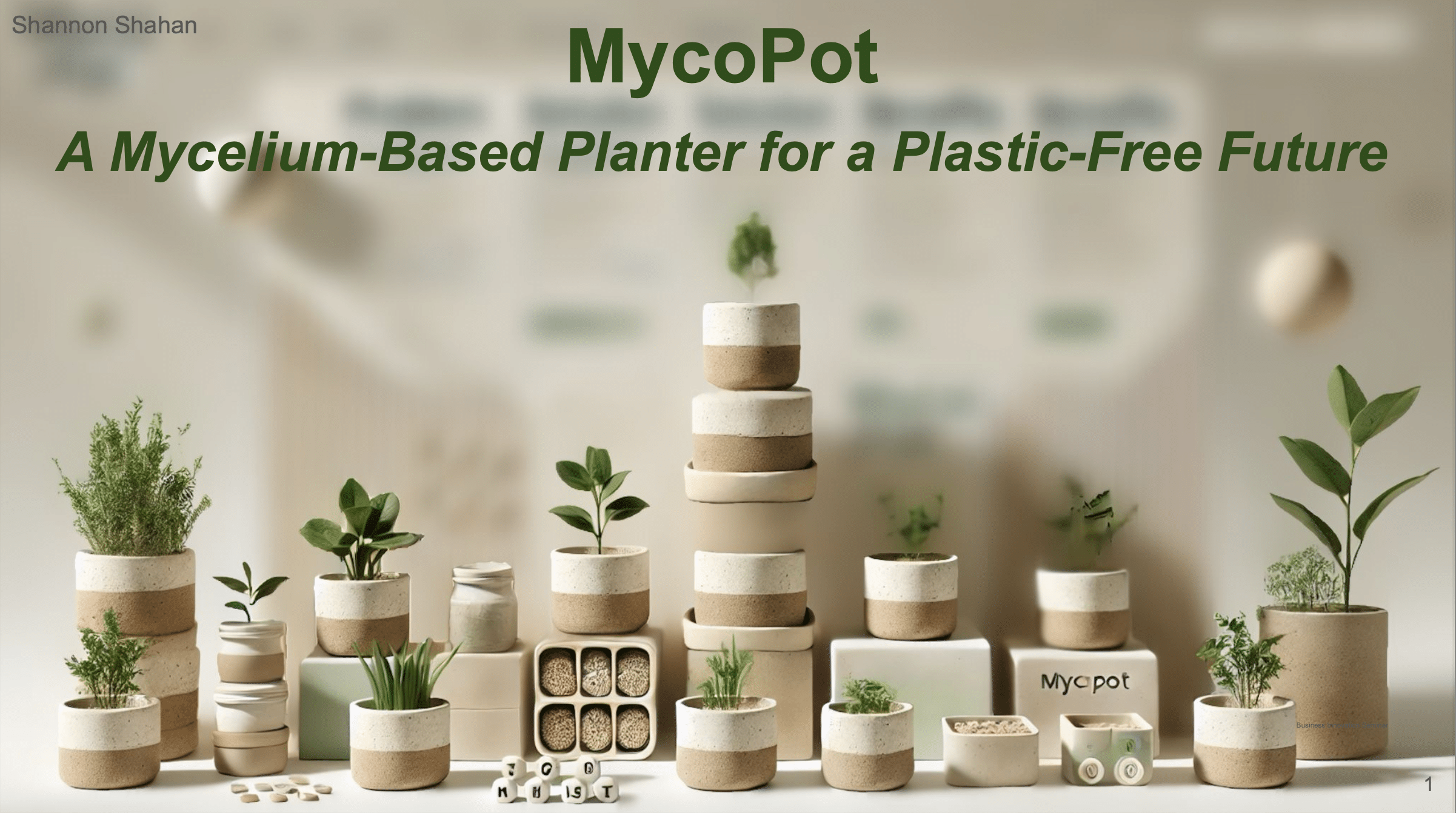
MycoPot: A Mycelium-Based Alternative to Plastic Plant Pots
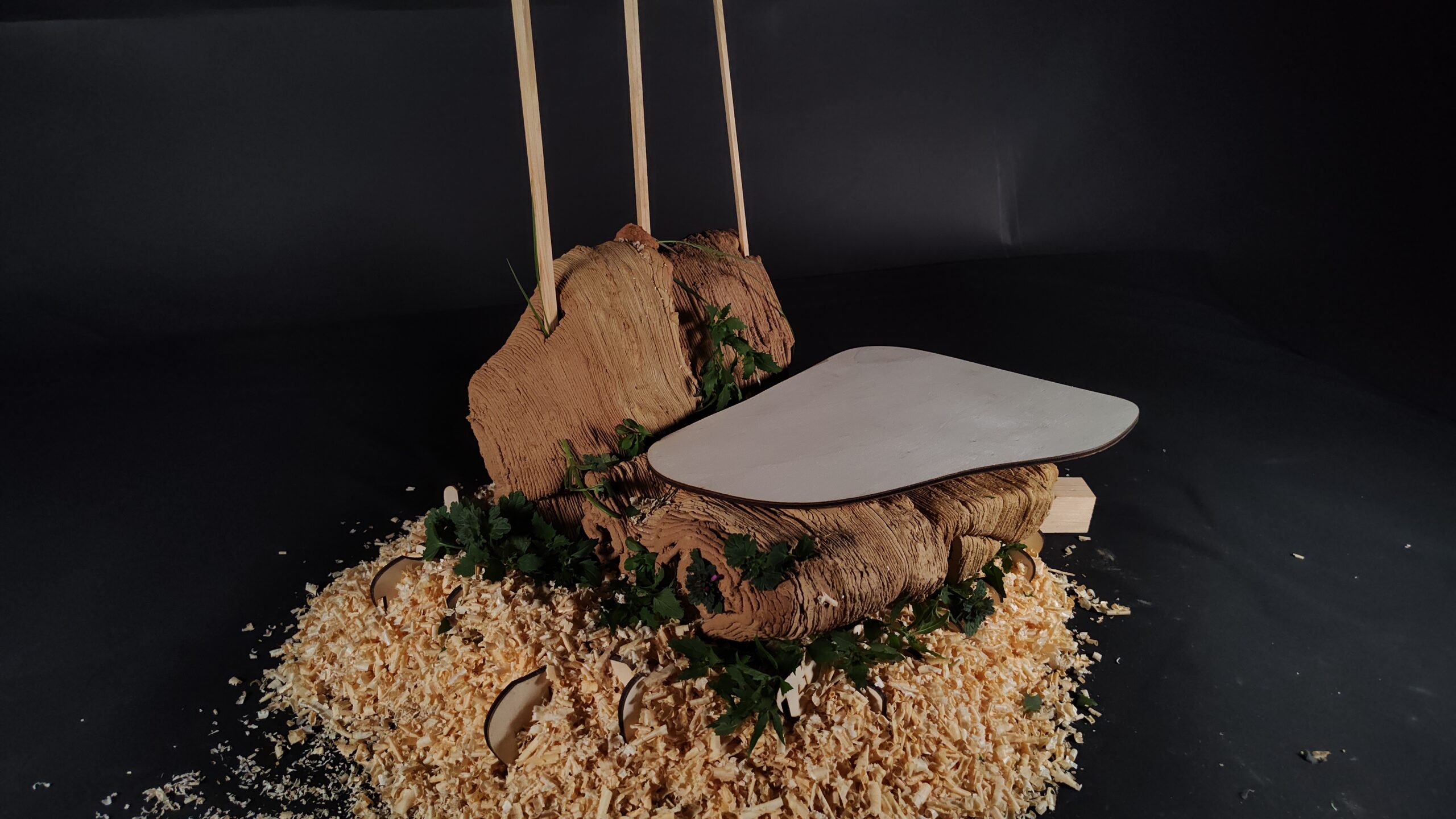
MycoPot is a biodegradable planter grown from mycelium and agricultural waste, designed to replace the millions of plastic pots discarded every year by nurseries and plant retailers. It offers a practical, scalable, and regenerative material solution for the horticulture industry—one of the most overlooked contributors to plastic waste. Why We Started: The Problem Across Europe, … Read more