Introduction
OpenStreetMap (OSM) stands as a testament to the power of collaborative mapping, where a community of volunteers comes together to create a detailed and constantly updated geographic database. This free and open resource is not just a map; it’s a versatile tool used for everything from navigation and humanitarian aid to data visualization. OpenStreetMap provides valuable data for the analysis of urban landscapes, encompassing both qualitative and quantitative aspects. Leveraging Grasshopper and the “Elk” plugin streamlines the process of working with this information, unlocking its potential for in-depth exploration and interpretation.
Methodology
- Data Acquisition: Acquire OpenStreetMap (OSM) data by exporting the OSM file from any location worldwide using OpenStreetMap. For datasets larger than 50,000 nodes, alternative sources such as Overpass Turbo can be employed.
- Leveraging Elk Plugin in Grasshopper: Integrate the Elk plugin into Grasshopper, the versatile parametric design platform. Elk acts as a conduit, seamlessly connecting OpenStreetMap’s robust data with Grasshopper’s design and analytical capabilities. This integration empowers users to extract, manipulate, and visualize intricate cityscape data directly within the Grasshopper environment.
- Defining Analysis Questions: Pose specific analysis questions using the data within the OSM file. For instance, one might seek to understand the distribution of building uses in a given area and explore spatial characteristics by comparing data such as building height and footprint.
- Grasshopper Analysis: Utilize Grasshopper to compare data on each cube plane. In this scenario, qualitative data is presented on a scatter chart to gain insights into the visual representation of buildings in the area. Additionally, qualitative data is compared to assess the mix of building uses across different planes.
- Dynamic Study Area Exploration: Facilitate easy exploration of various study areas globally by simply changing the input OSM file. The script automatically adapts the analysis and visualization parameters to the new location. This flexibility enables users to compare cities or regions using the same set of information and easily modify the data for specific analyses (e.g., evaluating the proximity of each building to amenities in a given area).
Analysis
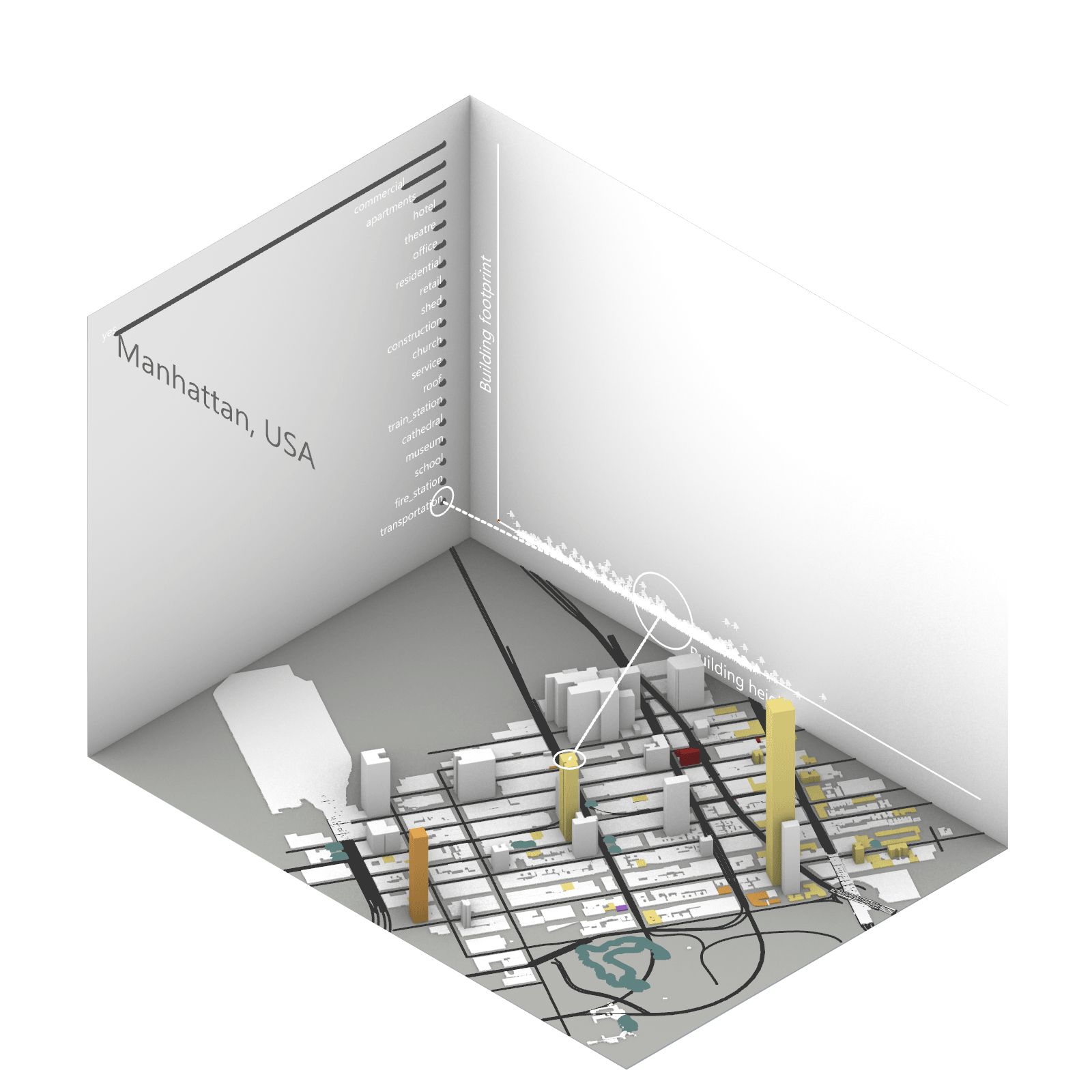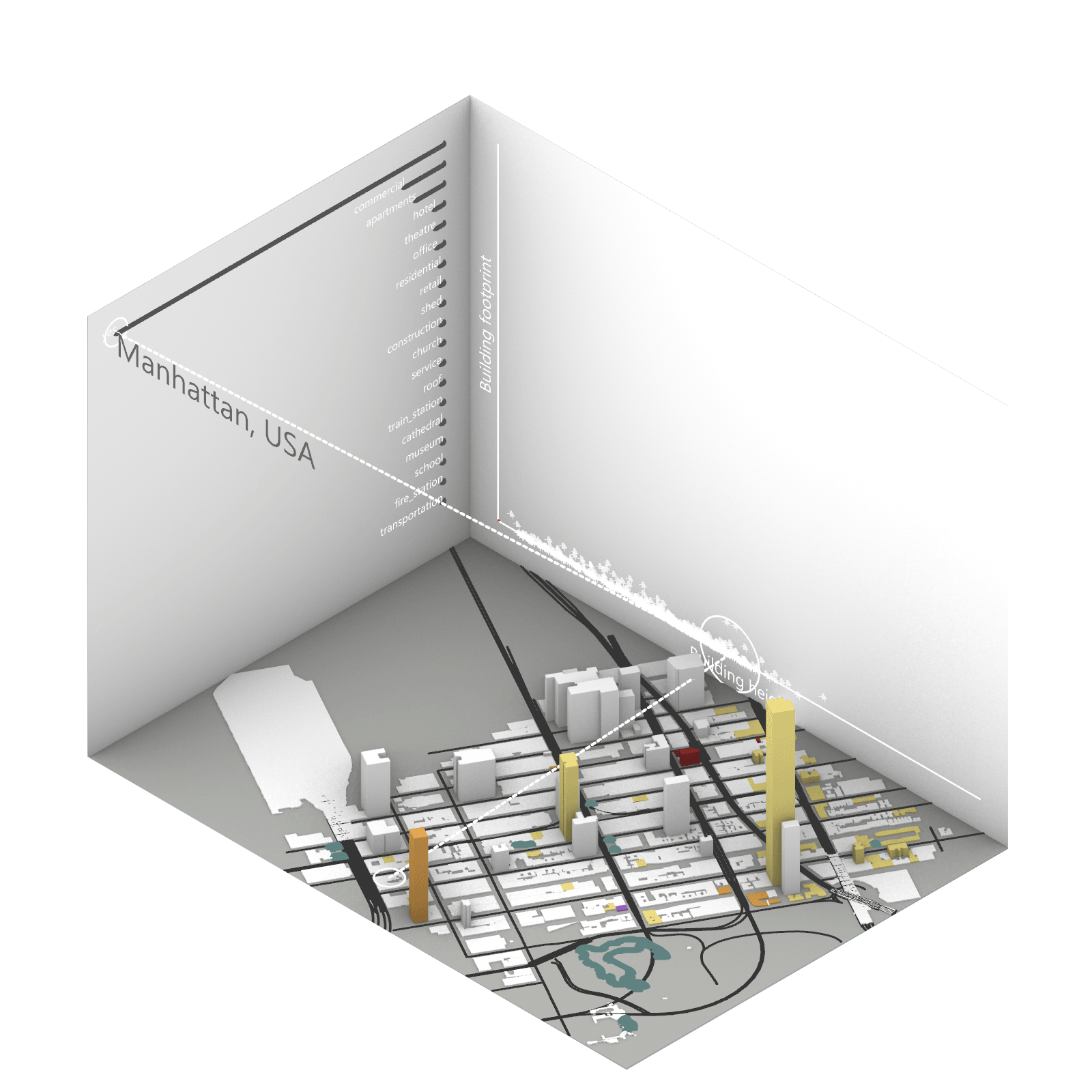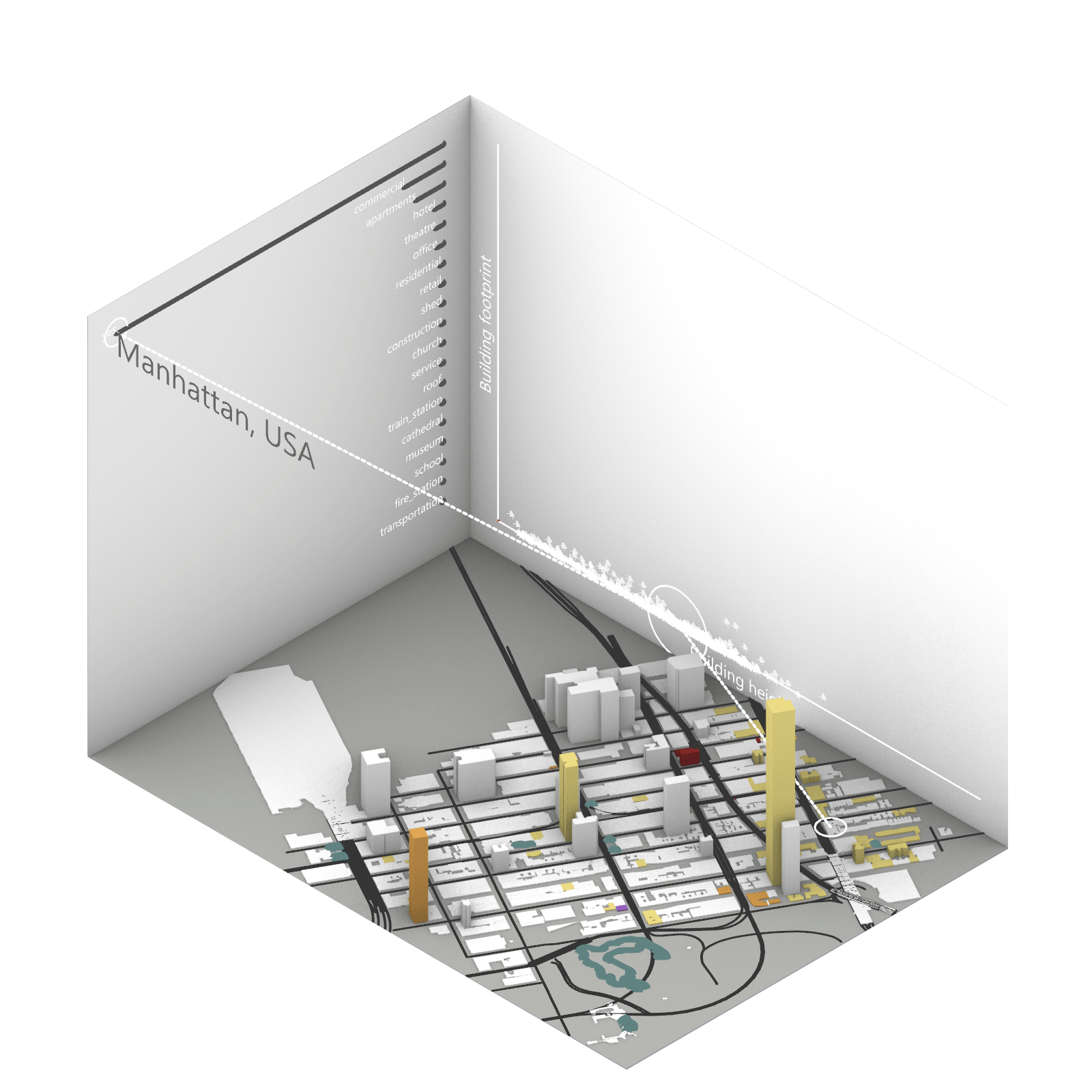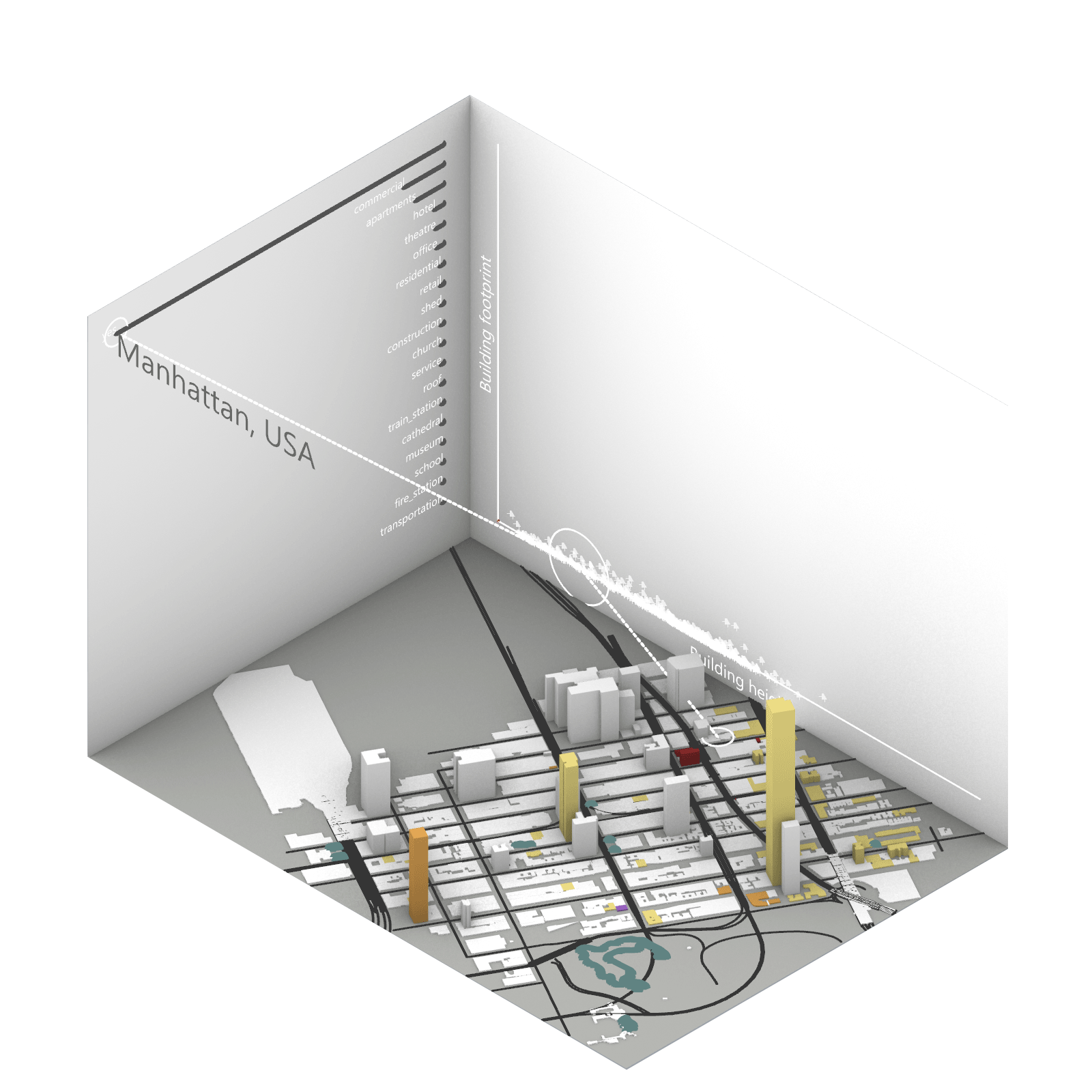
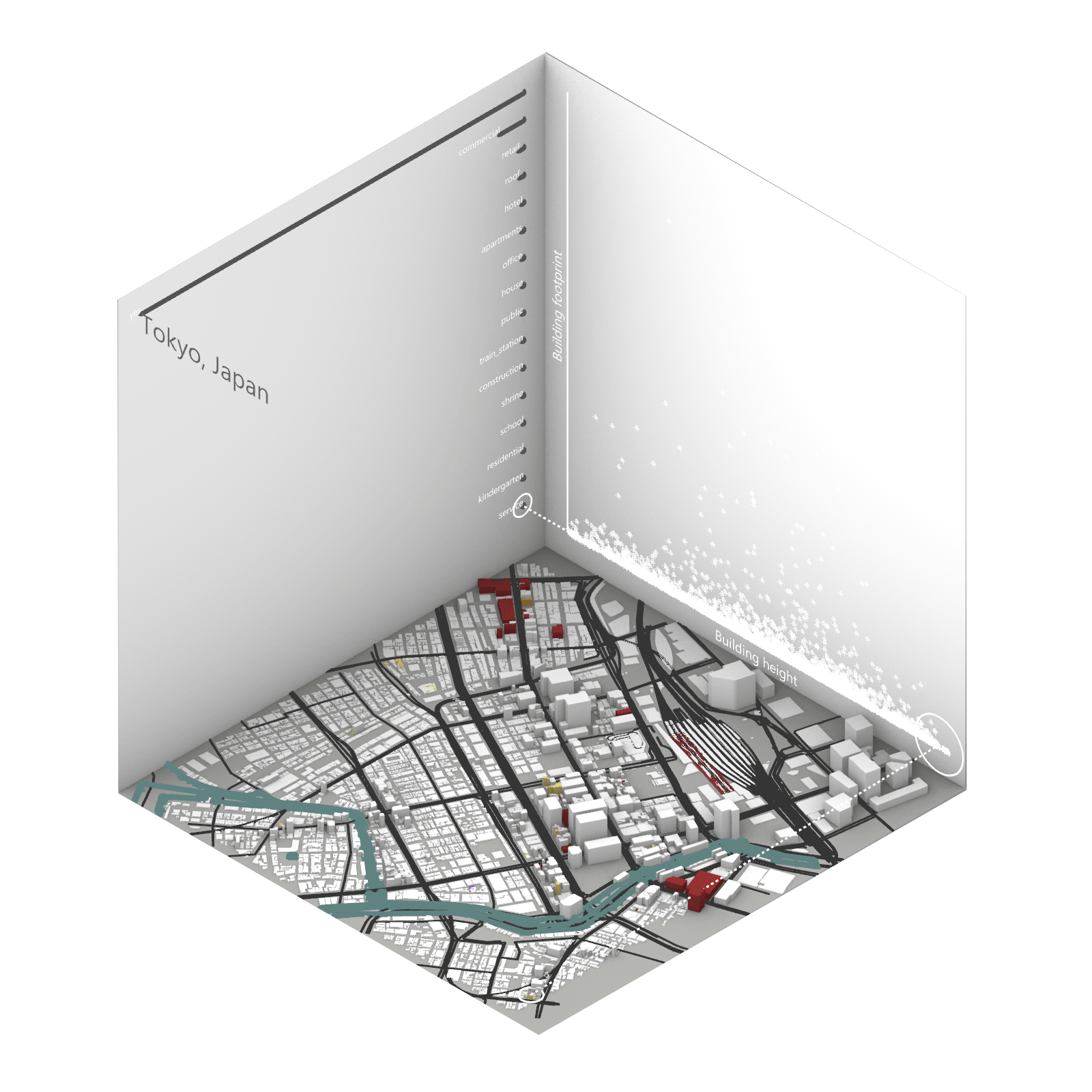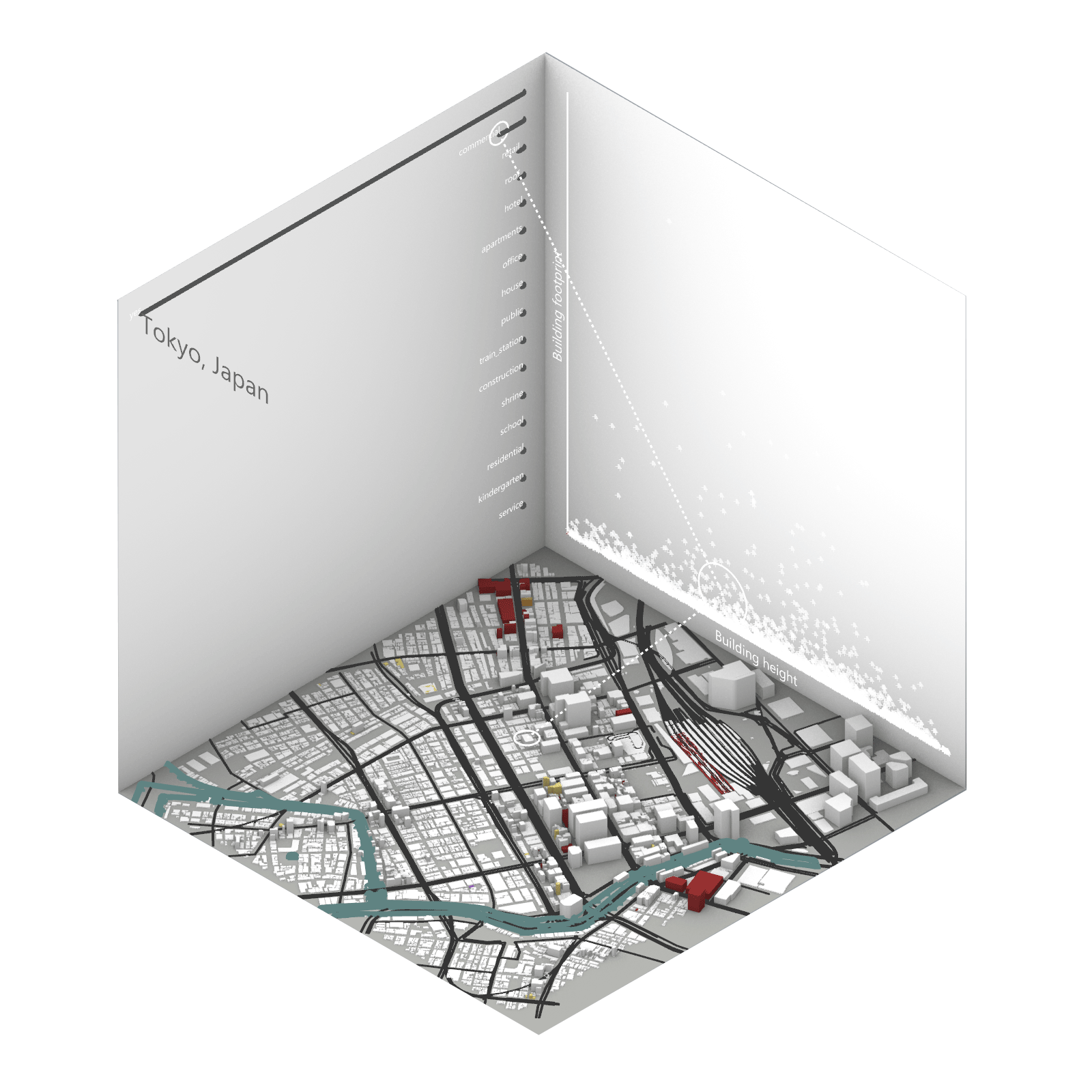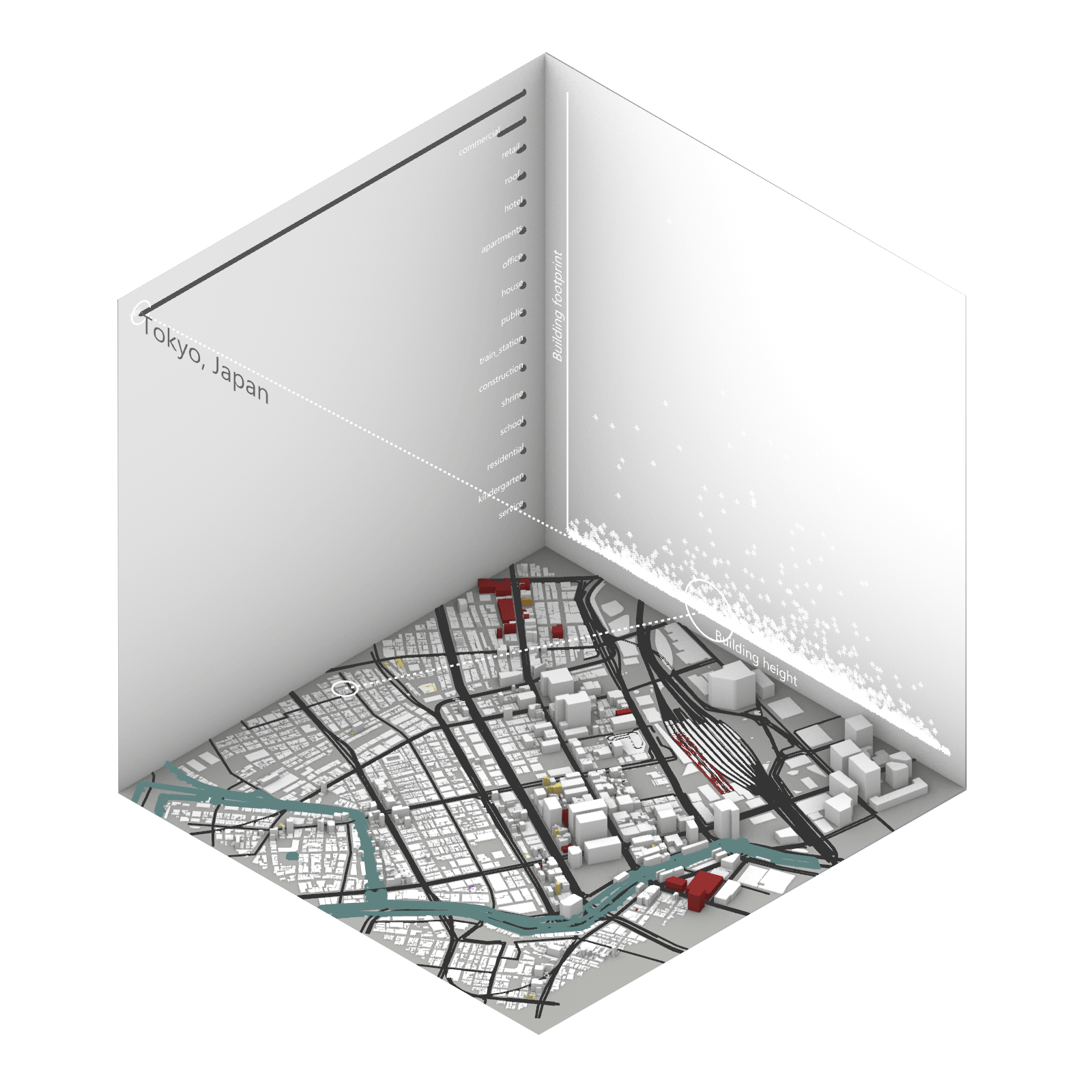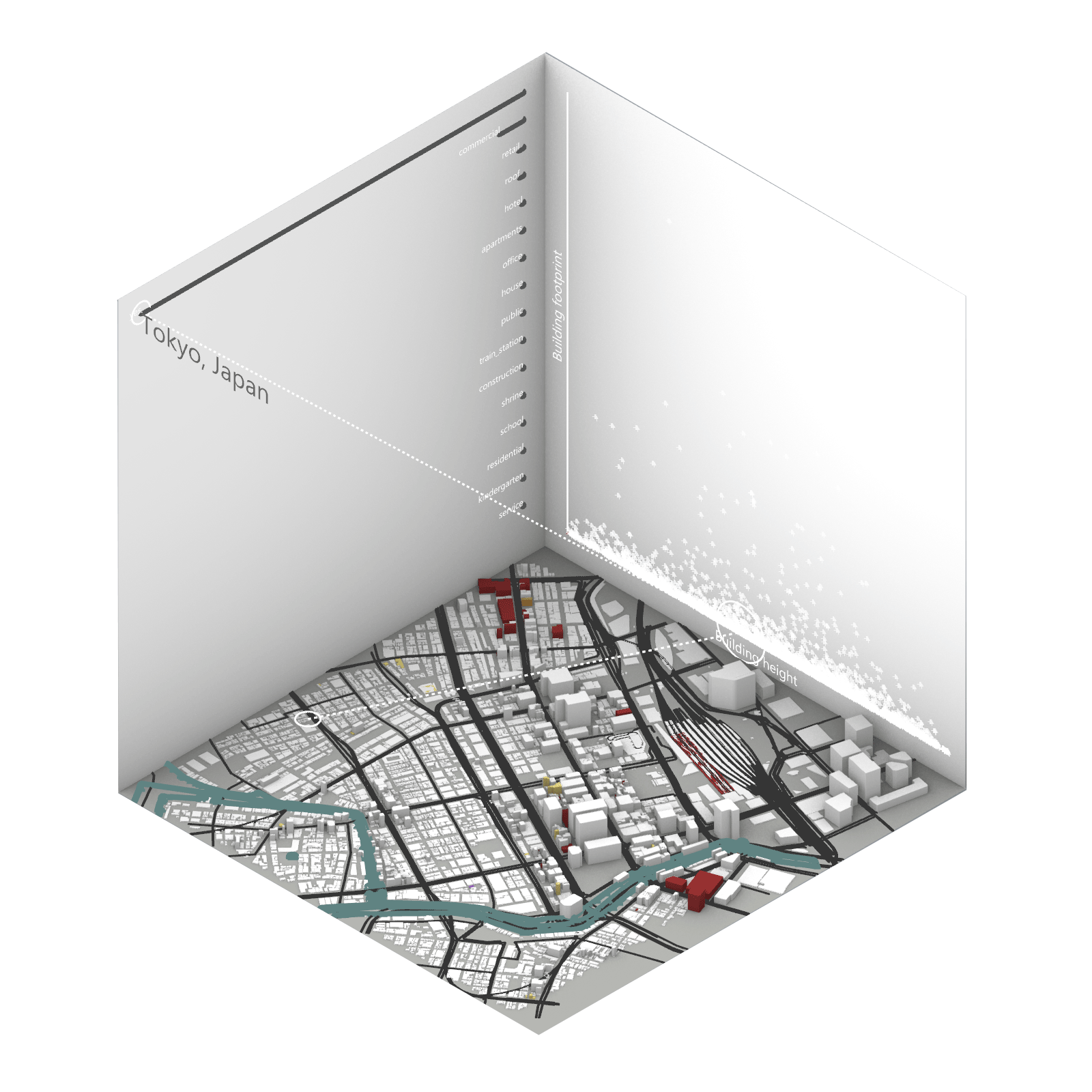
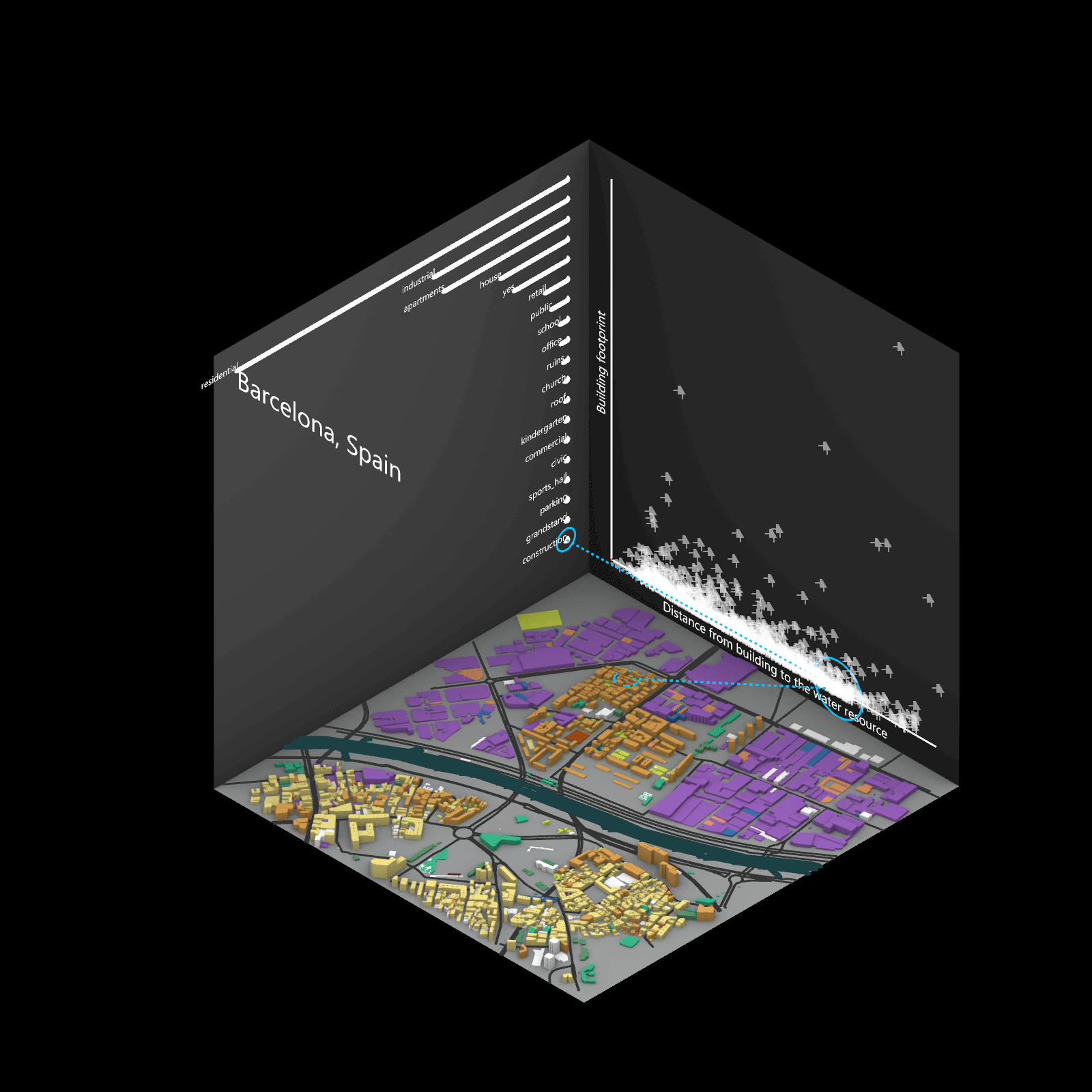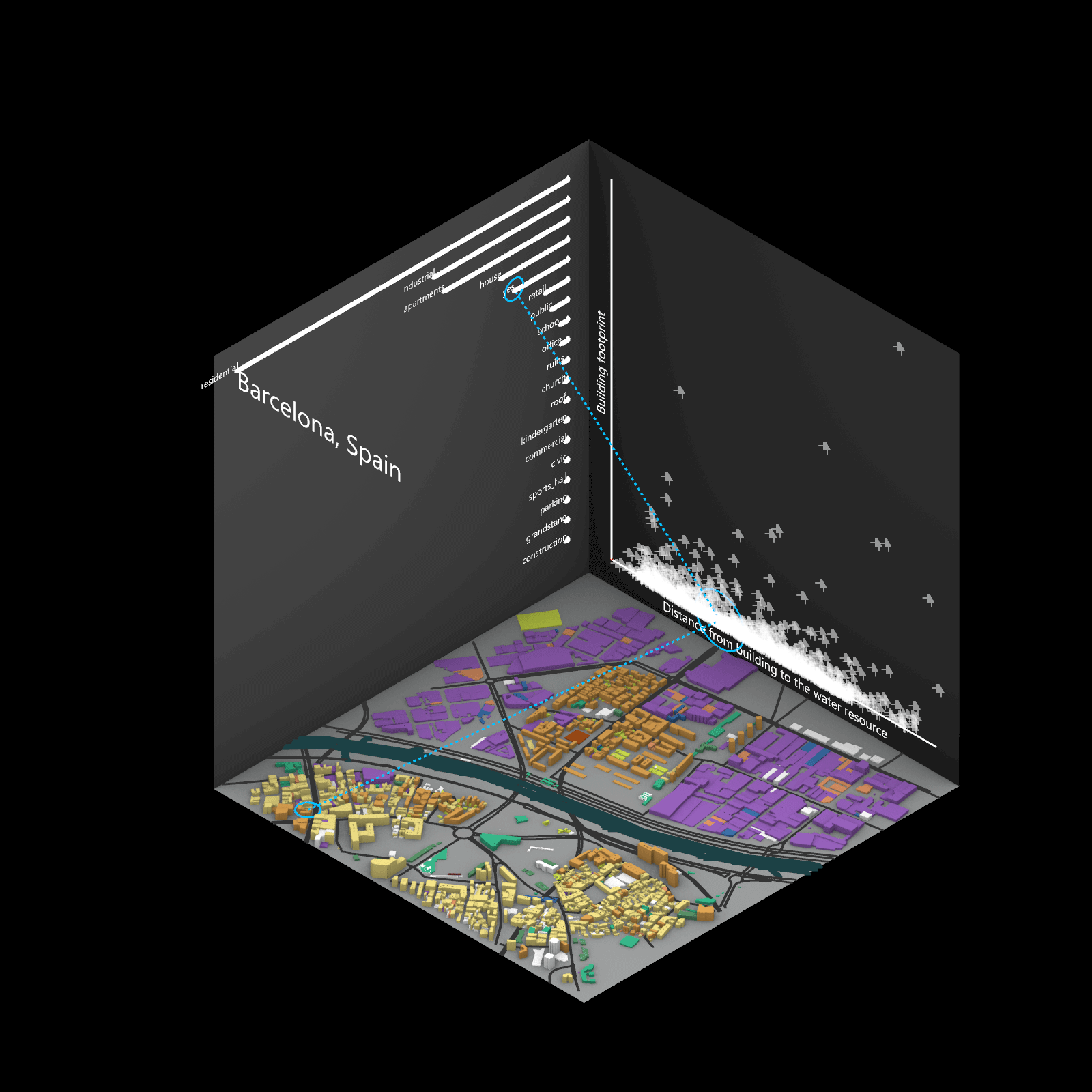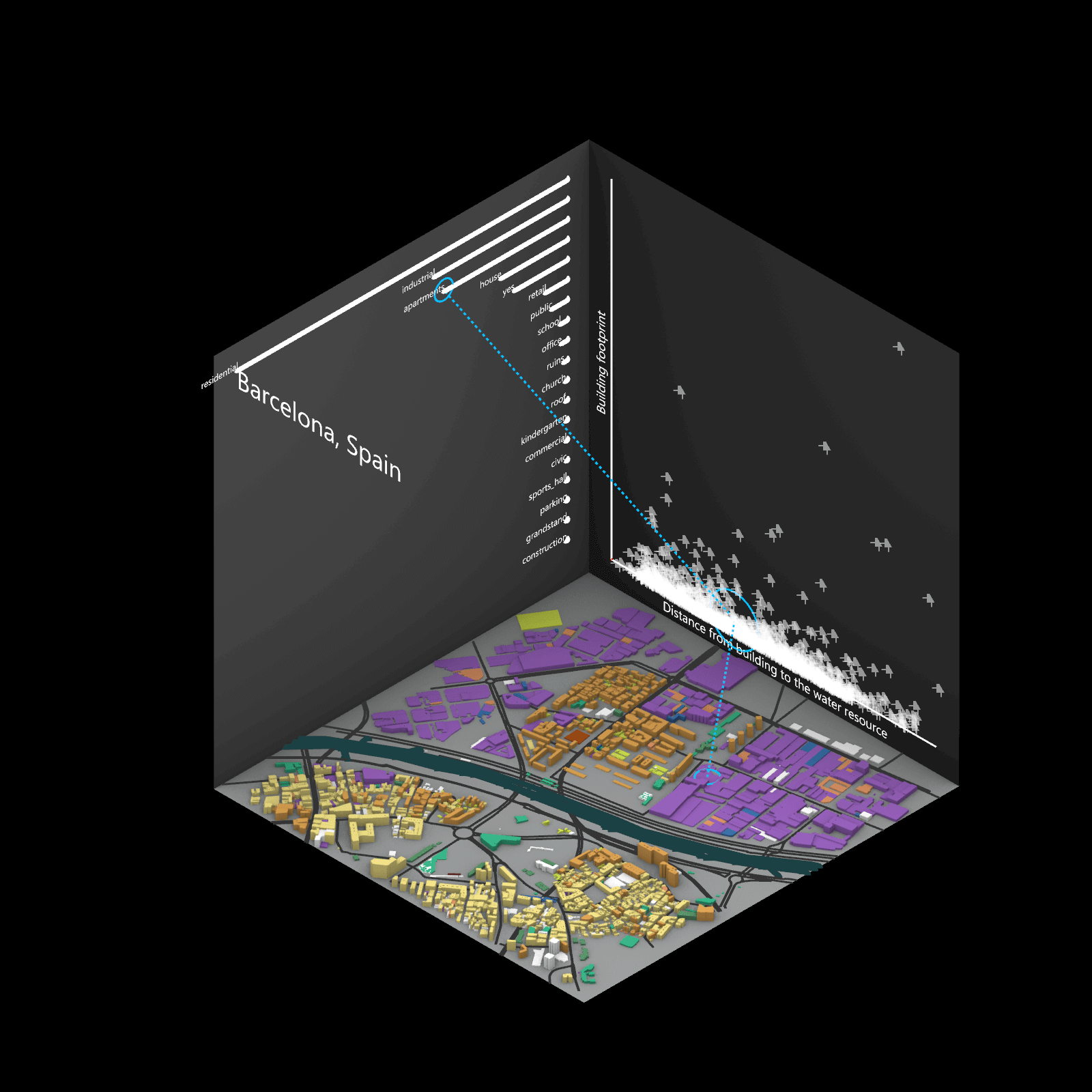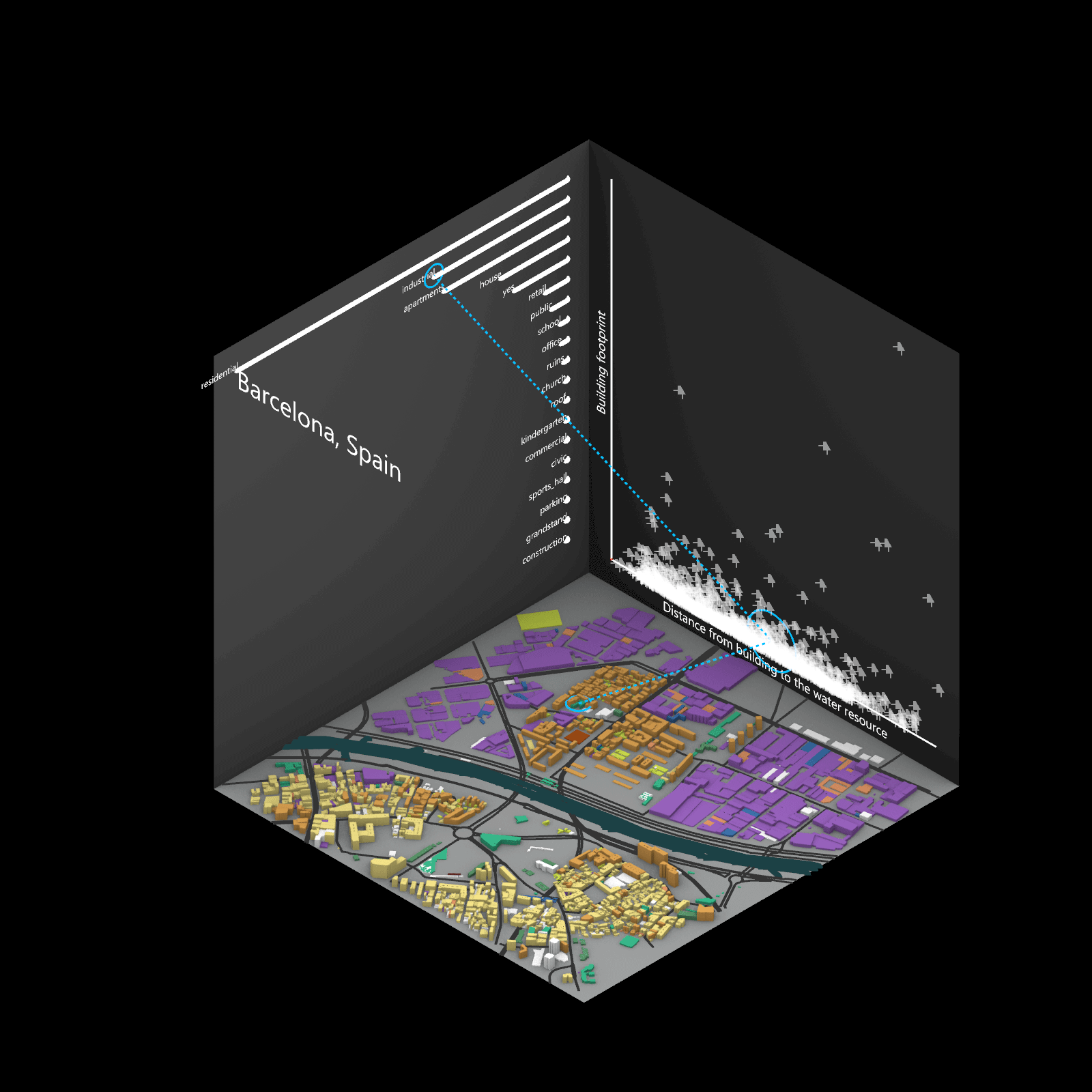
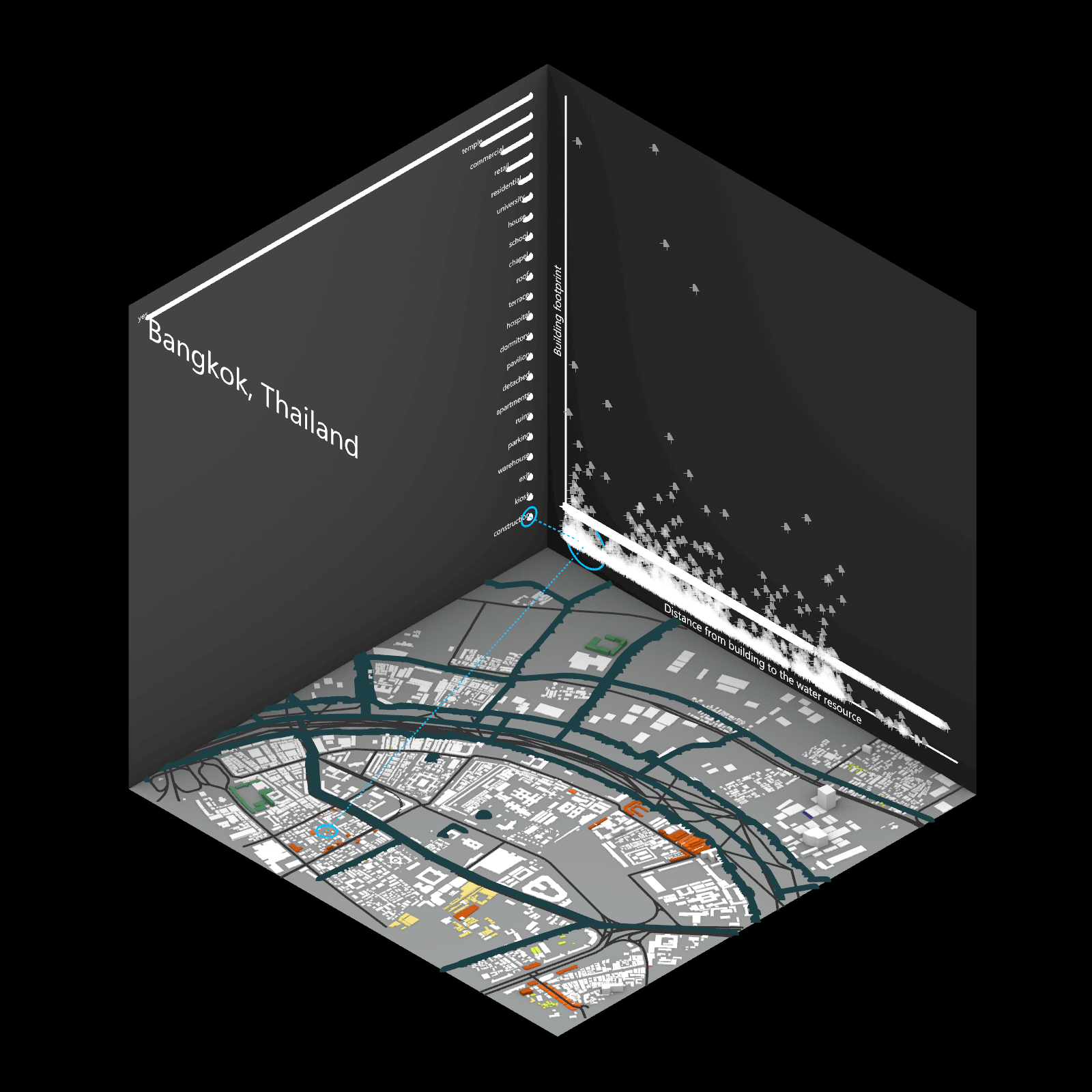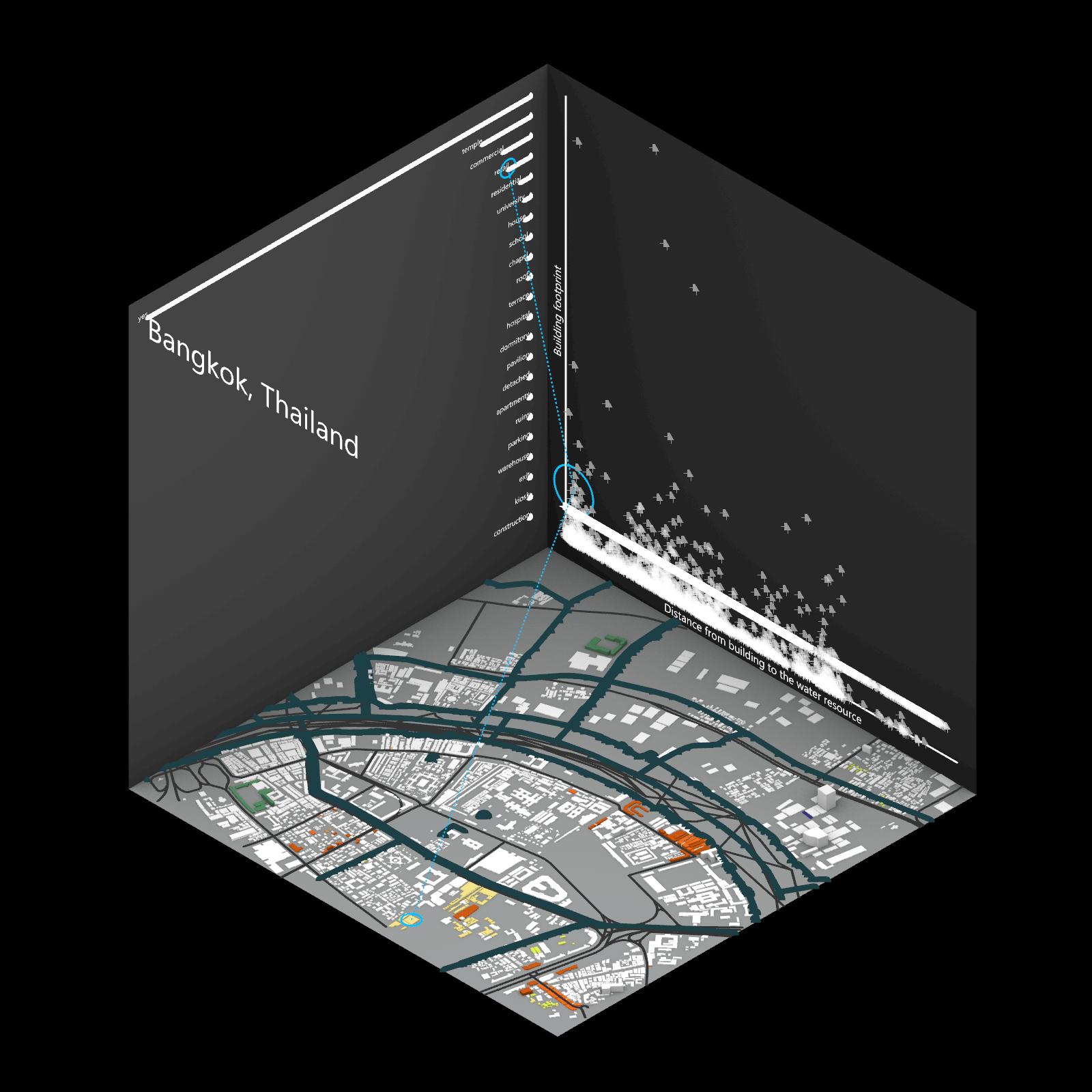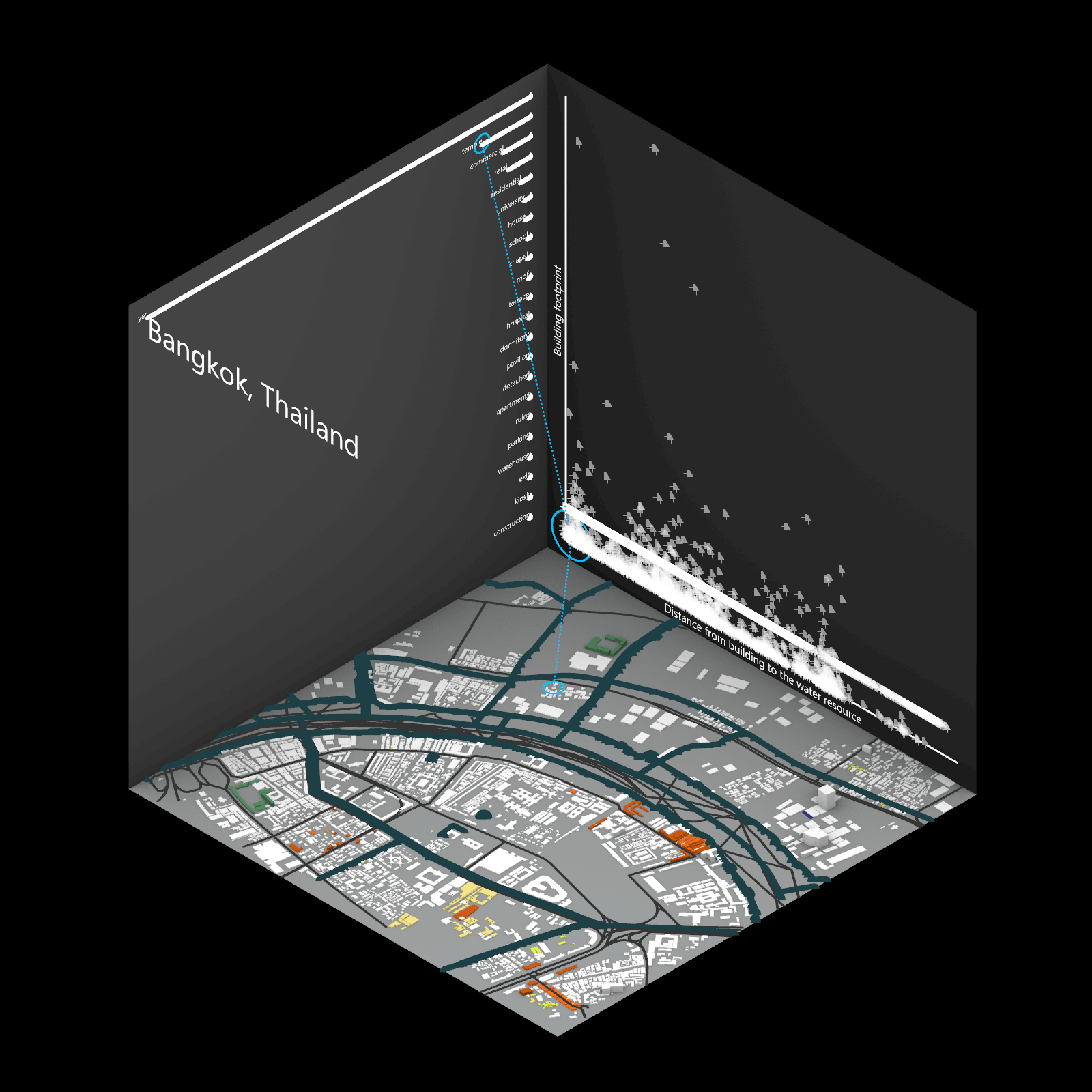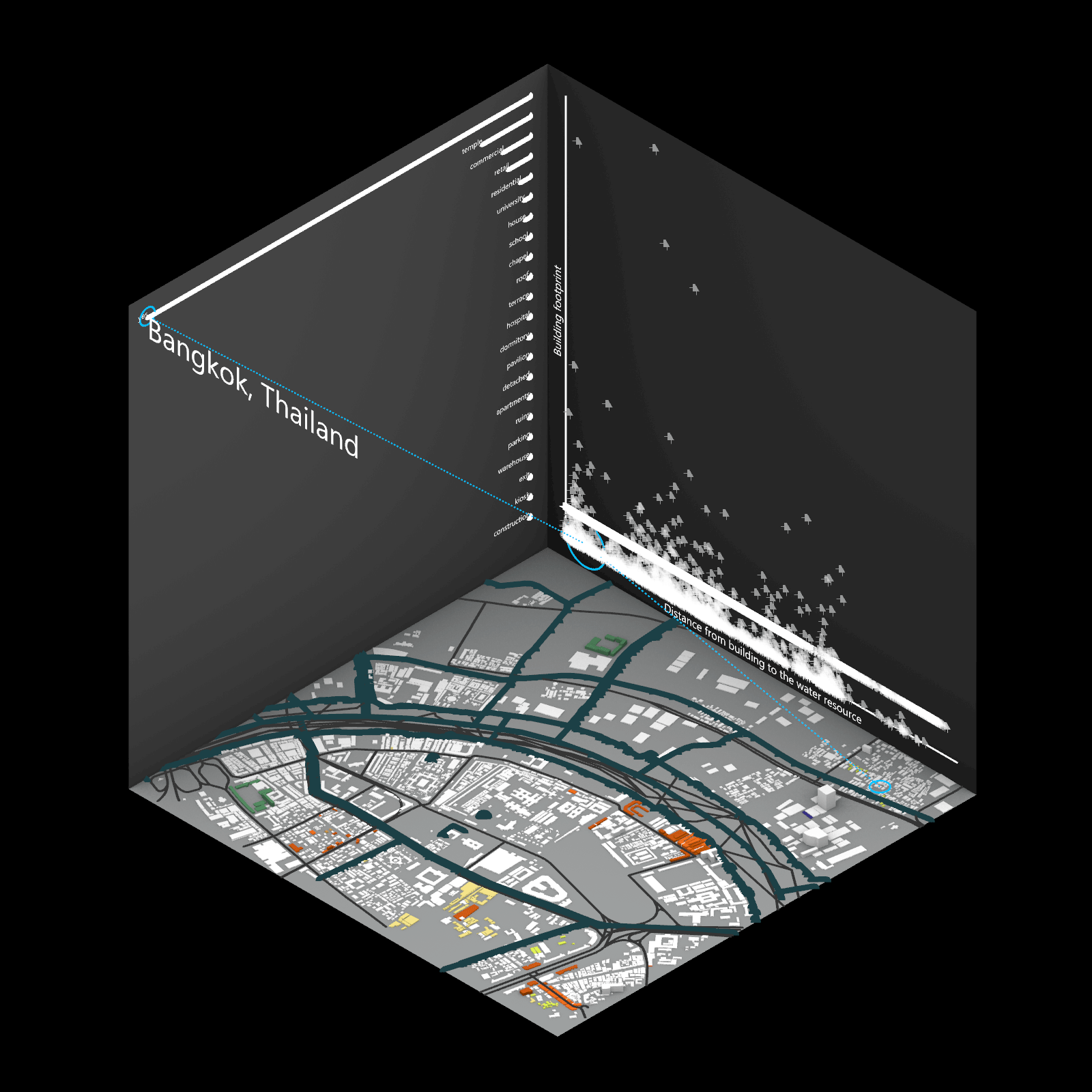
Playing with 3 flexible data plane:
1. Spatial 3D Model: Embark on a journey through the city’s 3D model, delving into the intricacies of cityscape. This exploration, tailored to individual contributions in the specified area, emphasizes collaborative data efforts for a variety of analysis.
2.Dynamic Scatter Chart: The chart providing insights into the nuanced connection between building size and height. Users wield the ability to uncover spatial intricacies, particularly in relation to building proximity to amenities. Customize your analytical trajectory to align with personal research interests.
3. Bar Chart: The bar chart aiding in comprehending the proportional dynamics of building use within the locale. Rooted in simplicity, this visual tool assists in revealing primary urban characteristics and outlining land use patterns—an effortless transition from raw data to meaningful insights.
This function encourages individuals to exercise discretion, fine-tuning variables for a nuanced and personalized analysis. Propelled by the wealth of data within the OpenStreetMap file, this exploration invites users to navigate urban landscapes with both ease and scholarly acumen.
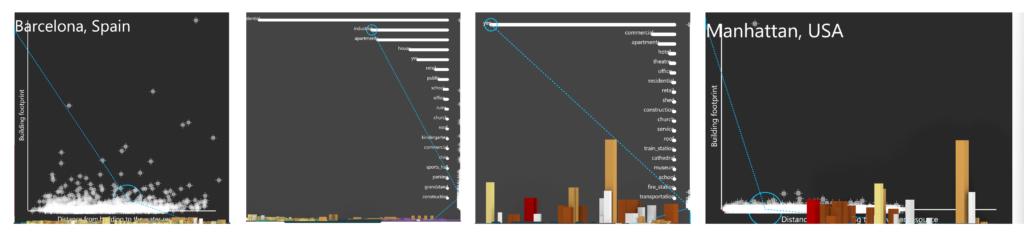
Conclusion
This exploration of the city’s 3D model and dynamic scatter charts, coupled with user-friendly bar charts, is designed to empower users in deciphering urban data on their terms. Offering tailored exploration and ease of understanding, users can contribute to the analysis, fostering a collaborative approach to urban landscape interpretation. Looking ahead, potential improvements could include refining the user interface for intuitive interactions, expanding the analytical toolkit for diverse insights, and implementing measures to enhance the accuracy of user-contributed data—ultimately aiming to make urban data exploration more accessible, collaborative, and impactful for a diverse user base.
References
https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=11/40.7811/-73.9771&layers=P

