Within the current global context of rapid change, integrated with the potentials of digital technologies, IAAC’s Master in Advanced Architecture (MAA) is committed to the generation of new ideas and applications for Urban Design, Self Sufficiency, Digital Manufacturing Techniques and Advanced Interaction.
In this context IAAC works with a multidisciplinary approach, facing the challenges posed by our environment and the future development of cities, architecture and buildings, through a virtuous combination of technology, biology, computational design, digital and robotic fabrication, pushing innovation beyond the boundaries of a more traditional architectural approach.
Course: MAA01 23/24 Ecological Interactions Seminar
The ecological interactions seminar explores state of the art monitoring techniques being developed in the fields of biology, ecology and agricultural sciences and repurposes them to form new systems of observation that can be applied to design practices and the built environment. Advances in data science and the growing access to DNA barcoding, and remote sensing devices are allowing scientists to detect signals from the natural world that were previously unreadable, and are revealing animal behaviours and communication channels and senses that were unknown. The seminar explores what can be learned by intercepting these signals and what might be learned from the senses of other organisms to inform our design decisions, reduce environmental impacts and deploy nature based solutions.
view Syllabus & FacultyMicrobial Influence on Building Decay
Our project investigates how bacteria living in historical buildings contribute to decay. We aim to enhance resilience of architectural elements and harness microbial interactions to create sustainable and self-repairing building materials.
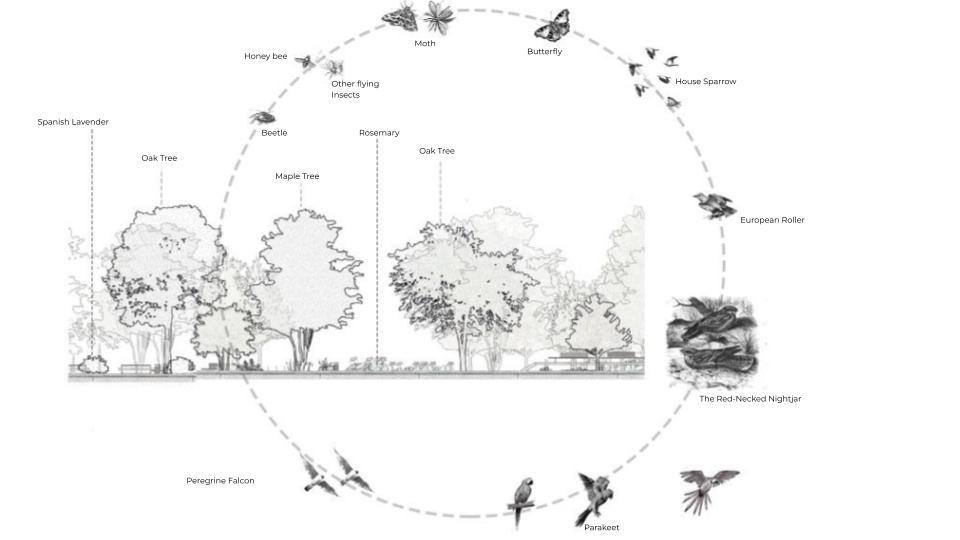
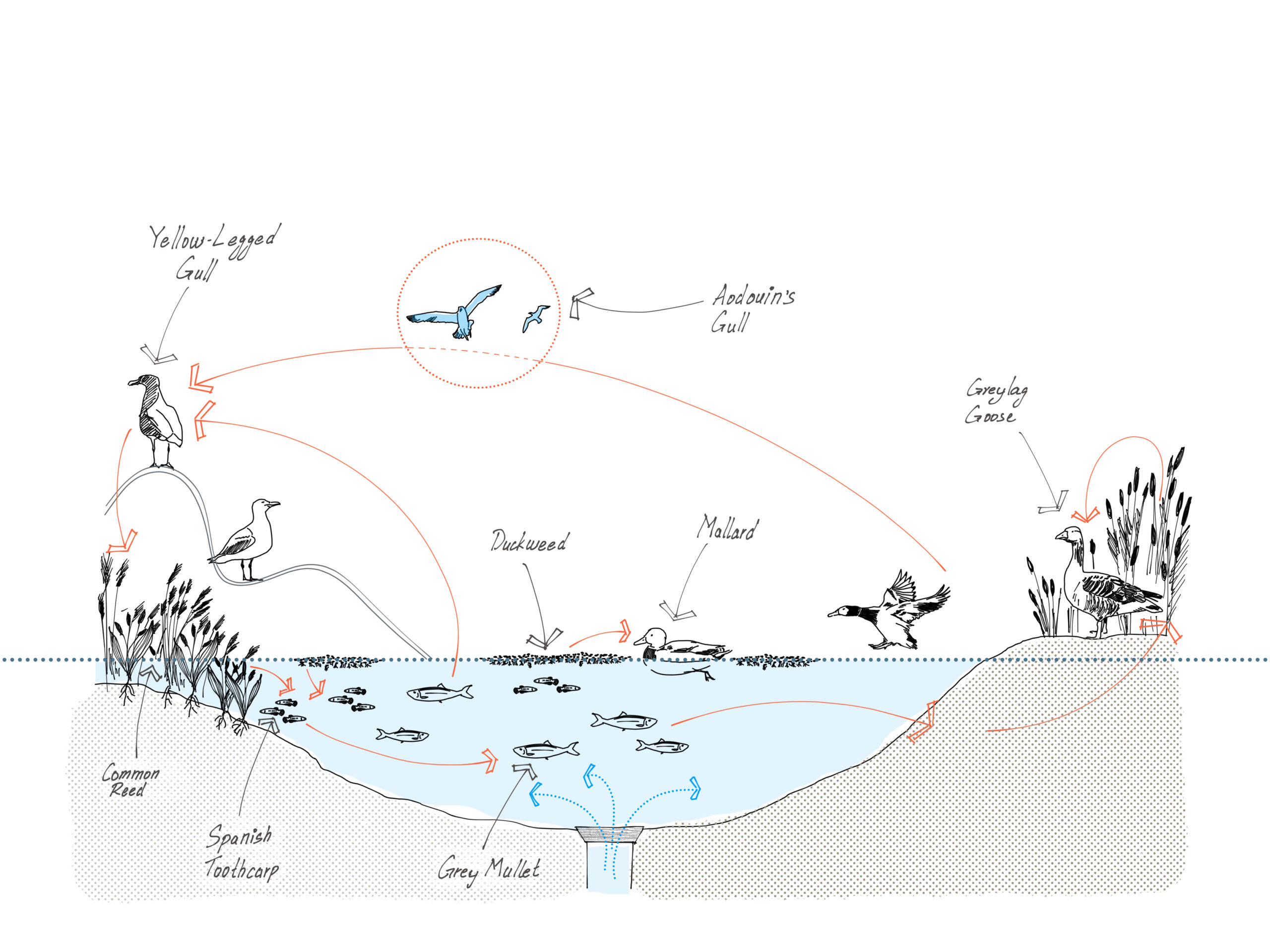
Data Informed Trophic Cascade : a wetland recreation at Parc Diagonal Mar
Keywords : TROPHIC CASCADE – A trophic cascade occurs when a change at one level of the food web (often due to the addition or removal of a keystone species) causes a series of indirect effects on lower trophic levels. This can lead to significant and widespread changes in ecosystem structure and nutrient cycling. KEYSTONE … Read more