Supply Chain Opportunity to Solve
The immense volume of organic waste generated by Brazil’s agricultural and food industries, including residues from cocoa, açaí, Brazil nuts, passion fruit, cupuaçu, buriti, and murumuru, represents a significant untapped resource. These byproducts, often discarded without proper utilization, contribute to environmental challenges and economic losses.

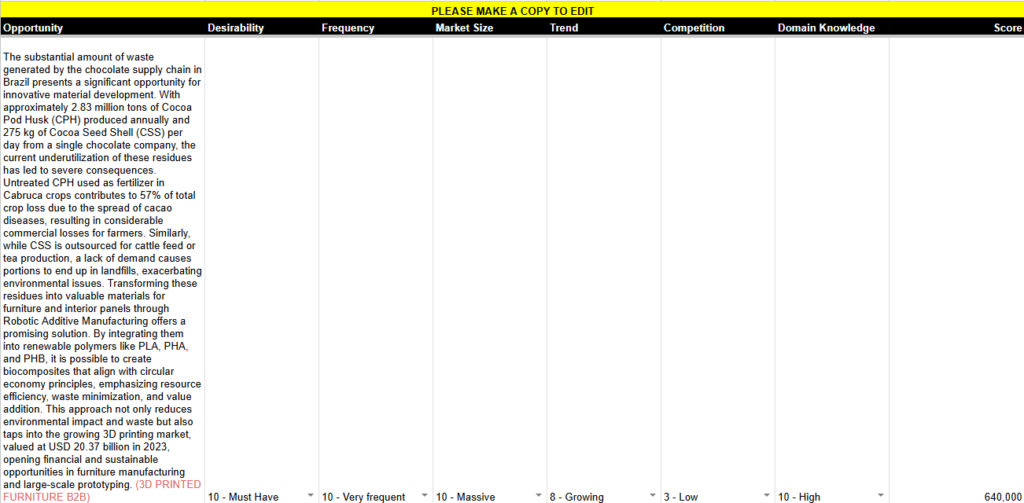
Many of the companies highlighted, such as Natura, O Boticário, Dengo, Cacau Show, and others, depend heavily on fruits and vegetables as key resources for their products. However, their large-scale production generates massive amounts of organic waste that often exceeds the soil’s absorption capacity, creating environmental issues such as landfill overflow. Additionally, specific cases like cocoa and cupuaçu waste exacerbate crop diseases, leading to significant economic losses for farmers, while açaí waste creates urban logistic challenges. These issues present a unique opportunity to tap into a blue ocean market niche by transforming this underutilized waste into innovative products, such as biocomposites for furniture or interior panels, through partnerships with these companies. By applying circular economy principles—emphasizing waste valorization, resource efficiency, and sustainability—this approach not only mitigates environmental impacts but also creates untapped economic potential. This strategy could redefine waste management as a profitable and sustainable market, fostering new business opportunities in a rapidly growing sector.


Current 3D printing market worlwide – Polymers Supply Chain
According to the Grand View Research report of 2023, the 3D printing market was valued at USD 20.37 billion in that year with an expected CAGR of 23.5% between 2024 to 2030. During 2022, the building segment (commercial, residential, industrial) and infrastructure, such as furniture and bridges had a total value of USD 18.2 million
Robotic Additive Manufacturing offers several advantages on product design and manufacturing such as, customization, on-demand production, fabrication with varied materials, large scale fabrication with an emphasis on waste minimization.
Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) are bioplastics with significant environmental and commercial relevance due to their biodegradability and renewable origins. PLA, derived from starch-rich crops like corn and sugarcane, has become a leading material in the bioplastics market due to its cost efficiency and versatility, while PHB, produced from bacterial fermentation of organic matter, offers superior biodegradability and thermal resistance. The global bioplastics market, valued at USD 10.75 billion in 2023, is growing rapidly, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable materials and stringent regulations on single-use plastics. Both PLA and PHB are widely used in industries such as packaging, medical devices, and 3D printing, reflecting their commercial viability.
From an environmental perspective, PLA and PHB significantly reduce dependency on fossil fuels and lower carbon footprints compared to traditional plastics. Their ability to degrade in industrial composting facilities also minimizes the long-term environmental impact, aligning with circular economy principles. However, challenges such as the use of agricultural resources for production and limited end-of-life recycling options highlight the need for innovative applications.
One promising avenue is the development of biocomposites by using PLA or PHB as a polymer matrix combined with powdered food waste, such as cocoa pod husk, açaí seeds, or cupuaçu peels. This approach not only addresses the issue of agricultural waste but also enhances the mechanical and thermal properties of the bioplastics, making them more durable and suitable for structural applications like furniture, interior panels, or prototyping. By leveraging waste as a filler, companies can tap into a growing market for sustainable products, reduce production costs, and contribute to waste valorization efforts.
This synergy between bioplastics and food waste utilization represents a significant opportunity to explore new, eco-friendly materials that align with market trends while addressing pressing environmental challenges. The incorporation of food waste into bioplastics offers dual benefits: creating high-value products from waste streams and expanding the functionality of PLA and PHB in innovative applications, potentially unlocking a new frontier in sustainable material development.


Business Opportunities and How to diversify portfolio
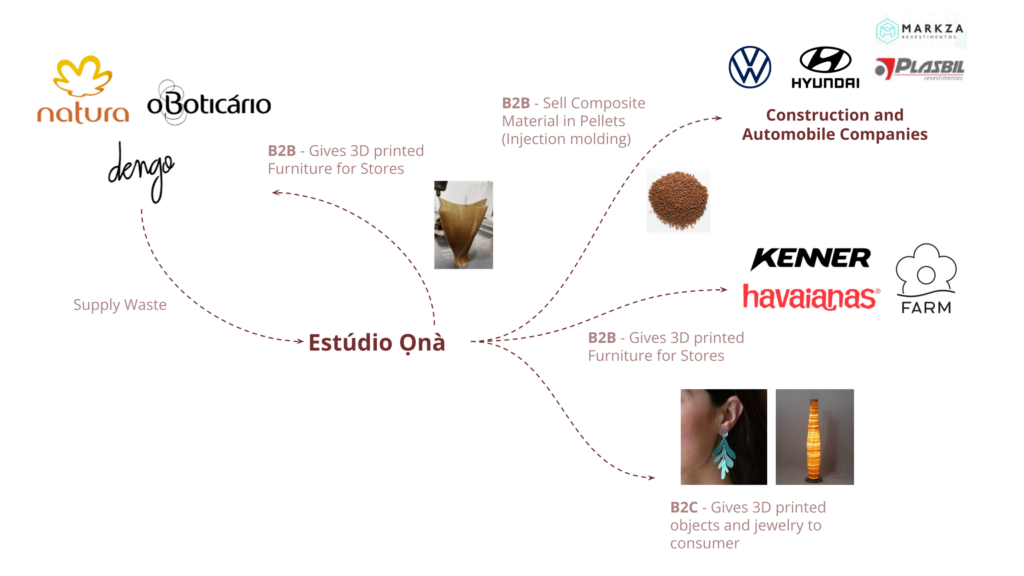
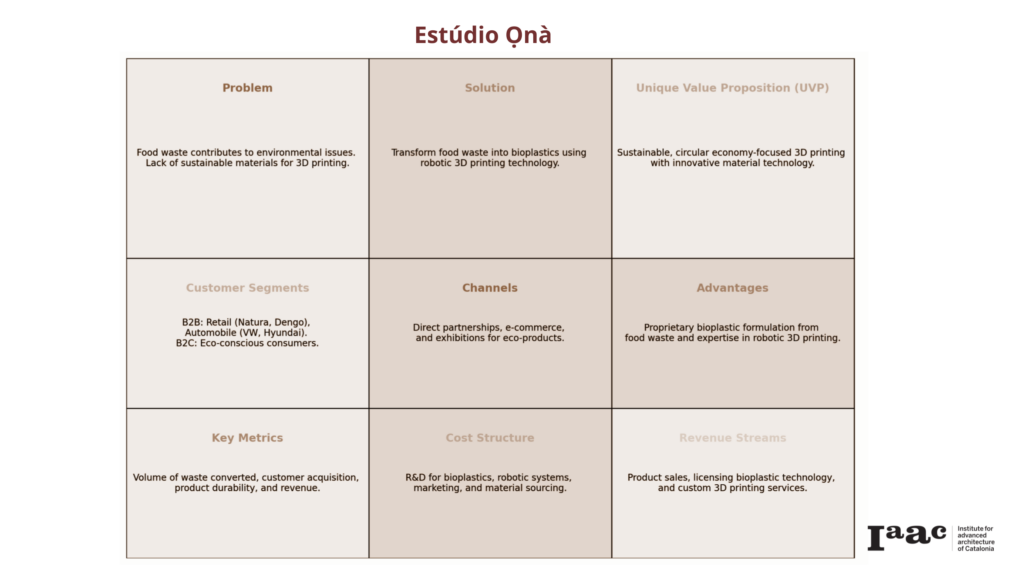
Estúdio Ọnà presents a dynamic range of business opportunities that capitalize on sustainable innovation and market diversification. By transforming supply chain waste from companies like Natura, O Boticário, and Dengo into biocomposite materials, the studio develops 3D-printed furniture for B2B clients, such as store interiors for Kenner, Havaianas, and FARM or the same suppliers as well, selling products to be exhibited in the commercial architecture. Additionally, couture 3D-printed objects and jewelry are offered directly to B2C clients, emphasizing the exclusivity and high-end appeal of the products. To diversify its portfolio and bridge the gap between early adopters and the traditional market—”overcoming the chasm”—Estúdio Ọnà also produces and sells composite pellets for injection molding to industries in construction and automotive sectors, such as Volkswagen and Hyundai. This dual approach not only positions the studio in niche luxury markets but also secures a foothold in established industrial supply chains, ensuring both innovative and scalable growth.
Challenges , Team and main inspiration drivers
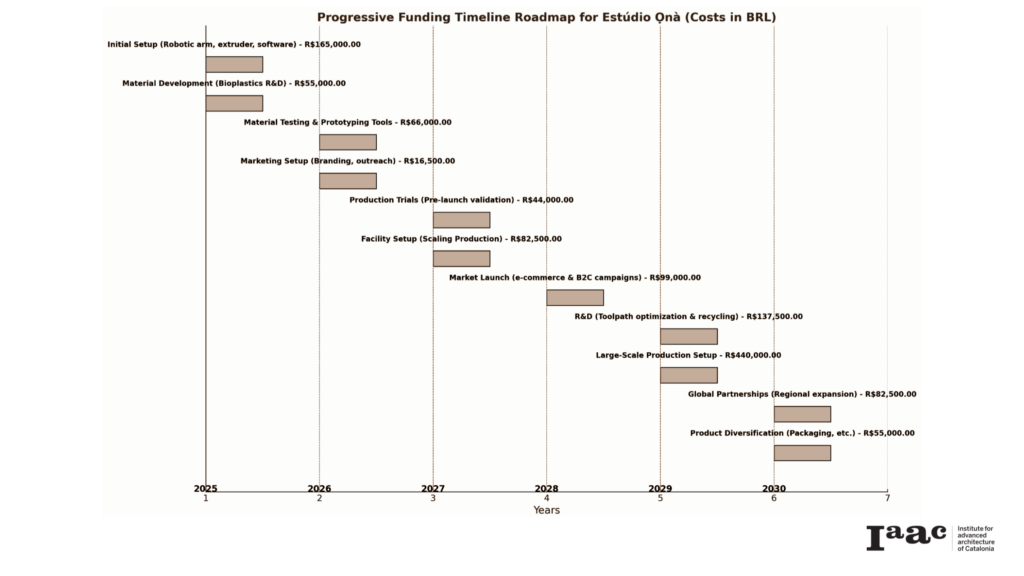
To reach high scale furniture, of the sectors to sell plastic pellets, big investments are necessary like a compounding machine and a pellet extruder, some ecommerce can be explore with small pieces such as ear rings and jewerly with small percentages of material to sell to customer to gain cash flow, at the same time, time inside a robotic fabrication incubator woulde be necessary to start understanding the pipeline of production and refining it without having the need of buying a robotic arm. Incubator also functions as a showcase for possible clients and investors. We are starting with a 3 partners with similar technical skills but very different soft skills to handle different parts of the business , from marketing to gathering clients and investments to fabrication and talking to suppliers to quality assurance of the product and to be delivered in time.