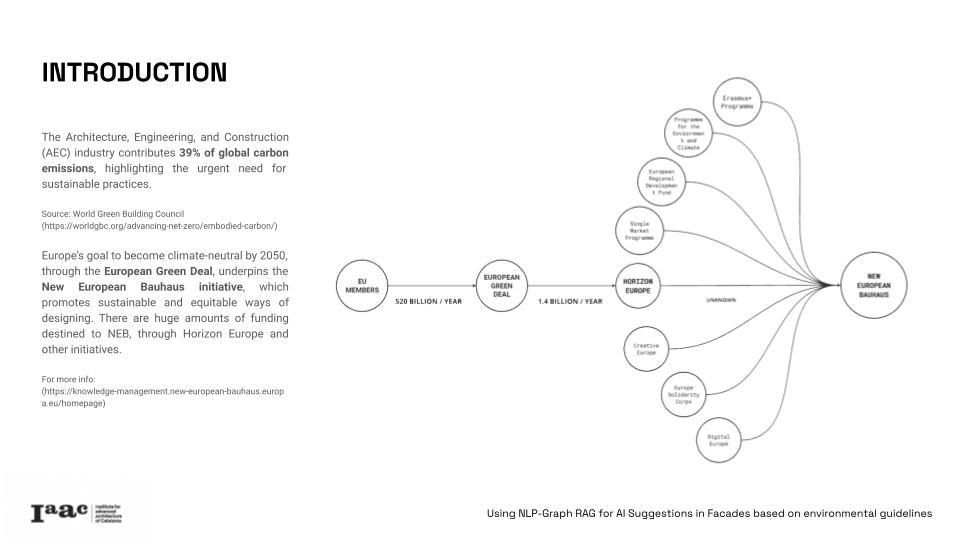
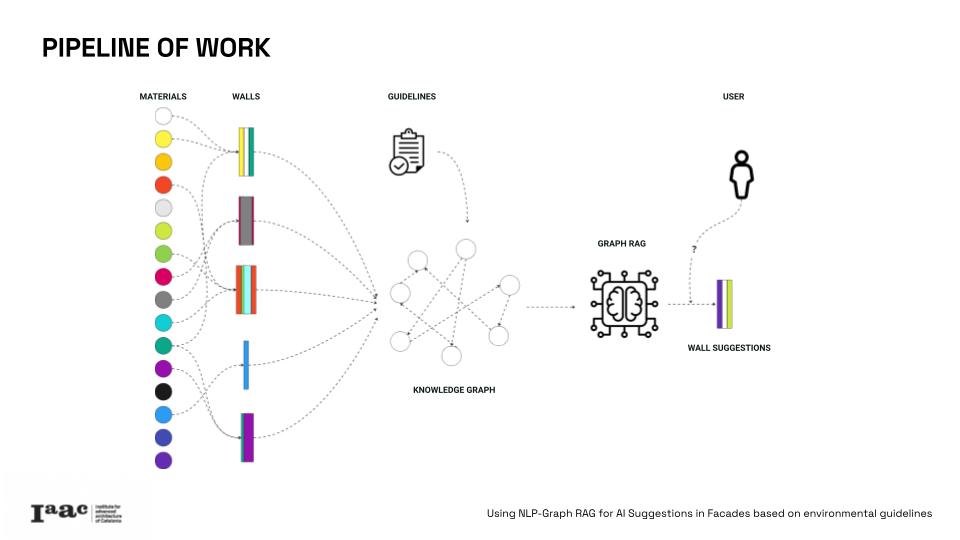
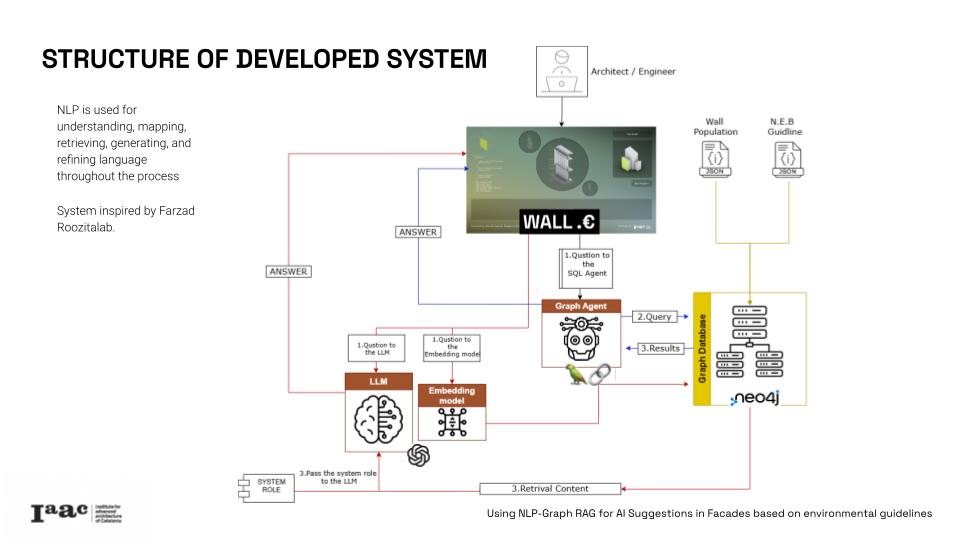
This project leverages Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Graph RAG) to provide intelligent facades configuration recommendations aligned with the New European Bauhaus (NEB) principles. This post presents how we apply AI theory approaches for reaching the stablished target.
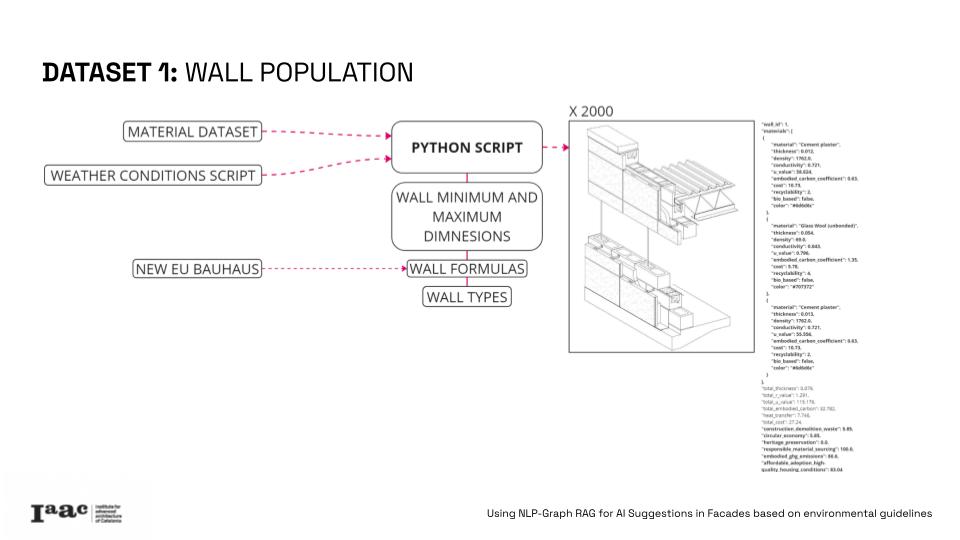
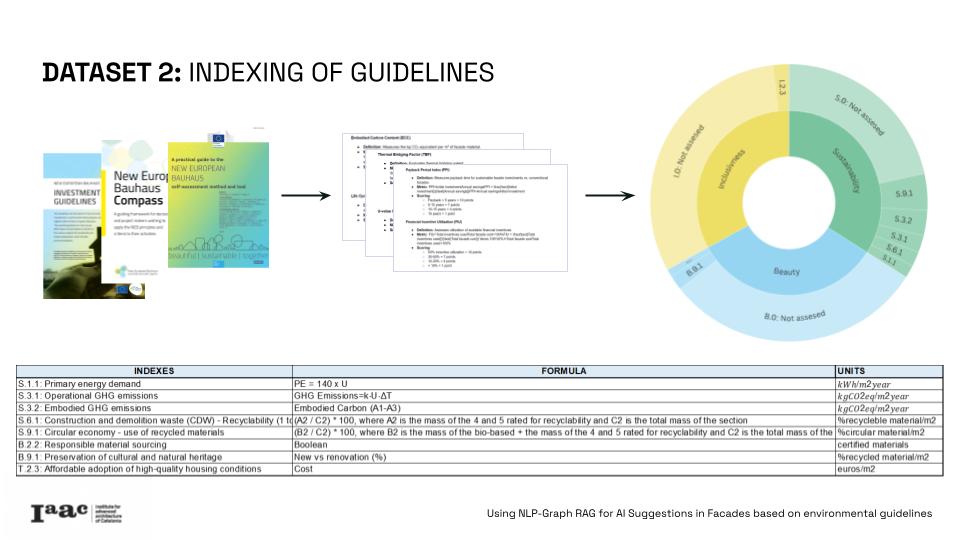
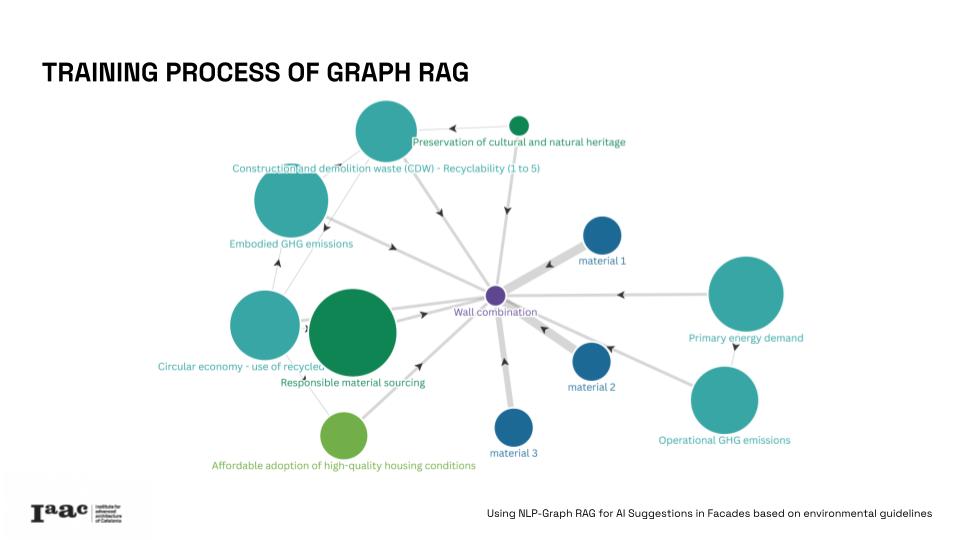
The project correlates quantitative data and qualitative guidelines, by integrating 17% of the assessed metrics in this guidelines and creating relations with a database of materials and wall section. Metrics such as primary energy demand, greenhouse gas emissions, and recyclability and 8 indexes of the New European Bauhaus, like circular economy, embodied GHG emissions or responsible material sourcing.
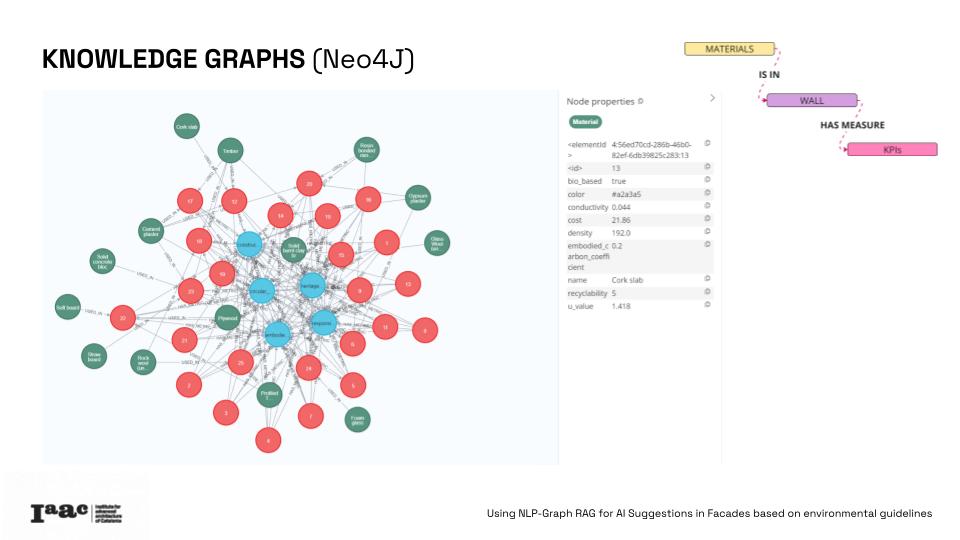
Using a detailed knowledge graph, this research enables advanced queries to identify optimal, eco-friendly wall combinations that relate to the user established necessities and the guidelines priorities, towards a more “sustainable, beautiful and inclusive” design. This innovative tool offers data-driven insights for architects struggling with complex regulations and guidelines but trying to design in a more resilient and sustainable way.
MOCK UP OF PLATFORM

DATA COLLECTION
The wall dataset visualization includes scatter plots for Total Cost vs. Embodied Carbon, UMAP projections for clustering, and rank-value plots for Total Cost and Embodied Carbon.
These graphs reveal clustering patterns and provide detailed insights into thickness, heat transfer, cost, and embodied carbon.
REFERENCES
New European Bauhaus
https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/investments-into-the-sustainability-transition
https://knowledge-management.new-european-bauhaus.europa.eu/homepage
https://worldgbc.org/advancing-net-zero/embodied-carbon/
Retrieval Augmented Generation
https://microsoft.github.io/graphrag/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3NP1llvtrbI

