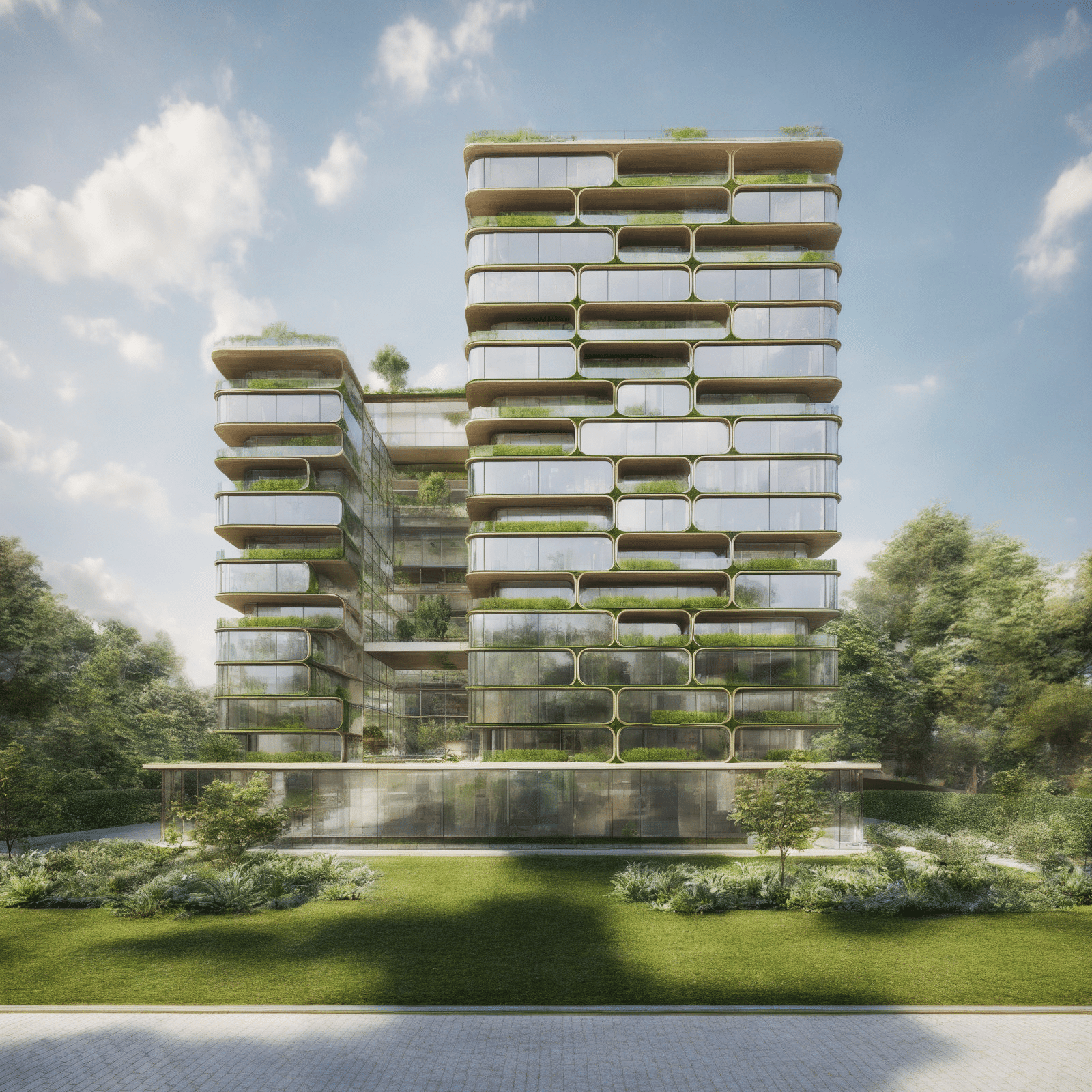
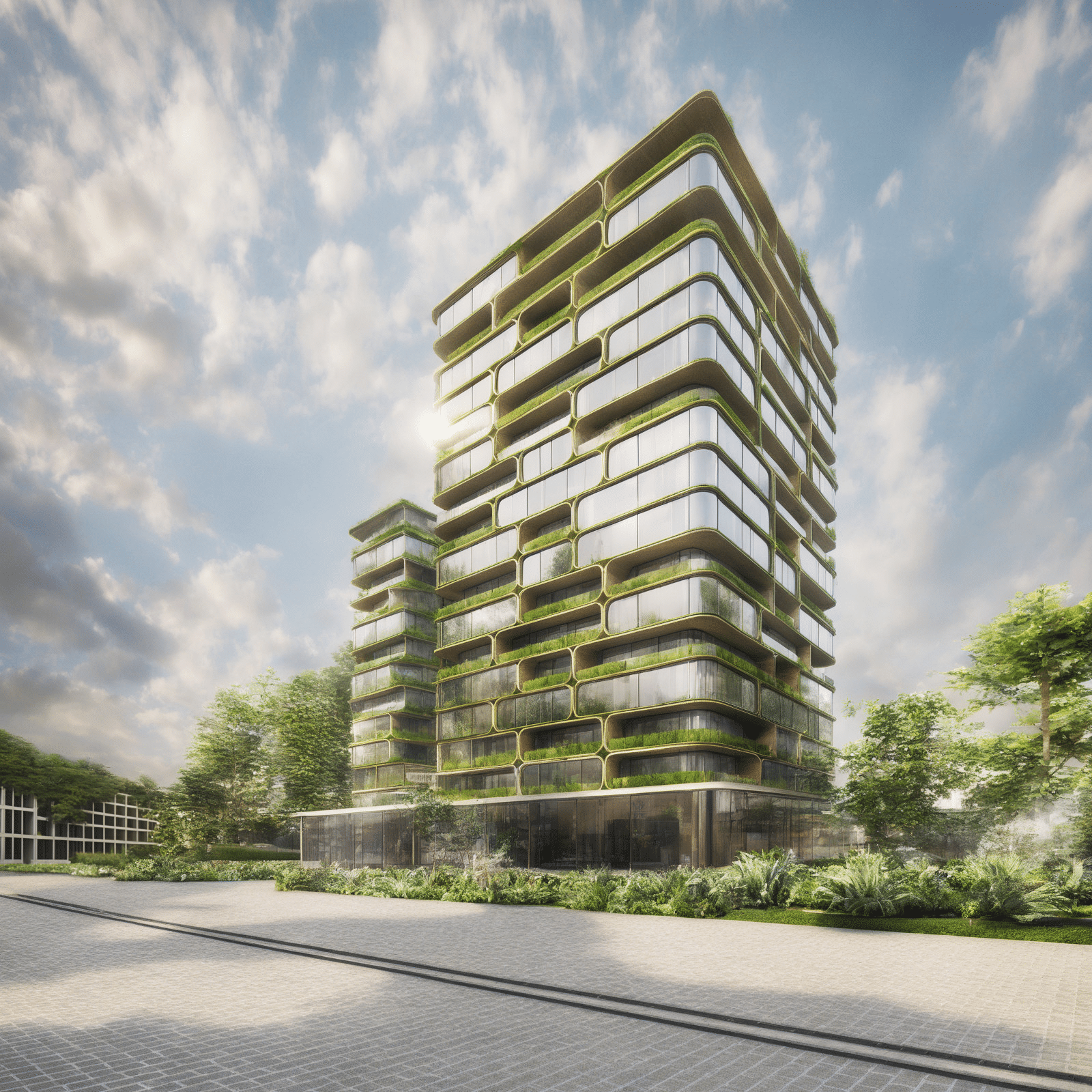
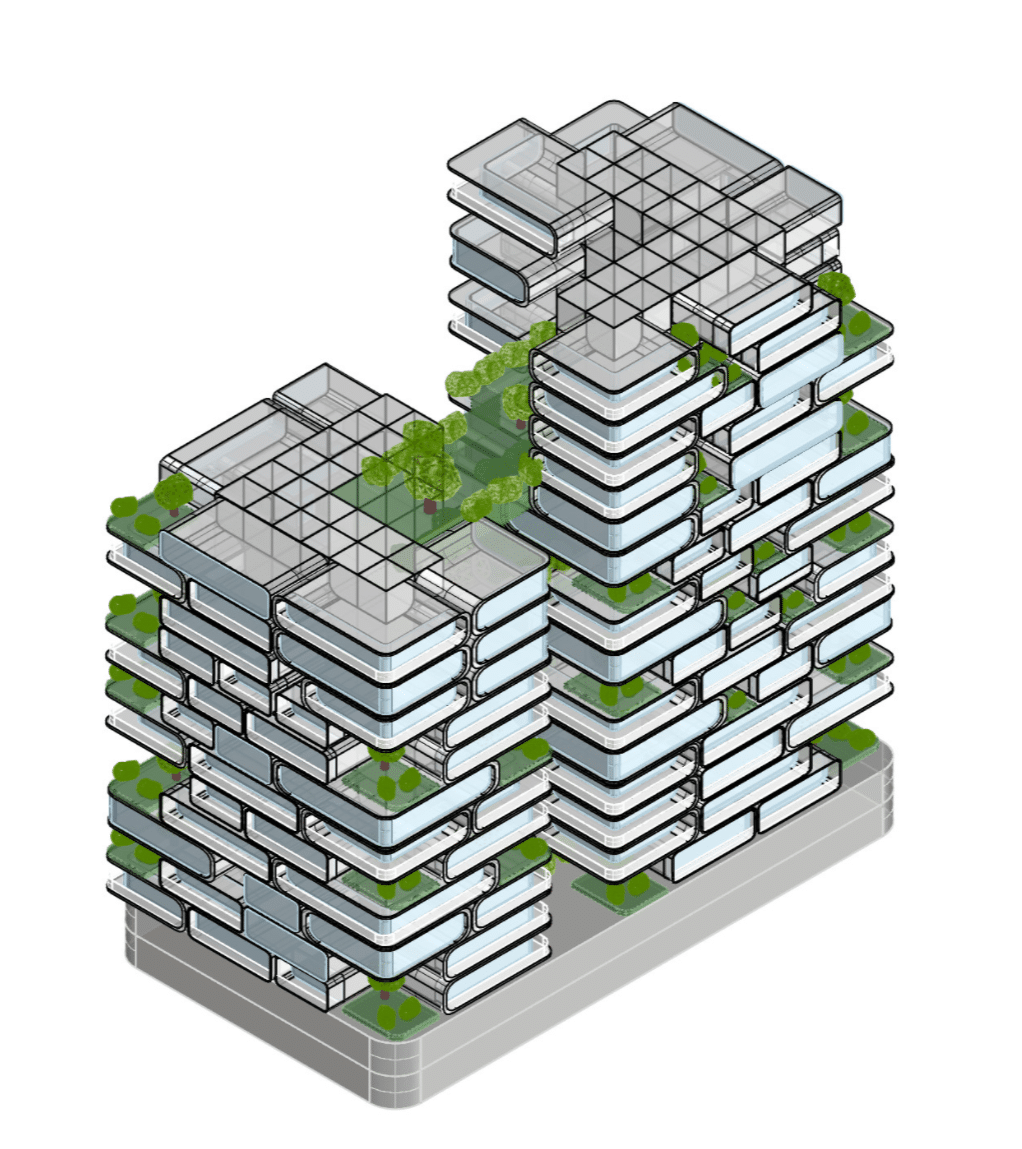
NeoCapsules is an innovative residential project inspired by the Nakagin Capsule Tower, reimagined to suit modern needs. Unlike the original design, which featured small, single-use capsules, NeoCapsules offers modular units in different sizes to accommodate families, young professionals, and individuals with diverse lifestyles. This flexibility allows residents to select layouts that best match their needs, whether for shared family living or compact spaces for individuals.
The variety of module sizes ensures adaptability and functionality, providing options for growing families or those seeking efficient urban living. The building’s parametric design supports this flexibility by enabling easy reconfiguration of spaces without major structural changes. This approach not only enhances usability but also aligns with sustainable practices by reducing construction waste.
NeoCapsules also emphasizes community living, with green spaces, rooftop gardens, and shared amenities that foster interaction and connection to nature. The ground floor integrates seamlessly with the urban environment, offering retail and dining spaces that invite engagement from the wider community.
Redefining Urban Living – NeoCapsules combines sustainability, adaptability, and community into a forward-thinking solution for urban living.
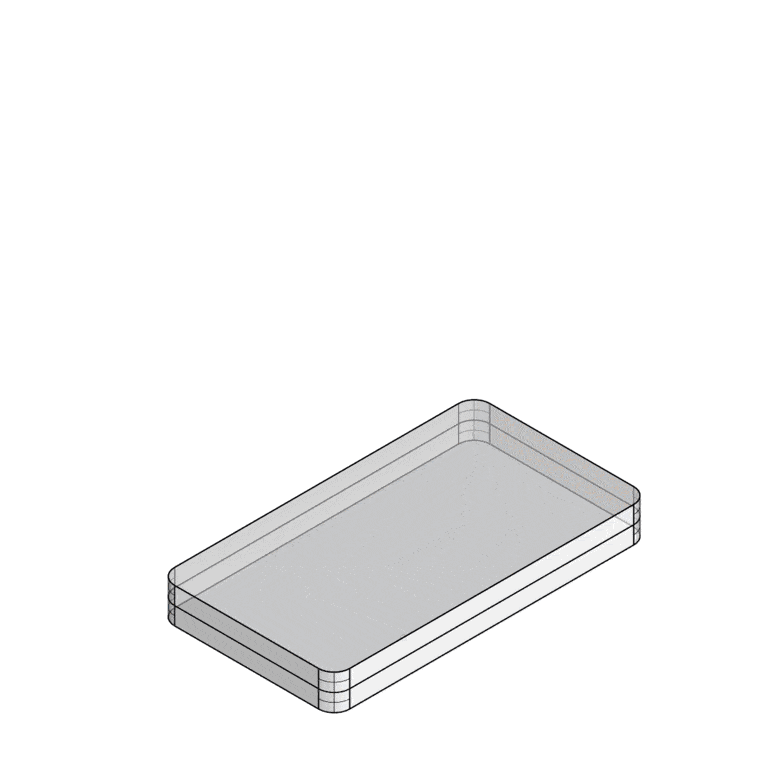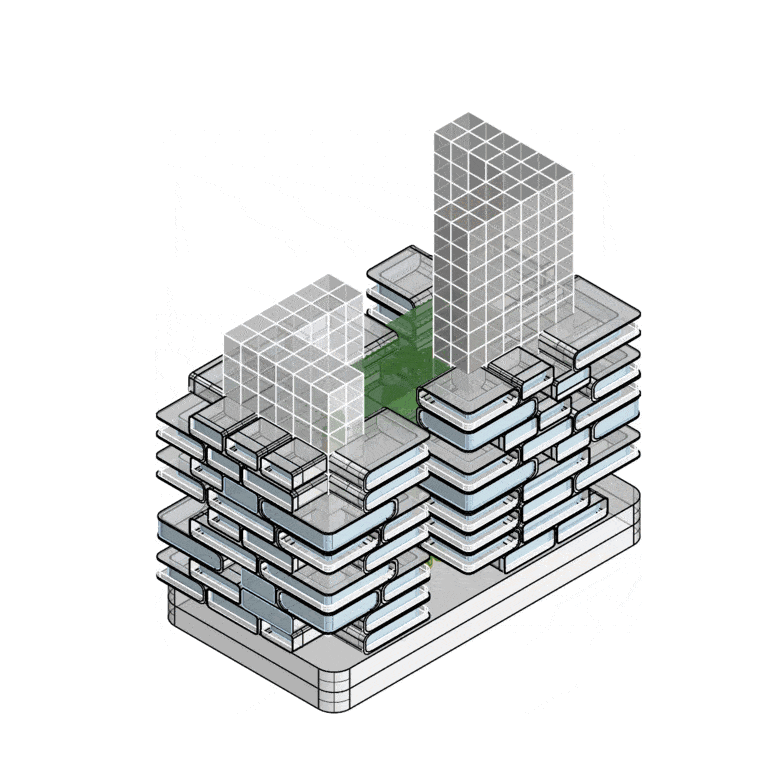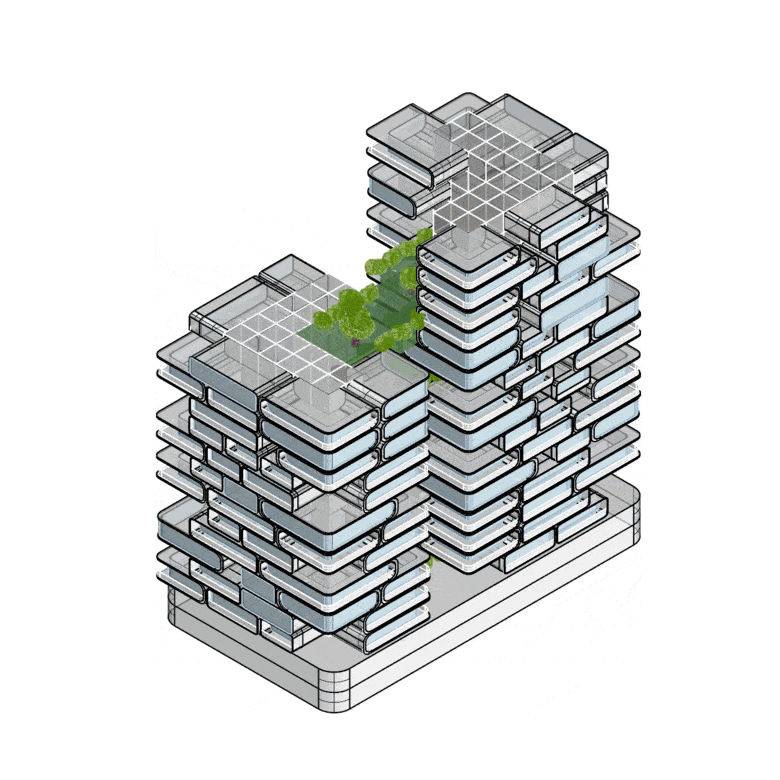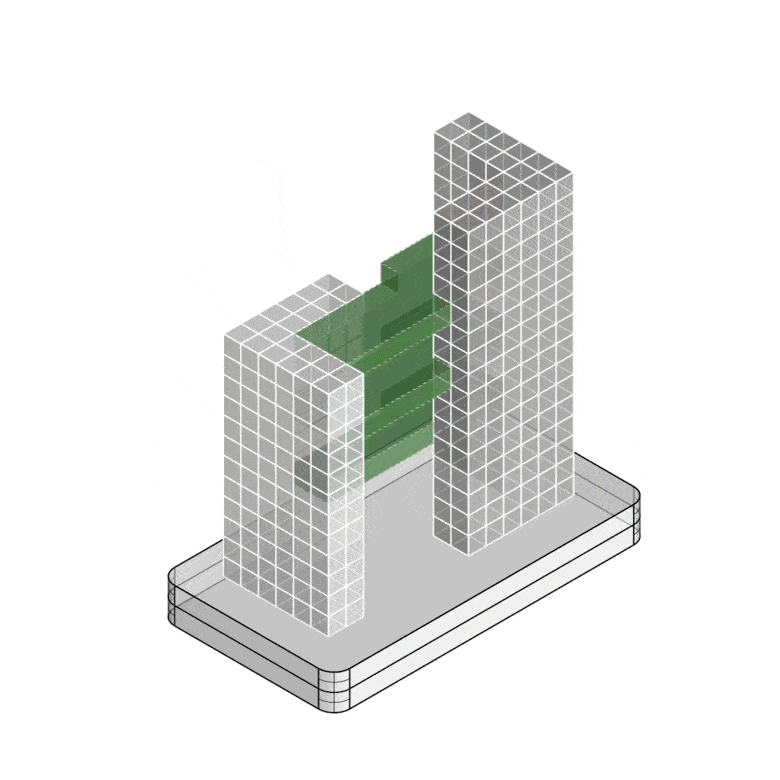




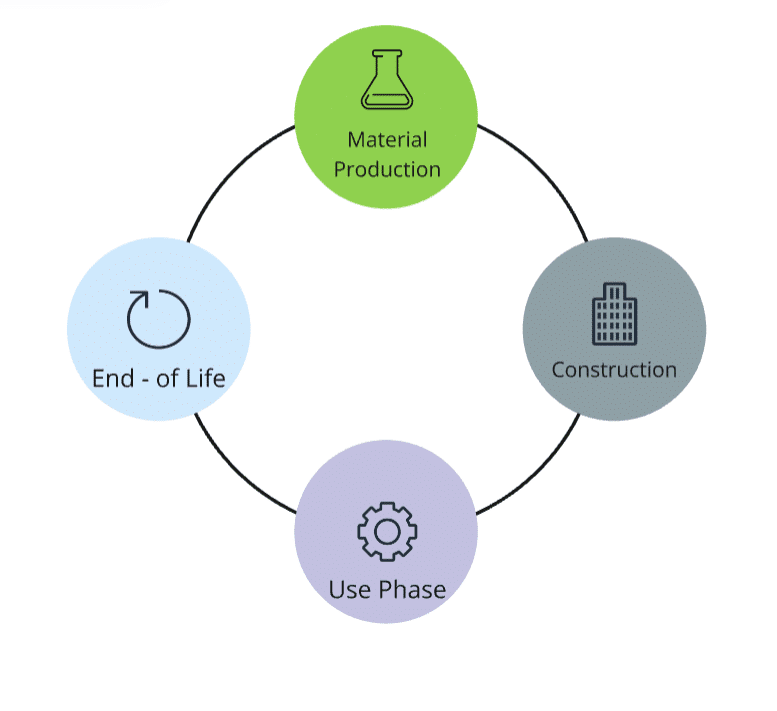
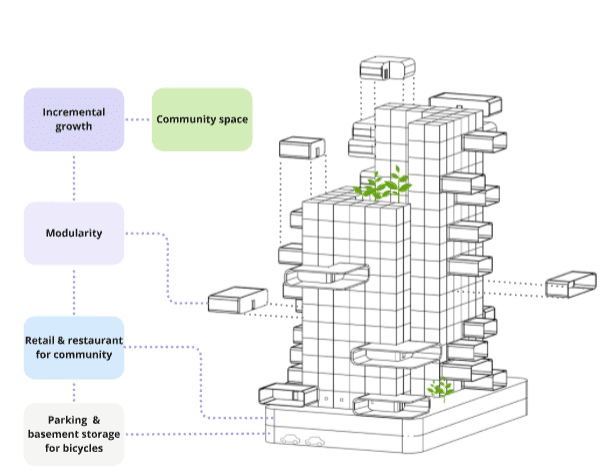
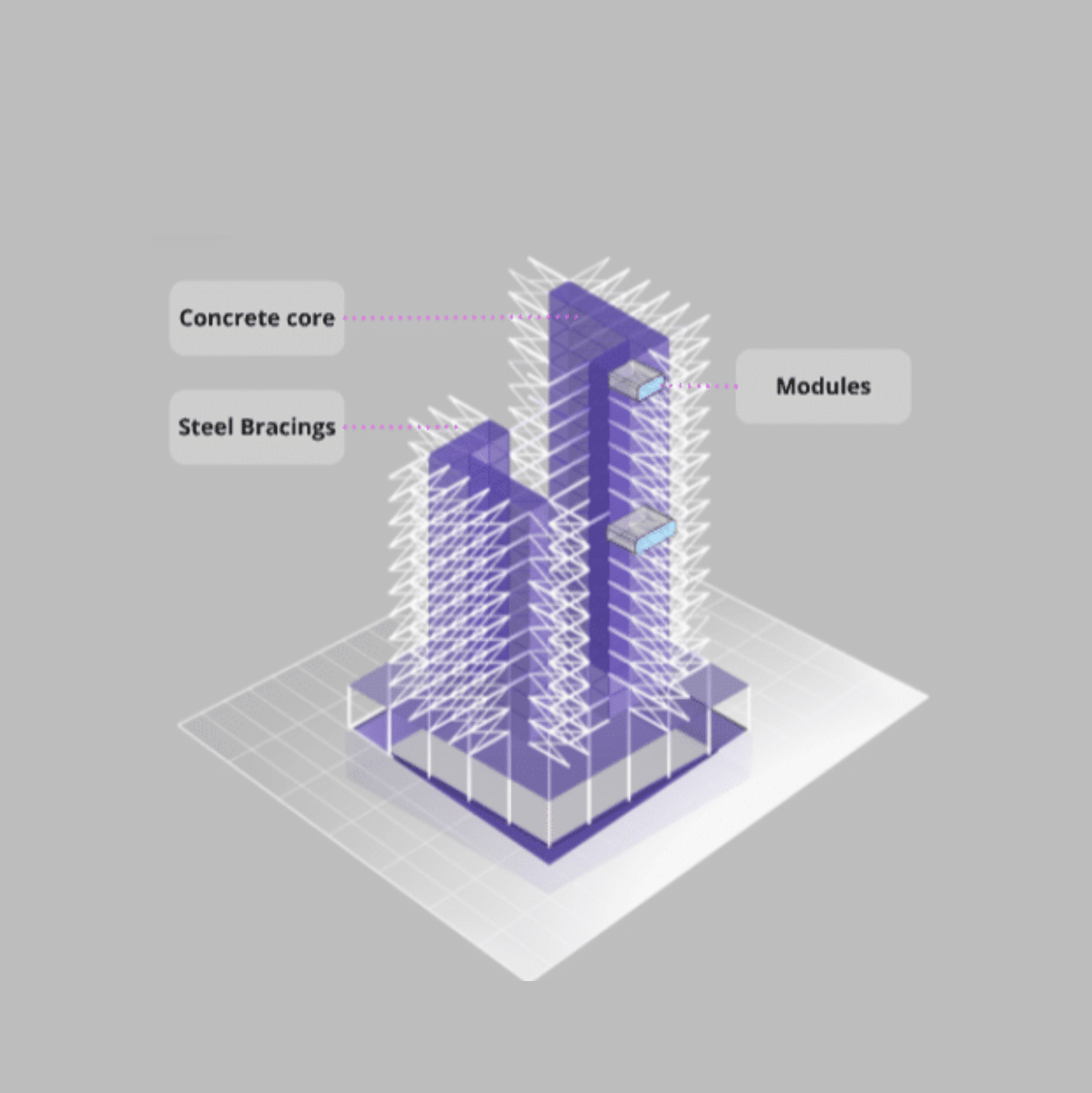
Structural Concept and System Boundaries
Nakagin-Inspired Building: Structural Concept and Lifecycle Stages
Structural Improvements:
- Concrete core for enhanced stability
- Steel bracings for additional support
- Lightweight modular capsules for adaptability
System Boundaries (Lifecycle Stages):
- Material Production
- Construction
- Use Phase (including potential replacements)
- End-of-Life
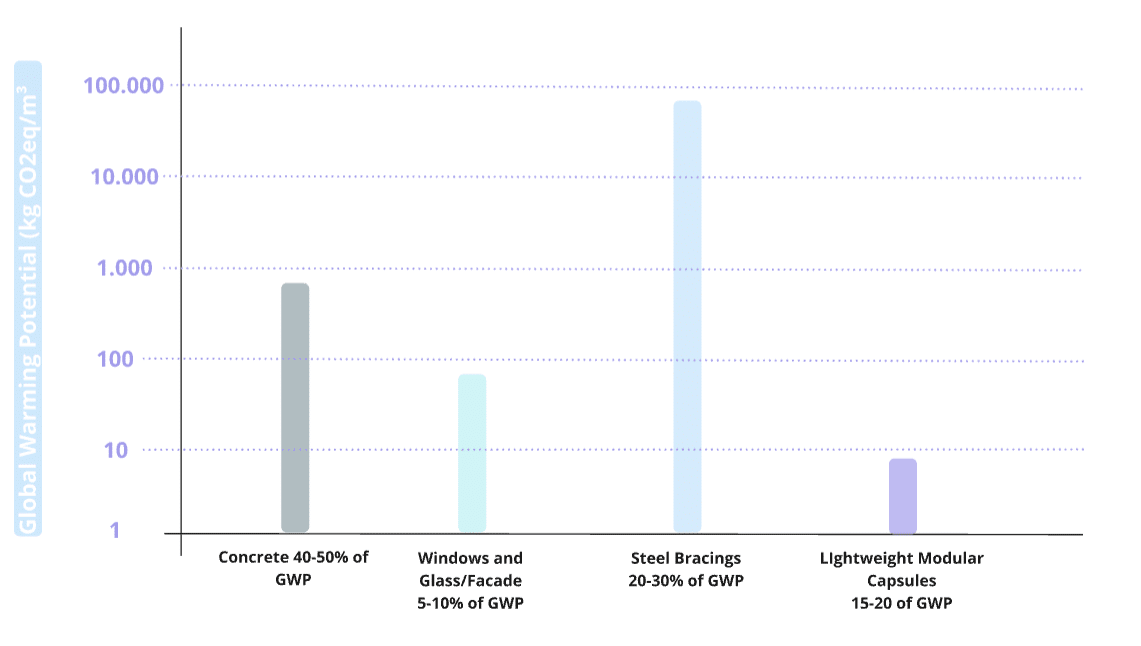
Environmental Impact of Key Materials – Comparison
Compare Global Warming Potential (GWP) of:
- Concrete core
- Steel bracings
- Lightweight modular capsules
Highlight the benefits of module replacement:
- Extended building lifespan
- Reduced environmental impact over time

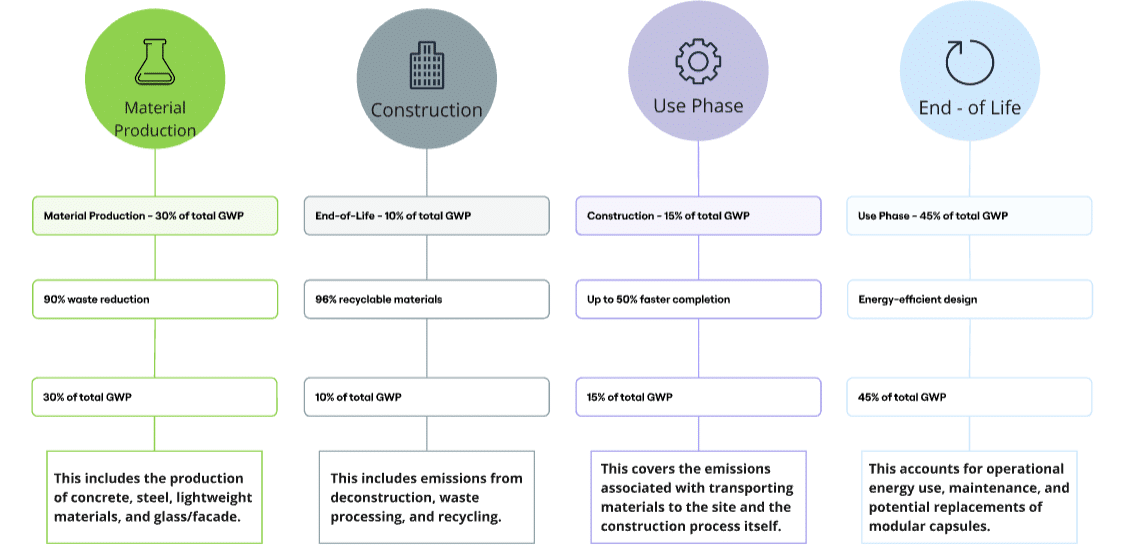
Lifecycle Assessment and Environmental Benefits
Material Production:
- Efficient manufacturing of modular components reduces waste by up to 90%
- Controlled factory environment allows for precise measurements and accurate cutting
Construction:
- Modular construction can reduce project timelines by 20-50%
- Fewer on-site workers needed, reducing labor costs by 16-25%
Use Phase:
- Modular buildings designed for adaptability and potential upgrades
- Energy-efficient designs reduce operational environmental impact
End-of-Life:
- Up to 96% of materials in modular buildings can be recycled
- Design for disassembly (DfD) allows for component reuse, creating multiple lifecycles
GWP Comparison:
Modular construction reduces total greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 30% compared to traditional methods
Conclusion
- Sustainability Focus: The modular design significantly reduces environmental impact throughout its lifecycle.
- Lifecycle Efficiency: Each stage — Material Production, Construction, Use Phase, and End-of-Life — contributes to a lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) compared to traditional construction methods.
- Adaptability and Longevity: Modular components allow for upgrades and replacements, extending the building’s lifespan and reducing waste.
- Recyclability: High recyclability of materials at the end-of-life stage supports circular economy principles.

