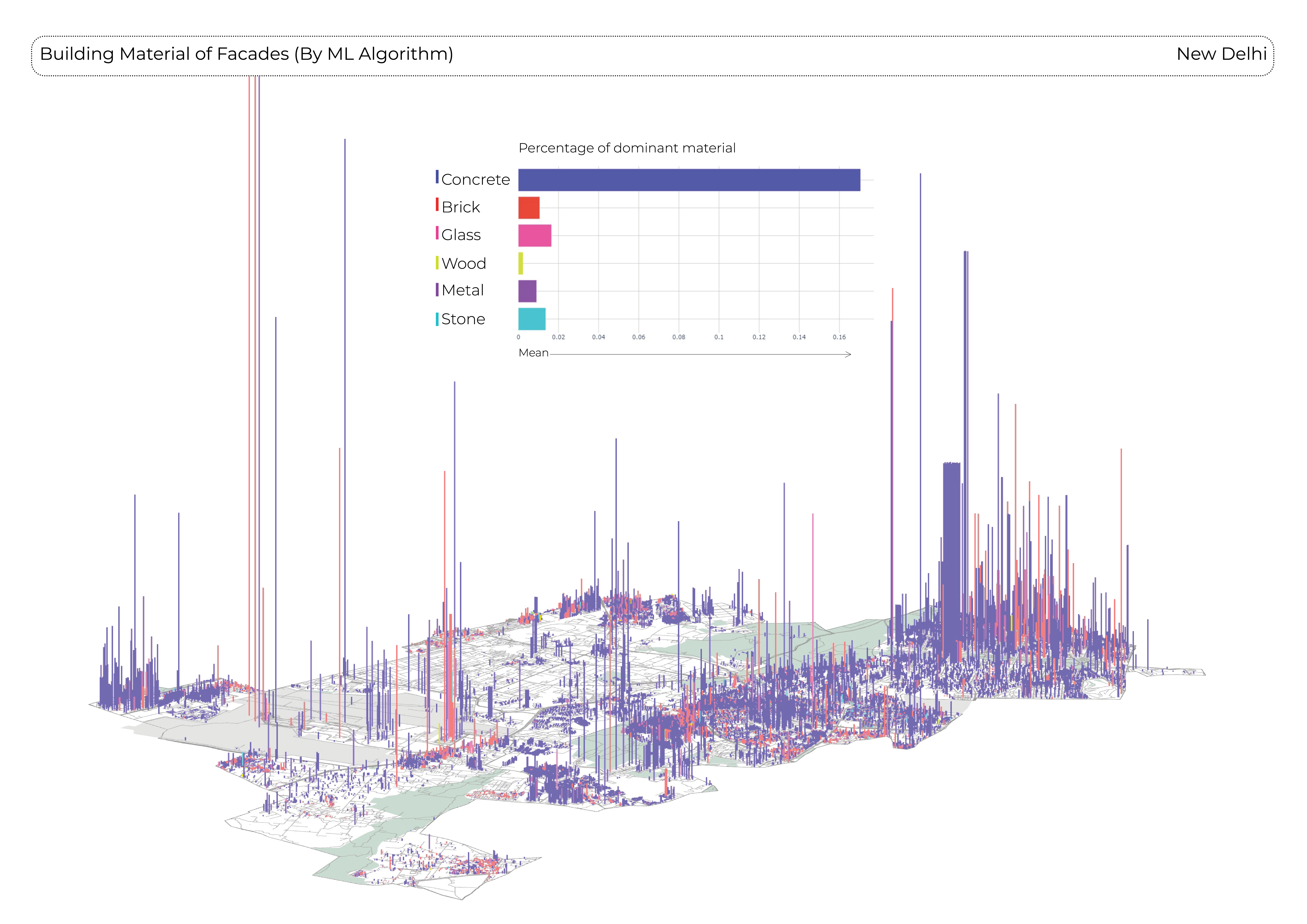
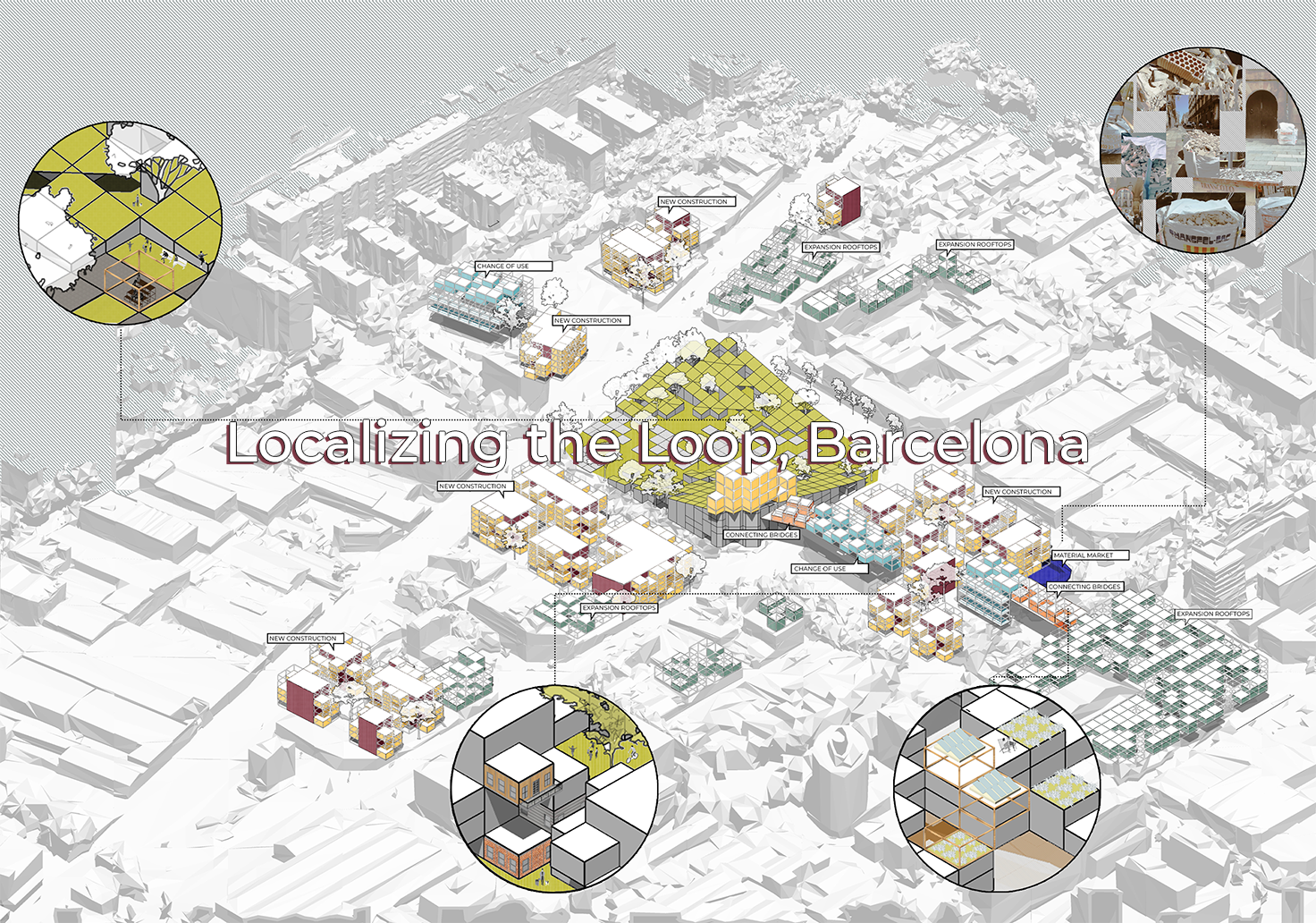
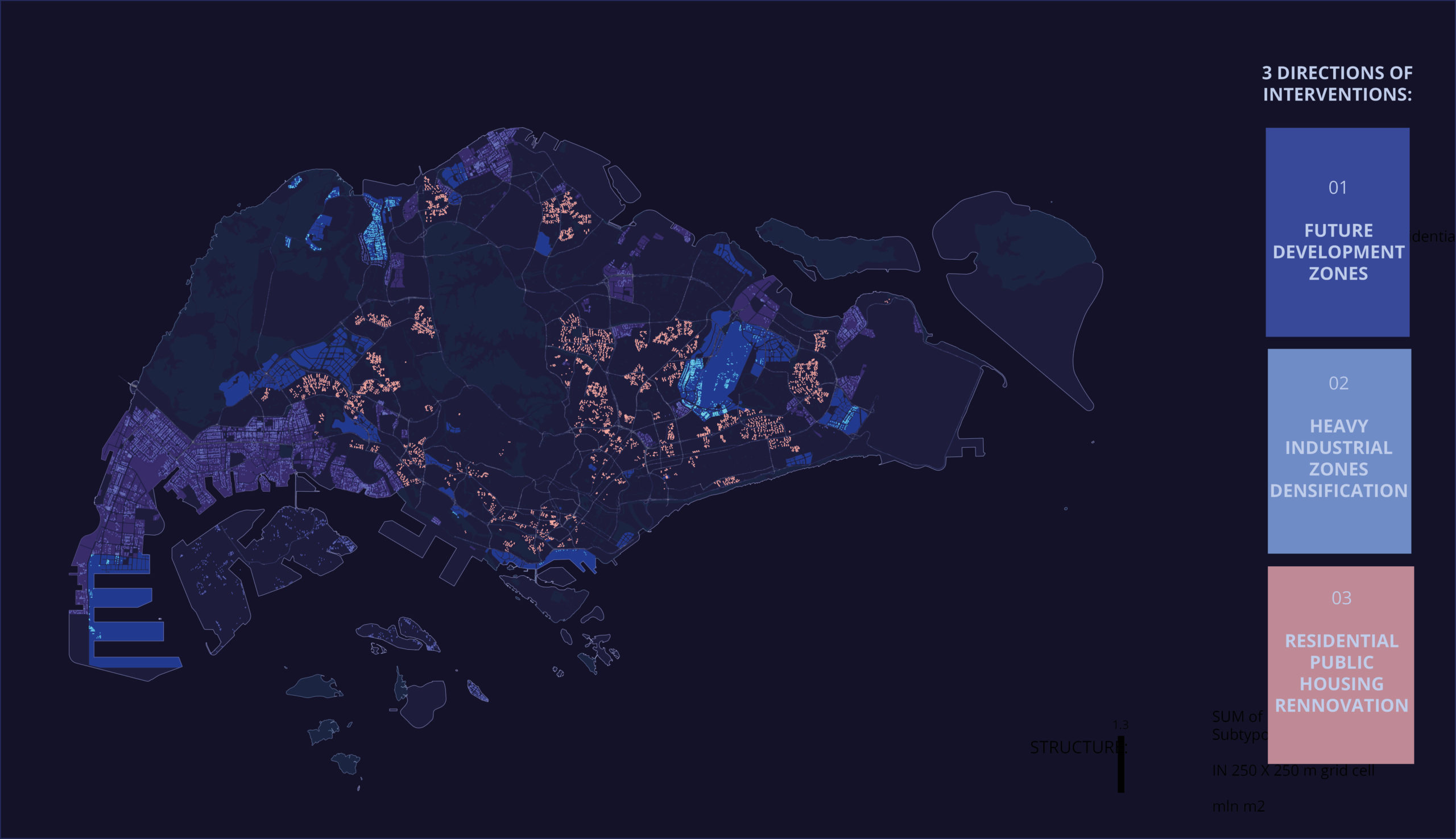
Jakarta
Jakarta’s rapid urbanization has outpaced the development of equitable mobility infrastructure, exacerbating safety disparities, particularly for low-income women navigating the city at night. While formal policies fall short, informal transport networks like Angkot fill critical gaps, despite exposing riders to physical and psychological risks. This study explores how machine learning can be used to fill … Read more