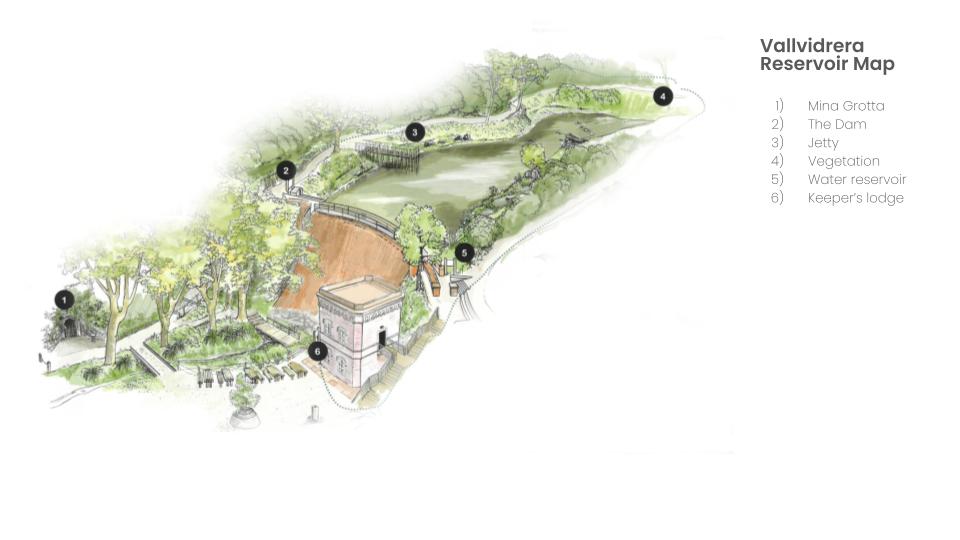
Developing visions of a future forest architecture, in Valvidrera Reservoir; a landscape that provides accesibility to, flora, fauna and open space to surrounding communities.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
To gain an understanding of digital modelling of complex timber structures.
To demonstrate an understanding of design-to-fabrication workflows and principles.
To demonstrate an understand of digital fabrication methodologies for complex timber structures.
To gain basic competency in digital simulation of material and structural behaviour.
RE-IMAGINING THE KEEPER´S LODGE
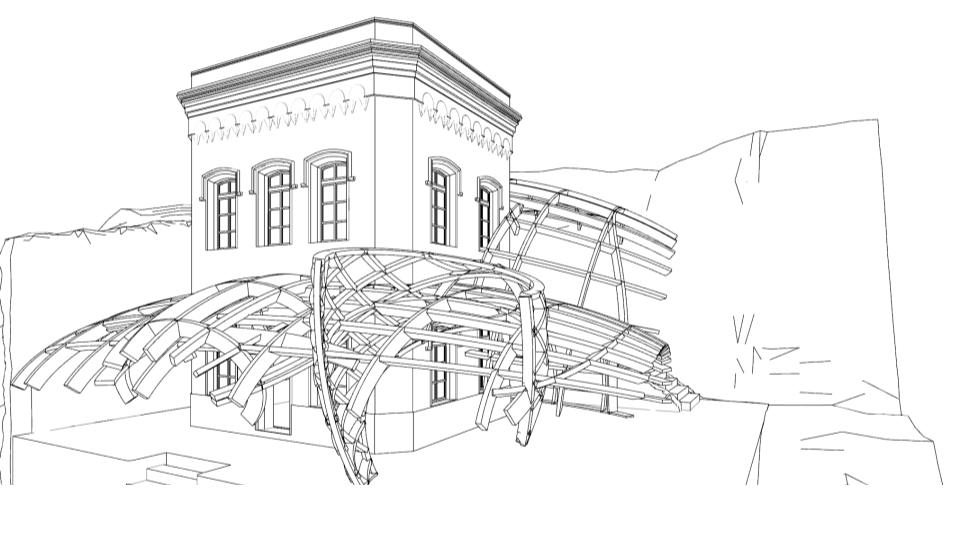
The major driver of the project was to reconsider the Keeper’s Lodge as a timber structure. The existing Lodge will be converted to a timber frame structure and a new free-form lattice will create an expanded covered area around it.
We physically prototype a section of this new proposal at a 1:2 scale, addressing all of the challenges that come with resolving complex timber structures. As part of the team in charge of the segment blank structure, we used were able to fabricated double curved connections and confront the problem of fabricating joints within specific production limitations (i.e. a 3-axis CNC machine).
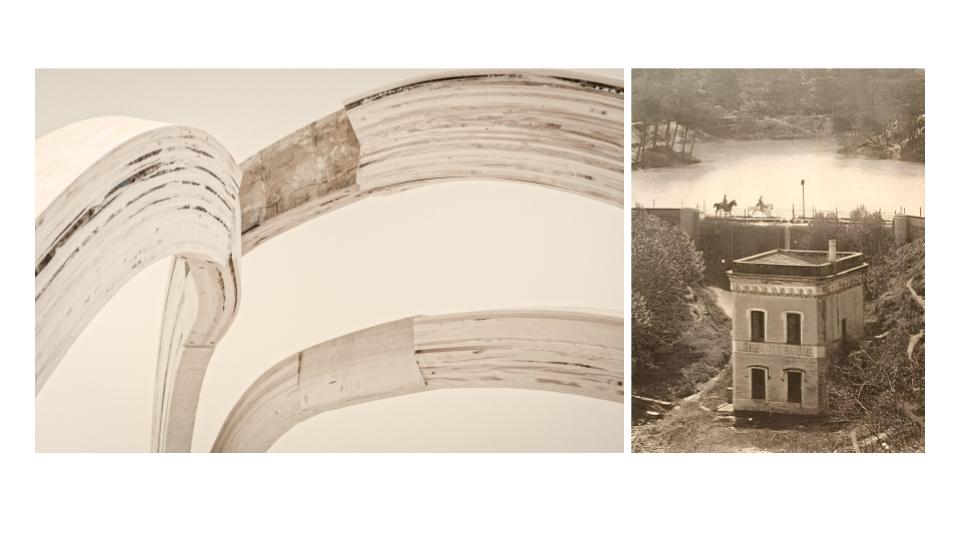

THE STRUCTURE
We took inspiration from recent post-and-beam frame structures. Often appareaing simple, they hide intricaate detailing and complex internal geometries that are necessary to resolve multi-elemt node connections. In our case, our team focused on frabricated one of the major colums of the setion structure, that involved a double curvature, in a Y shaped beam that will connect to the rest of the top structures. The interlocking system was built through the use of intricate joinery, that came into place post CNC processing, so that the joints will be hiden in between the segmented blanks that were designed.
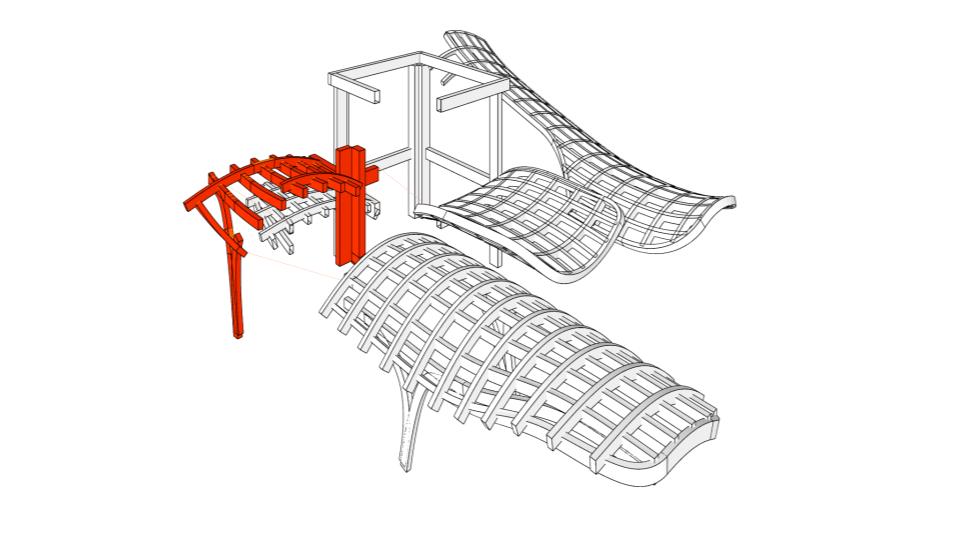
IMAGE: Red section from structure, picked for production, in a 1:2 scale.
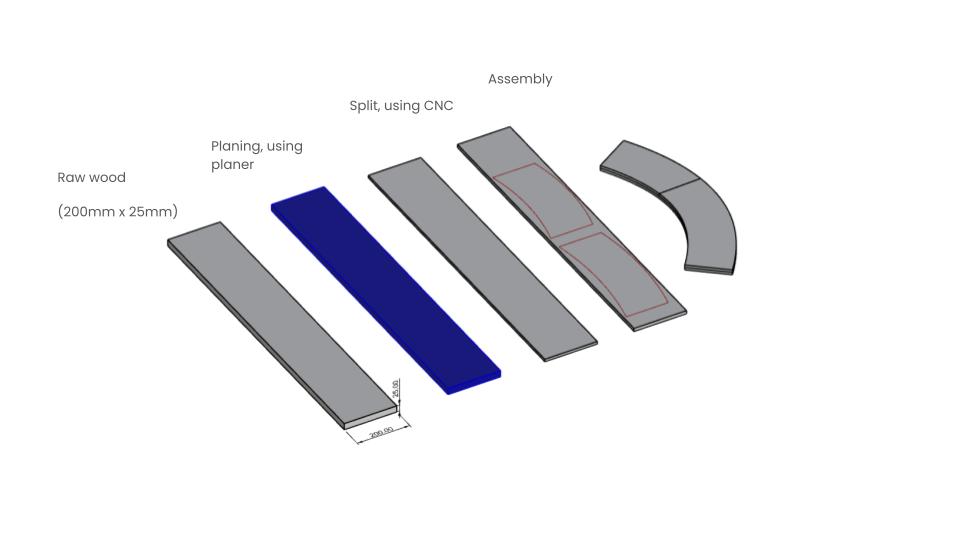
The fabrication process of the segmented blank consisted of picking physical dimensions of wood that we could glulamb in order to create complex geometries like double sided curves or on this case a T shape base structure. This particular project focuses on further analyzing how we can achieve the double curved structure, through fabrication, digitalization for optimization and joinery.
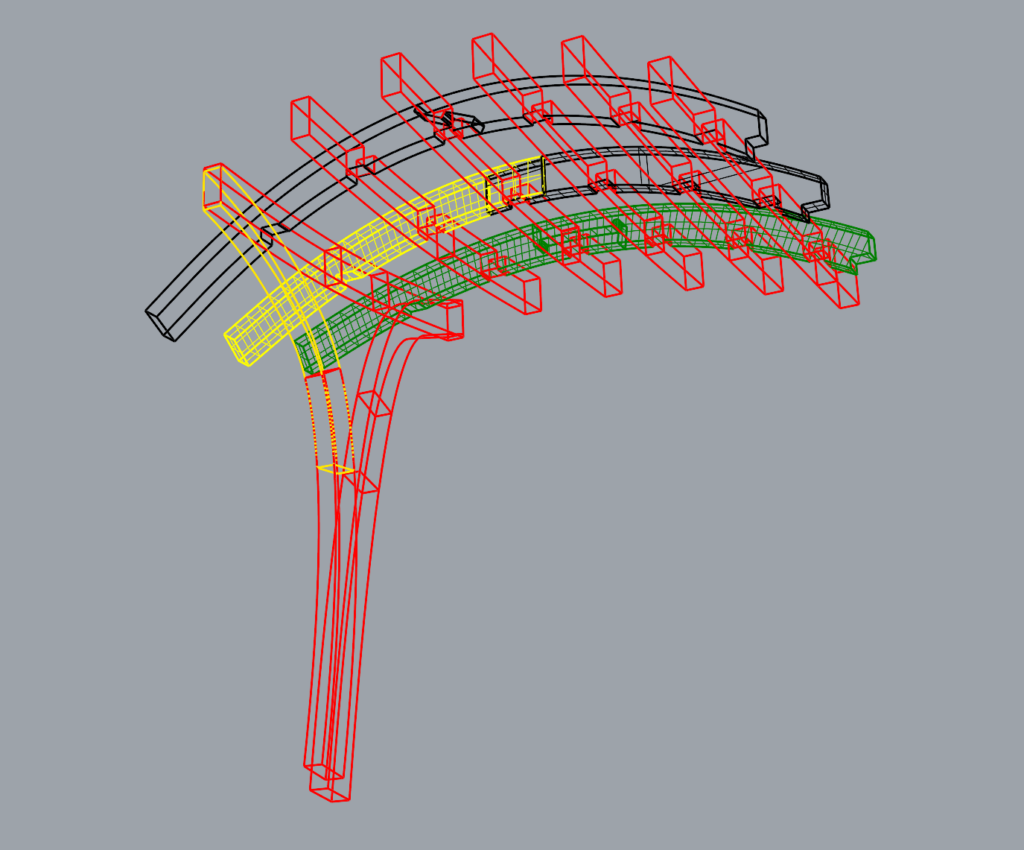
IMAGE: The digitalization of our design started with splitting a section of the surface into different blanks that could be fabricated with different techniques of wood bending and timber shaping. A special plug in was used to further optimize the segmented blank technique through the Glulamb plug in from grashopper to further understand how a double sided curve could be achieved.
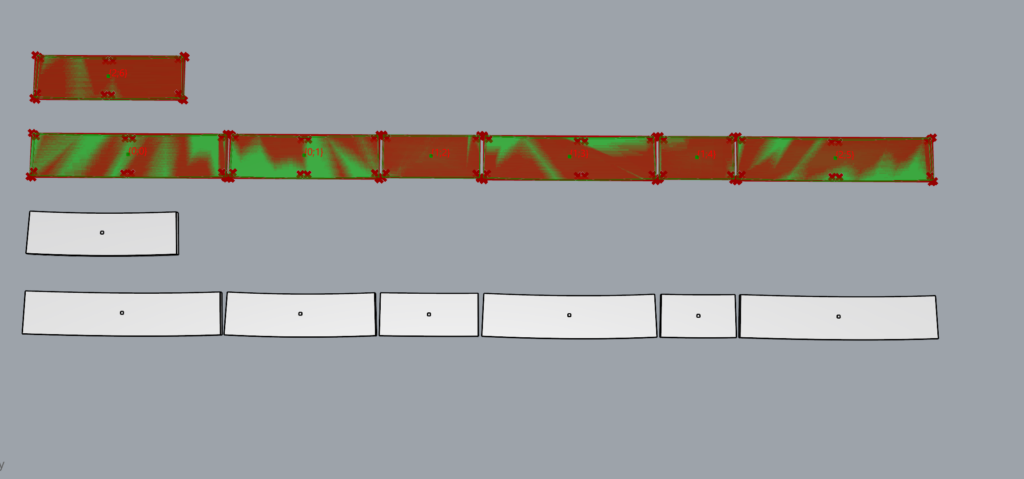
The grashopper script is allowing us to bring a physical design, into a digital design that can be optimized and adapted in regards to production, thickness, and width of the physical wood blanks that will be processed and shape with the CNC milling machine.
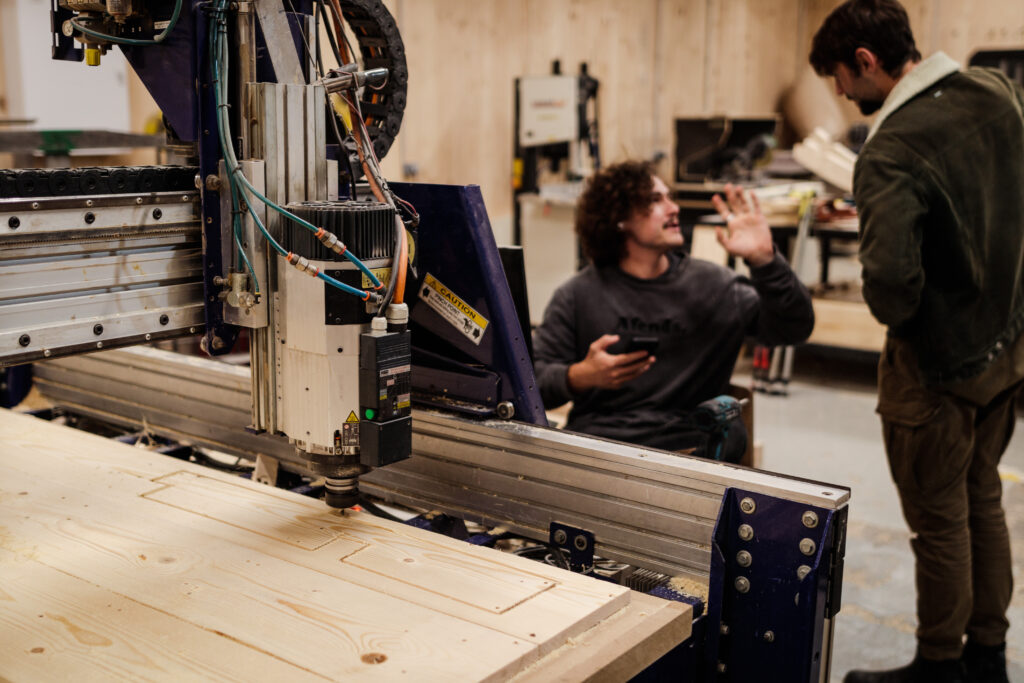
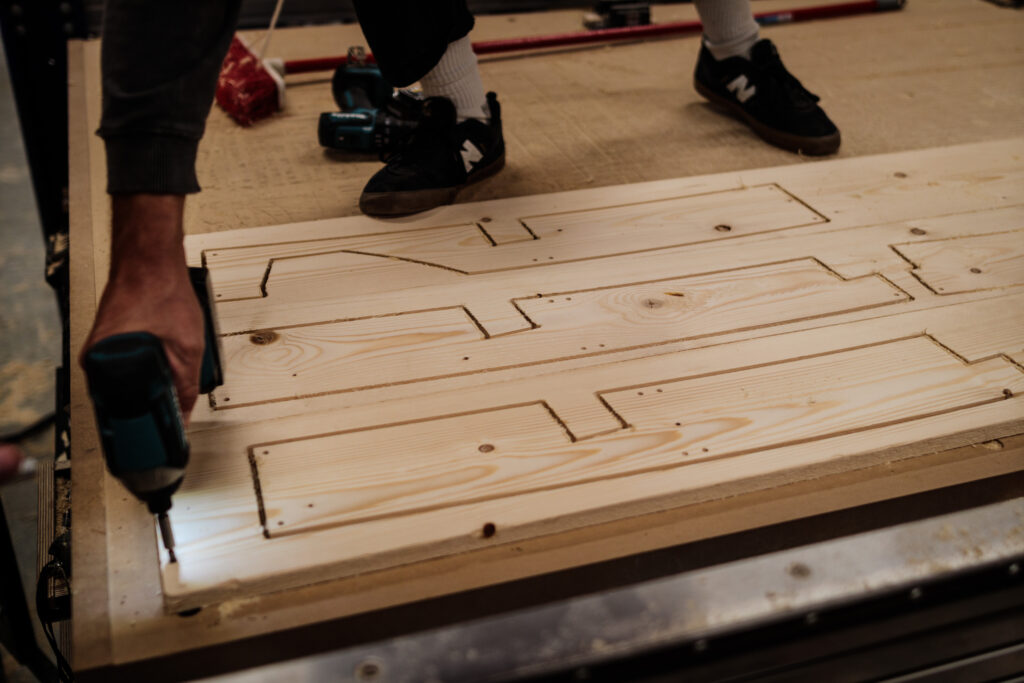
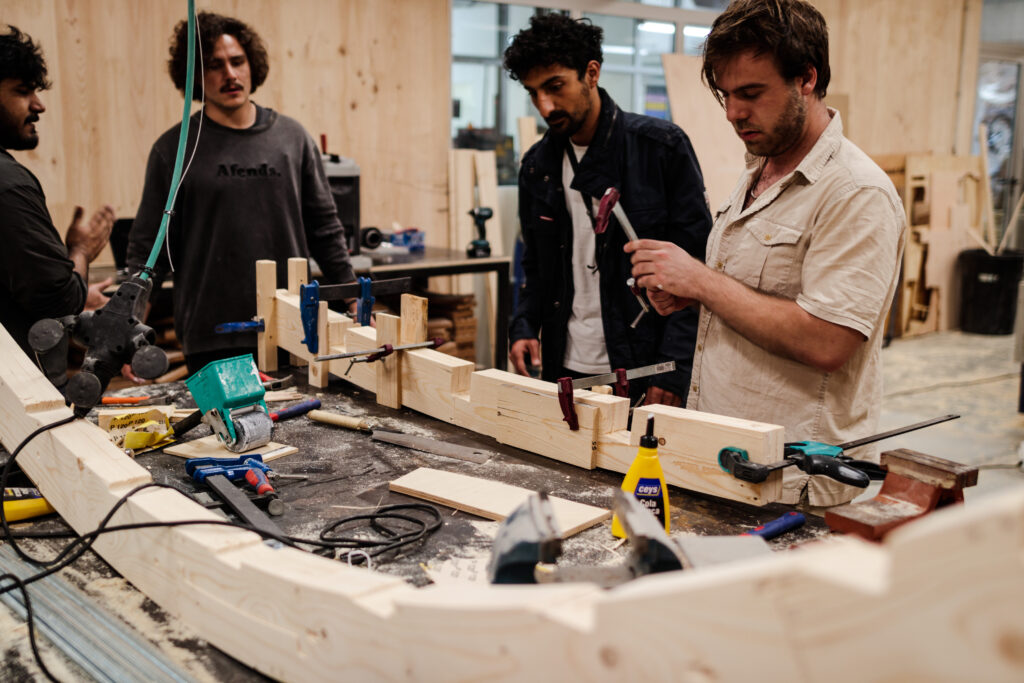



Once the segmented blank pieces were fabricated we used the glulamb technique, with clamps, and dowels in order to join pieces together and later on have a single blank with a specific shape and joinery that can later be assembled. The process took around 5 to 7 hours per blank, counting CNC milling, pre and post processing of each blank, and design of particular joints based on the final section that was fabricated.

