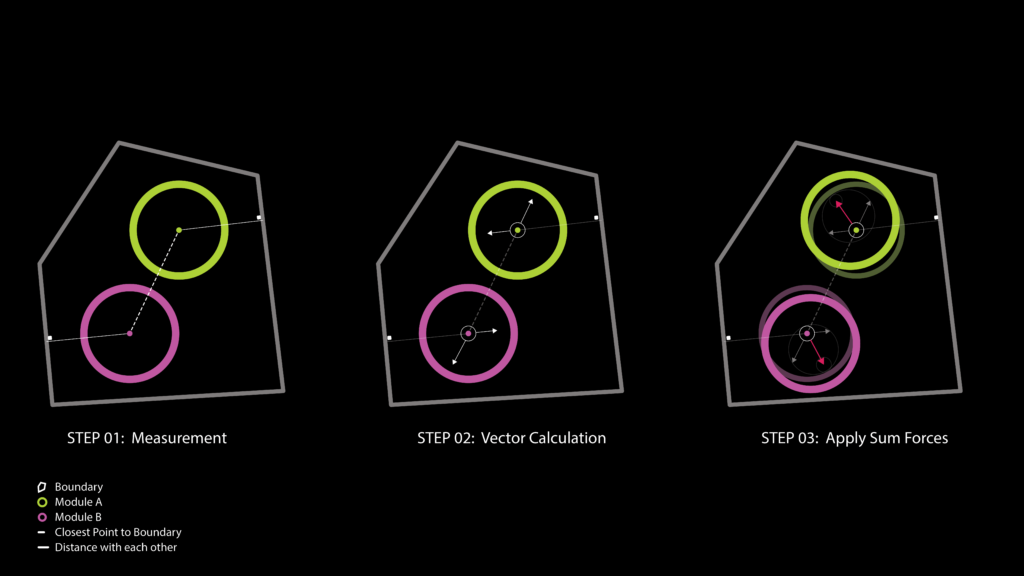

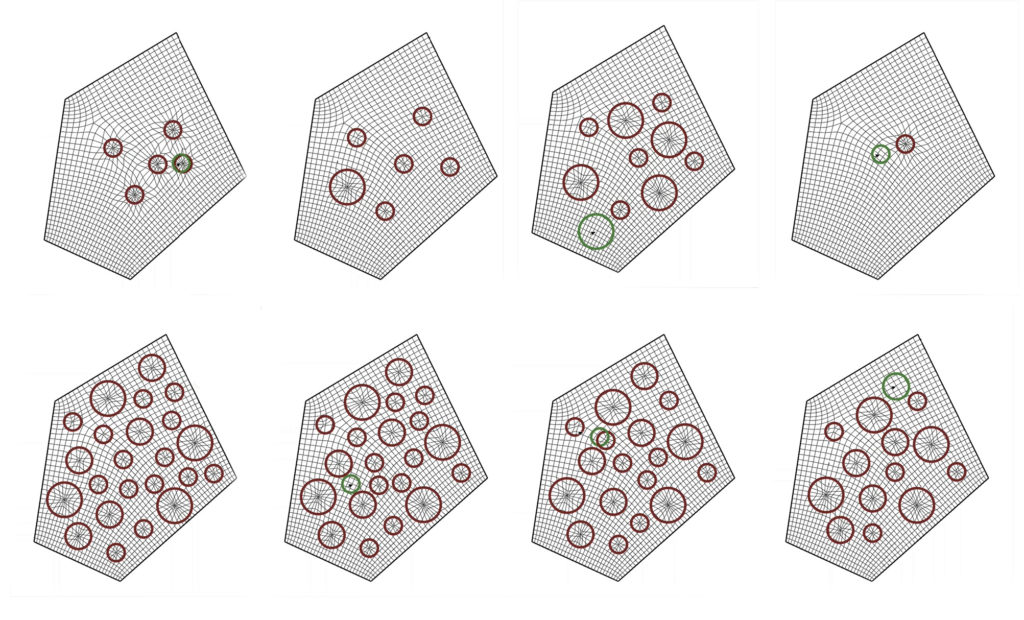
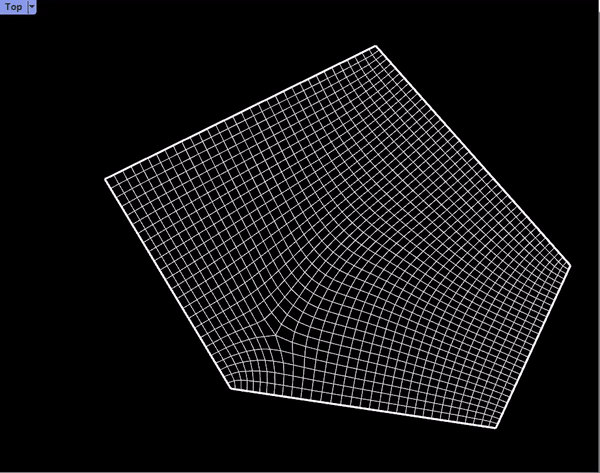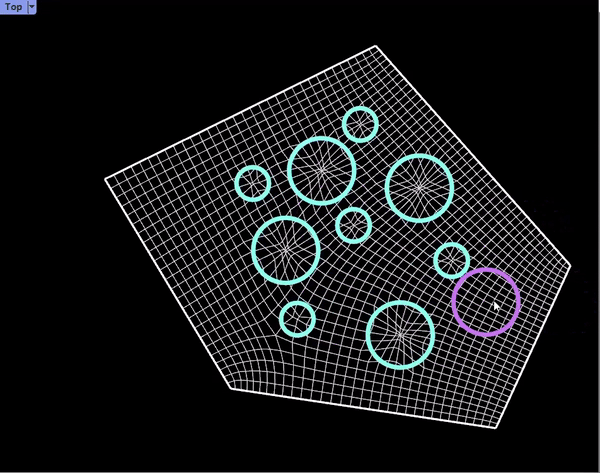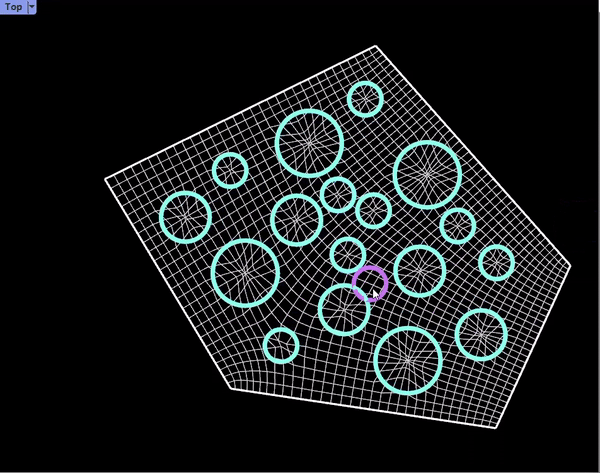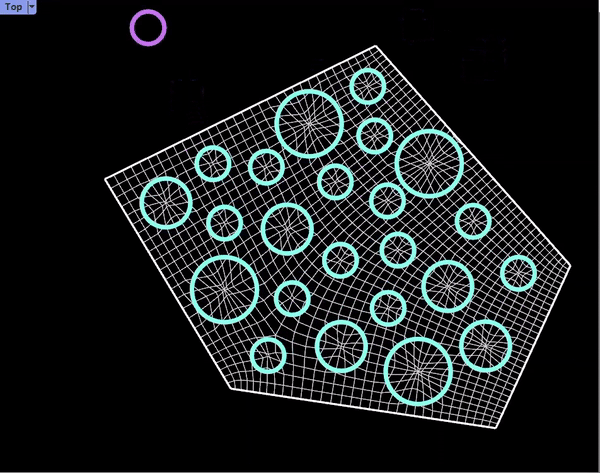
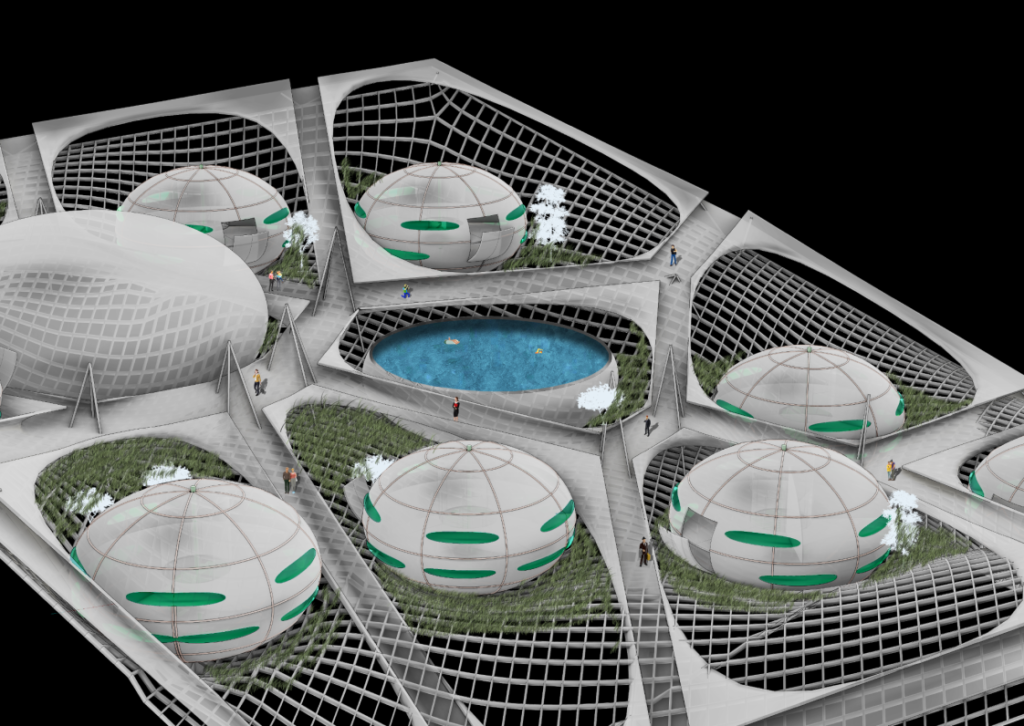
Proposal /Module Distribution on Surfaces
Prototypes:


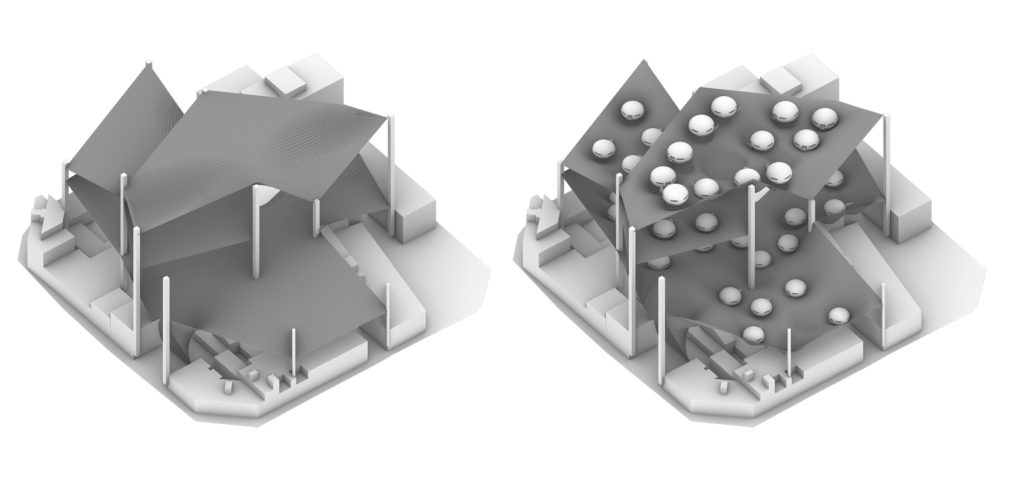
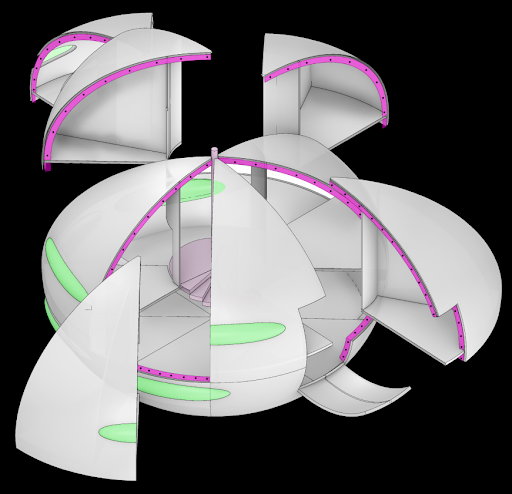
Proposal/ Module Design
Modules are created in a way that can be easily transferred from fabrication facilities to assembly site. The shape which basically drive from an oval shape made out of 16 pieces and 6 inner slabs
.
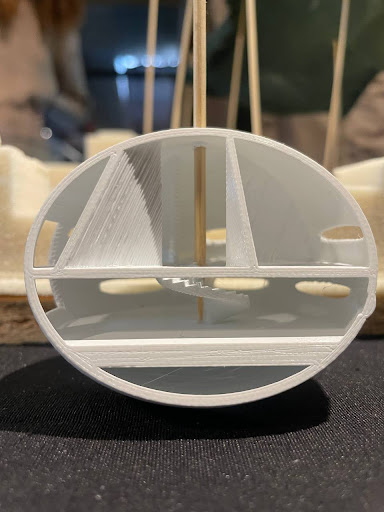
Module Prototype
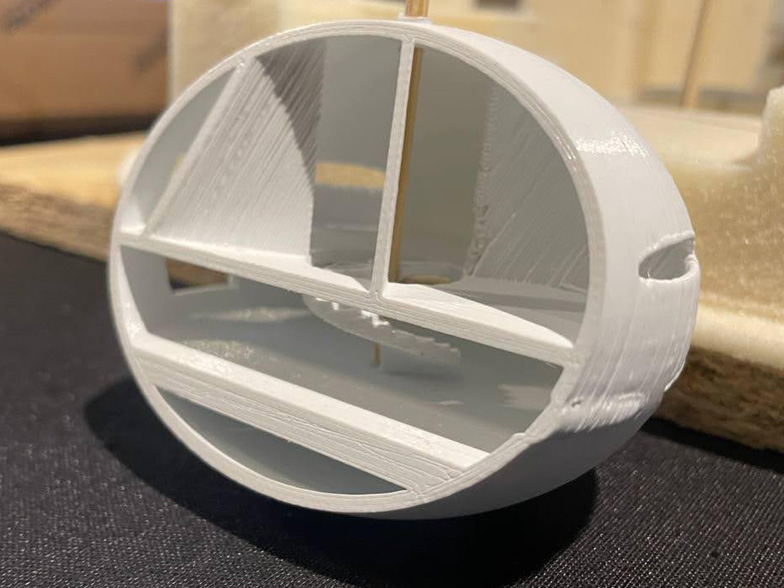

…
Proposal/ Documents
Jellyfish Section