THERMAL QUESTIONS:
Q1. Having studied the sun path diagram, it is observed that there are low sun angles in the east and the west throughout the year. How can thermal heat gain be prevented from the east and the west direction?
– To prevent the heat gain from the lower angle of the sun from the east and the west, there is a 2m wide patio created along the side of the structure and fenestrations have been provided to block out the heat and insulation is provided on the facade.
Q2. How can the design tackle the perpendicular radiations and heat gain?
– the design uses large overhangs, breathable roofs, insulated surfaces and patios to avoid heat gain. Additionally, through good natural ventilations, the heat and humidity is taken out of the spaces which aid in cooling and heat loss.
QUESTIONS THAT GUIDE THE ANALYSIS THROUGH THE USE OF ADVANCED DIGITAL TOOLS:
Q1. What is the percentage of Glazing for the East and the West ?
Q2. Understanding the shading through overhang context to Optimize cooling loads.
Q3. How can vertical louvers and fins help and facilitate thermal heat loss and prevent thermal heat gain for the project?
Q4. What can be done through Natural ventilation to help with cooling and avoid heating?
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS:
This analysis helps understand the temperatures of the building keeping in mind the context, the shading and the cooling of the structure. This analysis gives us the required values to design the windows and the openings on the facade.
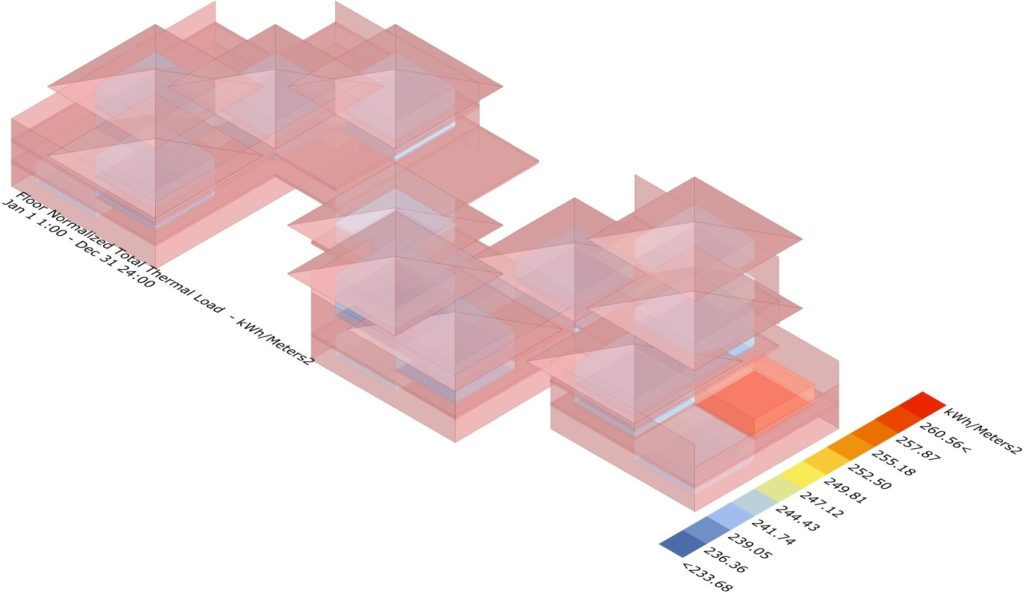
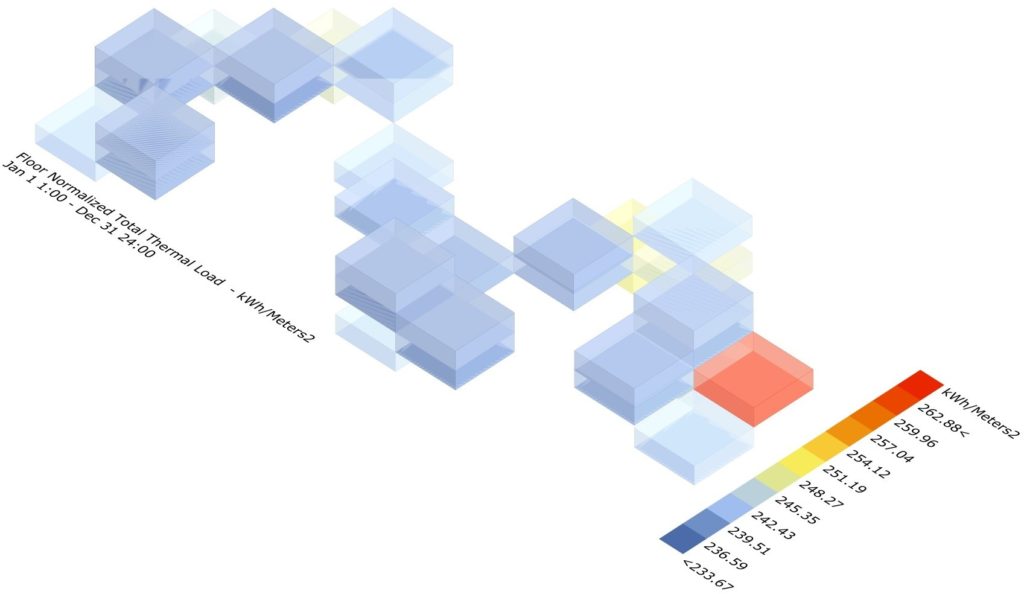
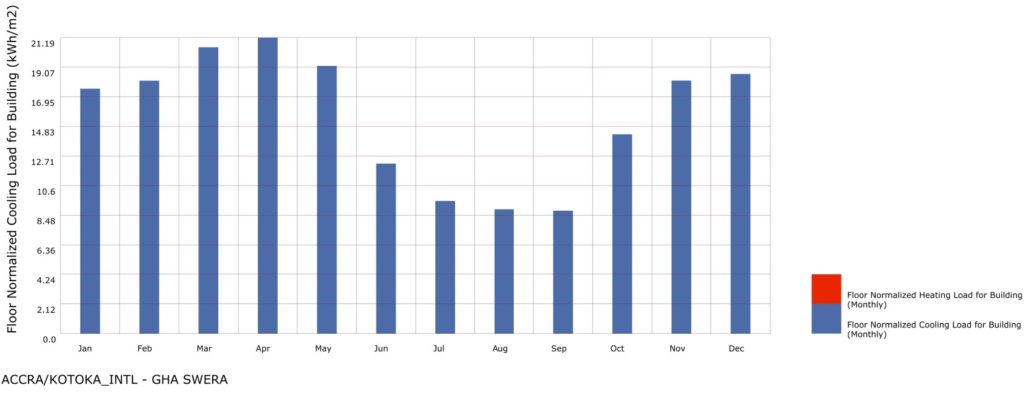
Even though the temperatures remain relatively constant in Accra, Ghana, the graph shows different values across the year as the angle of the sun on the structure, the intensity of the angle and the orientation of the building impact the overall heating in the structure.
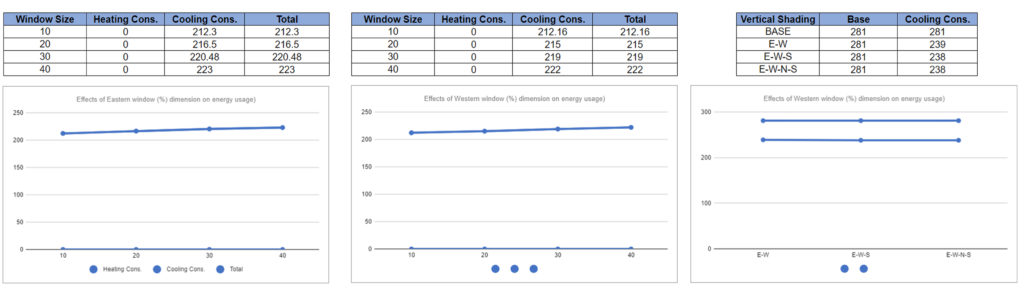
Through the analysis we can see that the double facade and the fenestrations provide the required shading for the massing and in doing so bring down the cooling load in the structure significantly. Additionally, the design requires high cooling loads and no heating loads as the site is located in the tropical climate which is hot and humid in nature.
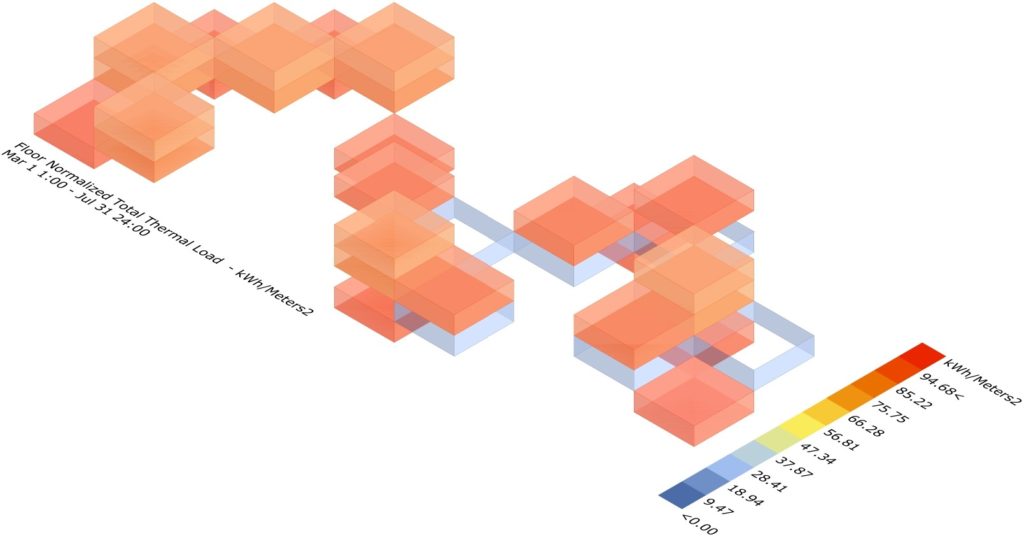
ENERGY ANALYSIS:
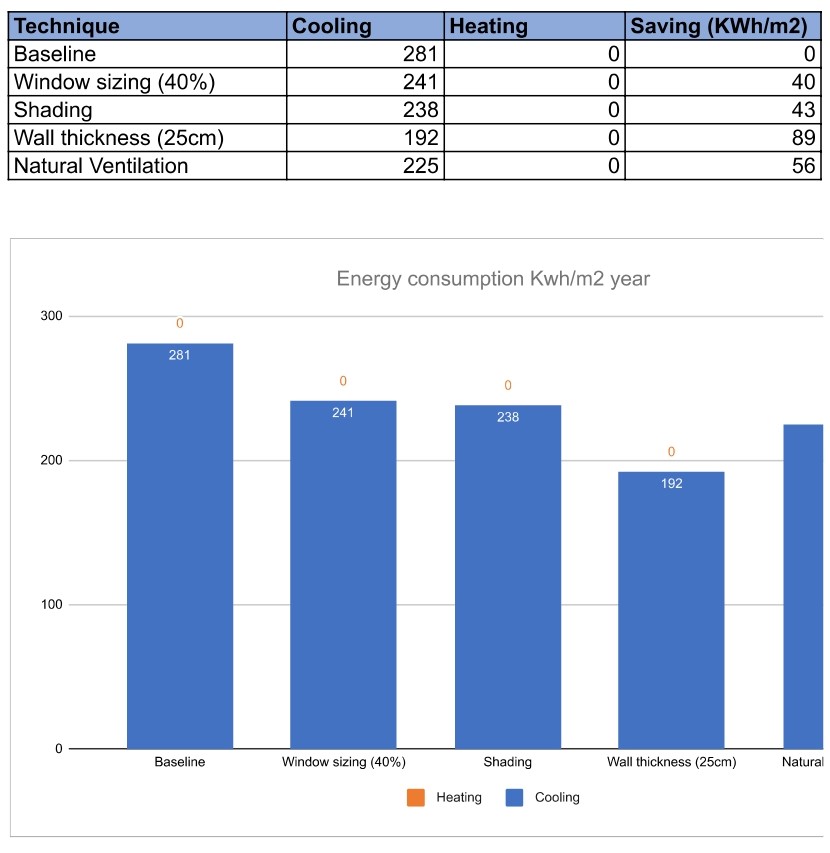
For our design, Natural Ventilation plays a significant role in cooling the structure down and the analysis does not reflect in the graph and as a result the analysis is not accurate for our design. Hence, this led us to do a microclimatic analysis to better understand how ventilation works on our design.
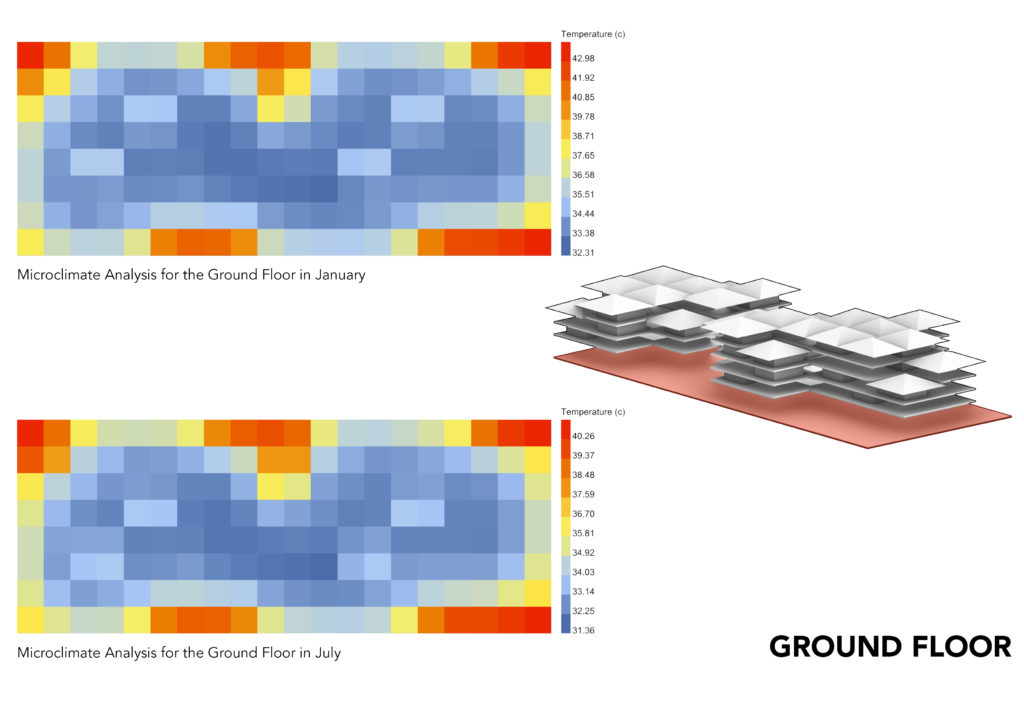
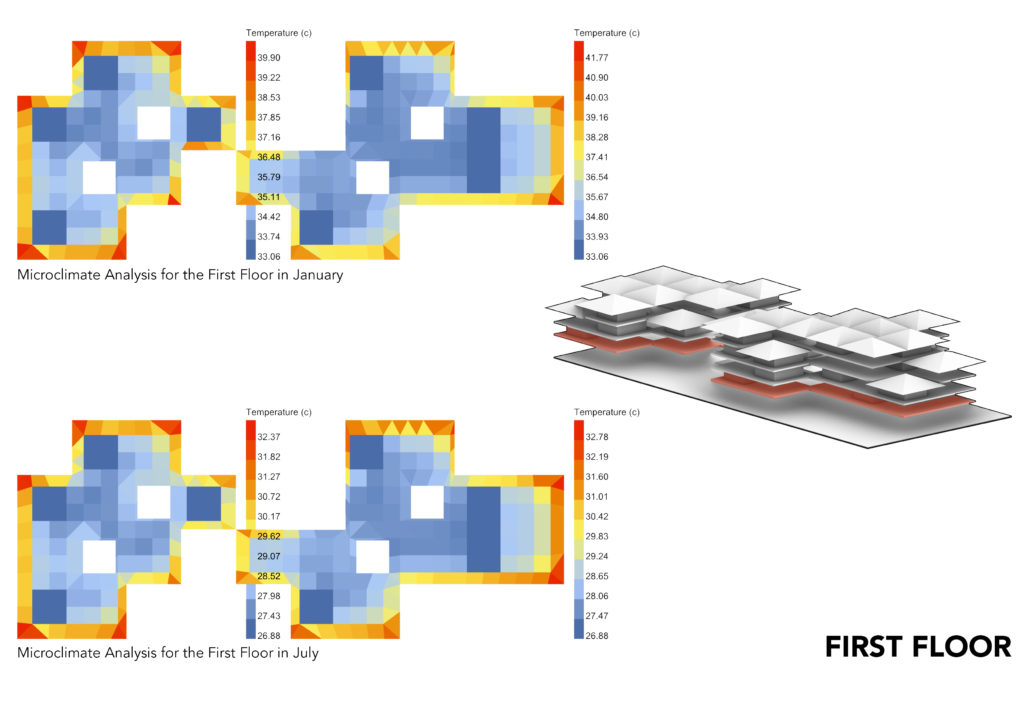
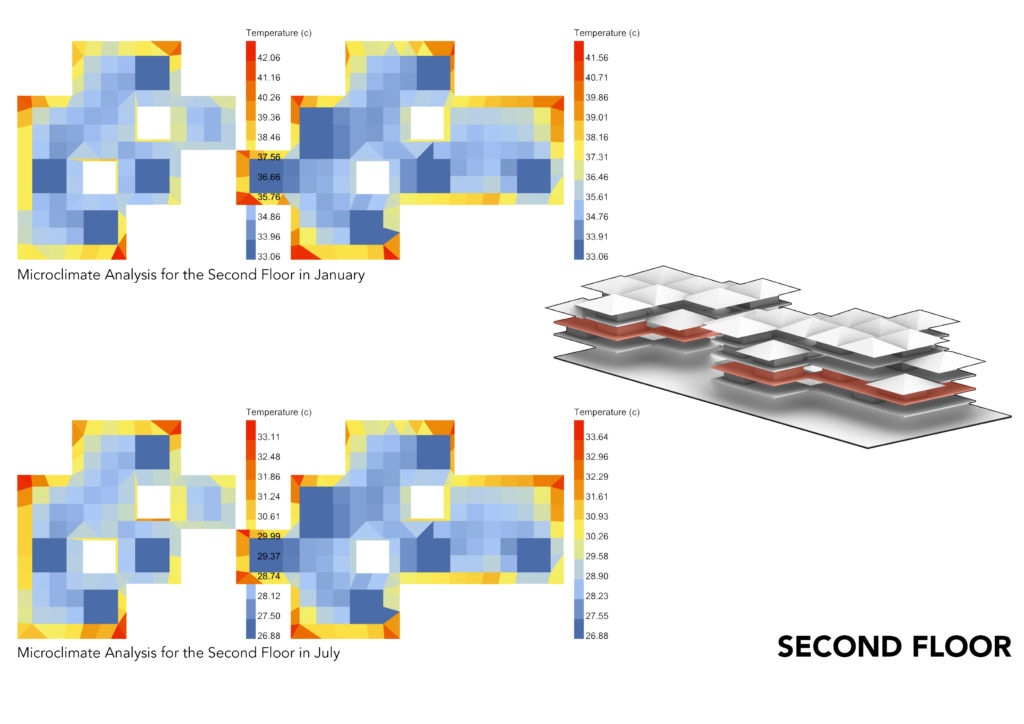
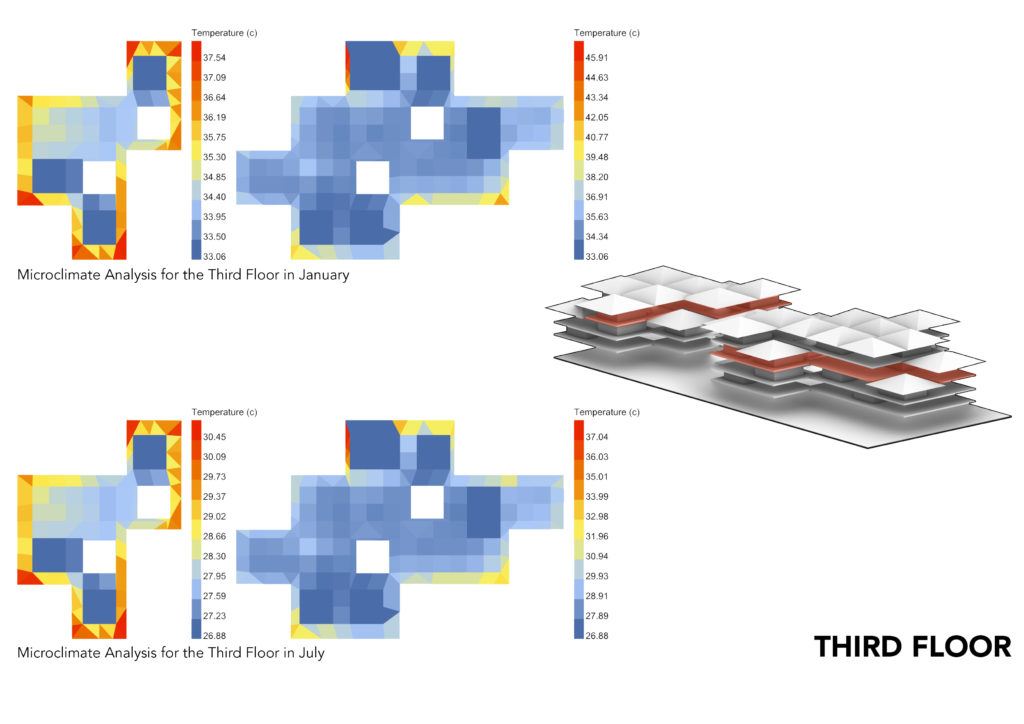
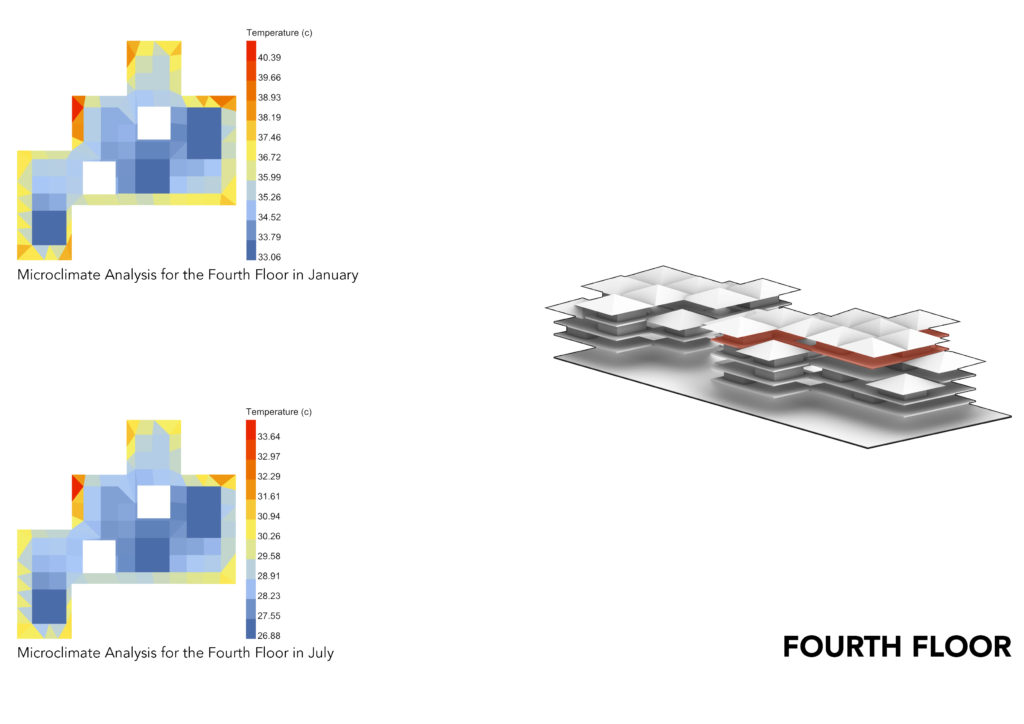
MICROCLIMATE ANALYSIS:
The Microclimate Analysis takes into account the dry bulb temp, human to sky ratio, relative humidity, wind direction and wind speed. The resulting analysis gives you the feel like temperature which shows the comfort level in the space. Keeping in mind the subjective comfort levels, what might appear to be higher temperatures by western standards, it appears to be comfortable for Ghanaian standards.