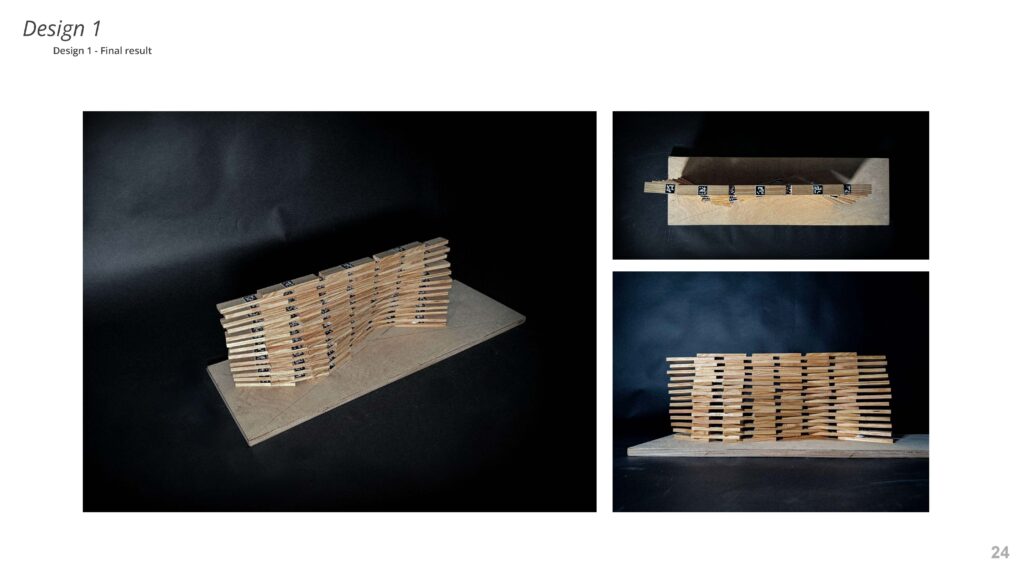
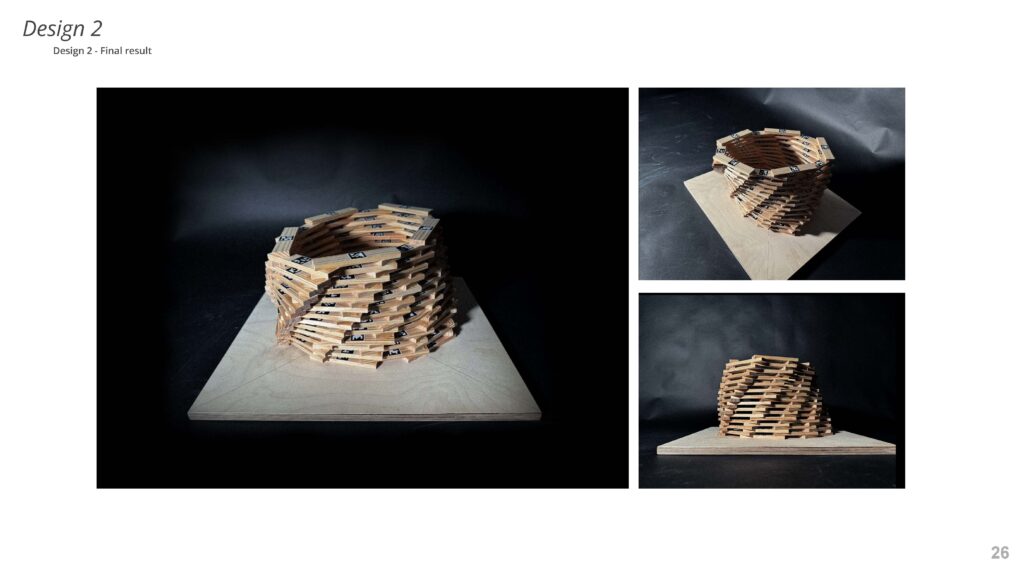
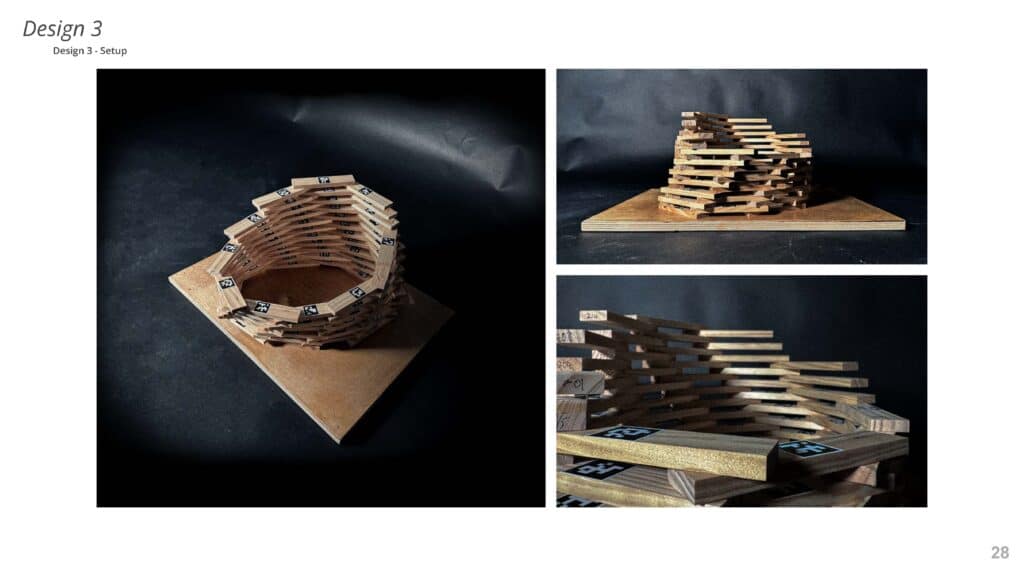
“Spatial Cognition in Robotics: Optimizing Construction Workflow with AI”
Shu Xiao – MRAC02 Thesis, IAAC 2024–2025
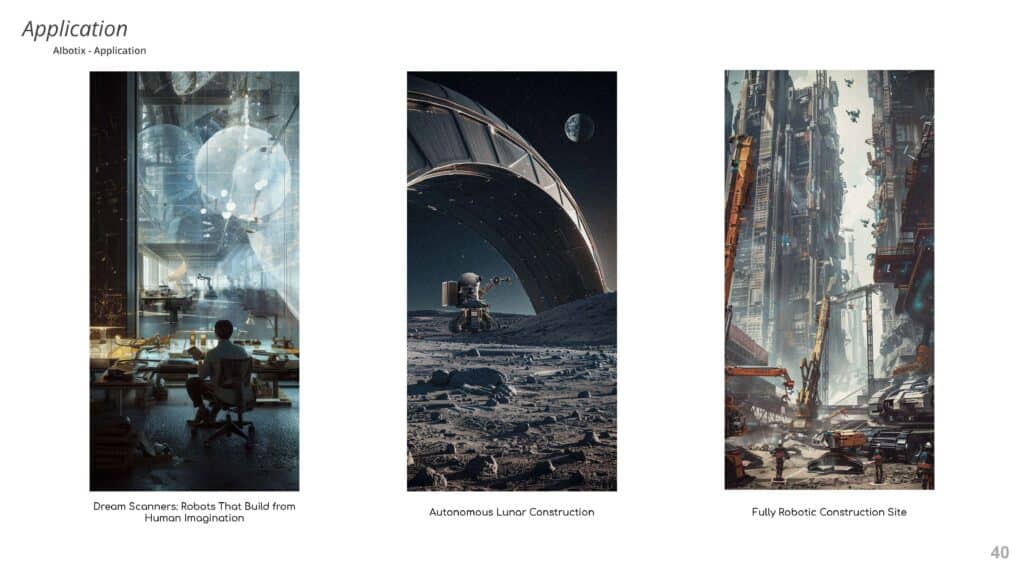
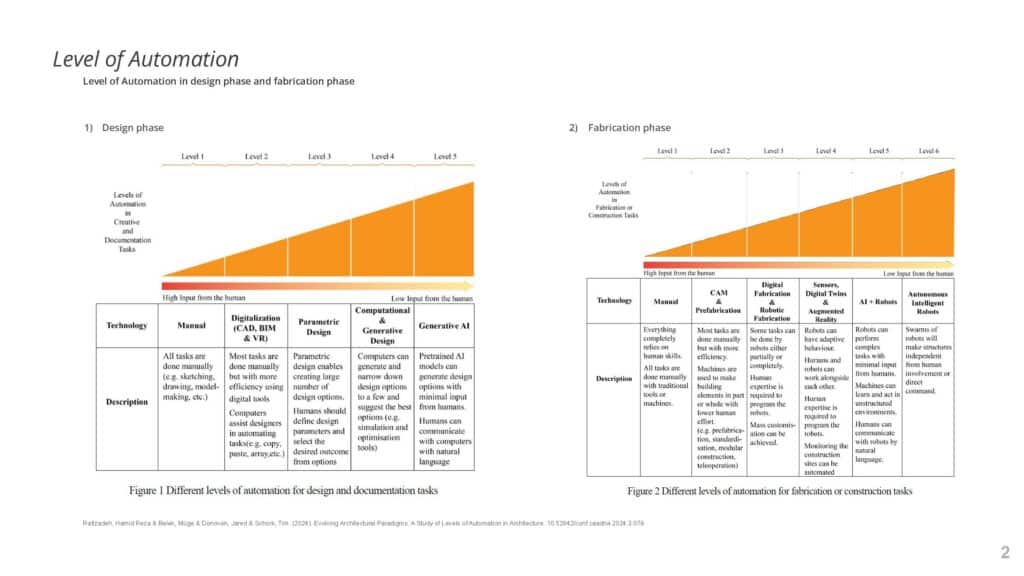
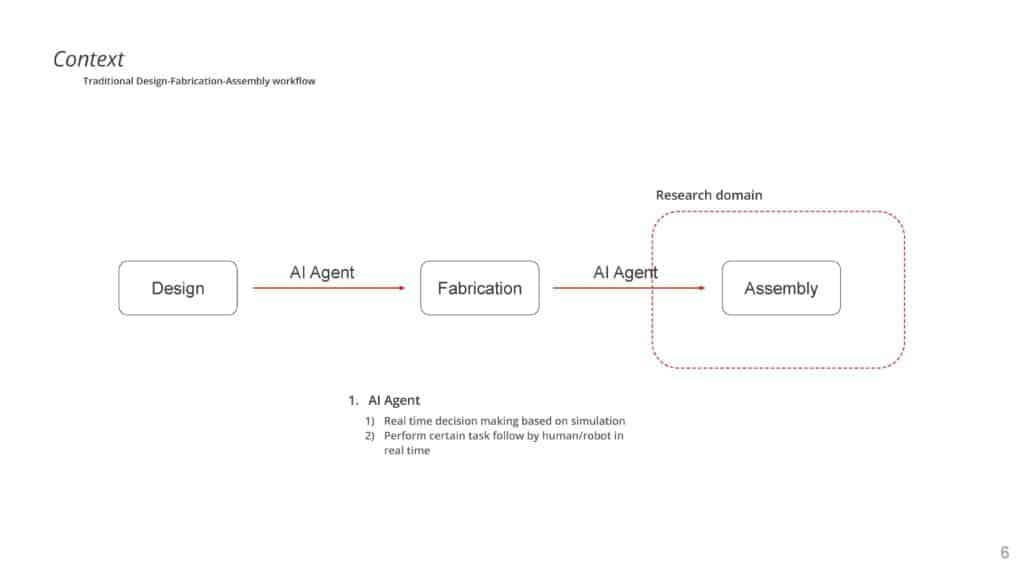
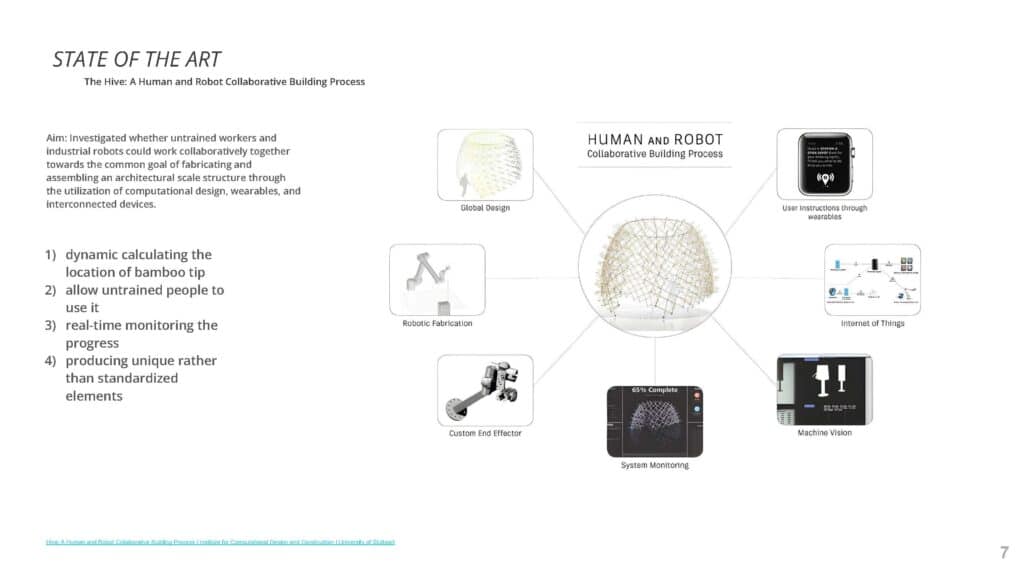
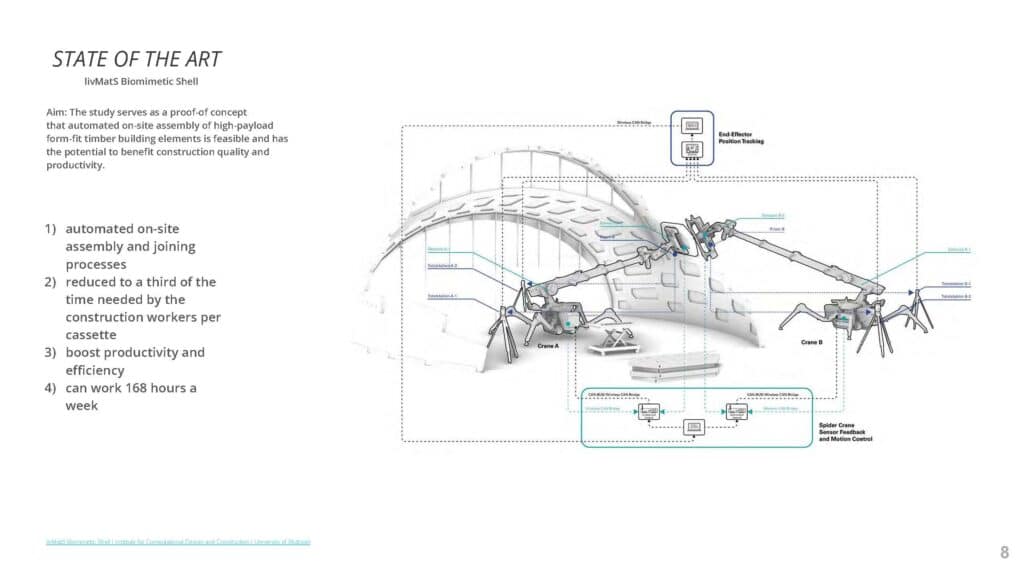
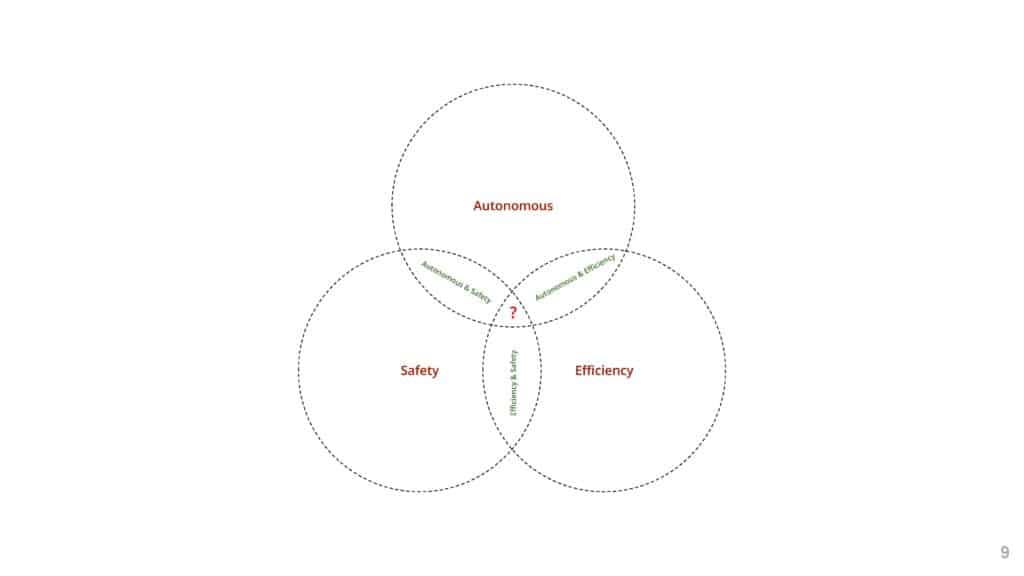
Despite advances in manufacturing automation, the construction industry continues to rely heavily on manual labor due to its unpredictable environment, safety concerns, and fragmented workflows. This project explores how vision-guided robotics and real-time AI agents can close that gap by introducing autonomy into the on-site assembly process.
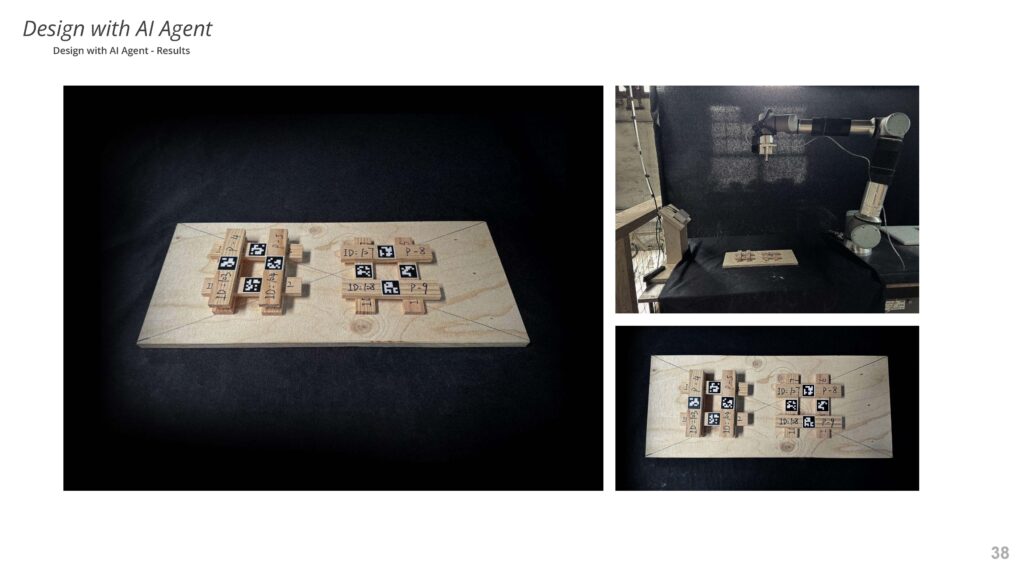
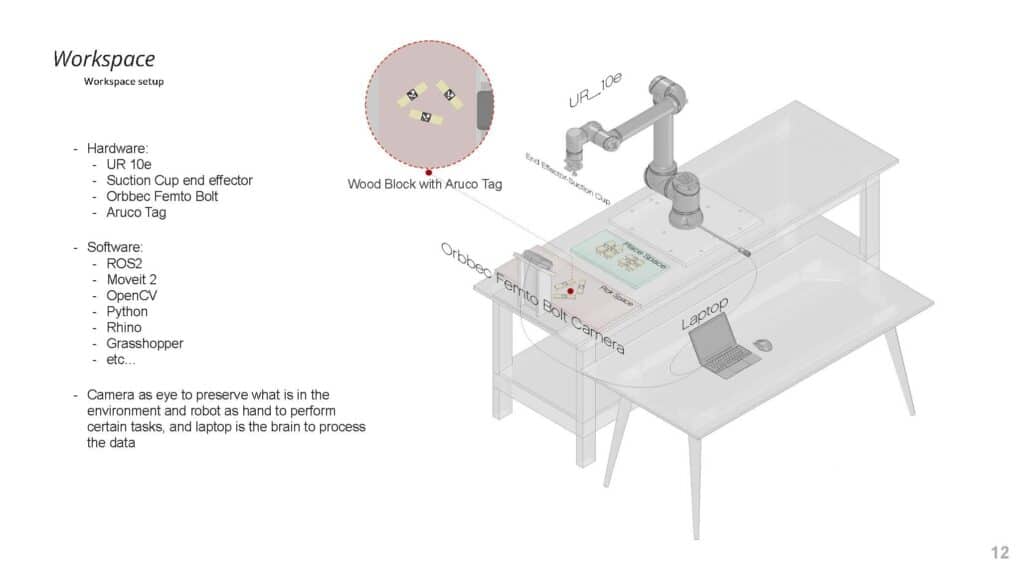
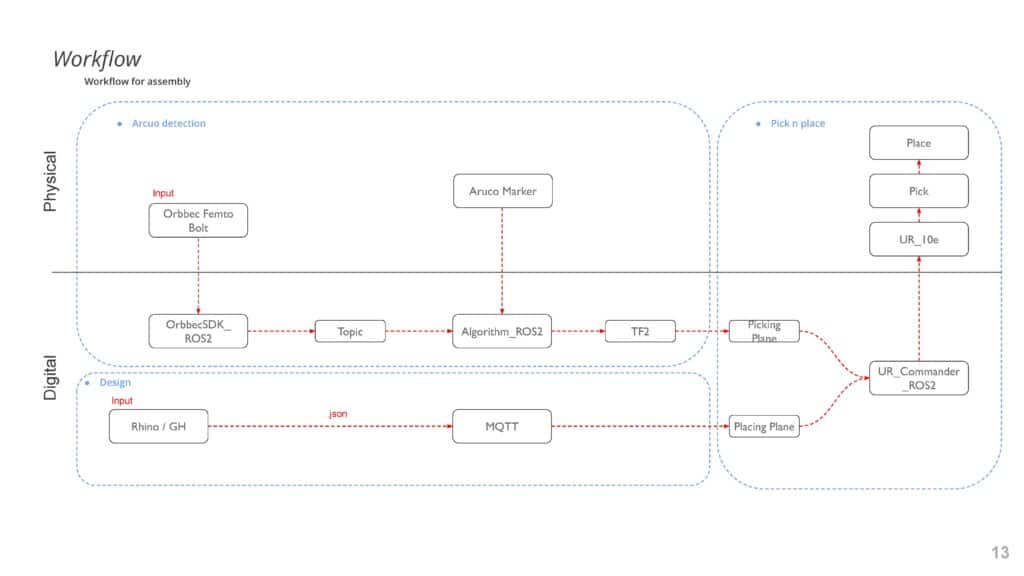
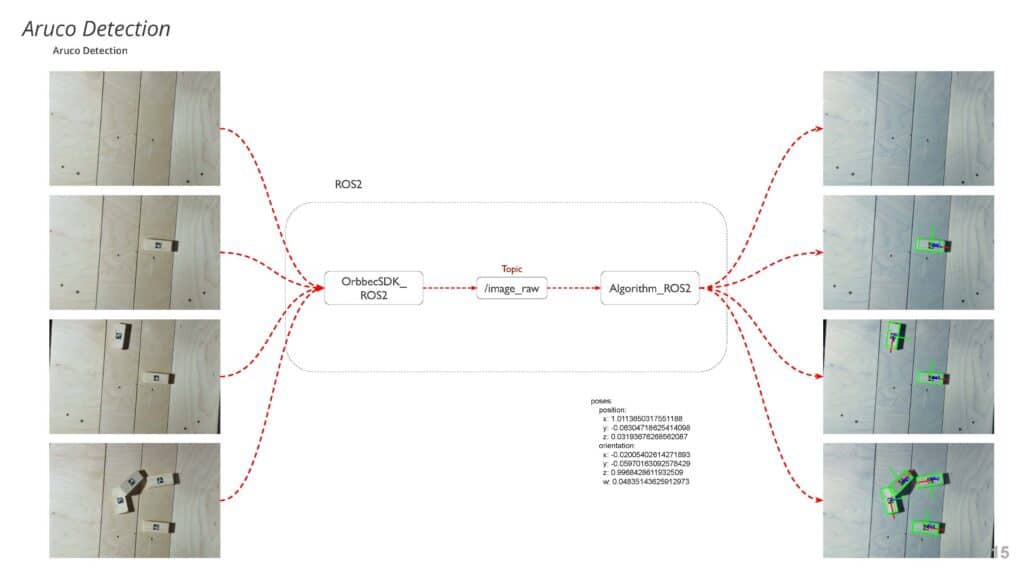
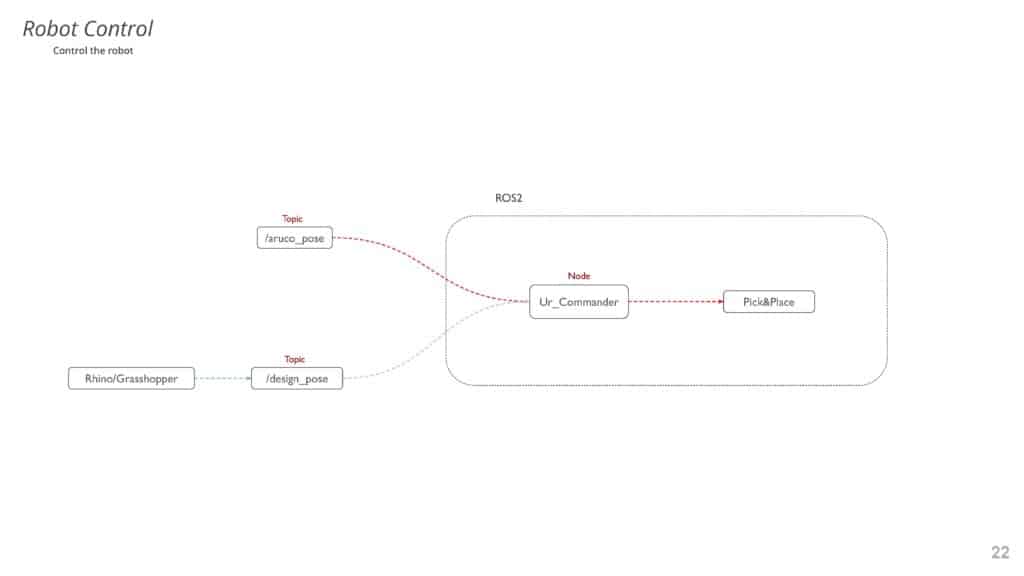
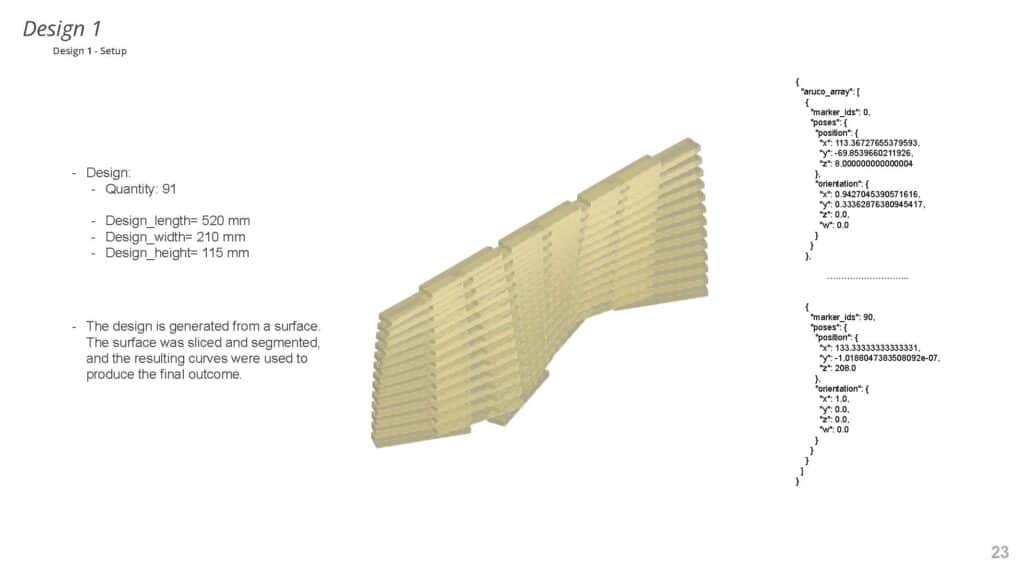
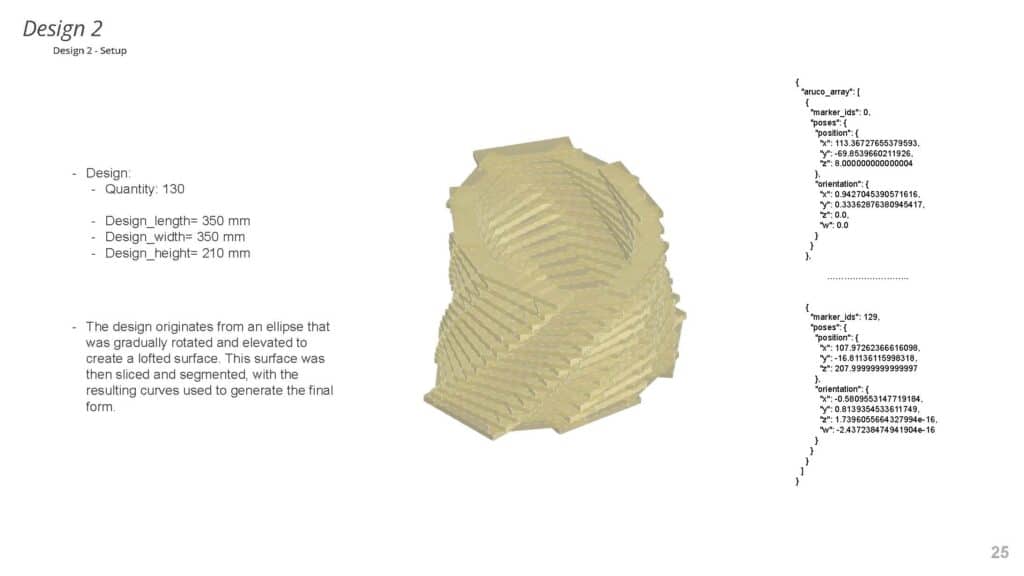
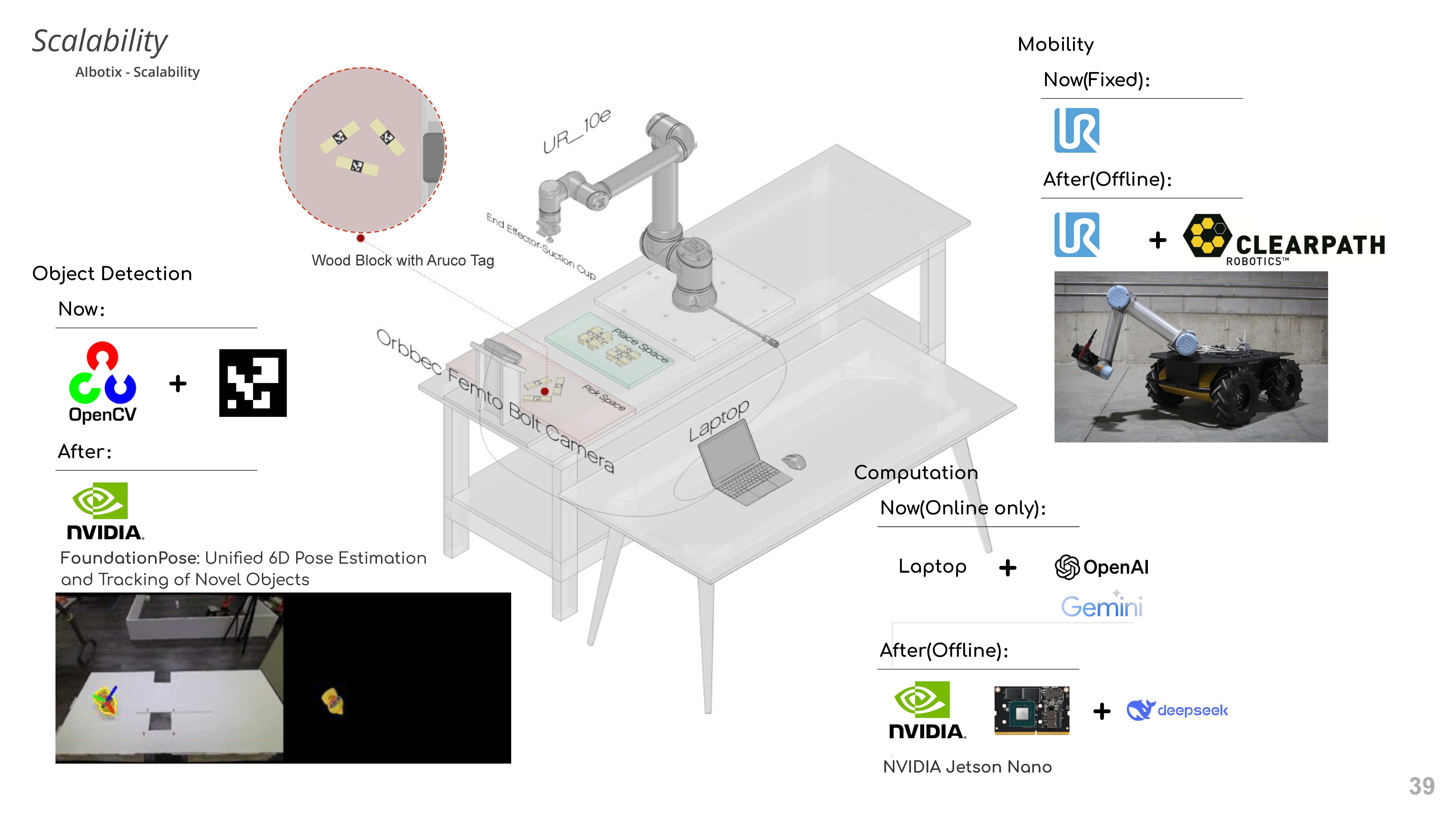
At its core, the project proposes a 1:1 scale robotic assembly system that uses computer vision (with ArUco markers and depth cameras) to enable real-time decision-making and execution. A robotic arm (UR10e) acts as the “hand” guided by a depth camera (Orbbec Femto Bolt) as the “eye,” executing pick-and-place tasks of wood blocks in a structured yet adaptive pipeline.
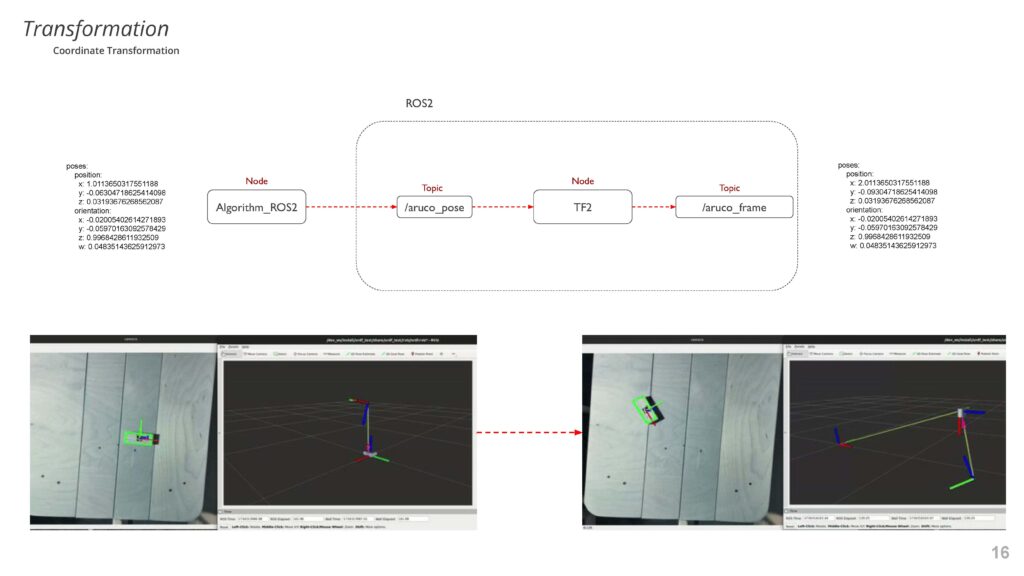
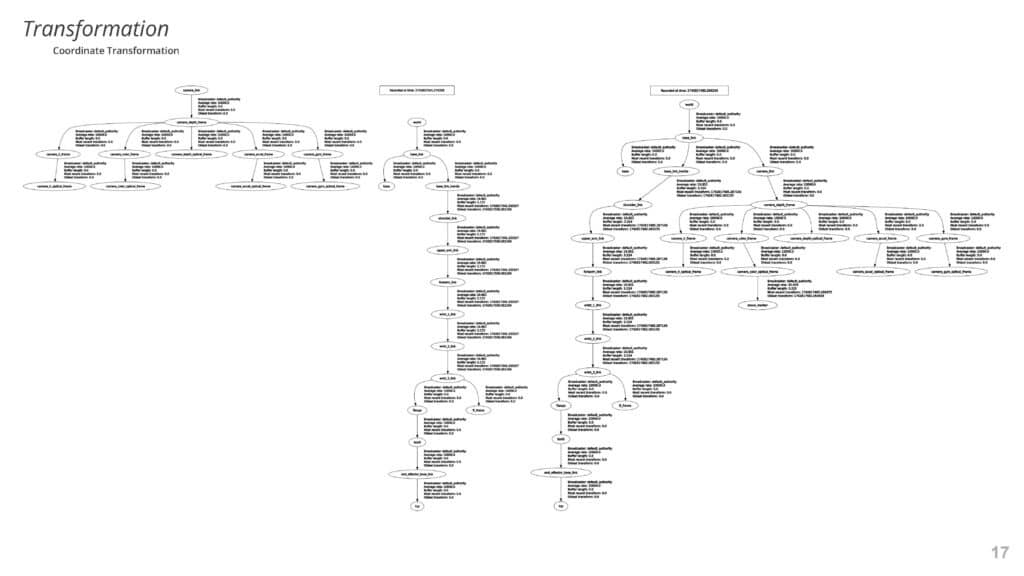
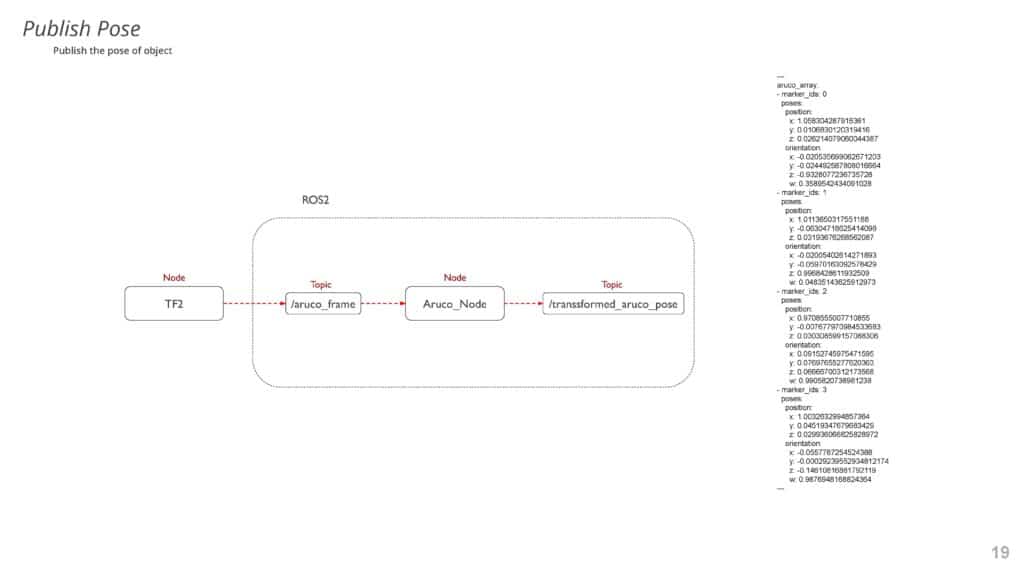
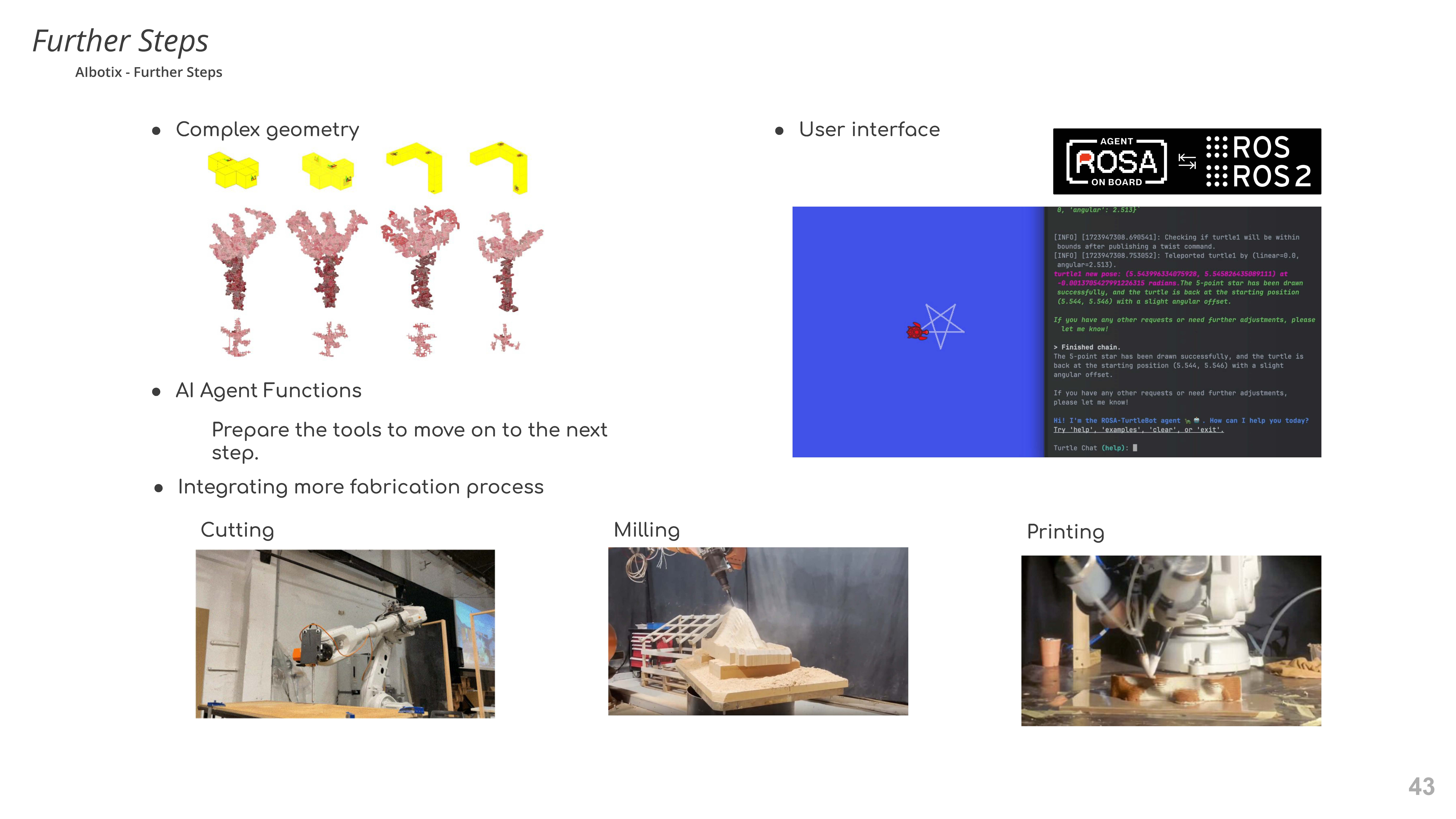
By integrating ROS2, TF2, and Rhino-Grasshopper design input, the system dynamically interprets its environment and adjusts actions accordingly—enhancing efficiency, safety, and autonomy in architectural assembly.
The project positions itself as a step toward collaborative human-machine workflows in construction, where intelligent systems respond to unpredictable site conditions and reduce the burden on human labor.