Cities are ever-evolving and growing, meaning natural environments are eradicated or transformed from native biodiversity to a collection of artificial materials. This has a significant impact on all organisms, including human beings. However, both natural and built environments are fundamental for quality of life.
Nevertheless, the need for balance between both in urban spaces is a growing issue, and increasing evidence shows that more natural environments within urban areas provide substantial benefits to humans.
This analysis provides a script to assess the historical growth of the built environments vs the decline or transformation of natural biodiversity.
Using:
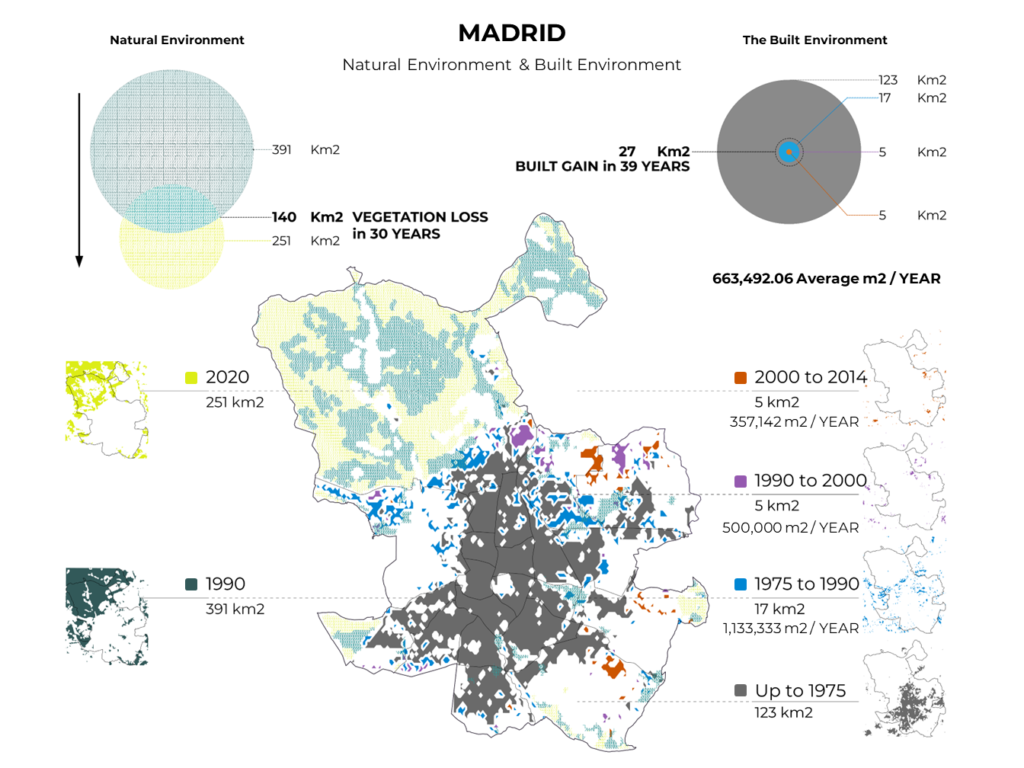
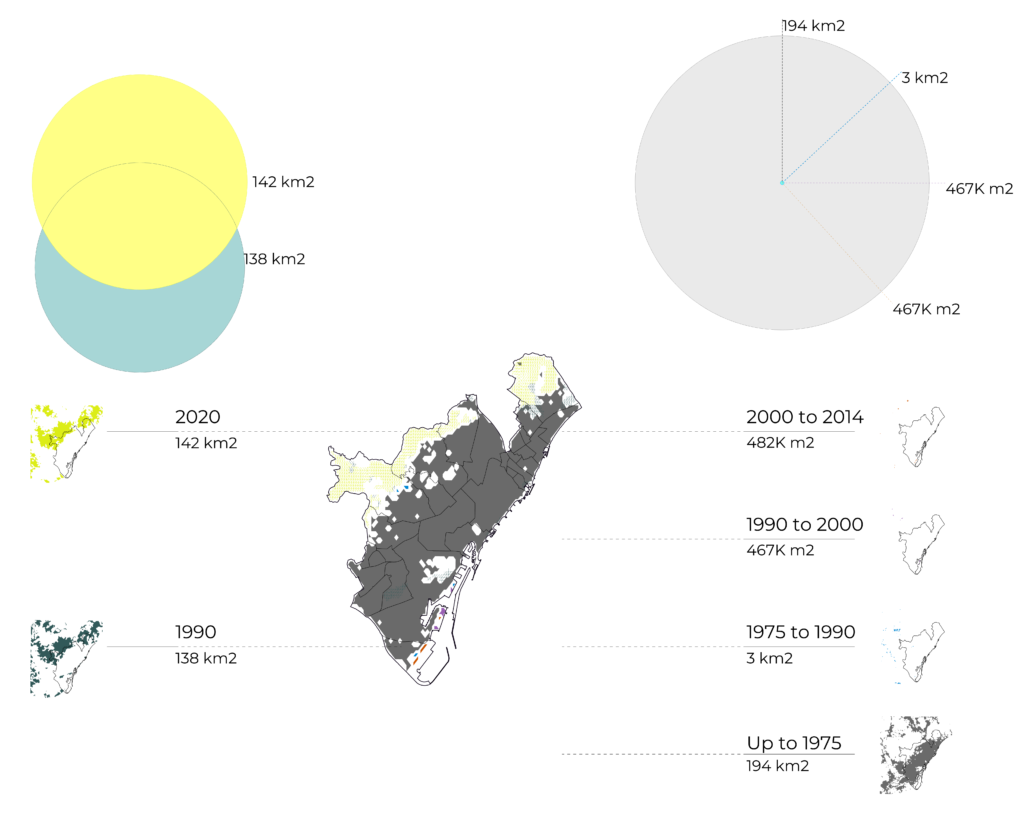
GHSL: Global Human Settlement Layers, Built-Up Grid 1975 / 1990 / 2000 / 2015 (P2016). An assessment of the values related to the built environments took place, extracting said values and representing them individually, differentiating them by year and color.
Similarly using:
Copernicus CORINE Land Cover from (1990 and 2018). An extraction of the values representing Forest and Wetlands was utilized and joined to compare the difference between years and overlayed with the growth of the built environment.
MADRID

The Script
The script can be used to assess the growth of the Built Environment and the Natural Environment in other European cities, and utilizing other datasets (Google Earth Engine), it can be used worldwide.
BARCELONA
The Values
The values extracted from the GHSL: Global Human Settlement Layers, Built-Up Grid 1975-1990-2000-2015 (P2016) and Copernicus CORINE Land Cover from (1990 and 2018) are:
Built-up from 2000 to 2014 epoch. Built-up from 1990 to 2000 epoch. Built-up from 1975 to 1990 epochs. Built-up up to 1975 epoch.
Forest and semi natural areas > Forests > Broad-leaved Forest. Forest and semi natural areas > Forests > Coniferous Forest. Forest and semi natural areas > Forests > Mixed Forest. Forest and semi natural areas > Scrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations > Natural grasslands. Forest and semi natural areas > Scrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations > Moors and heathland. Forest and semi natural areas > Scrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations > Sclerophyllous vegetation. Forest and semi natural areas > Scrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations > Transitional woodland-shrub. Forest and semi natural areas > Open spaces with little or no vegetation > Beaches, dunes, sands. Forest and semi natural areas > Open spaces with little or no vegetation > Bare rocks. Forest and semi natural areas > Open spaces with little or no vegetation > Sparsely vegetated areas. Forest and semi natural areas > Open spaces with little or no vegetation > Burnt areas. Forest and semi natural areas > Open spaces with little or no vegetation > Glaciers and perpetual snow. Wetlands > Inland wetlands > Inland marshes. Wetlands > Inland wetlands > Peat bogs. Wetlands > Maritime wetlands > Salt marshes. Wetlands > Maritime wetlands > Salines. Wetlands > Maritime wetlands > Intertidal flats.
Reference
Arigoni, D., Cochin, T., Frece, J., Gitlin, S., Jamawat, J., Klinger, A., Mcconville, M., Nelson, K., Ramsey, K., Susman, M., Thomas, J., Torma, T., Akkeren, B. van, Zgoda, B., Adler, K., Angel, S., Bailey, C., Berry, L., Brunner, G., … Rodriguez, D. (2013). Our Built and Natural Environments.
Copernicus CORINE Land Cover | Earth Engine Data Catalog | Google Developers. (n.d.). Retrieved December 23, 2022, from https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/COPERNICUS_CORINE_V20_100m
GHSL: Global Human Settlement Layers, Built-Up Grid 1975-1990-2000-2015 (P2016) | Earth Engine Data Catalog | Google Developers. (n.d.). Retrieved December 23, 2022, from https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/JRC_GHSL_P2016_BUILT_LDSMT_GLOBE_V1
Streimikiene, D. (2014). Natural and built environments and quality of life in EU member states. Journal of International Studies, 7(3), 9–19. https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-8330.2014/7-3/1
Yao, W., Chen, F., Wang, S., & Zhang, X. (2021). Impact of Exposure to Natural and Built Environments on Positive and Negative Affect: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in Public Health, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPUBH.2021.758457

