1. Abstract
Healthy Spaces of Viladecans is an Internet of People studio project which forces designers to reimagine the city of Viladecans as a hub of spaces that enhance the mental, physical and social health of the users of these spaces. This project aims at understanding the intangible concept of “Healthy” through identification of parameters to measure these spaces to see what is the level of social, physical and mental well-being of people in these spaces. These parameters could lead us to key performance indicators that can help designers to numerically locate spaces of more requirement for healthy development as opposed to those which already function as healthy spaces as a case study to re-imagine all of Vilaadecans in the same manner. Through this project, designers focus on the needs and requirements of the most vulnerable inhabitants of Viladecans and transform spaces to healthier spaces in their perspective. Subsequently designers also look at various ways of including the municipality along with various stakeholders, through policy making and feasibility study, into the execution of smooth development of the identified spaces in this project, that in turn can be scaled up to all of Viladecans. In the process, the project finds ways to tackle a majority of challenges mentioned in the Viladecans 2030 challenges to make Viladecans a sustainable city.
2. Objective
- address a majority of challenges mentioned in the Viladecans 2030 challenges, actively or passively,
- understand the subjective and intangible concept of what is healthy and what is not within the context of Viladecans and through the lenses of the most vulnerable inhabitants of Viladecans.
- Identify ways to making health and wellbeing tangible through parameters that translate to key performance indicators that can help with an impact analysis
- Design healthier spaces for the well-being of the older and more vulnerable population of Viladecans
- Strategise ways of including the municipality along with all the other stakeholders of Viladecans through participatory processes and policy making
3. Scope

The scope of this project is to identify a few parameters that can give the designers a way to achieve some KPI’s that can be a way to give scores to spaces. However, the scope of the KPI’s are not limited to just those mentioned within the framework of this project. As the project develops further into the participatory process with the stakeholders, KPI’s of the project can see changes according to the feedback from participatory processes. Nevertheless, the project’s scope extends to emerging with spatial organisation of requirements of the people to strengthen mental, social and physical health of spaces. However, the project does not tackle all of the challenges of Viladecans through the framework of KPI’s, design for spaces and the policies made for their execution and running.
4. Methodology and Concept
The methodology followed for the project is to understand ways of connecting people to space which together creates the identity of cities. The initial steps included doing a basic research about healthy spaces and what do they signify. This research required to be cross-referenced with the context of Viladecans and hence a participatory process of speaking to the people of Viladecans was started. Simple interviews of what signifies health to the people was conducted over a smaller sample size. However, during the participatory process, designers also take notes of their observations of public spaces throughout Viladecans.
From all the observations and inferences, designers come up with some vital parameters that can play a tangible role in the design of spaces with better mental, social and physical health. These parameters are used to analyse better the existing health and well being of Viladecans. Nevertheless, these parameters can only be made tangible through some scores that arise from key parameter indices concluded from the same parameters that are used for analysis.
From analysis of the various parameters some centralities and connections between these centralities emerge that require special attention through design and policy making, in order to transform the health of the spaces and their users. Amongst the identified centralities and connections, a pilot stretch is selected for a more detailed design of spatial organisation through identified KPI’s. The pilot stretch transpires through the overlapping of several layers of analysis. Once the design for pilot stretch is put into place, strategies for policy making for execution and maintenance of the project from the get go to handover of these spaces to the people. The policies take into account the municipality and all the users of the urban public spaces.

PILLARS OF SUSTAINABILITY
The widely adopted model of sustainability, often depicted as three intersecting circles representing social, economic, and environmental dimensions, emphasizes the central goal of overall sustainability. These are called the three pillars of sustainability. The three-pillar conception of sustainability did not originate from a single source but rather evolved gradually from critiques within early academic literature. These critiques emerged from diverse perspectives, including social and ecological, challenging the economic status quo.
TYPES OF HEALTH
There are numerous interpretations of health, each serving different purposes throughout history. Promoting health involves encouraging beneficial activities like regular exercise and sufficient sleep while minimizing or avoiding detrimental behaviours. Some factors affecting health are due to individual choices, which makes the concept of health and healthy living a very subjective matter. This means that health is a resource to support an individual’s function in wider society, rather than an end in itself. A healthful lifestyle provides the means to lead a full life with meaning and purpose. In the urban life of people living in urban context health is broadly divided into social, mental and physical health.
The concept followed for this project is to connect people to spaces within the city through resonating with their social, mental and physical health to develop these spaces on the pillars of sustainability.
5. Viladecans
Viladecans is a city located in the south of Barcelona and has a population of almost 70.000 people. There are 3 main areas in terms of use of land. The eastern area closer to the see is mostly agricultural, the area in the middle is mostly industrial and the western area is the residential where almost all the residents live. The residential area represent just a 20% of the total area of Viladecans and we will focus our analysis there since this is a project that has people as the central point.

6. Understanding health in Viladecans
We went to Viladecans to talk with people and understand how we could make healthier spaces in the city. We were able to engage conversations with different groups of people (age, gender, residents, workers, retired, etc) and this were the main takeaways from this talks:
– Old people walk around the city
– Everything is within walking distance
– Some sidewalks are too narrow to walk comfortably
– Bus connects very well Viladecans with the surrounding cities
– Sometimes cycles and electric scooters can be dangerous for pedestrians, especially old residents
We used this feedback to understand what people might need in a healthy and safe space. This was a glimpse of the participatory process that we would like to achieve for this project but it is a good starting point.

7. Analysis of Health for KPI
SOCIAL HEALTH
Social health in an urban context refers to the aggregated health of a neighbourhood, society or a community within the boundaries of the urban fabric. The social health of a city encompasses the well-being and interconnectedness of its residents within the community. It is reflected in the quality of relationships, sense of belonging, and level of social support available. A socially healthy city fosters inclusivity, diversity, and cohesion among its inhabitants, promoting a sense of unity and shared responsibility. Strong social networks, active community engagement, and accessible resources for mental health and social services contribute to the overall social health of a city. Additionally, initiatives that address issues such as poverty, homelessness, and social isolation play a vital role in creating a supportive environment where individuals can thrive socially and emotionally.
A challenge that the designers faced was to come up with spatial parameters to analyse social health. Nonetheless, few of the simpler ways were to analyse spaces of social engagement where people would exchange intellect and points of interest and their accessibility where people would go to on a more frequent basis. These were indeed spaces of creating more relationships but also spaces that enhanced the sense of belonging for the vulnerable inhabitants of Viladecans.

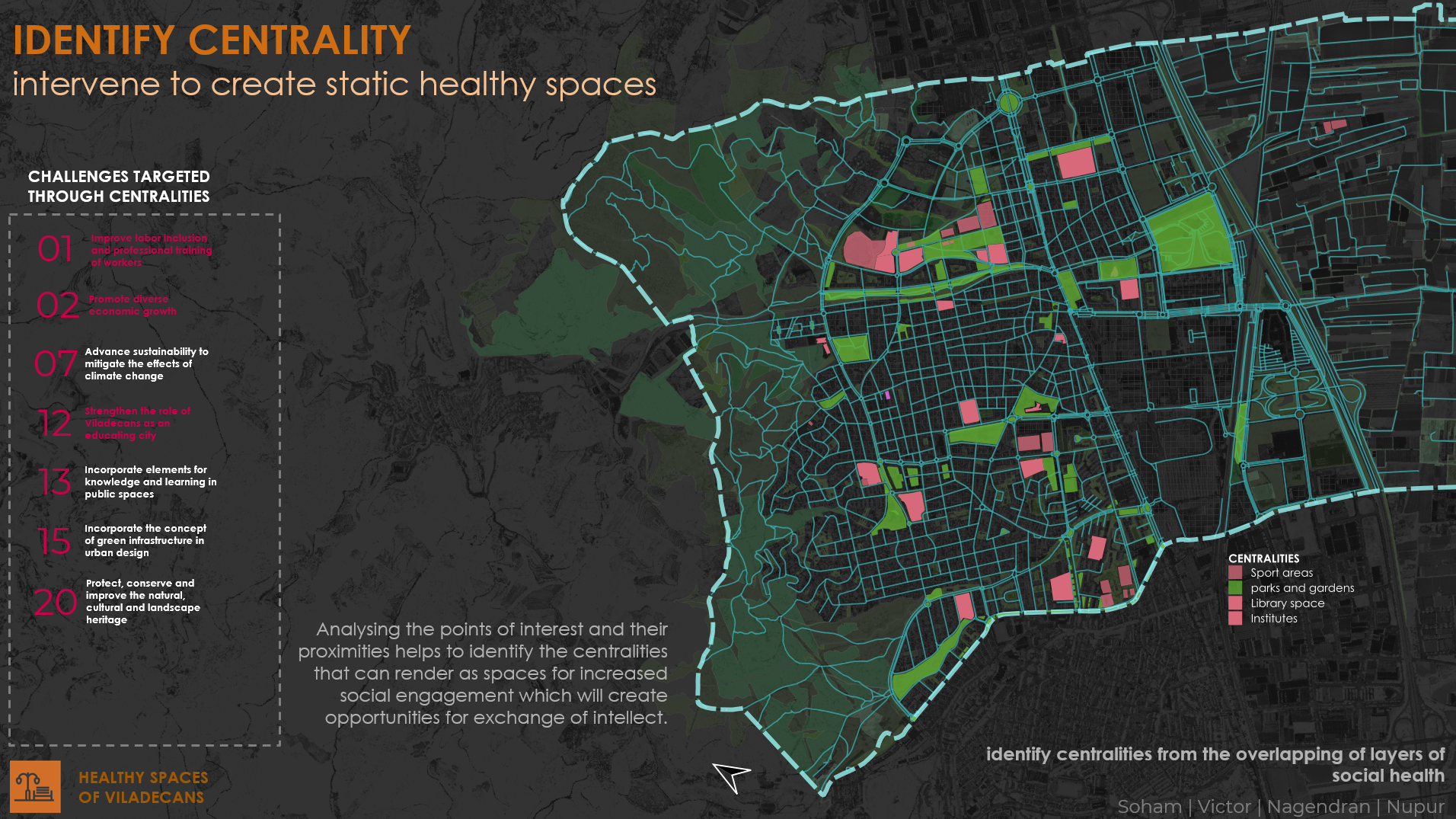
CENTRALITY
Analysing social health and the spaces which can help monitor better social health, designers identified centralities within the city which can foster very high social activity and can serve as a platform for exchange of intellect and relationship building. These centralities are also all the space within which give an increased sense of belonging to people of Viladecans. These centralities include sports areas, parks, libraries, institutes and public city hall.
MENTAL HEALTH
In the context of urban life, the mental health of inhabitants is profoundly influenced by the dynamics of city living. Urban environments often present unique challenges such as overcrowding, noise pollution, socioeconomic disparities, and limited access to green spaces. These factors can contribute to heightened levels of stress, anxiety, and depression among city dwellers. However, urban settings also offer opportunities for social connection, cultural enrichment, and access to mental health services. Initiatives that promote mental well-being, such as community-based support programs, mental health awareness campaigns, and urban planning strategies that prioritize green spaces and recreational areas, are essential in addressing the mental health needs of urban populations. Additionally, fostering a sense of belonging and social cohesion within neighbourhoods can help mitigate the negative effects of urban stressors and enhance the overall mental health of inhabitants.
Aspects of mental health and social health are very inter-connected and can affect each other in many intangible ways. However, designers have kept the parameters for mental health more in terms of how the physical environment affects the mental health the inhabitants of Viladecans. Environmental parameters like NDVI, which is an index that determines the level of greenery in a space, and noise pollution to understand how people’s mental health reacts to their surroundings.

PHYSICAL HEALTH
In the context of urban life, the physical health of inhabitants is influenced by various factors inherent to city environments. Urban areas often present both opportunities and challenges for maintaining physical well-being. On one hand, cities typically offer access to a wide range of healthcare facilities, recreational amenities, and transportation options that can facilitate healthy lifestyles. On the other hand, factors such as air pollution, traffic congestion, sedentary lifestyles, and limited green spaces can pose significant health risks. Addressing these challenges requires holistic urban planning approaches that prioritize pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, safe cycling routes, and the creation of parks and public spaces where residents can engage in physical activity. Additionally, promoting initiatives such as public health campaigns, workplace wellness programs, and policies that encourage active transportation can contribute to improving the physical health of urban inhabitants.
Although mapping parameters for physical health is much simpler a it is more tangible, it is also something which is based the existing facilities and utilities of the city. Since the target group of this project is the vulnerable crowd of Viladecans, the two most important parameters for physical health were walkability and safety in the streets. People living in Viladecans usually walk more than taking vehicles to stroll around, so it was imperative to see look deep into their safety and their ease in walking.

IDENTIFYING CONNECTIONS
Selecting a pilot route that effectively connects Viladecans’ main residential areas to education hubs is essential for achieving the goal of prioritizing education in the city’s development by 2030. Through rigorous analysis of demographic data and existing transportation infrastructure, key residential areas are identified, forming the foundation for route selection. Mapping out connectivity gaps and inefficiencies allows for strategic intervention. Monitoring route utilization and gathering feedback from residents and stakeholders enable identification of necessary improvements, such as infrastructure enhancements and traffic management measures. Collaborating with local authorities and community organizations, these interventions are implemented to enhance safety and accessibility. Continuous evaluation and adjustment ensure the pilot route evolves to meet changing community needs, fostering a more inclusive and vibrant educational environment for Viladecans in the future.

8. Design Intervention
After bringing the analysis to a conclusion, designers arrive to the identified pilot stretch that connects two of the key centralities, i.e. sports centre and the city library, for implementation of a more detailed design. The two identified centralities were concluded from the short participatory process done in the beginning of the project, as most people walk to these centralities to spend more leisurely time in the city. Designers also infer that the citizens of Viladecans prefer to walk and hence the pilot stretch also focuses deeply on the pedestrianisation o f the identified route.
Utilizing key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge various facets of health promotion in Viladecans, a dynamic pathway animation was devised. This animation serves to integrate targeted interventions aimed at positively influencing existing KPIs. Each intervention is categorized based on its impact on specific health dimensions, facilitating a more focused approach to improving overall well-being.
The interventions are broadly classified into 3 typologies: Pedestrian Pockets, Pedestrian Junctions and Pedestrian Crosswalks
PEDESTRIAN POCKETS
Pedestrian pockets is a typology where all the spaces which are paved and extended parts of the vehicular area are included with the clear walkable area. This helps in widening the bottle necks for better pedestrian activity but also helps in the strategic placement of urban infrastructures like light poles, green planters, seating spaces , etc.
PEDESTRIAN JUNCTIONS
The inhabitants of Viladecans are more probable to walk around the city, hence some of the streets in Viladecans have already been transformed into a complete pedestrian street. The typology pedestrian junctions, shows the design intervention at the junction of an existing pedestrian street an the proposed walkable street of the pilot stretch. These junctions are the best nodes for increased social, mental and physical health.
PEDESTRIAN CROSSWALKS
Even though Viladecans has high Pedestrian activity within the vulnerable groups, the city also has a very well-connected bus circuit that connects all of Viladecans but also connects Viladecans to its neighbouring cities. The third typology of intervention, pedestrian crosswalks, is the detailed design for the junction between a vehicular street and the walkable street of the pilot stretch. This typology focuses primarily on the aspects of physical health through safety, while also increasing mental and social health.
9. Policy, Impact and Feasibility
After the design, it’s important to understand how this project would be implemented. We have analysed other similar projects in Viladecans and other cities to come up with a timeline and the necessary policies to make this project a reality.
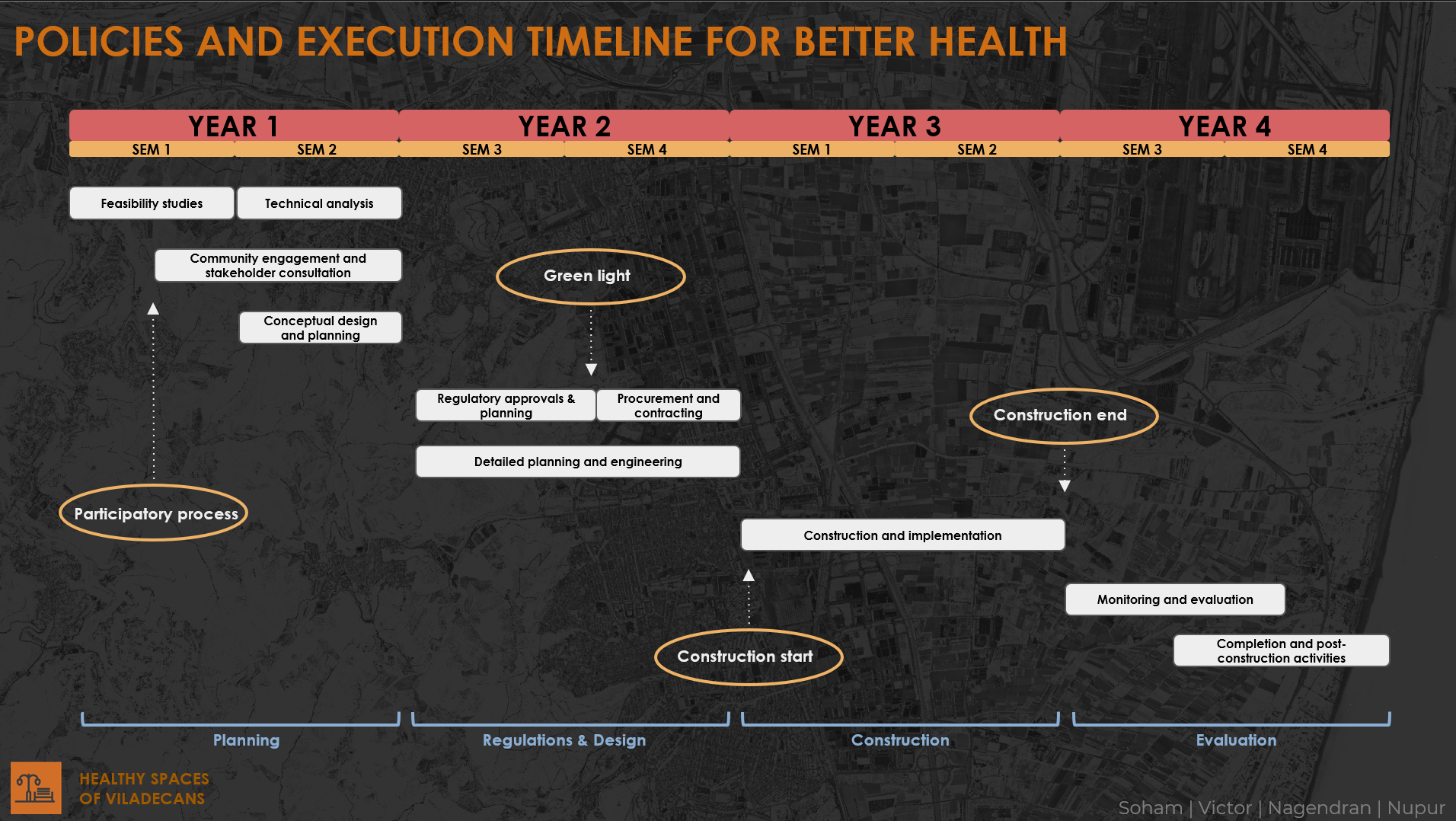
This is a projected timeline for the project. It would be divided in 4 phases (one year each). The first year would be the planning and that is when the participatory process would take place. The second year would be focused on regulations being approved and a detailed planning. The 3rd year would be entirely dedicated to the construction work and finally a 4th year for monitoring and evaluation.
10. Impact
Eventually, designers try to look deeper into the impact of design and policy through the KPI’s identified during analysis of existing health conditions of Viladecans. To see the impact designers keep the same KPI’s but now look at how the upper or the lower limit of these KPI’s have been impacted on because of the design strategies and policies implemented. Since health is a very intangible concept designers also look into the intangible benefits of their design and policy on their social, mental and physical health but also how this shift in health brings a change in the three pillars of sustainability

11. Future Developments
To continue developing this project we would like to analyse much deeper ‘what is healthy’. It is very difficult to quantify something intangible and that is why it requires further analysis with new KPI.
Engaging people with the project is also an important factor that can contribute to this project and that is why the participatory process is key to understand the needs of Viladecans residents. We would like to use similar approaches than in other projects and spend some months gathering and processing this information.
After the planning phase is crucial to make a cost analysis to see the real feasibility of the project and finally a quantitative impact analysis.

