Austin, a Lonely City
Context
Over the last decade, Austin’s status as a state-of-art technology hub along with its high concentration of venture apital, warm climate and vibrant cultural offerings has set the Texan city as the 2nd faster-growing U.S. city in 2022, only after San Francisco. But paradoxically , urban loneliness reflects as one of the most important issues among its citizens. While multiple social, financial and technological factors are likely to be at play, increasing evidence also suggests that rapid urbanisation might be a factor. So, to which extent is the city planning impacting the mental health of the population. Are the majority of Austinites lonely?

Urban Loneliness: Main Causes

Network of Urban Challenges
Problem Framing
The Literature review developed throughtout a selected source of references framed the scope of the problem within Austin’s built environement. The main challenges are defined across four main topics: the Housing Market, the Business Ecosystem, the Public Space and the Mobility infrastructure.
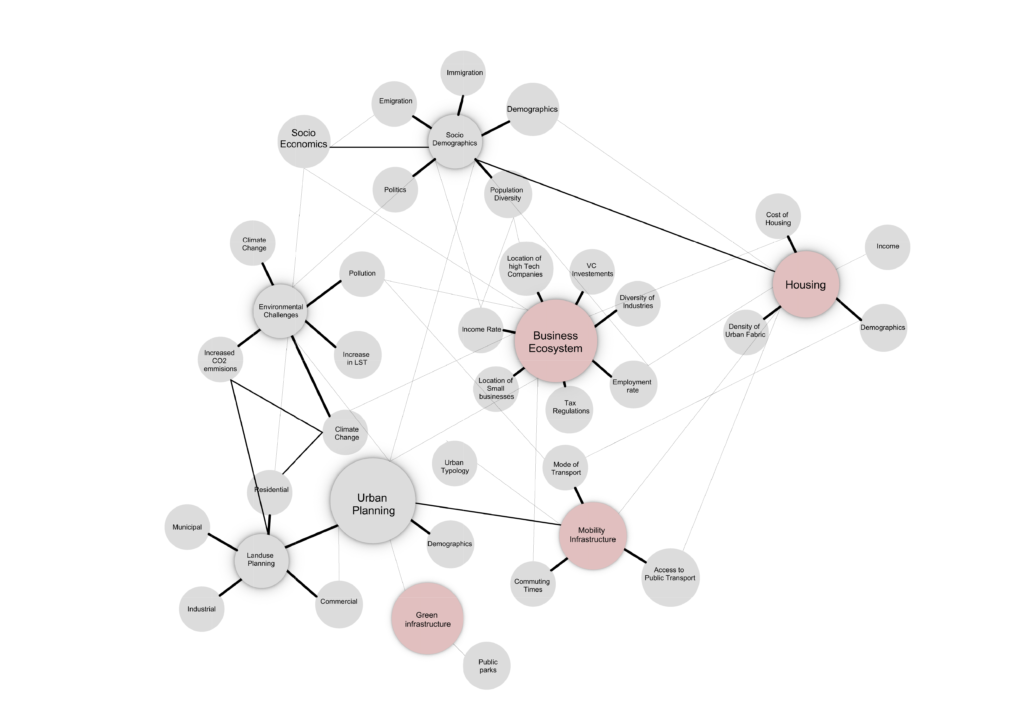
Field of Focus
Austin: Loneliness in the 2022’s 2nd fastest-growing city in U.S.
Housing Market
Business Ecosystem
Mobility Infrastructure
Public Space
Problem Definition
The project seeks to takle the urban challenges related to urban loneliness in Austin, which is specially affected by the consequences of its rapid-growing development as a new state-of-art tech hub. Considering the incured costs, a team of designers in the intersection of architecture, urban planning and city science, will develop an analytical and design model to achieve the objectives of the challenge.
Hypothesis
Implementing an urban planning strategy based on inclusivity and proximity of uses across its public infrastructure will to help mitigate unwanted loneliness among all citizens in Austin
Assumptions
1) Promoting social contact, physical activity
2) Ensure proximity and connectivity to public transport network
3) Promote community housing schemes
4) promote a healthy work-life balance
5) Ensure a community network of engagement for new employees
Measuring & Evaluating the Objectives
General Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
Across the four main categories of action, the project sets a series of general indicators according to the scope of study. Moreover, individual KPIs serve as a tool to measure particular parameters within the city

Analysis
The interaction with nature is key to develop a positive mental health. The indicator measures access to parks and open spaces, where access is defined as a 5-minute walk in the urban core, and 10-minute walk outside the urban core.
The commuting time and the used mode of transportation impacts on how residents experiene loneliness . The indicator measures proximity to the public transportation network, including bus, metro and tram, as a key factor for social isolation.
The housing market in Austin will need to be redifined as thousands of new employees arrive. The indicator measures the density of the households and the location of tech companies in order to develop policies for new schemes of affordable houses and co-living system that seek generational interaction.
Context: Austin, the new U.S.A tech city
Business Ecosystem
Comparison San Francisco & Austin
With the boom of technological companies from the ‘80s, some North American cities were determined to grow and transform themselves in hand to the demands of new businesses and their employees. The city of Austin, Texas, has become home to major companies across several industries., many of which are migrating from the Silicon Valley, SF. This labor phenomena, which establishes Austin as one of the fastest growing cities in US (U.S. Census Bureau), will put great pressure on the housing market, mobility infrastructure, work-life balance among other sectors. Indicators such as the employment rate, the income rate, and the diversity of industries and high education centers will help to measure the impact.
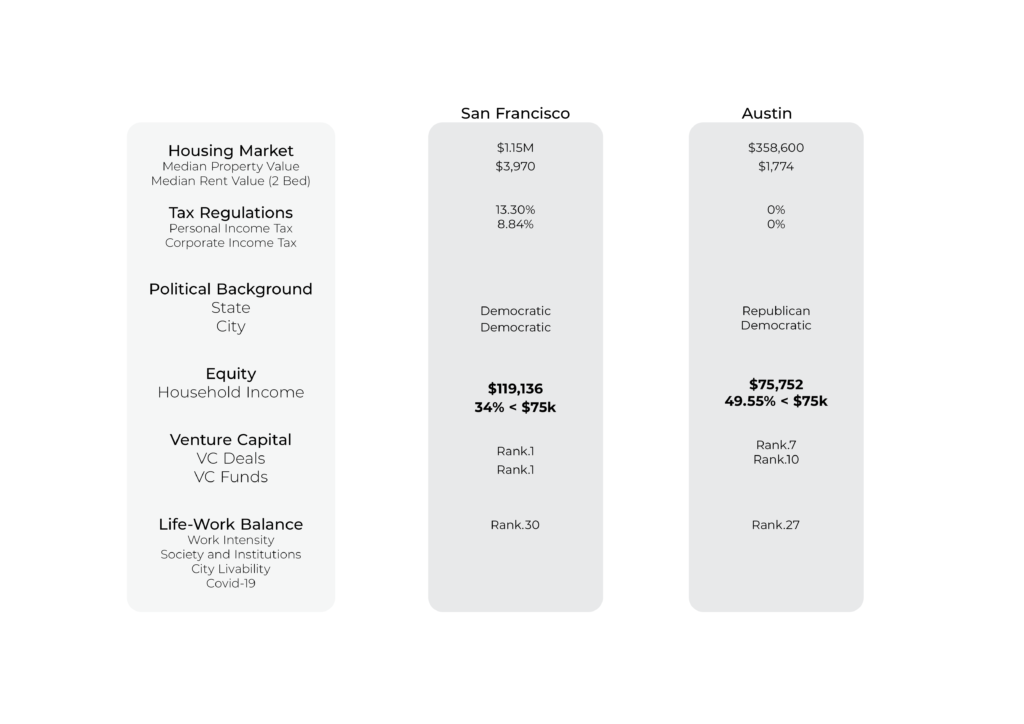
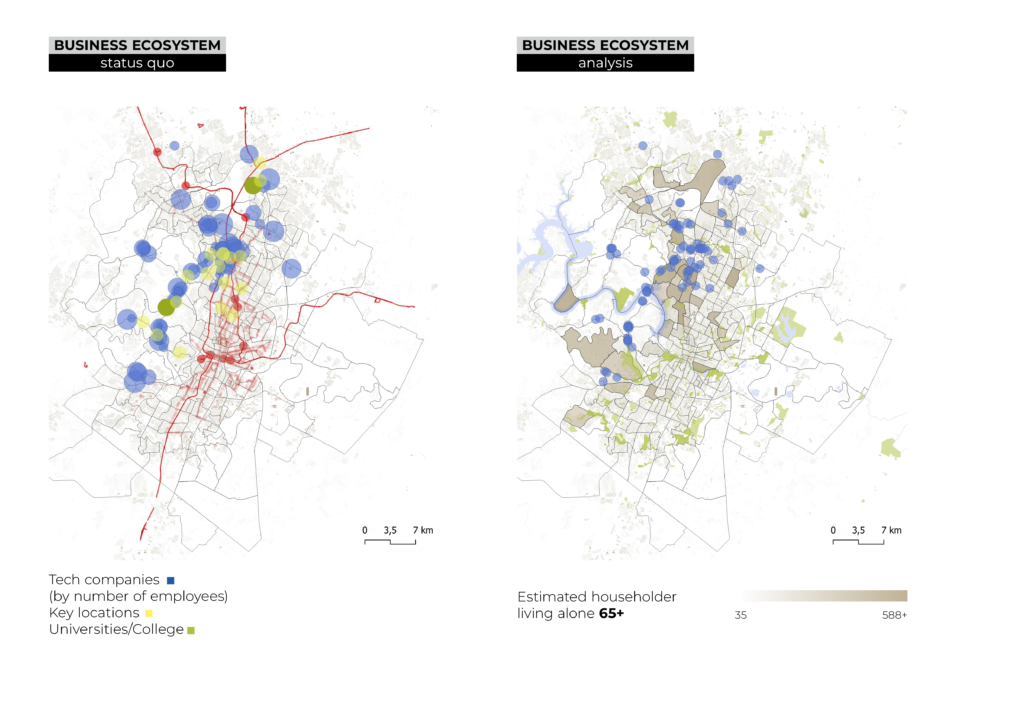
The arrival of creative industries will strengthen both the business and the academic/educational ecosystem. The indicator measures the relationaship between employment rates, income rates and diversity of universities that will improve the work-life balance and therefore the city transience among new residents.
Papers and Articles:
Okkels, Nielsa; Kristiansen, Christina Blannerb; Munk-Jørgensen, Povlb; Sartorius, Normanc. Urban mental health: challenges and perspectives. Current Opinion in Psychiatry 31(3):p 258-264, May 2018. | DOI: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000413
Hammoud, R., Tognin, S., Bakolis, I. et al. Lonely in a crowd: investigating the association between overcrowding and loneliness using smartphone technologies. Sci Rep 11, 24134 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-03398-2. https://rdcu.be/c4aHD
Mari, Jair; Galea, Sandro. Editorial: Cities and population mental health: present and future. Current Opinion in Psychiatry 34(3):p 275-276, May 2021. | DOI: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000703
Matthews. K. Understanding the Unique Challenges of Urban Loneliness.Planetizen Blogs
Kenan Institute of Private Enterprise. 2022’s Fastest-Growing Cities. https://kenaninstitute.unc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/american-growth-project-10172022r.pdf#page=5
People feel lonelier in crowded cities – but green spaces can help. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/01/lonely-study-green-space-city/
Austin Reaches Top 10 In US Venture Markets With Record Funding In 2019 https://news.crunchbase.com
Is Austin Emerging as the New American Technology Hub? Austin https://www.cmswire.com
Silicon Valley Is Flooding Into a Reluctant Austin https://www.bloomberg.com/
Geospatial Data (GIS and CSV):
Texas Open Data Portal https://data.texas.gov/
United States Census https://data.census.gov/
Data USA https://datausa.io
Office of the Texas Governor https://gov.texas.gov

