Multi-material Additive Manufacturing solutions.
CONTEXT
The synergy between clay additive manufacturing and computational design has revolutionized construction, bridging the gap between project design and production. This integration has established a direct-design-build system, facilitating seamless translation of intricate designs into physical structures with precision and speed. This transformative approach enables complex geometries, customization, and cost-effective sustainability while fostering iterative design processes. It represents a paradigm shift in construction, promising efficient, innovative, and sustainable built environments.
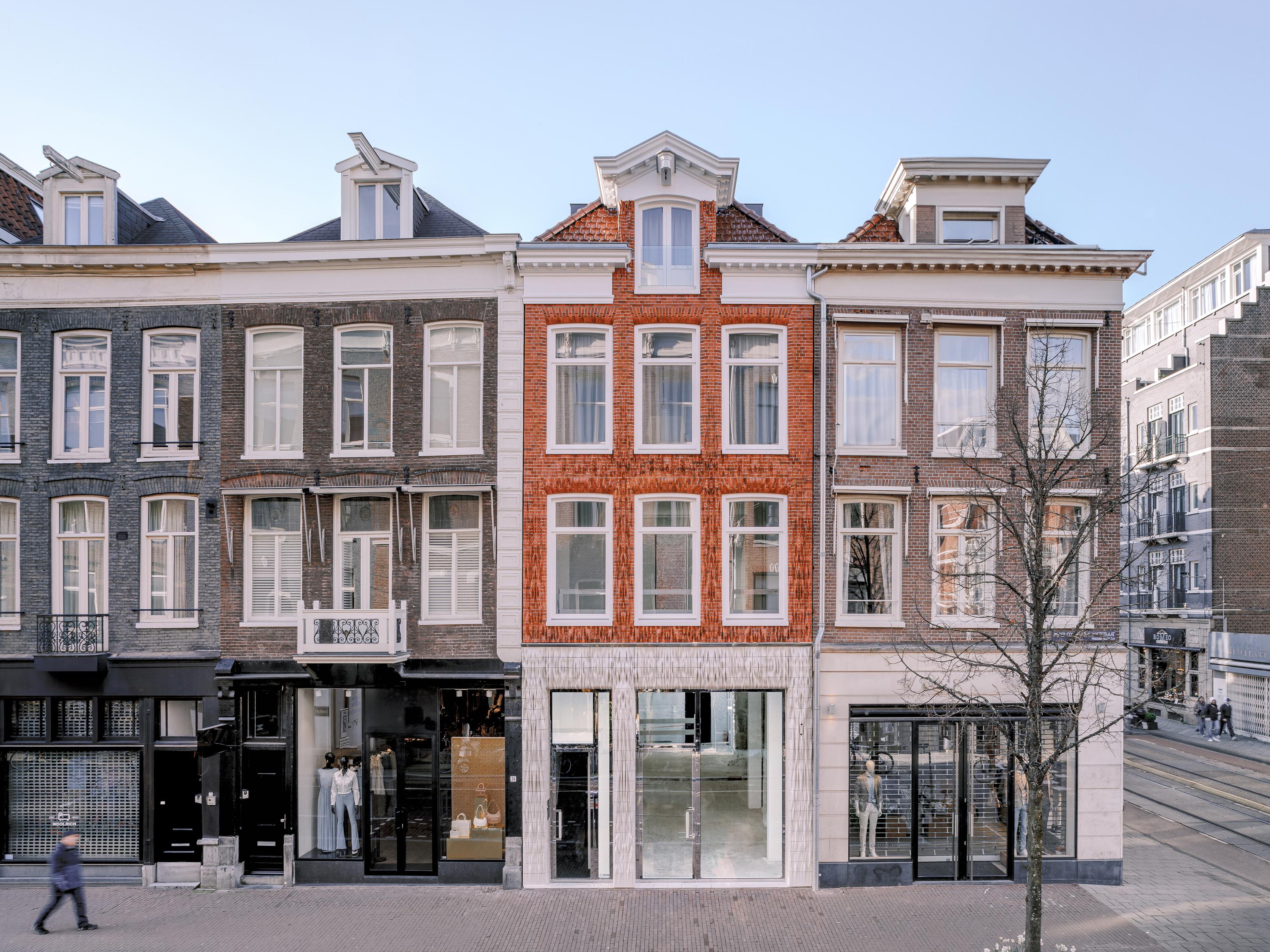

Ceramic House – Studio RAP 2022
PROBLEM
Extrusion-based 3D printing for clay assemblies encounters unique challenges that can limit the creation of ready-to-use components. Material performance, specifically shrinkage, poses a significant hurdle. Additionally, manufacturing considerations, like overhangs, often necessitate post-processing and manual intervention to rectify issues. This includes manually adjusting or fixing mechanical connectors within the printed components. These challenges result in the need for re-manufacturing or increased labor time for meticulous post-processing, impacting the final usability and functionality of the components.
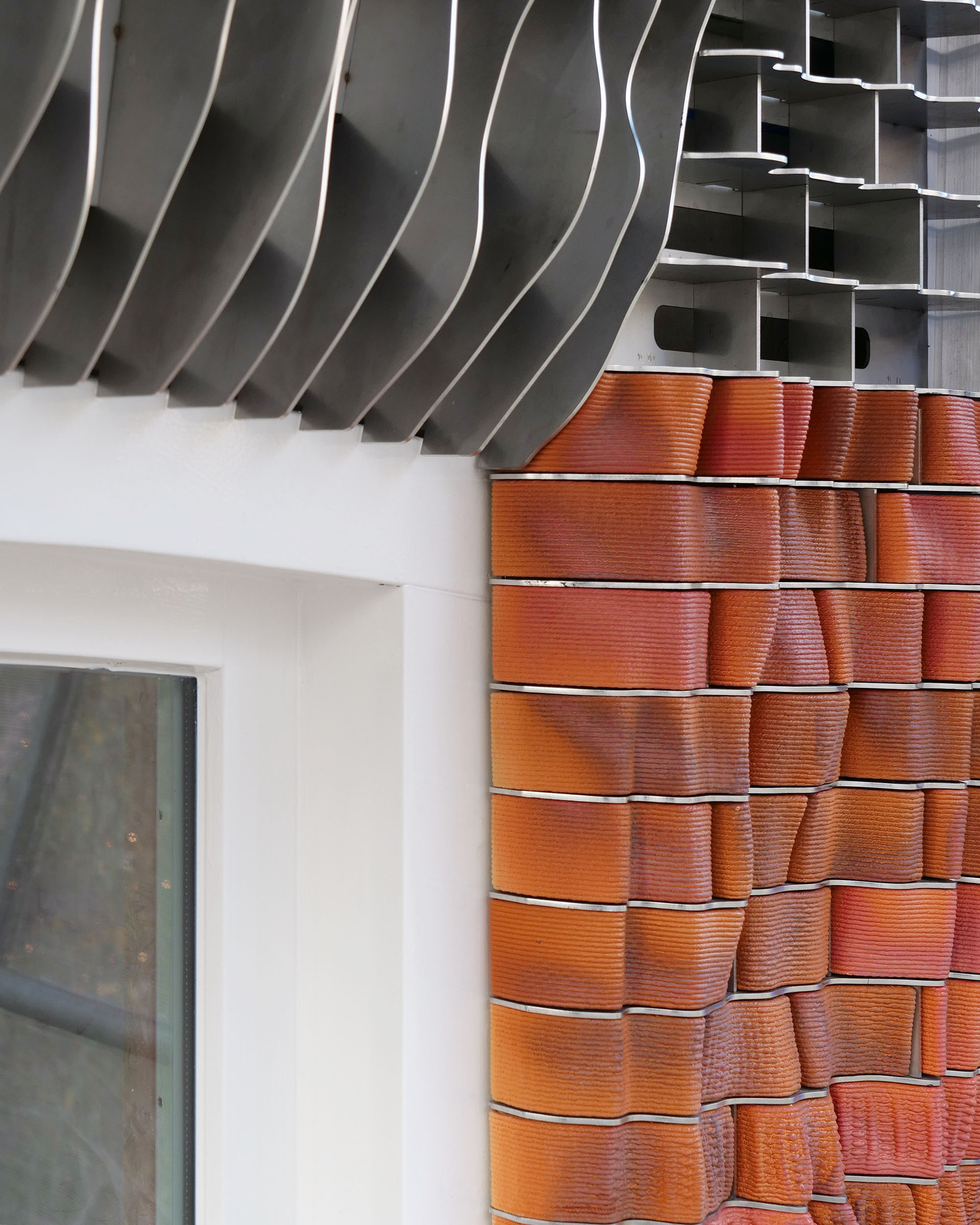

Ceramic House – Studio RAP 2022
SOLUTION
A hybrid workflow combining 3D printing with robotic pick-and-place material embedding streamlines additive manufacturing. This approach integrates precise layer-by-layer 3D printing with robotic systems seamlessly embedding materials or components during the same manufacturing cycle. The result? Complex, multifunctional parts with diverse properties produced efficiently and with high accuracy. This innovative process enhances customization, functional enhancements, and rapid prototyping capabilities, promising a more streamlined and precise manufacturing method.
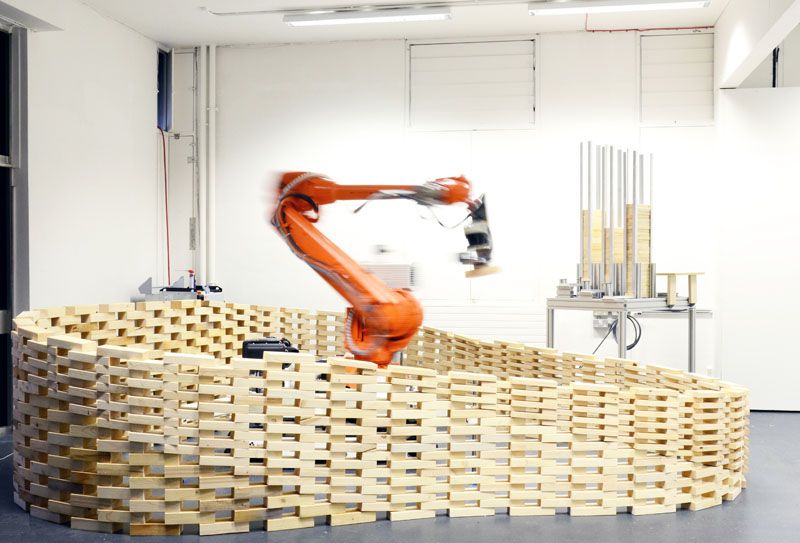

ETH ZURICH – Gramazio Kohler Research
PRODUCT
The multi-material additive manufacturing workflow for clay envelopes integrates embedded elements to revolutionize 3D printed systems’ assembly and disassembly. Strategically placed embedded elements serve as mechanical connections, streamlining assembly and ensuring easy disassembly when needed. This approach optimizes structural integrity, allows for intricate designs, and tailors properties for strength, flexibility, or specific functionalities. It simplifies assembly complexities, promotes sustainability, and offers versatile applications in various industries.
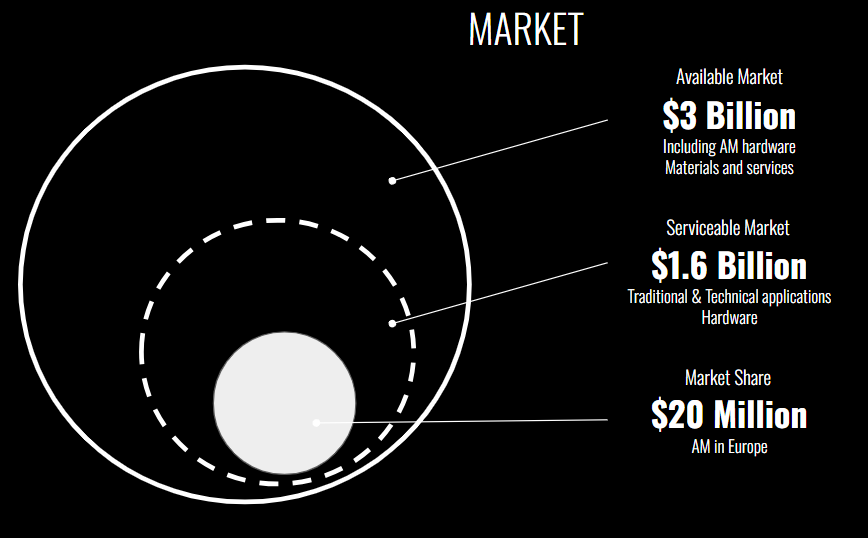
MARKET
Multiple reports anticipates a remarkable uptick in the annual worth of additive manufacturing (AM) parts, particularly within the industrial manufacturing and end-use consumer product sectors—areas where your business operates. By 2027, these sectors are poised to collectively exceed $2 billion in annual value. This growth trajectory is set to elevate the Ceramics AM segment, an arena your business engages in, to surpass $3 billion in generated revenues and value. This forecast underscores the thriving market landscape that directly intersects with your business domain, highlighting promising opportunities for growth and expansion within the ceramics AM market.
WHY NOW?
Additive manufacturing in construction has reached a turning point, offering a streamlined, automated process that consolidates multiple construction phases. This shift is propelled by several factors: efficiency in reducing time, labor, and material needs; advancements in specialized construction-grade materials for 3D printing; the rise of robotics and automation in precise material deposition; and a growing emphasis on sustainability. With increasing acceptance and regulatory support, now is the opportune moment to embrace additive manufacturing, transforming construction practices for efficiency, innovation, and sustainability.

3D printed Portable toilet – Nagami