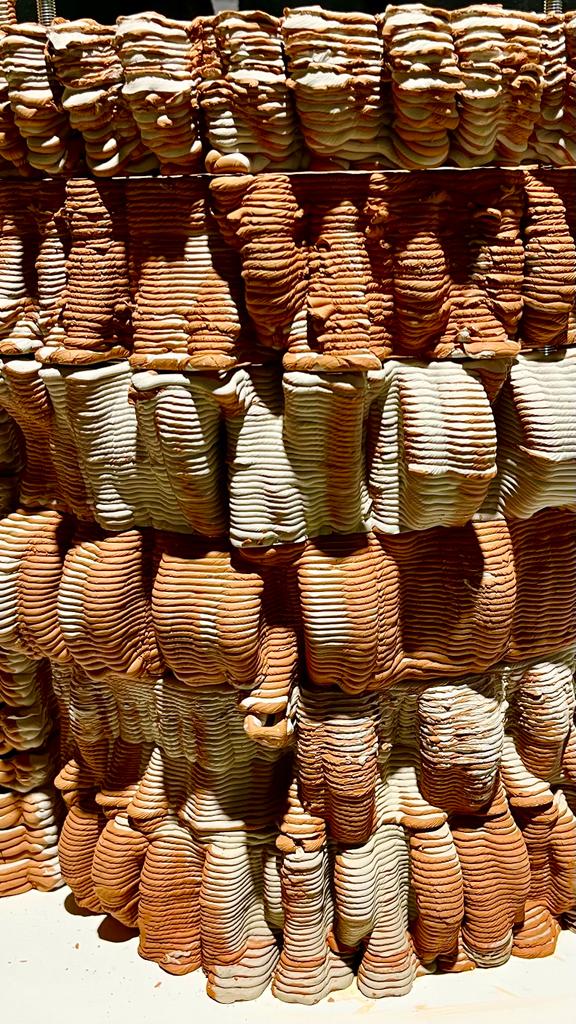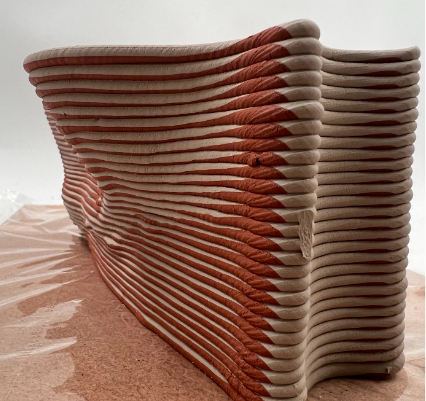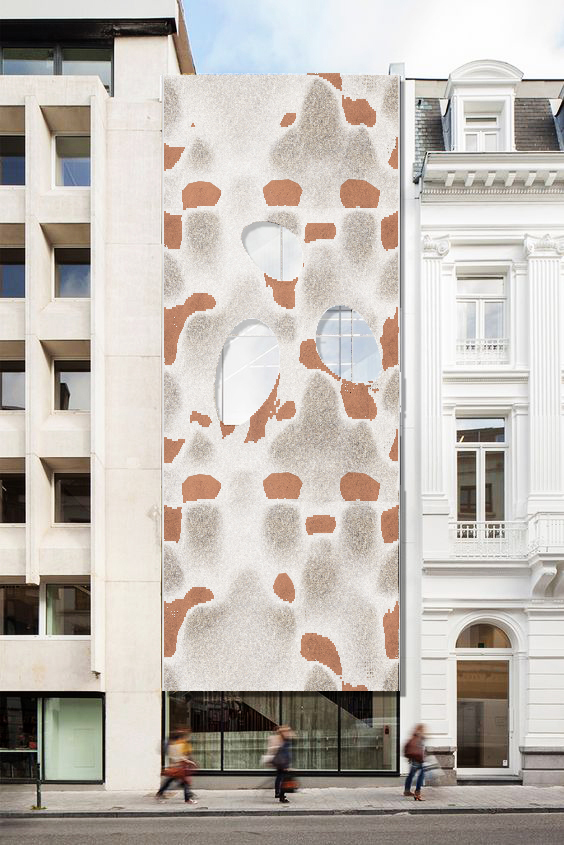
Photo credit: Multi-material printing, Sekisai Office print + 3DPA workshop, IAAC 2019
Rapid prototyping and advanced manufacturing are fundamental technologies that enable an integrative conception and production of fabrication-informed material design processes. Multi-material 3D printing techniques are being developed to produce structures with new mixed materials with completely novel properties. This will challenge prefabrication as machine learning algorithms will also become more critical in the design process. 3D printing multi-materials in gradients achieve more optimal behaviours than traditional materials in the construction industry.
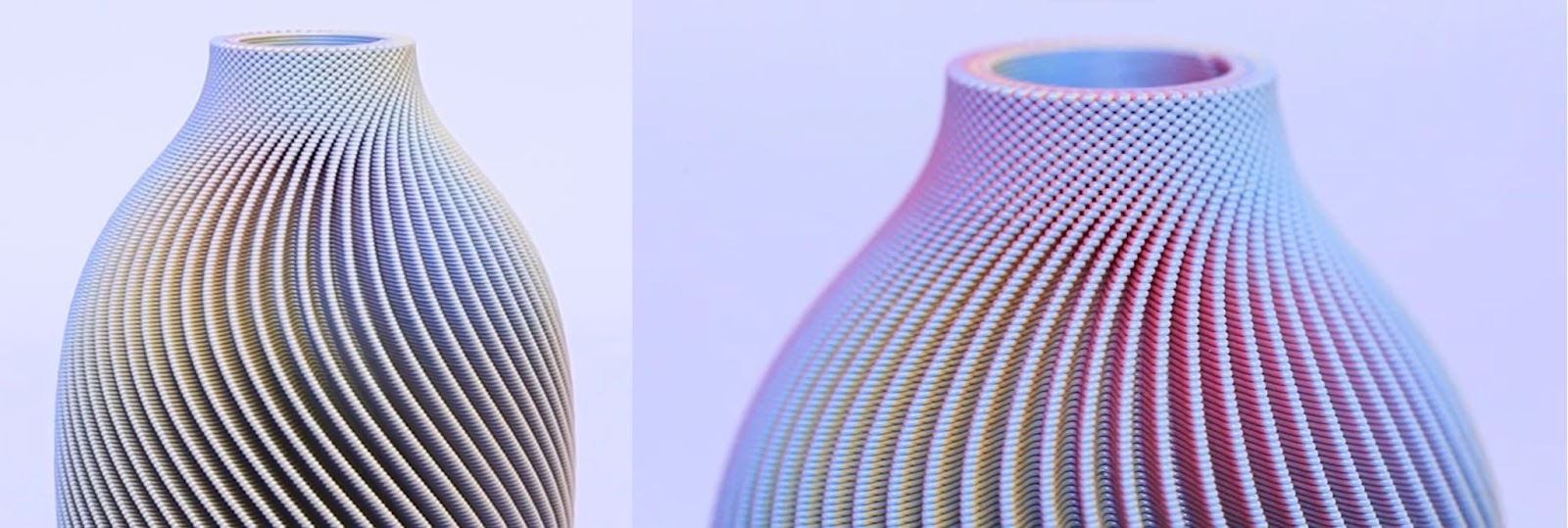
In the conventional colouring method, shape and color are designed separately, by first “creating shape” then “adding color”. This workshop will focus on exploring geometries through a multi-material printing method in which materials with different color pigmentation are adjusted at the same time, seamlessly integrating two processes of “creating shape” and “applying color”, thus making it possible to create more subtle and complex color expressions.
Building in this context, this workshop is the occasion to look at the question of materiality in architecture. Additive manufacturing of multi-material opens the possibility of carefully designing the material distribution over geometries, taking advantage of the wide palette of materials available to build architecture. The relation between form and material distribution has structural, thermal and aesthetic implications yet to be explored.
Following the method and workflow, students will also learn about material preparation and cartridge extruder refill to carry out the 3D printing system, hence learning how to implement design processes in robots.
Learning Objectives
The objective of the workshop is to prototype, fabricate and explore new possibilities in material through robotic additive manufacturing. With an overview of the state of the art in the syntax of additive manufacturing geometries and its influence on material capabilities. Discuss the practical implementation of custom end effectors, and brainstorm to later produce the most performative model with this technology. At course completion the student will learn:
- Have an overview of the possible robotic additive manufacturing processes available for architects and designers.
- Understand the basics of robotic kinematics, robotic simulation and robotic control.
- Communication between ABB arm robot and custom end effector
- How to calibrate/adjust end-effector tools and possible modifications of them
- Be capable of generating the robotic simulation and production files to produce a prototype.
- Be capable of integrating the limitations and opportunities of a specific robotics process into a final architecture design
- To think independently about novel robotic workflow concepts and implement them in small groups.
Keywords
Multi-?material 3d printing, Robotic additive manufacturing, Material design











