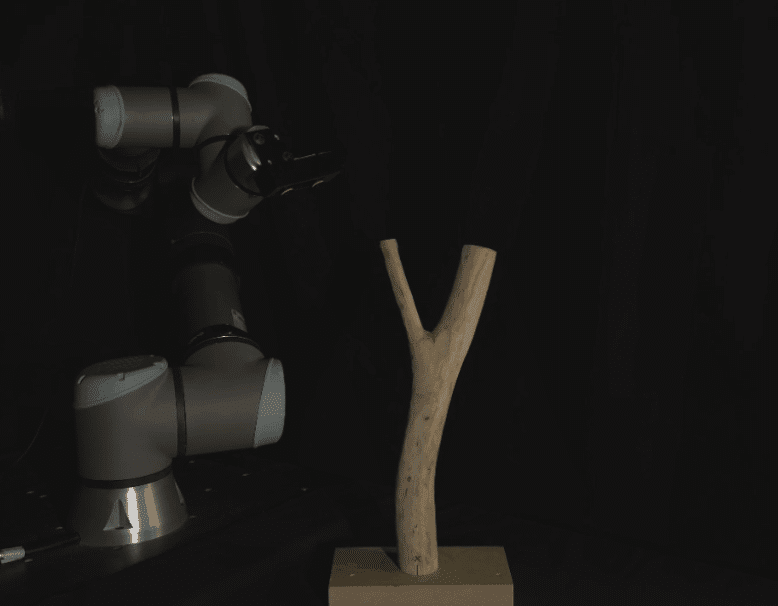STICKS & STONES
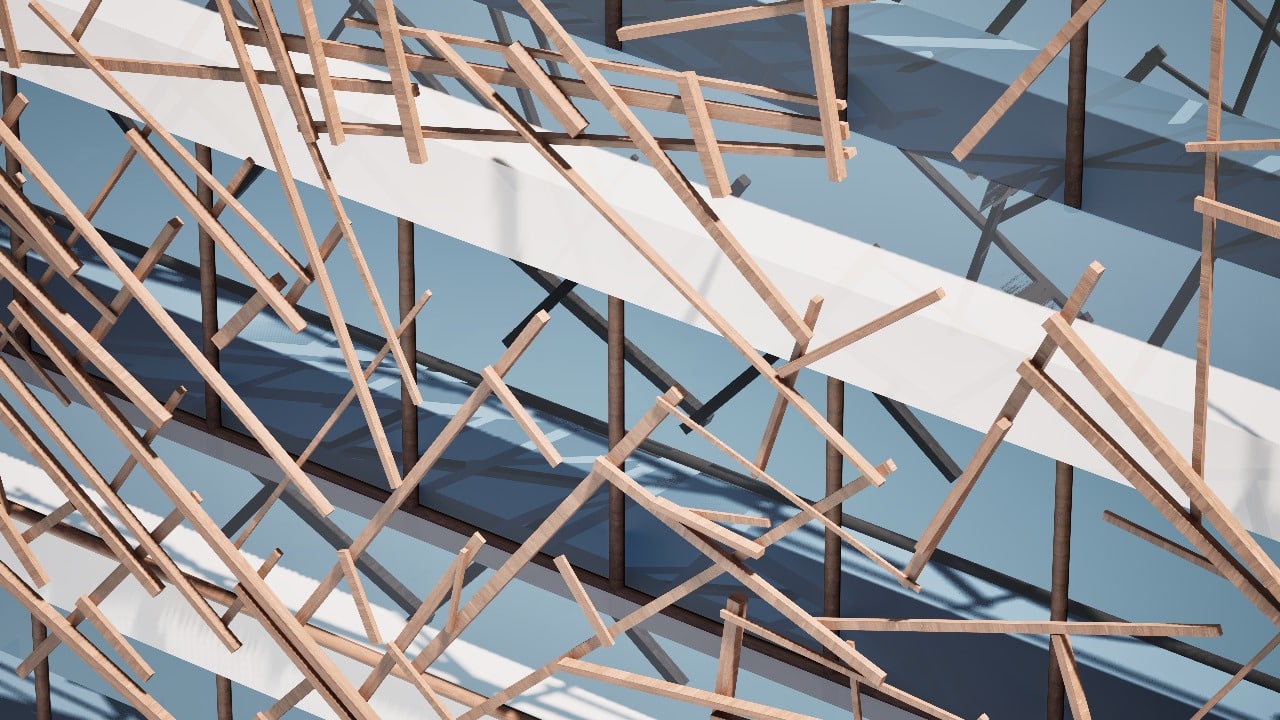
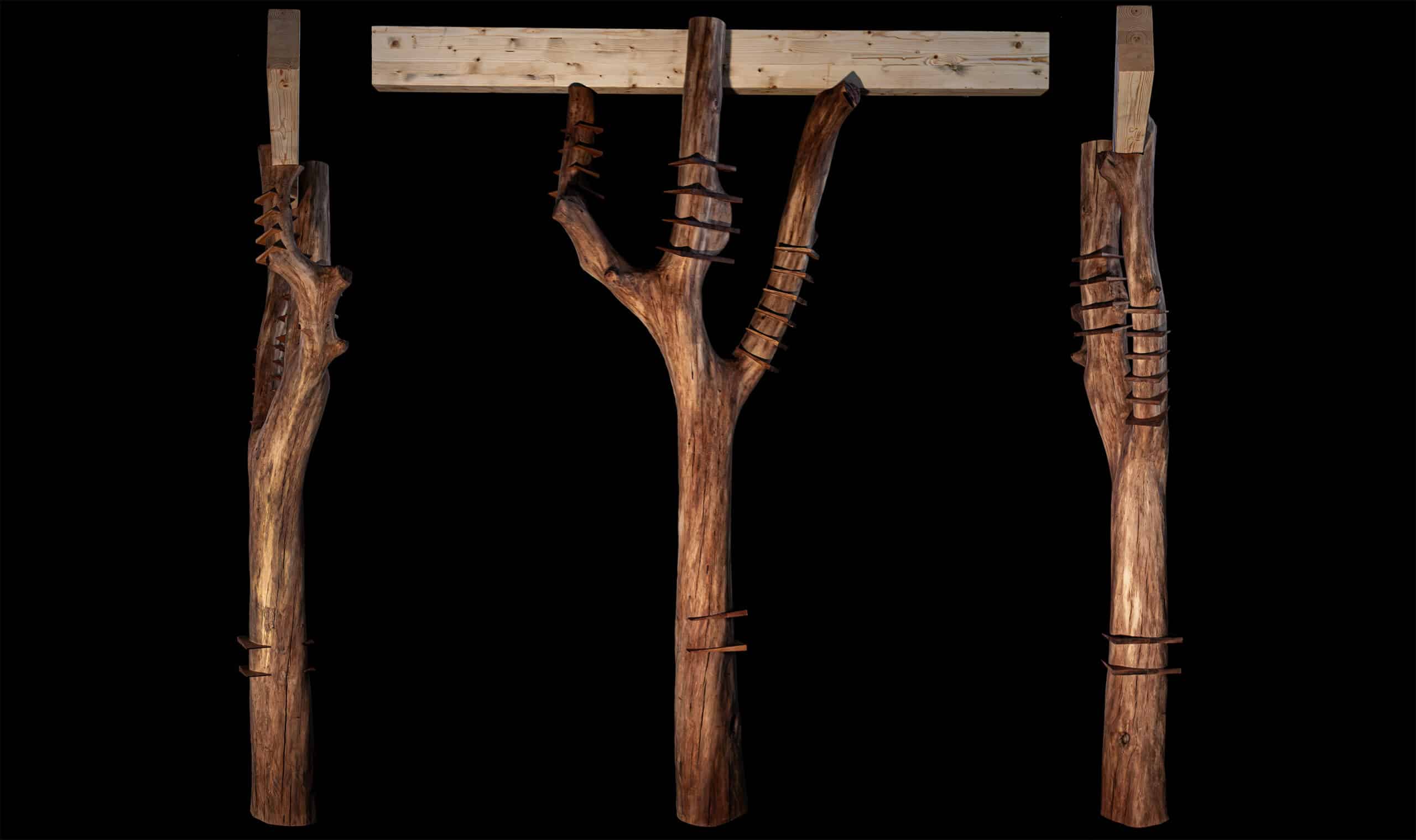
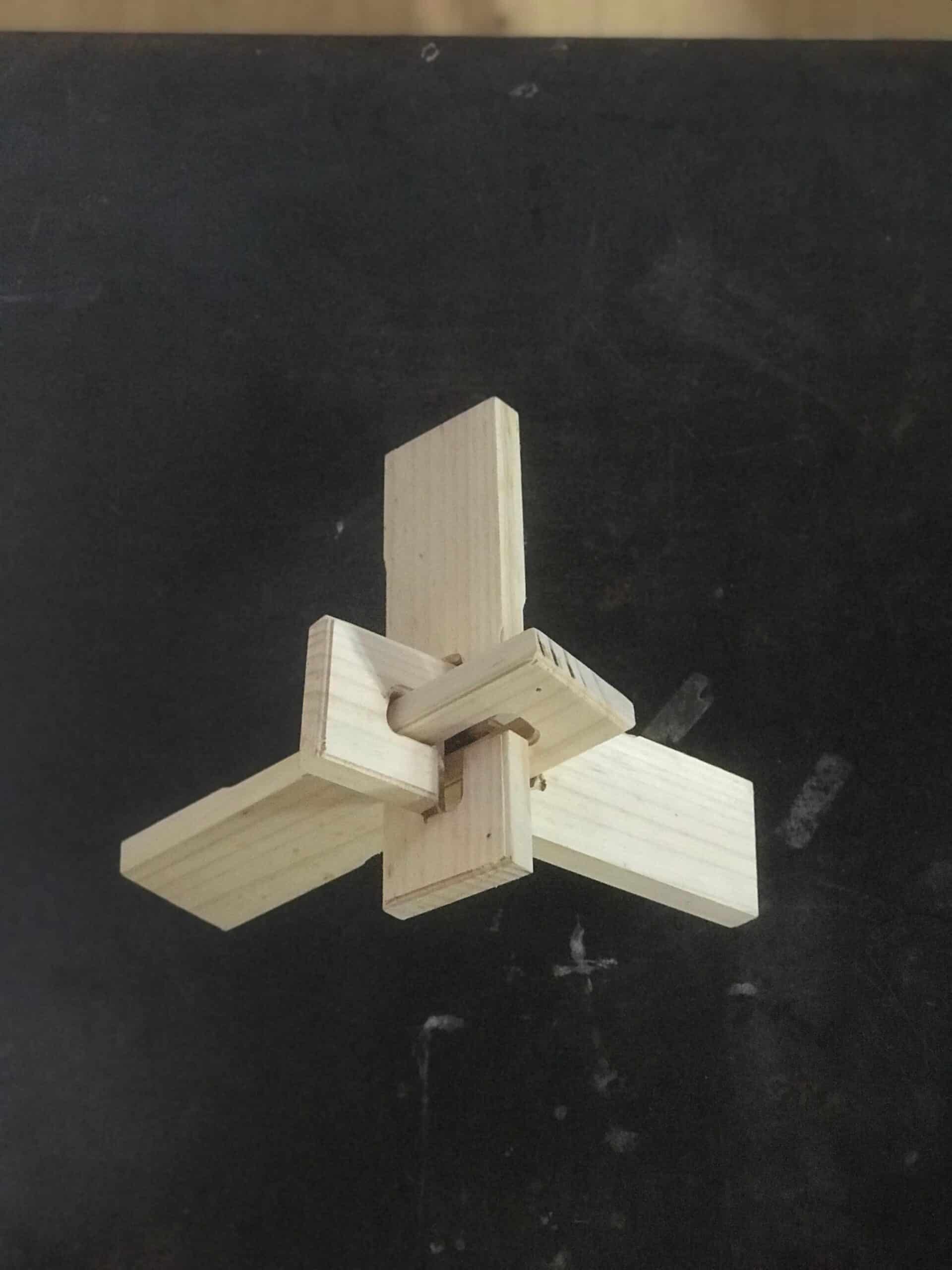
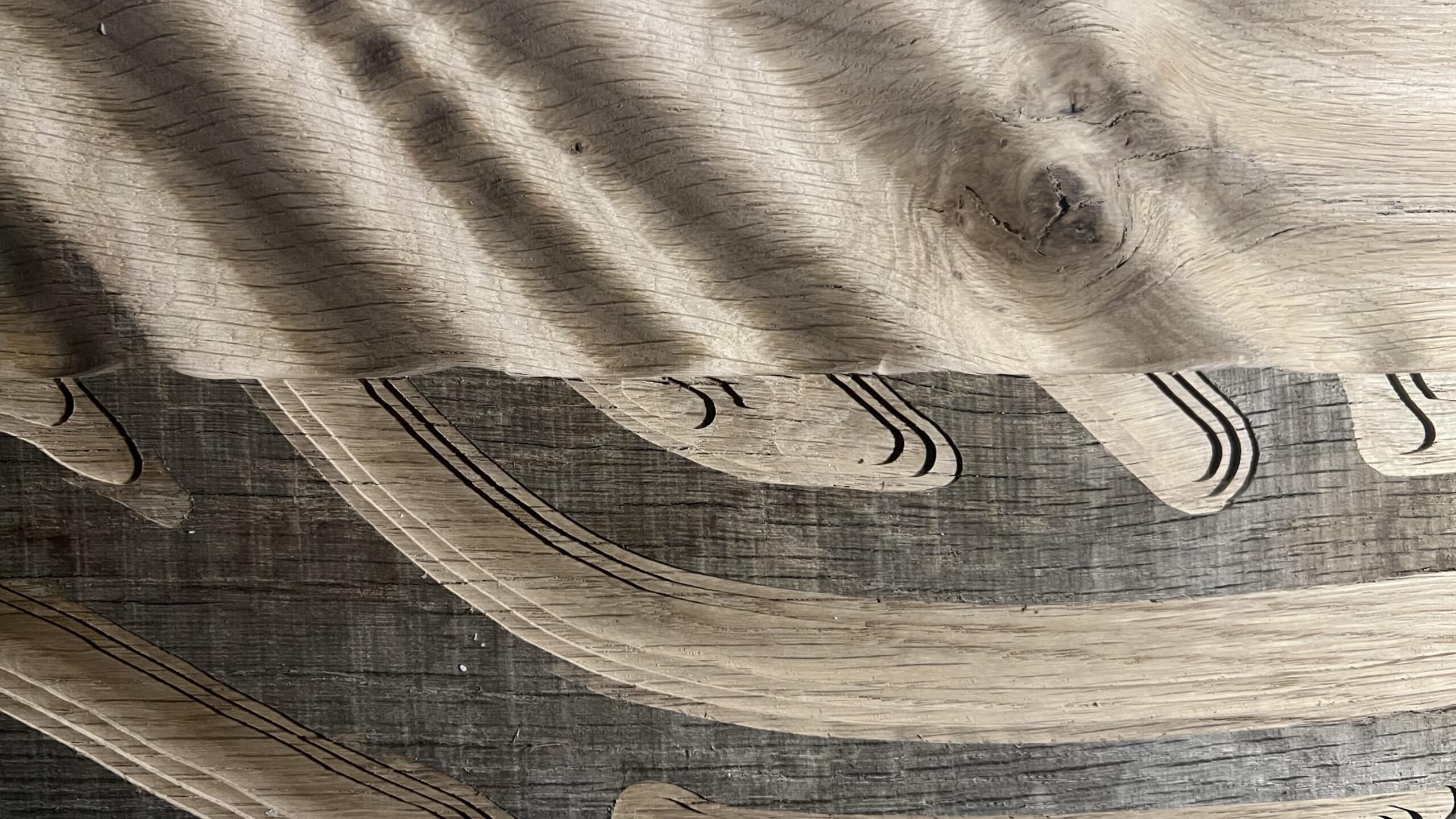
Hybrid Timber and Stone Constrcuction System Utilisng 6-axis Robotic Fabriction Our research begins with a critique of how we build today. Technological advancements have enabled rapid, standardized, and seemingly affordable construction. But these efficiencies hide deeper costs. In reality, we’re paying through the loss of cultural specificity, environmental integrity, and material identity. What emerges is … Read more