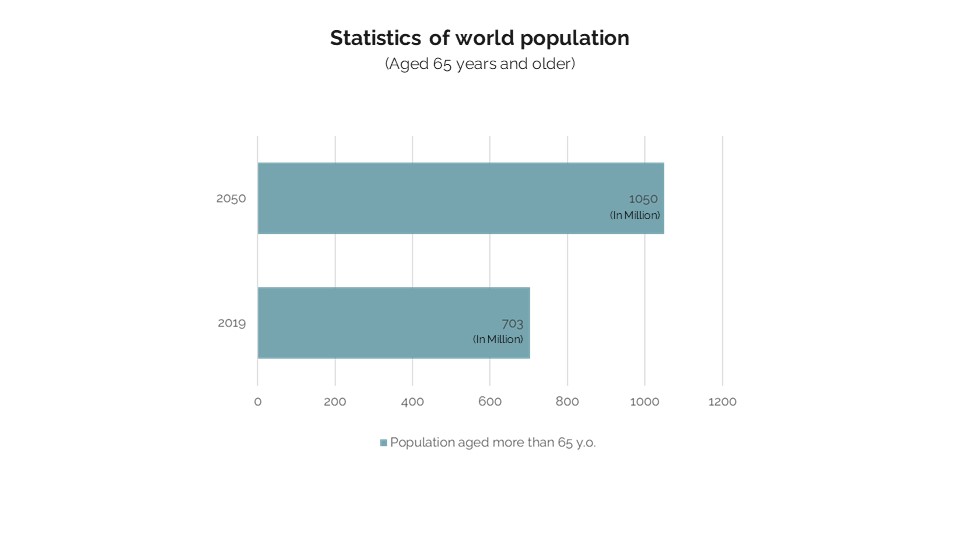
Ageing population is increasing around the world, many of the European countries and Japan, . The above graph shows the number of the population 65 years old and over people in World. In 2019, the total aged population was 703 million people and the projected population suggests that in 2050, it will be over 1050 million aged people. Projections also indicate that more than 79 percent of the world’s population will be living in the developing regions.
Aging is inevitable, and the world’s population is rapidly aging!

What is “Aging”?
At the biological level, aging results from the impact of the accumulation of a wide variety of molecular and cellular damage over time. This leads to a gradual decrease in physical and mental capacity, a growing risk of disease, and ultimately death. These changes are neither linear nor consistent and are only loosely associated with a person’s age in years. Beyond biological shifts, aging is often associated with other life transitions such as retirement, relocation to more appropriate housing, and the death of friends and partners. (Source- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health)
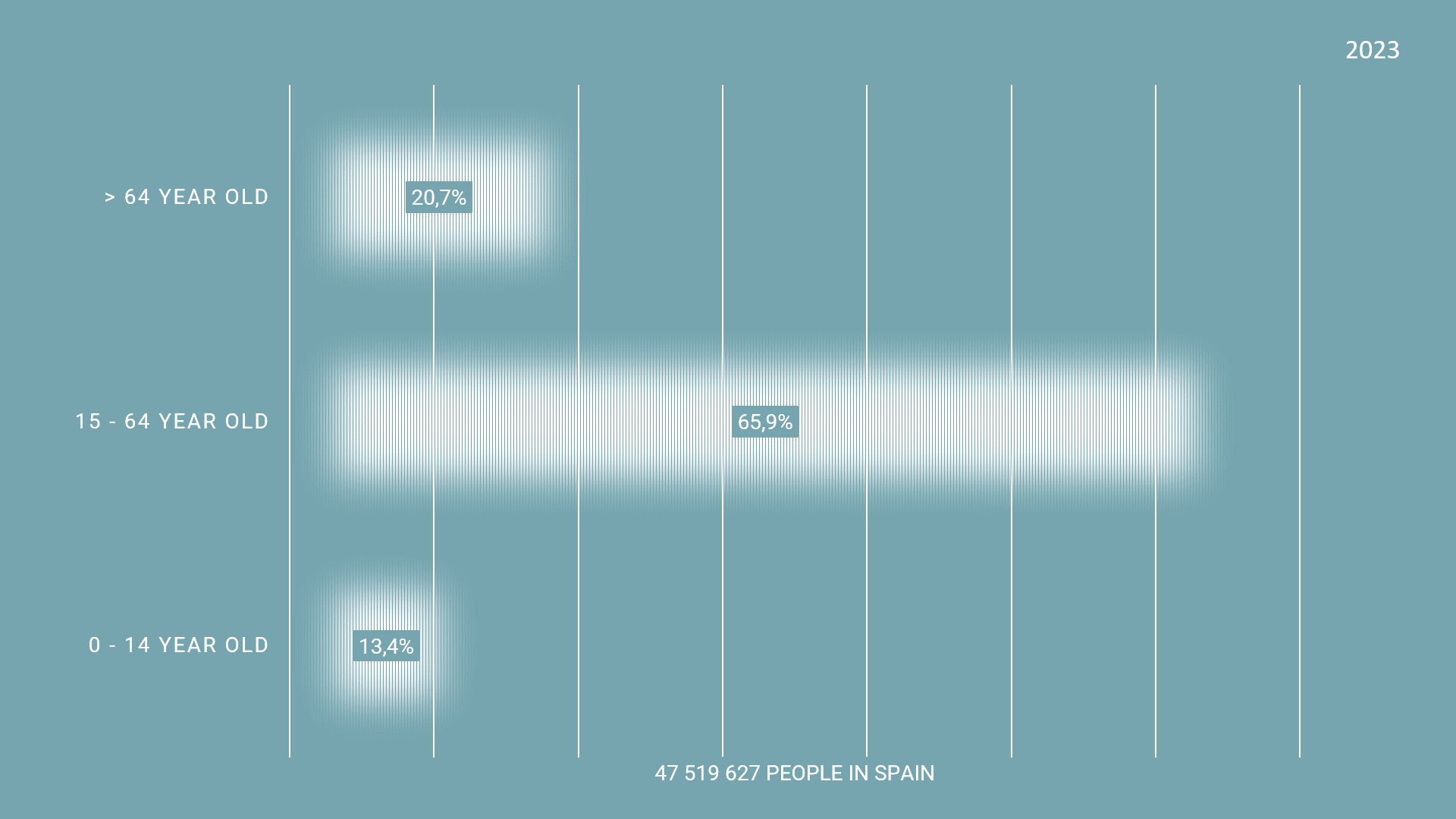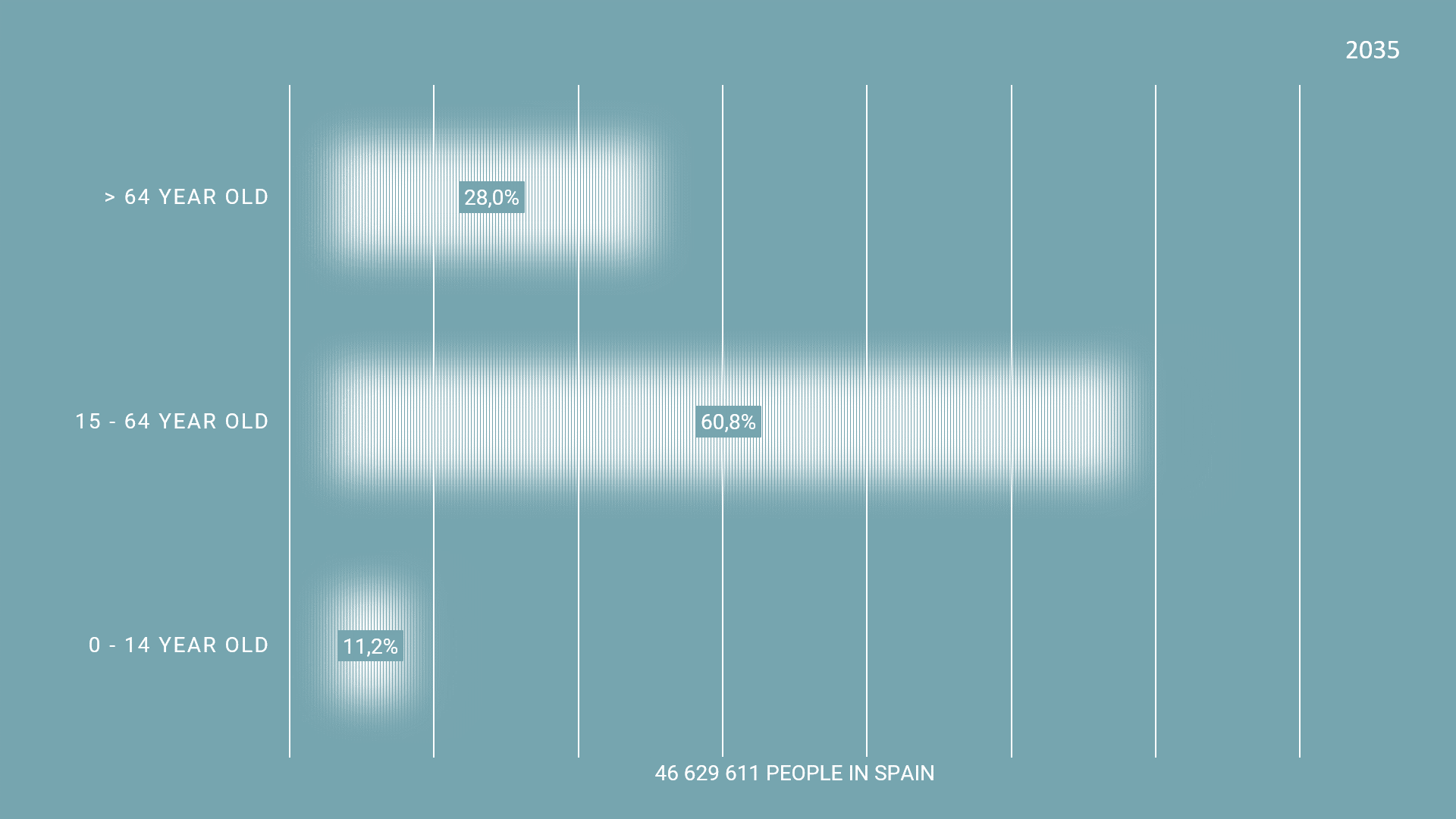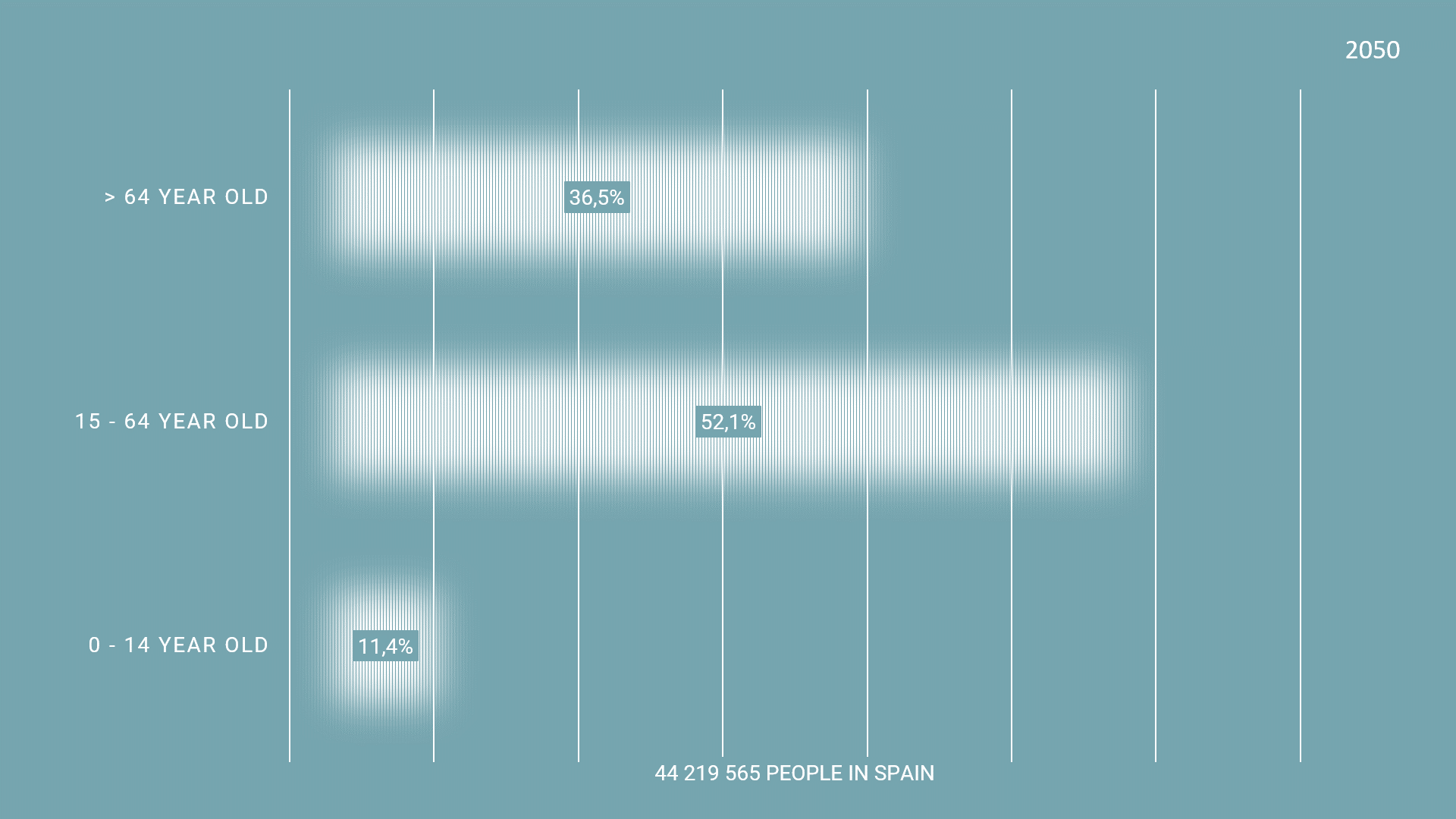
The graph shows the ratio of population in Spain. In 2023, the population of over 65 years old people is 20.7%. the projected population is 28.0% in 2035 and 36.5% in 2050. These statistics of the current population of 65 year old and older indicate that there needs to be a reformation in the urban policies to provide for the increased needs of the older population.
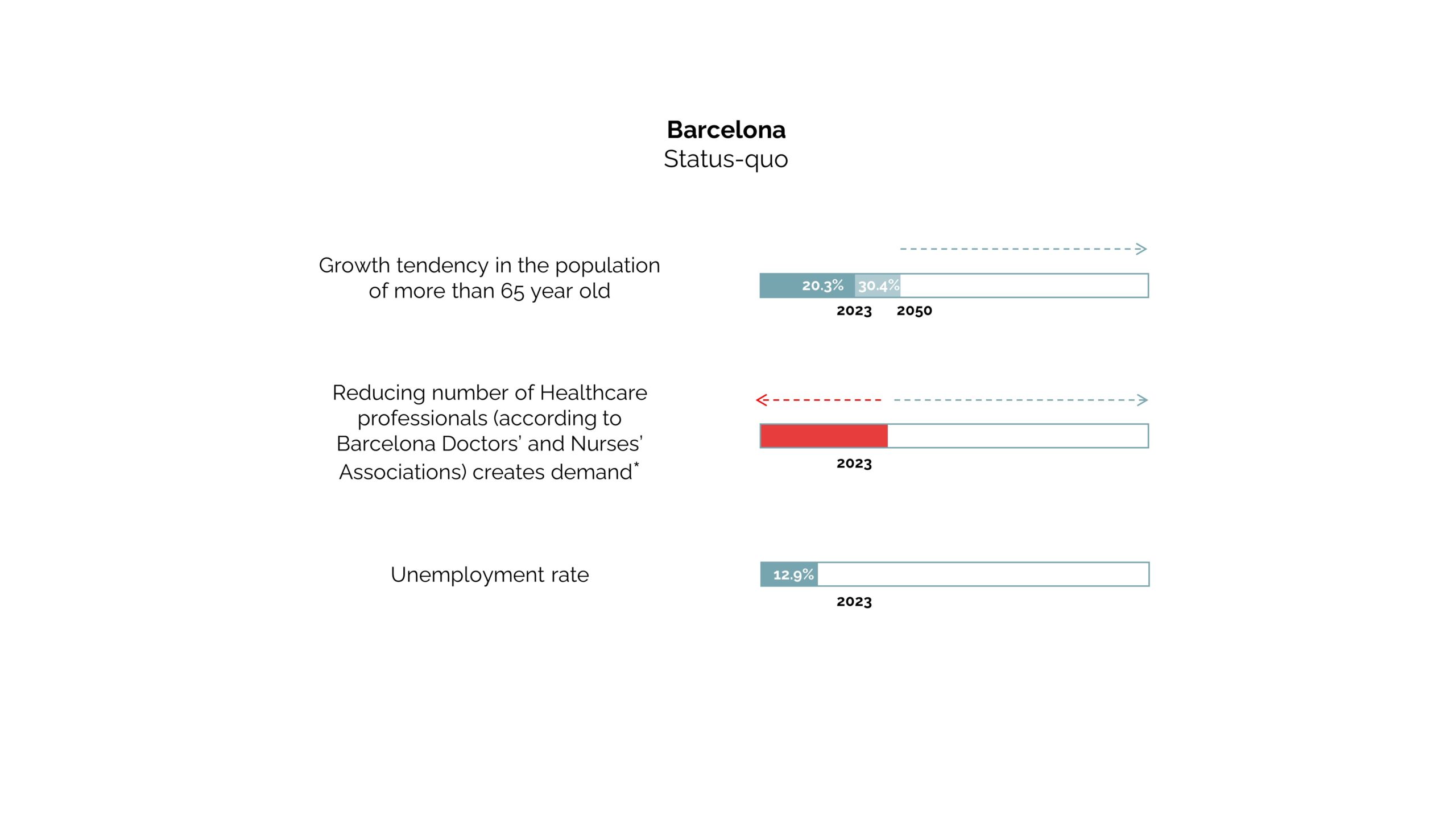
The rising gap of the increasing aged population between the current and the projected population in Barcelona, the reduced number of Health care professionals, the increased growth in the demand for the healthcare professionals indicates the areas of challenges for the possible policy proposals and reformations. A probable speculation is how the increased growth in the unemployed population could potentially be involved in addressing the increased needs of the older population. The further assessment of the same is done below.
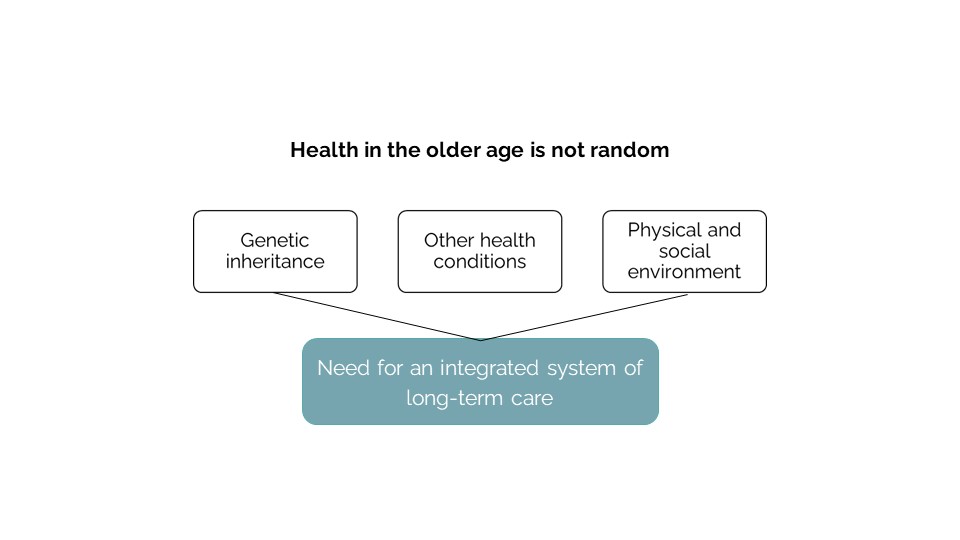
Health in older age is not random. three are many factors influencing the ageing which are – “Genetic Inheritance”, “Other health conditions” and “Physical and Social environment”. We need an integrated system of long-term care as prevention.
Spatial Analysis
Hospital Accessibility
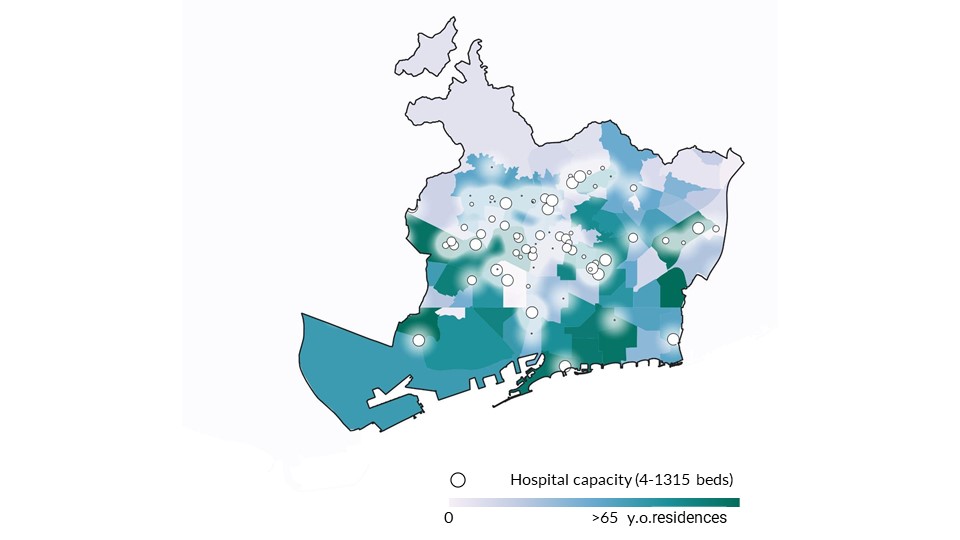
The above heatmap represents accessibility for an ambulance of 5-10 minute from the hospital with hospitalization possibility to the patient’s house as well as 15 min walk of a 65 year old. The distance for a person from home to the hospital (1 km), it does not cover all areas of the city, which can lead to inconvenience in walking distance and even a lack of emergency assistance in some parts of the city for the project age group. Nevertheless, these neighbourhoods of the city have an isochrone of 5-10 minute in the dense elderly people population areas.
Parks and recreation zones’ proximity
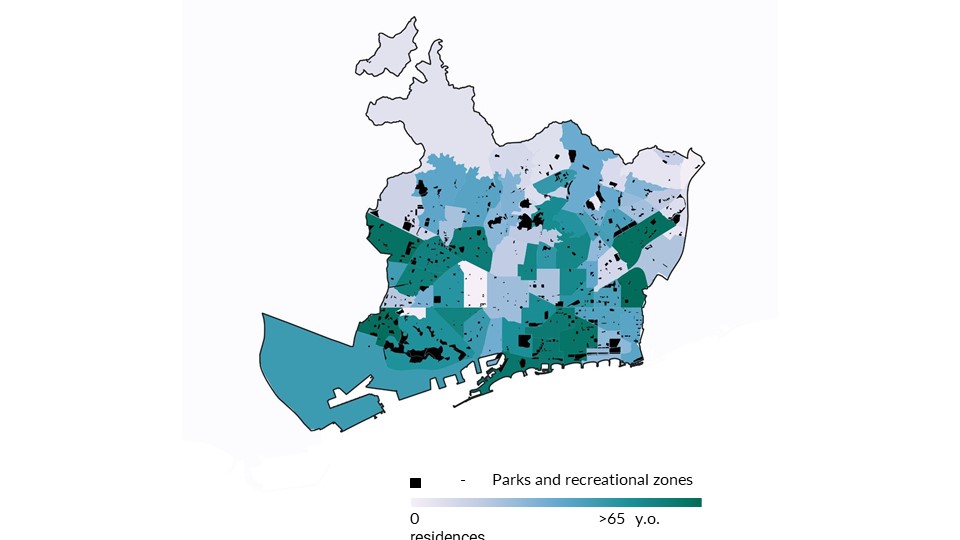
The map shows the density of the older population in different neighbourhoods overlapped with the green areas of the city. It is observed that there is a lack of parks and recreational zones closer to the residences of 65-plus-year-old citizens in the central part of the city.
Unemployment rates + elder people’s residences
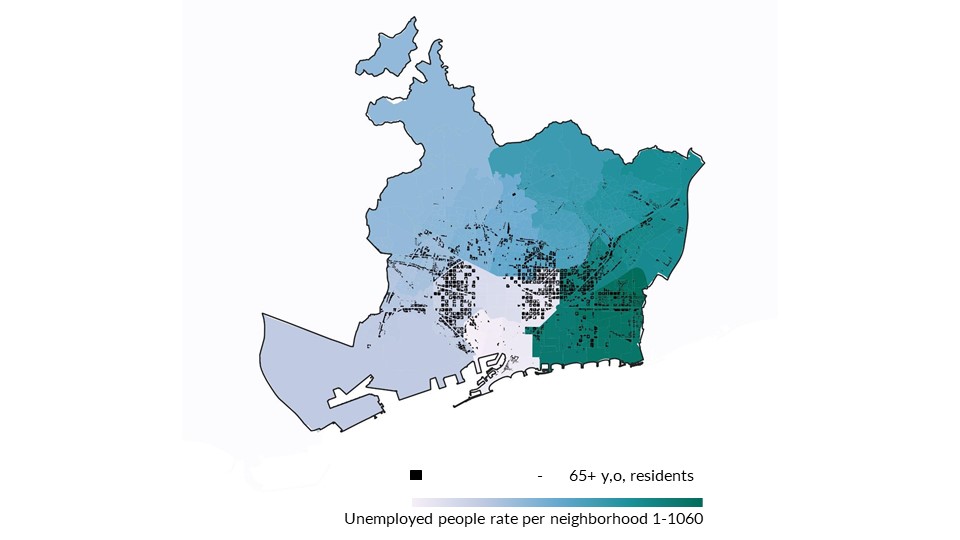
The map represents the unemployment rates in different districts with darker gradient shades and the houses in black where mostly old people live. These areas are identified to correlate the location of where the elderly people live in the city and this is used to find a strategy to enhance unemployment in the regions of low employment in the provision of health care facilities.
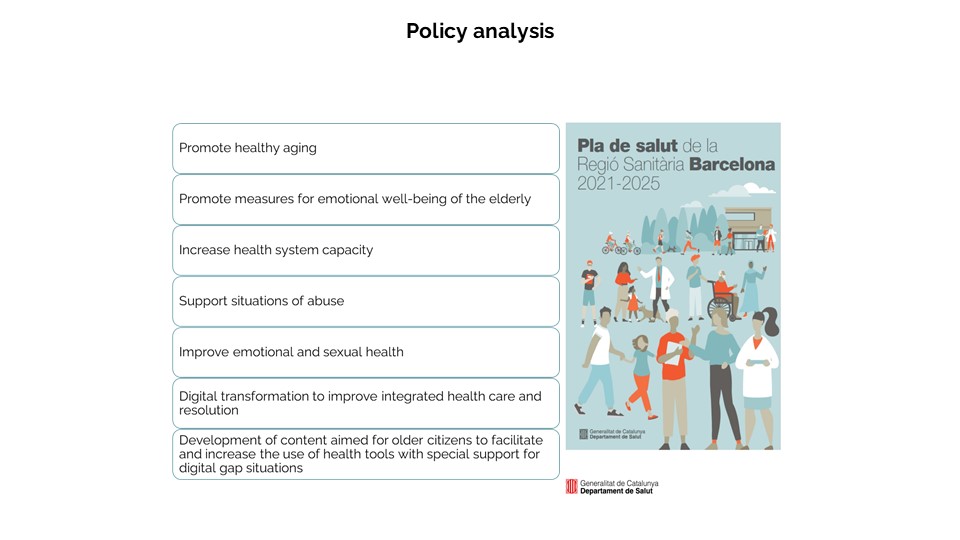
The existing policy of Barcelona for the health sector has several policy proposals and guidelines to promote active and healthy ageing for the elderly. Some of the key policy highlights are to promote healthy ageing, to promote measures for emotional well-being of the elderly, to increase the capacity of the health system, to support the situations of abuse, to improve emotional and sexual health of the elderly, to bring in digital transformation to improve integrated health care and to develop content aimed at the elderly to facilitate and increase the use of health tools with special support for digital gap situations.
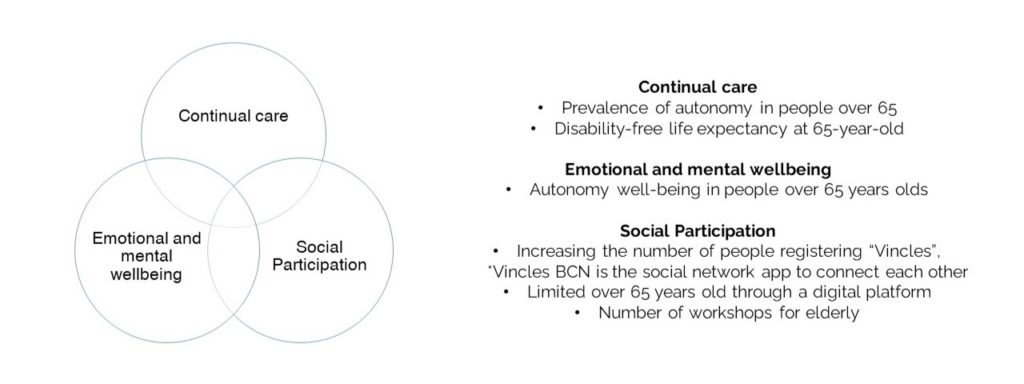
Stakeholders
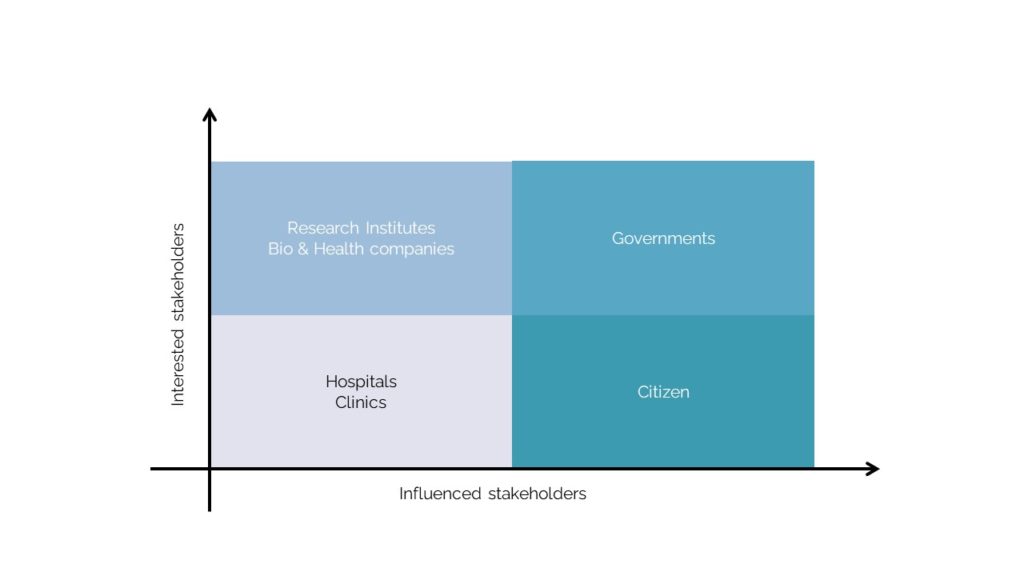
We set these stakeholders for our policy.
Governments
?Barcelona City Council
?Generalitat de Catalunya
Citizen
?Elder people
?Unemployment
Bio & Health companies and Research Institutes
?335 Biotech
?126 Pharmacy
?228 Meditech
?200 Professional Services Consulting
? 41 Research Center
? 19 University
Hospitals & Clinics
? 72 hospitals with beds
?4478 usual & technical clinic
The most Interested and Influenced are Government bodies. They can make new policies and take action for citizens. For citizens, the policy is more influenced but on the surface, and hence they aren’t a stakeholder as interested as the government entities, the health sector and the Bio-Industry that includes the R&D centers. We hope for the policy and the system to become a base system for citizens. For tech companies and Institutes, the data is important. And lastly, hospitals and clinics are involved in exchange and sharing of information, but as the points of interest and influence, it has less relativity.
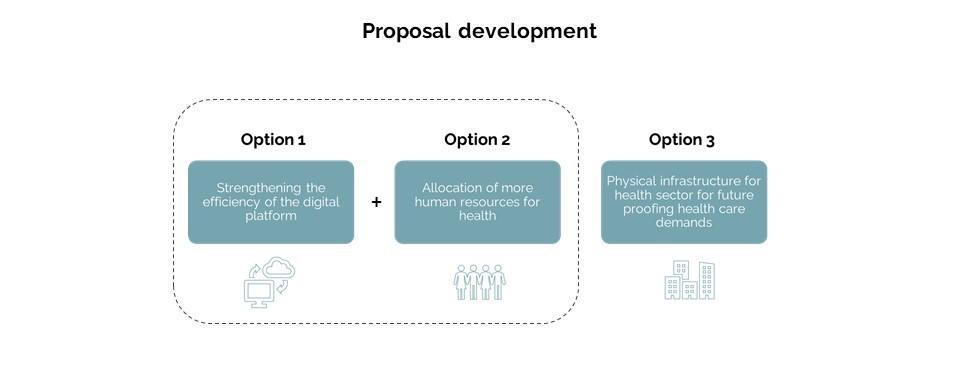
The proposal for the policy development has been narrowed to three options with the reformation existing policies proposed by the city council for the elder population and it addresses-
Option 1: Strengthening the efficiency of the digital platform
Option 2: Allocation of more caregivers for providing more health services
Option 3: Allocation of additional physical infrastructure for future-proofing healthcare demands.
From the map above which shows the proximity and assesses the accessibility to the hospitals from each of the neighbourhoods, it is seen that Barcelona has a well connected network. Although the need for physical infrastructure is obligatory for the areas that lack it, those regions have low elderly occupancy and with the development of the digital infrastructure, which is more economical and ecological, it is an aim to connect the missing ties and an aim to strengthen the existing health sector. The working of the digital system, it’s benefits and costs, the direct, indirect and the intangible costs, are further on elaborated on how the new addition of digital network would make it a holistic system and more integrated. The possibility and working is estimated based on the strategy assessments. The second strategy which is to bring in the allocate more human resources or the care givers is to involve the unemployed population. With the advent of the progress in technology, AI is said to take over many jobs, which suggests the projected population of unemployed people to increase quite dramatically. On the other hand, the elderly people would want the provision of care from a human which would make them feel an additional sense of security.
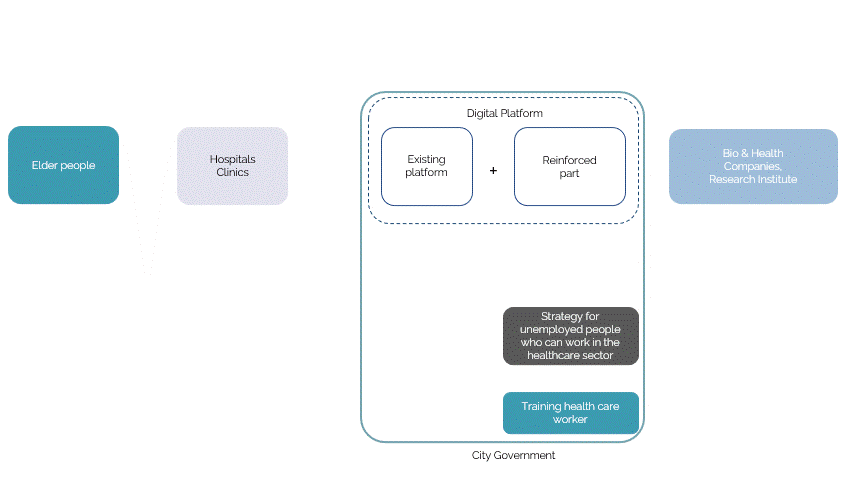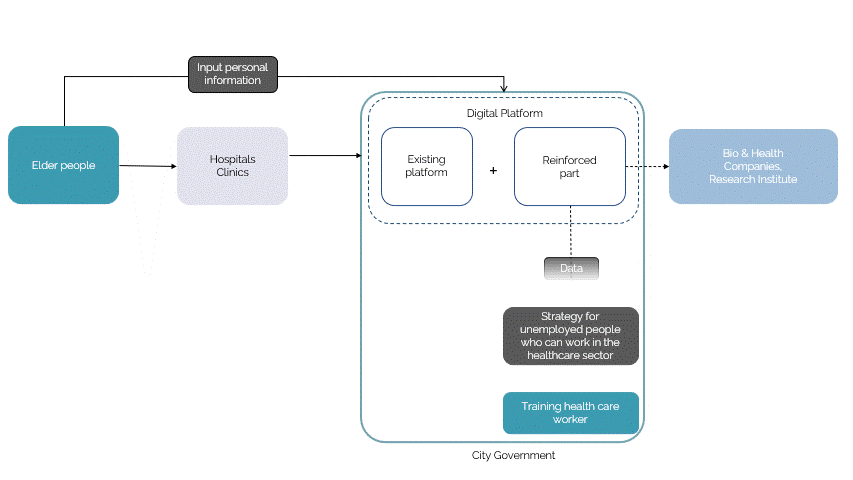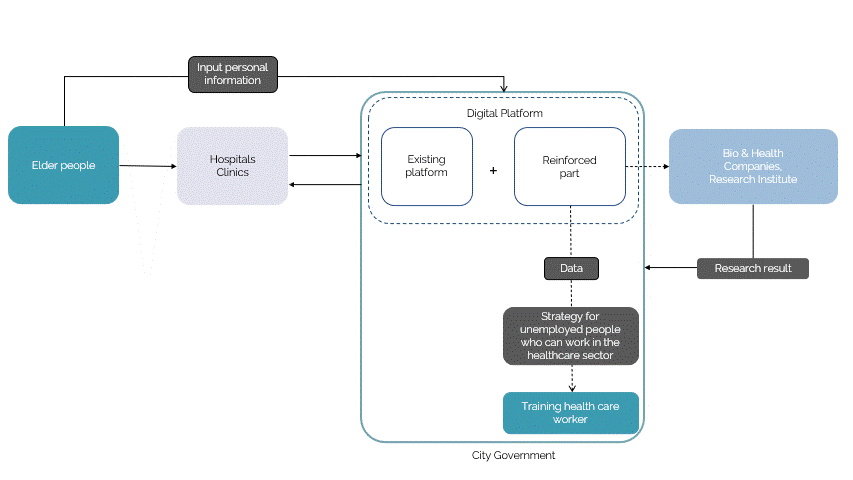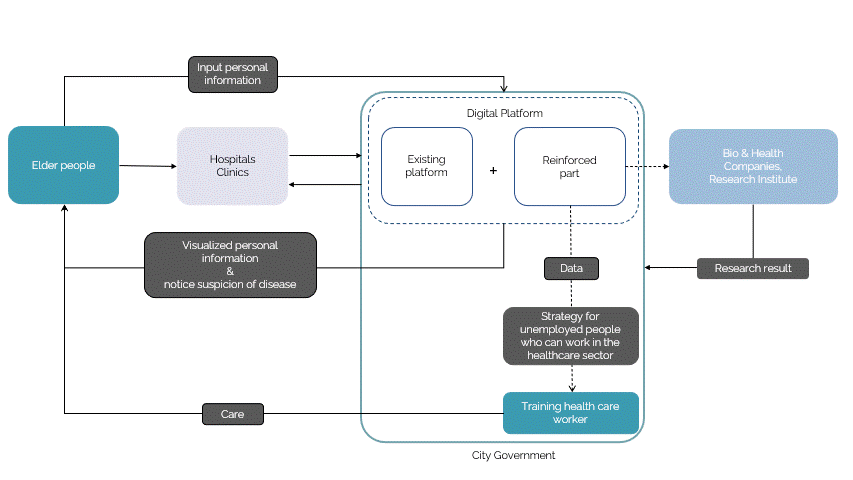
The digital platform is developed to be at the service of the elderly to provide immediate care. The strategy development is based on the continual system of a loop in which, the digital platform is fed existing information on the healthcare system as a tool to categorize the data collected from the elderly as and when the app is being used and this data will then be used in developing the platform with a machine learning algorithm to further provide the elderly with the necessary tailored care. Additionally, the app also hosts people who are unemployed, who could train from the software of some of the healthcare services to get a certification that could qualify them to serve the elderly.
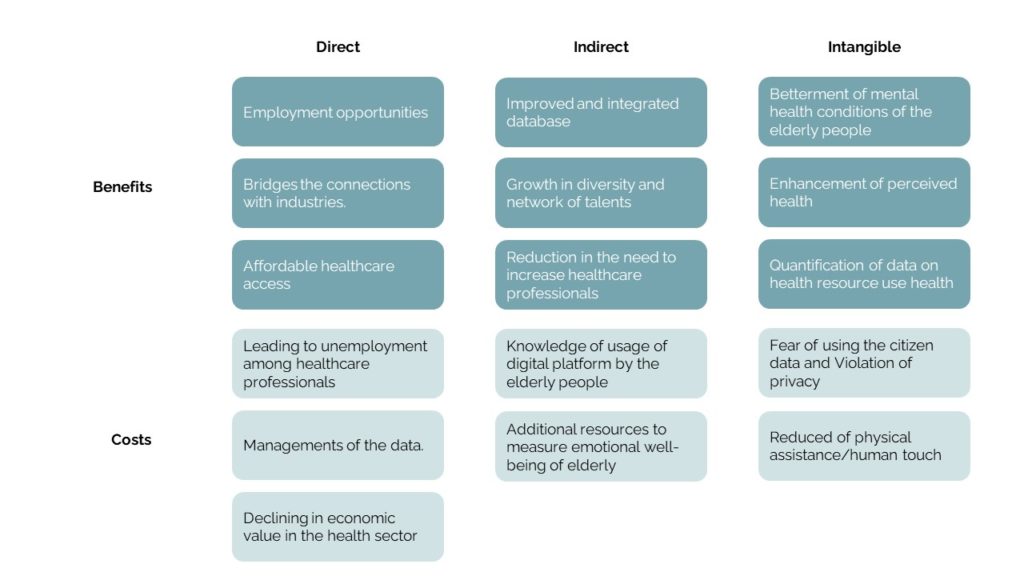
The main direct benefits of enhancing the digital system is the provision of quick and affordable healthcare access addressing the demand and enhanced employment opportunities. The noticable cost which comes with it is the management of the data and need to regularly update the digital health system model. The indirect benefits of the development of the policy is the enhanced growth in the network of talents which helps with development of the system to be more integrated and holistic in terms of management of the database. The indirect costs that come with it are the need for additional resources to measure some of the qualitative data. The intangible benefits include enhanced perceived health (present statistics indicated a low perceived health among the elderly, especially the women), betterment of mental health and some of the intangible costs include reduced physical assistance and violation of privacy.
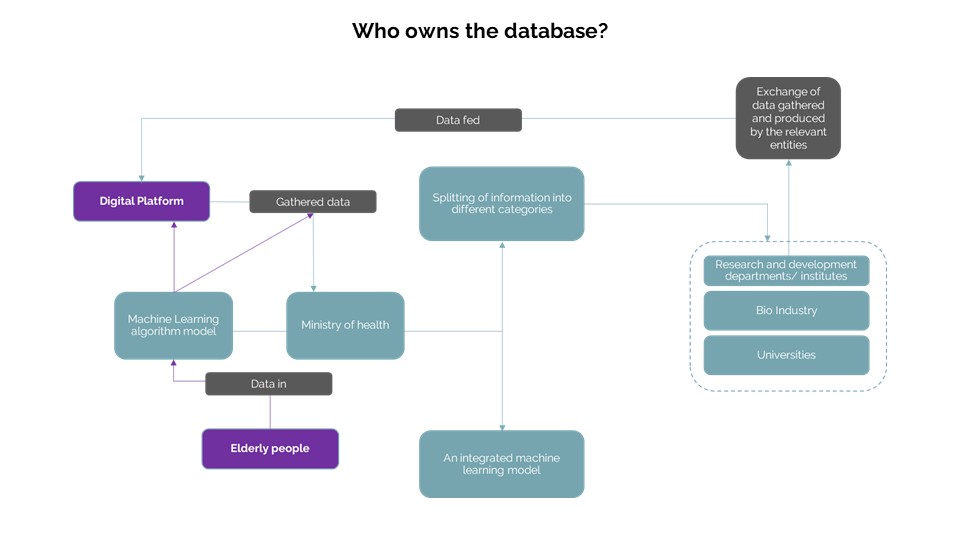
To further develop the digital system, the gathered data from the elderly could potentially be owned by the Ministry of Health department and the information can be categorized by them and have the provision of sharing limited information with the general public and the other organizations who would help with developing the system. This way, there is no breach of privacy of information acquired from the people and information is shared securely across various sectors. The machine learning algorithm can further develop the predictions and assessments from the data produced from the other organizations and research and development departments.
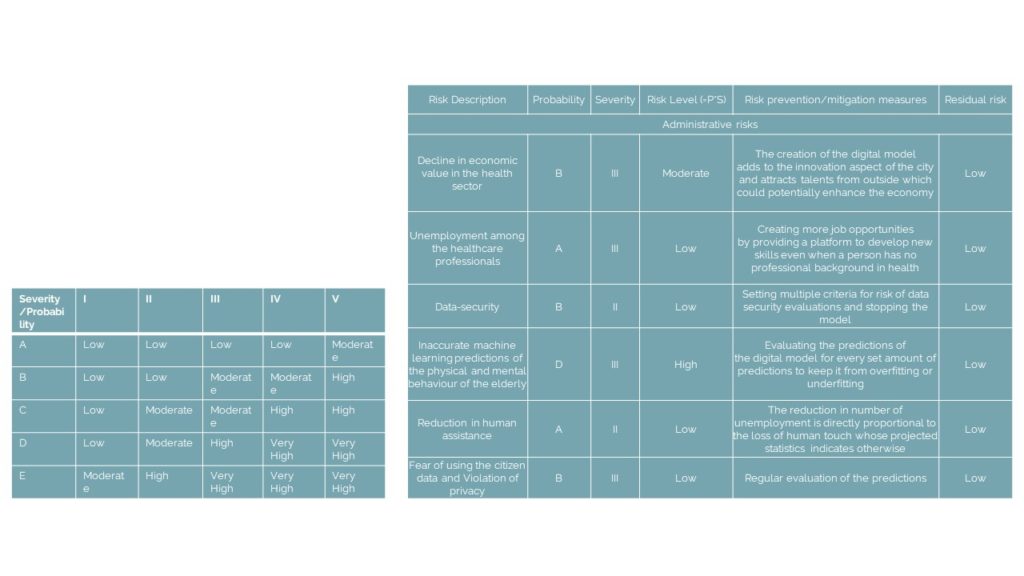
Overall understanding of the top risks and their probability and severity to better understand the risk level and how it can be prevented and the necessary measures that can be taken to have a low residual risk is assessed in the above table. To evaluate the same, some of the risks considered for the proposed policies are- the decline in the economic value in the health sector, unemployment among the healthcare professionals, data- security, inaccurate machine learning predictions, reduction in human assistance, violation of privacy and management of citizen data. The risks range between moderately low to high, and the measures proposed to mitigate same are based on how the digital system can be continually evaluated to remove the biases in the algorithmical model. The policy is designed such that the potentiality of the connecting the different health sectors with bio industry is enhanced to boost the economic sector. The unemployment population is well trained to be hired as a adequate professional to address the elderly. These risk factors from the digital platform are majorly addressed from regularly updating and evaluating the system.

