The Woven Contrast
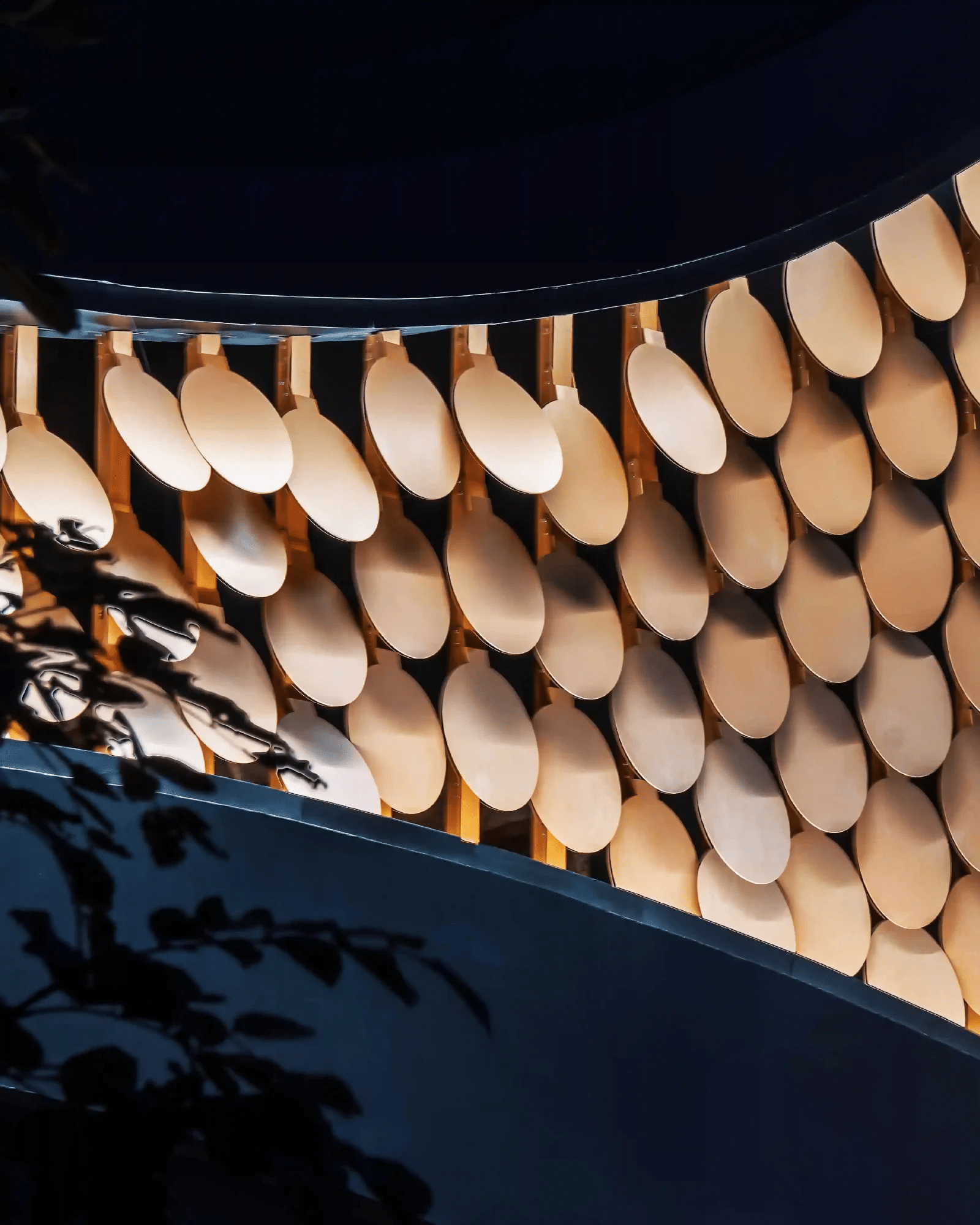
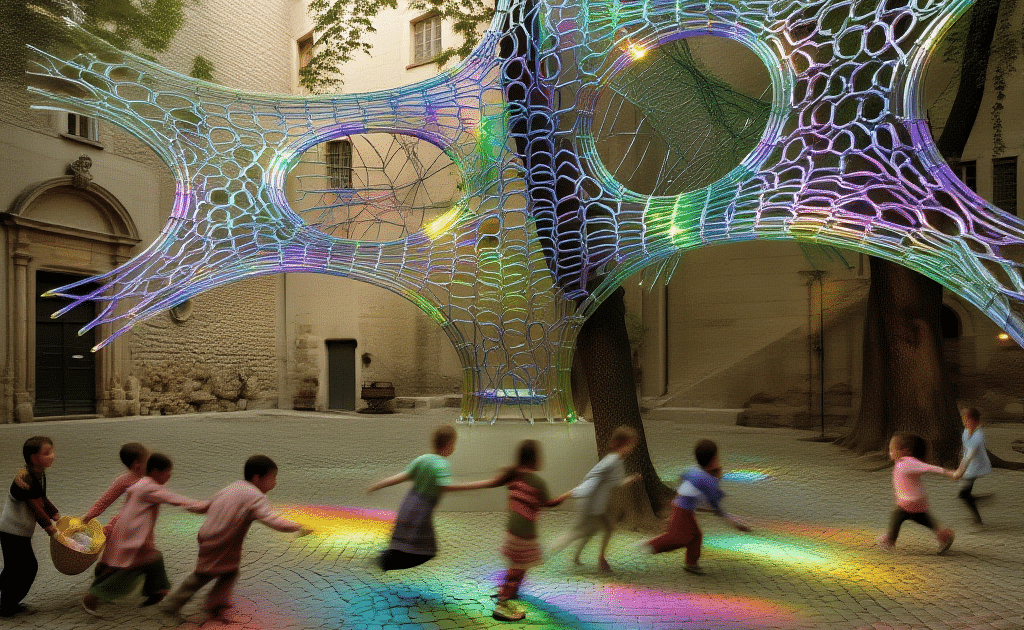
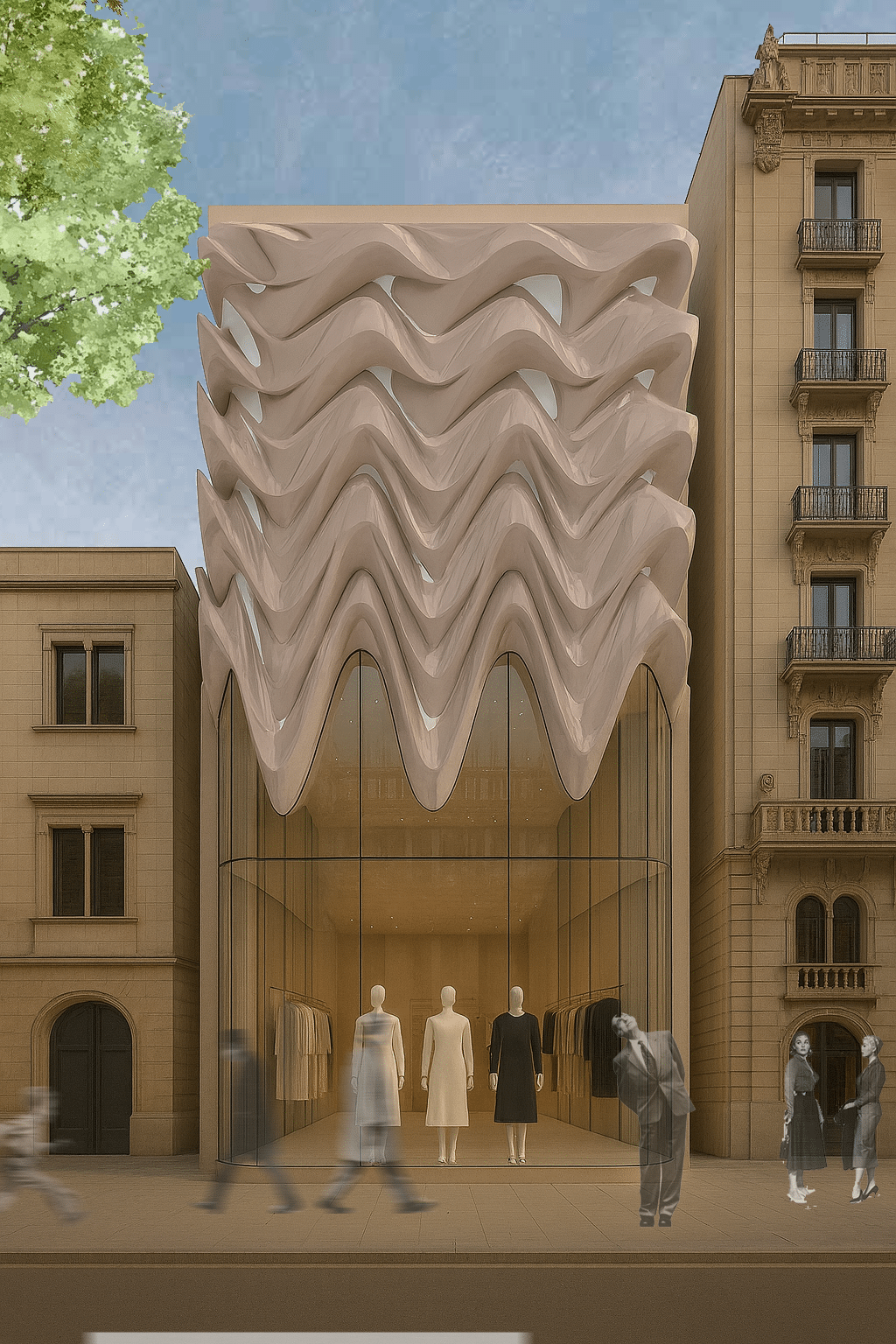
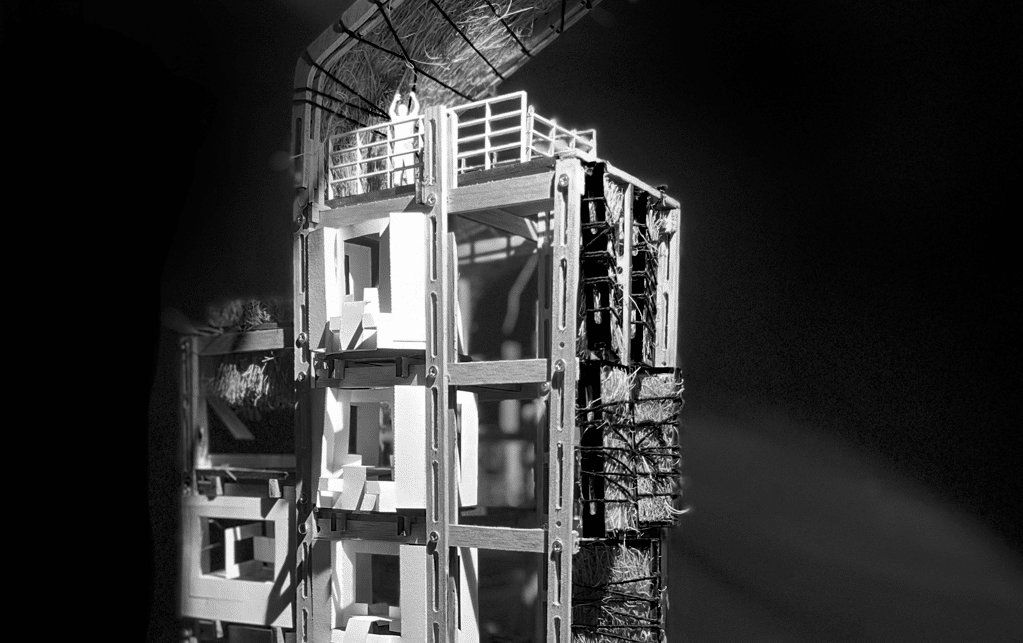
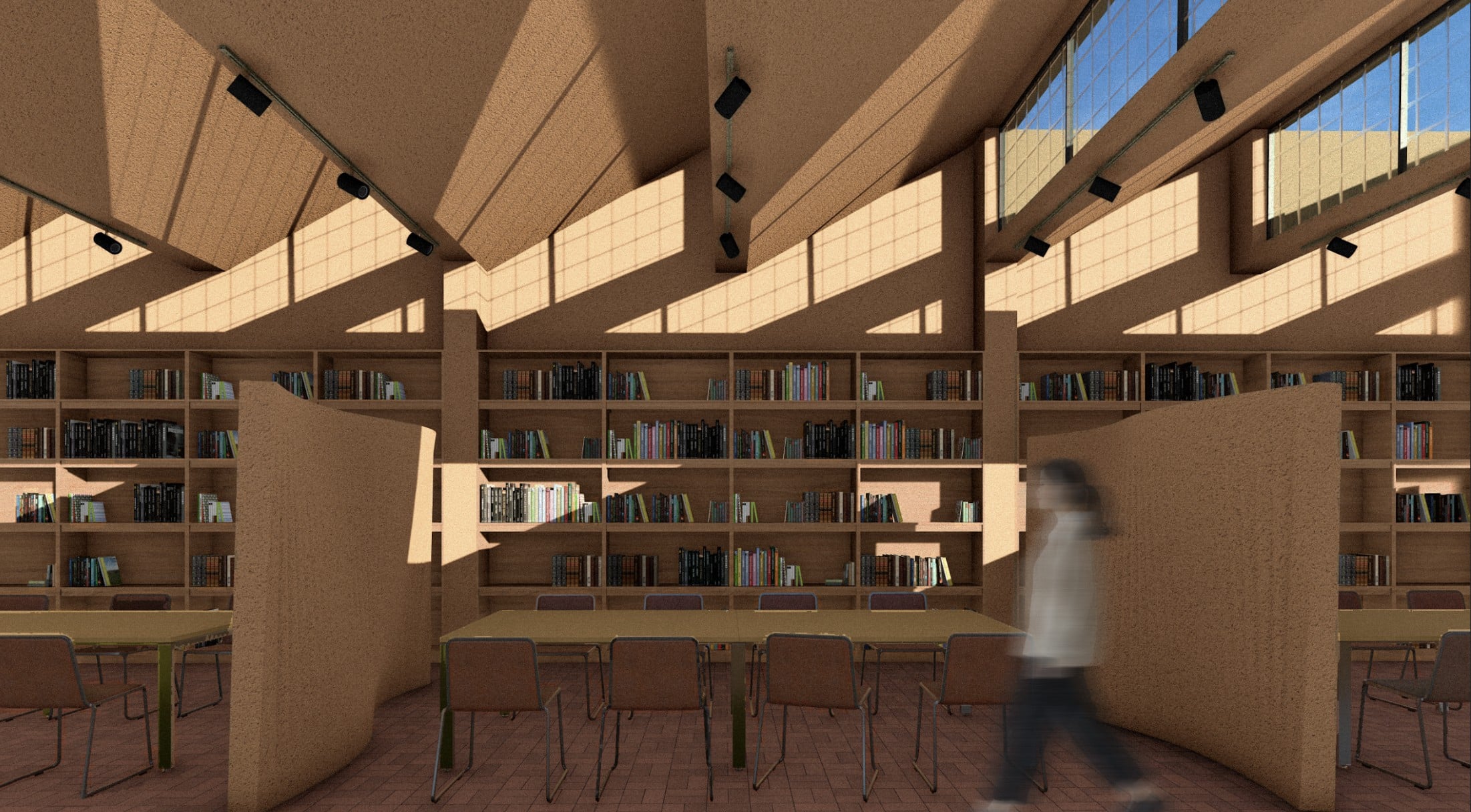
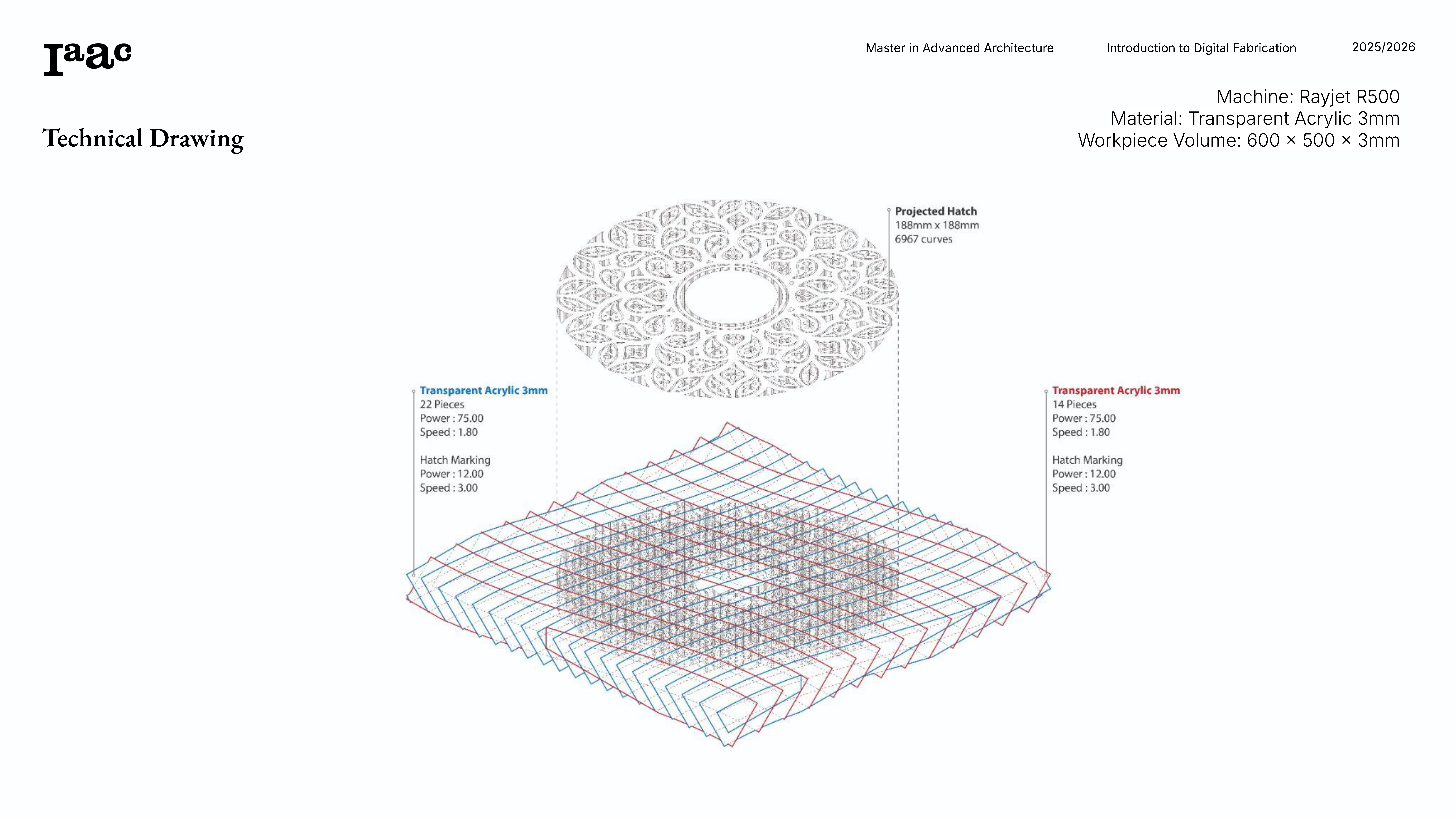
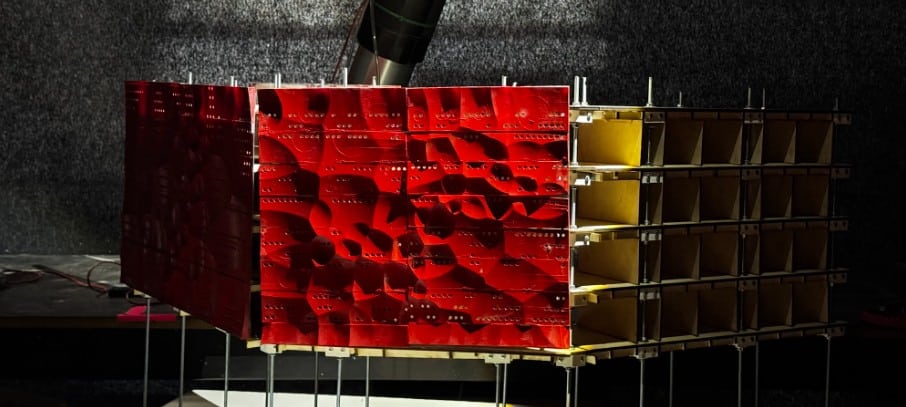
COMPUTATIONAL DESIGN I SEMINAR25/26 MAA01 (Level2) Abstract: Computational Weaving. This project, developed for the Computational Design I Seminar, explores the algorithmic generation of complex, recursive geometries through the logic of “Digital Craft”. Inspired by the material constraints of steam-bent timber, the design creates a “volumetric weave” rather than a simple surface. The computational workflow is … Read more