Programmed Shading devices for humans
1 > References 2
/ The integration of interactive architecture and responsive technology opens new frontiers in design, as exemplified by the Hylozoic Ground installation and its envisioned evolution into autonomous systems. Hylozoic Ground serves as a reference point, showcasing an immersive spatial installation that mimics nature’s behaviors. Through architectural responses driven by human interaction, proximity, temperature, and motion, this installation incorporates kinetic fabrication techniques to replicate organic phenomena such as the retraction and deployment of leaves. This model demonstrates how architecture can behave as a living entity, responding fluidly to environmental and human stimuli.
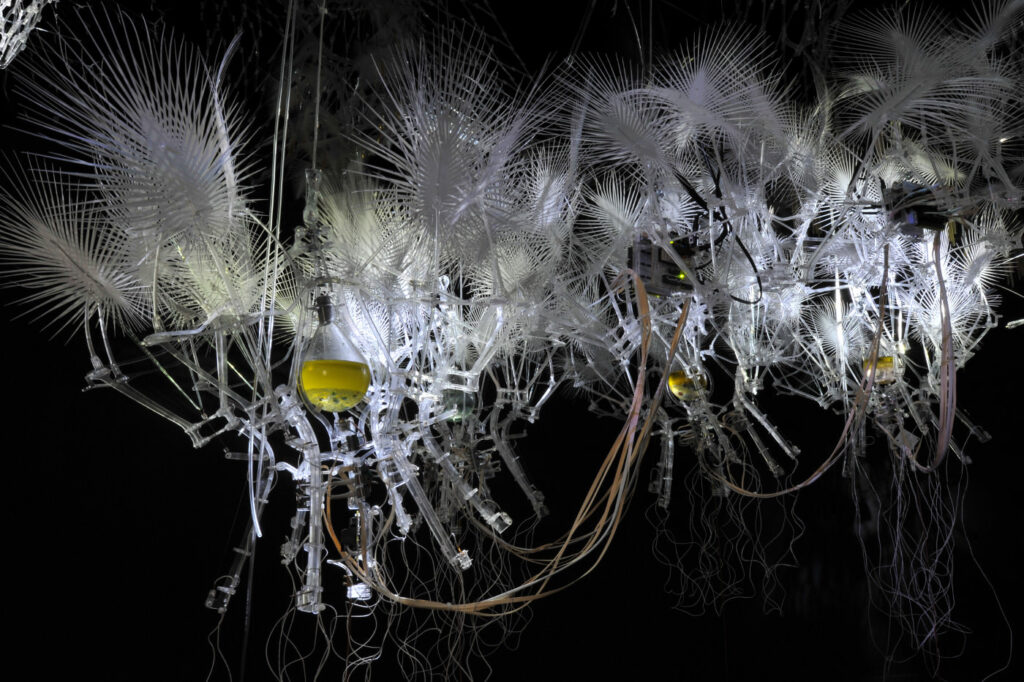

Philipp Beasley – Hylozoic Ground
2 > Strategy / Design approach
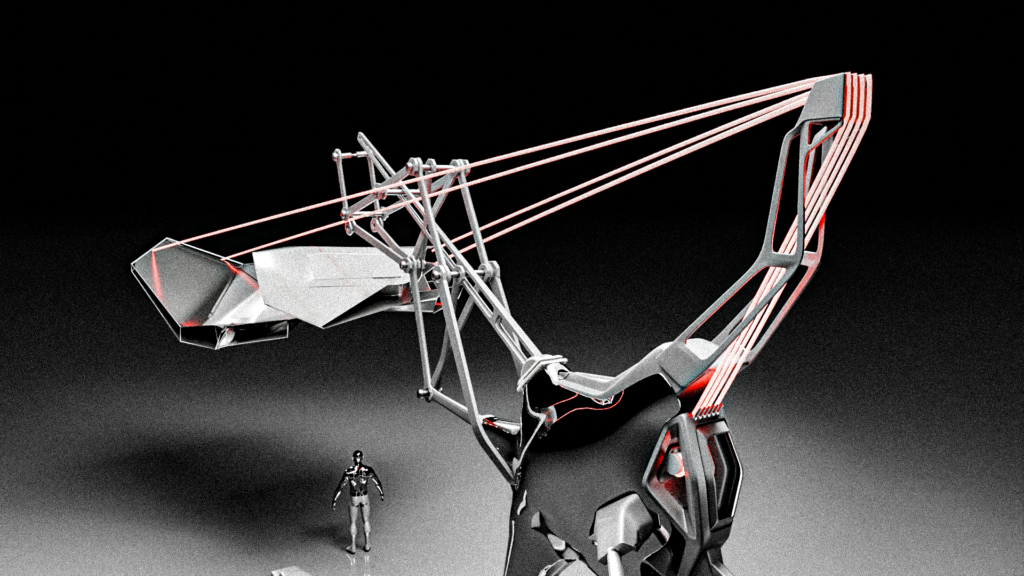
Building upon this concept, future architectural designs envision autonomous canopies capable of deploying dynamically to meet environmental and user-specific needs. These canopies would activate based on parameters such as temperature thresholds and proximity, creating tailored shaded environments. With kinetic capabilities enabling varying degrees of movement and shadow patterns, these systems offer both functional adaptability and aesthetic appeal, enhancing user comfort while fostering a deeper connection between built environments and nature.
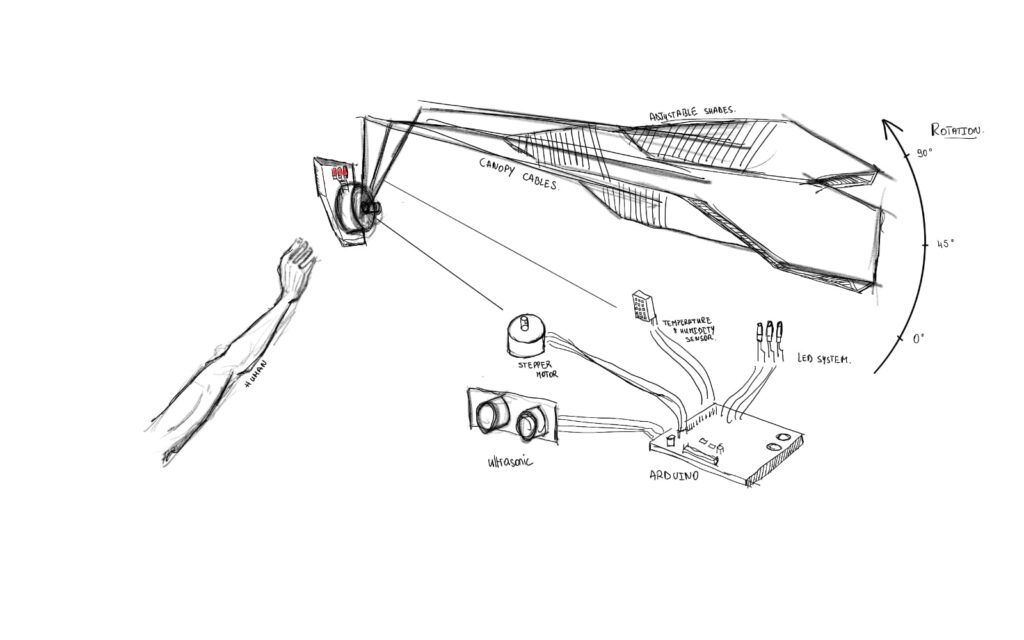
Components Relations Diagram
3 > Architectural Visualization
1 / This animation shows the canopy movements to adapt create shadows in relation with human activity around it
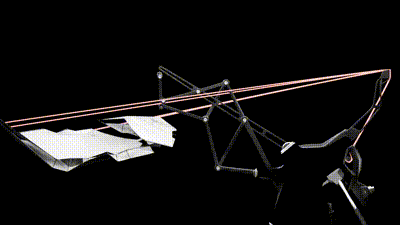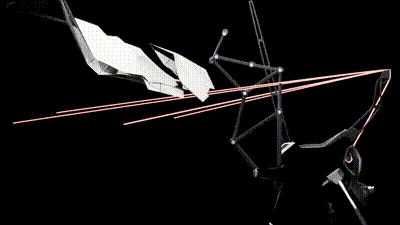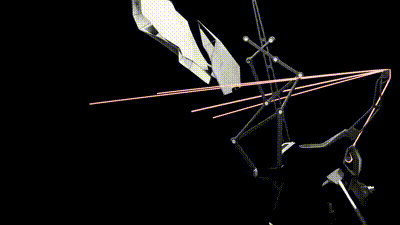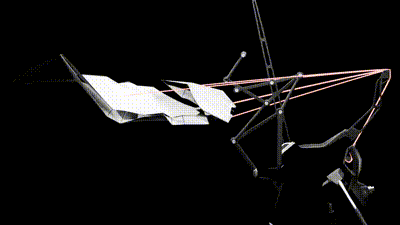
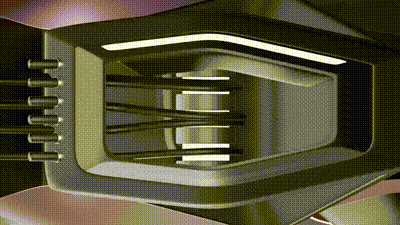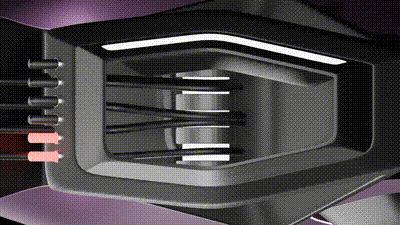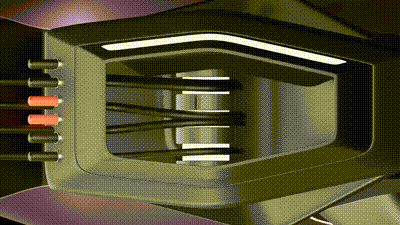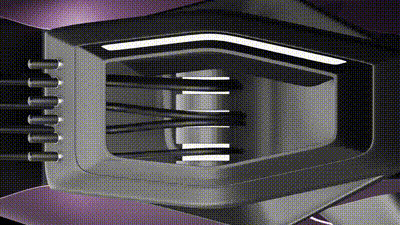
2 / This second animation shows the canopy Stepper motor that controls the degree rotation of the panels
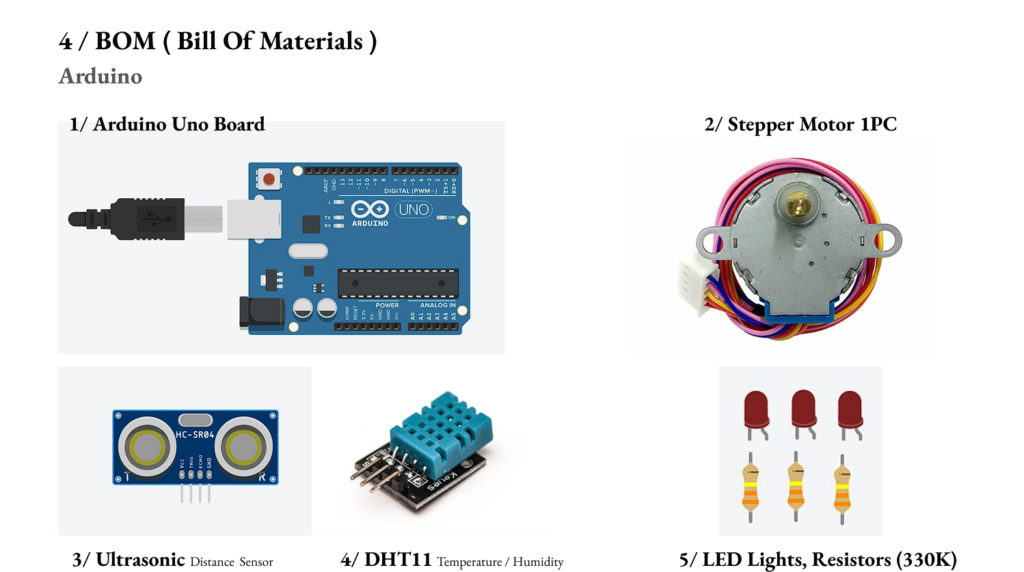
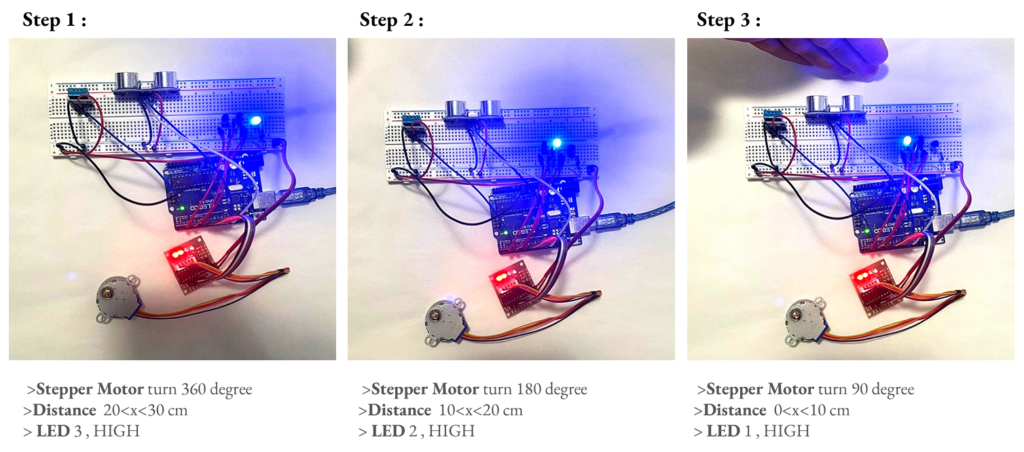
4 > System Defintion , Arduino
The development of such systems involves advanced sensor and actuator integration, as exemplified by strategies using Arduino-based technologies. Ultrasonic and temperature sensors, in combination with stepper motors, can simulate human heat and motion. These motors would drive cables to adjust canopy positions, modifying shadow patterns in real-time. Such precise, sensor-driven movements exemplify the role of robotics and automation in shaping responsive architectural elements
5 > System Assembly , Arduino
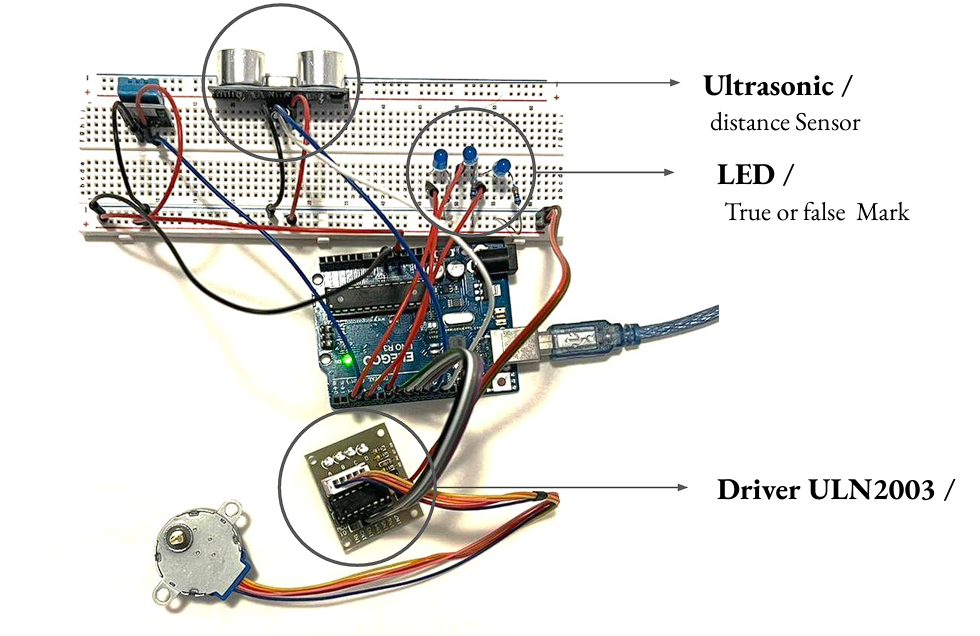
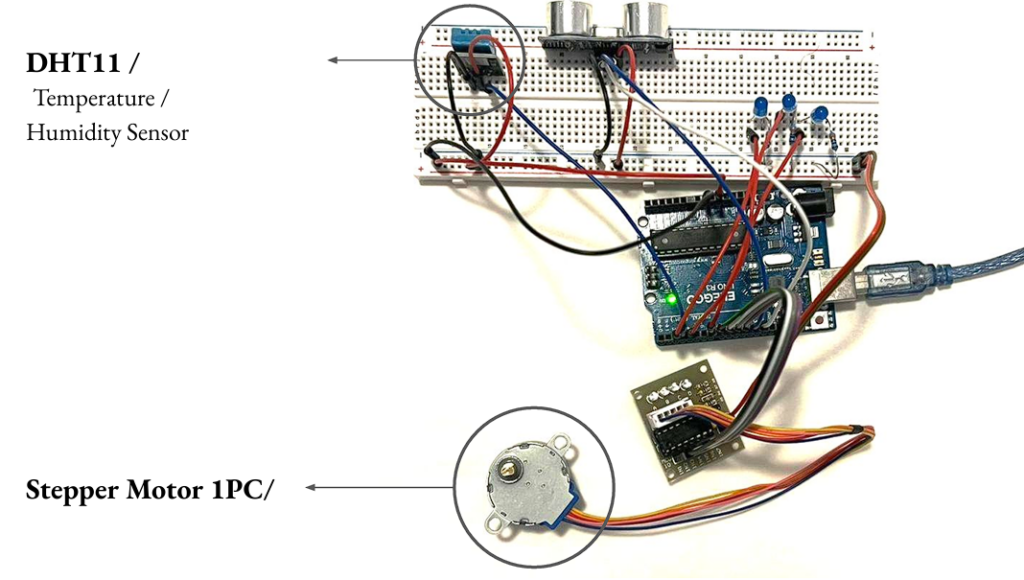
6 > Arduino
7 > Future Vision
Looking to the future, canopy systems could become even more sophisticated, leveraging enhanced sensor efficiency and intelligence. These systems would detect human presence with unparalleled precision, adapting their form and function seamlessly to create optimal environments for gatherings and events. By reacting instantly to human heat and motion within their radius, these canopies would redefine public spaces, making them more interactive, engaging, and user-centered.
This vision bridges the gap between nature-inspired design and technological innovation, offering a glimpse into a future where architecture behaves dynamically, interacts effortlessly with its surroundings, and elevates human experiences in outdoor environments
Video

