Crystallization. What is it?
Crystallization is a process in which a solid material forms from a liquid or gas phase, resulting in the arrangement of atoms or molecules in a highly ordered, three-dimensional structure known as a crystal lattice. This process is driven by changes in temperature, pressure, or the concentration of solute in a solution.
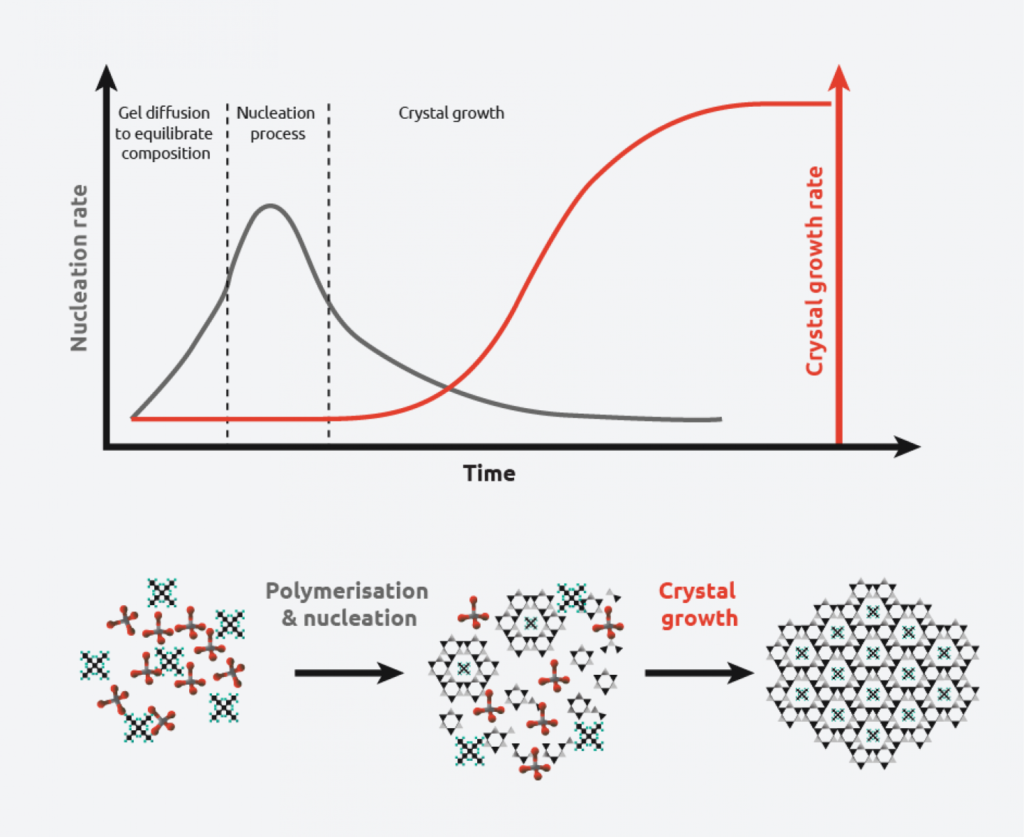
Crystallization requires two events to occur:
Nucleation – Molecules gather together in clusters in a defined manner. Clusters need to be stable under current experimental conditions to reach the “critical cluster size” or they will redissolve. It is this point in the crystallization process that defines the crystal structure.
Crystal Growth – Nuclei that have successfully achieved the “critical cluster size” begin to increase in size. Crystal growth is a dynamic process, with atoms precipitating from solution and becoming redissolved. Supersaturation and supercooling are two of the most common driving forces behind crystal formation.
Quartz structure. Why hexagon?
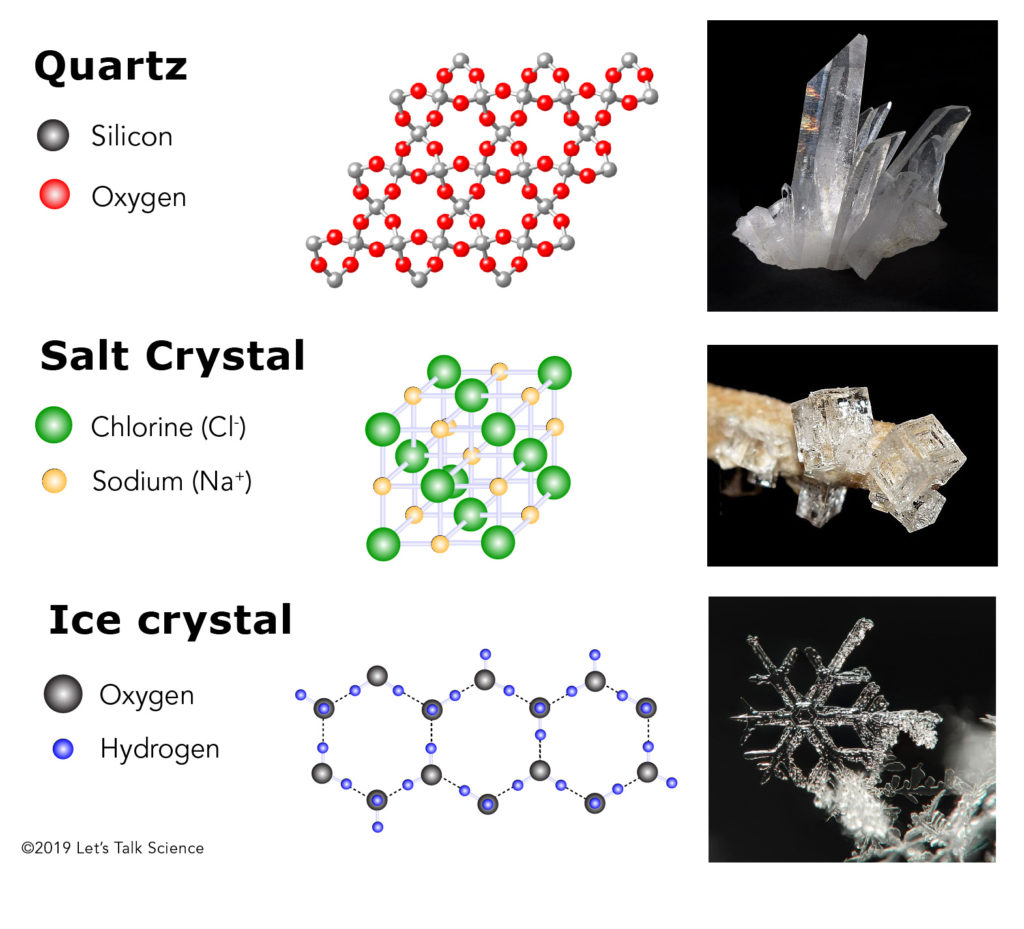
Different minerals have different molecular compositions. These molecular compositions form structures of different shapes. Quartz crystals, which are made up of silicon dioxide (SiO2) molecules, form hexagonal prisms with hexagonal pyramids on either end.
Quartz growth. Druzy crystal habit
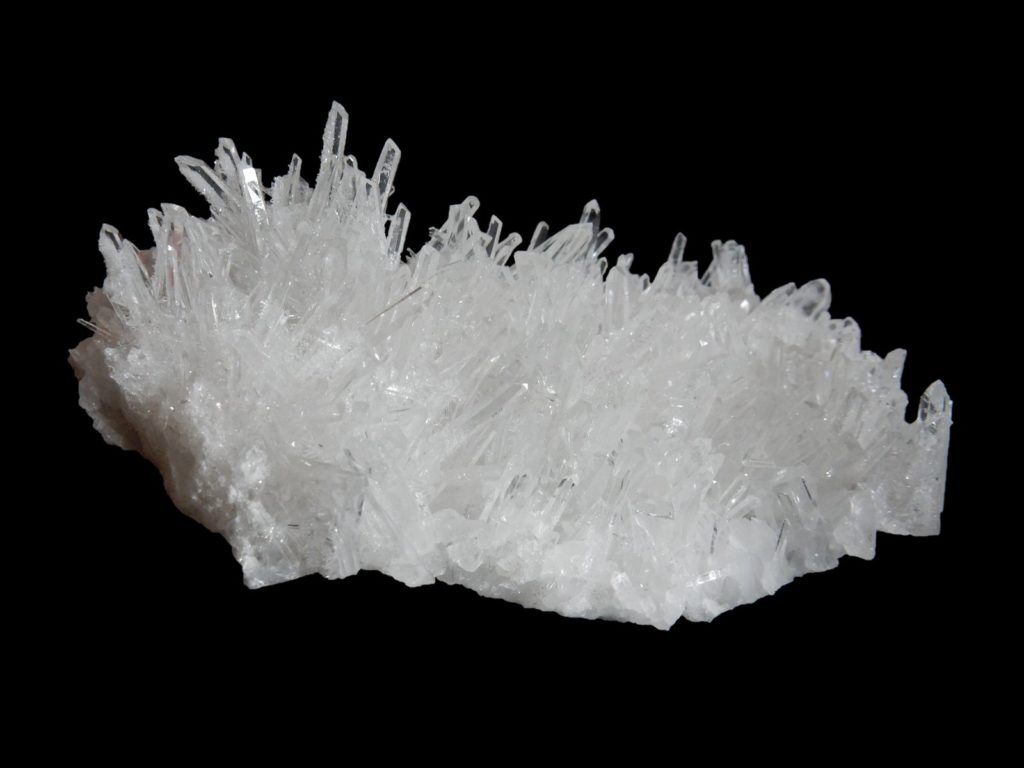

Druzy Quartz is a type of geode formation found in areas of Brazil, South America, Africa, Europe, and even the United States. This stone is sometimes spelled as Drusy, Drusie, or Druse. The word, druzy, actually refers to a group of crystals that forms on the surface of other stones. You’ll usually find druzy crystals where there is a source of water. This is because the crystals are created when water deposits minerals onto the surface of a stone. When the water evaporates, the minerals left on the stone begin to form the characteristic druzy crystals.
Strategy
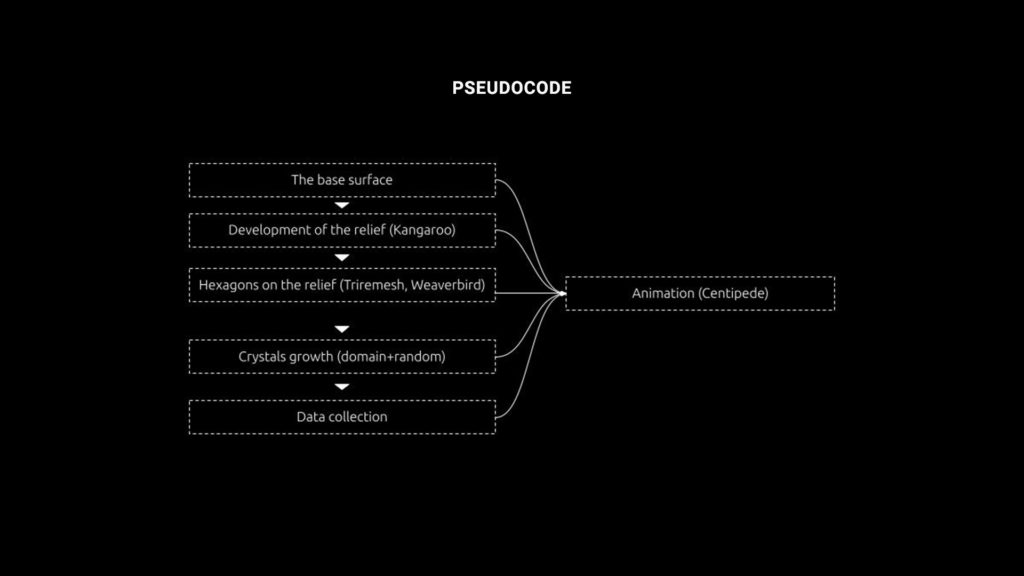
- Create the surface and paramatrize it
- Extrude randomized crystals
- Create crystals on the surface
- Collect the data
- Create the animation
Final result

