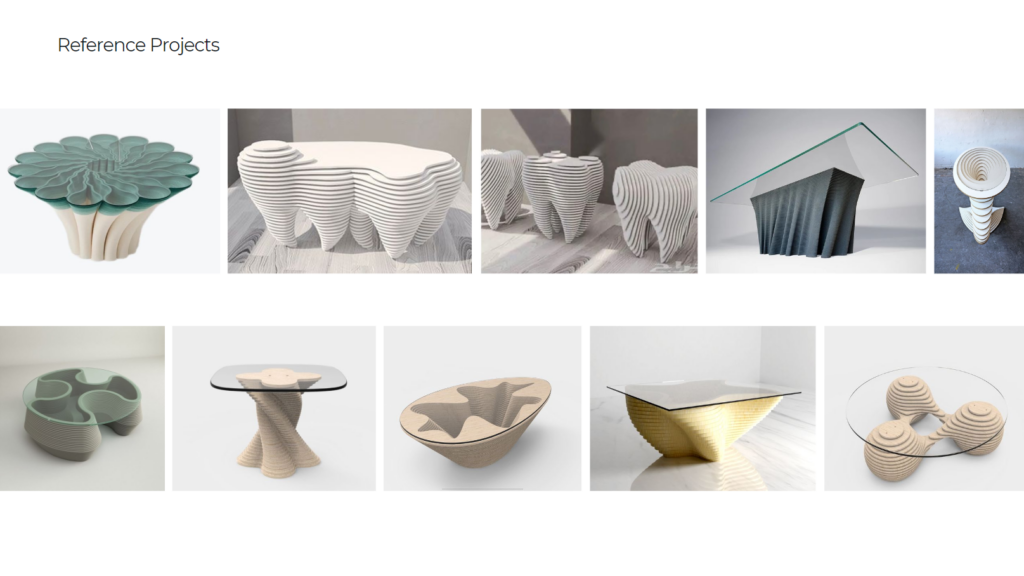
Cork-based 3d printing – Topological Optimisation Design
Introduction
The seminar invites students to explore new materials, additive processes and new fields of applications through robotic 3d printing taking advantage of the potential of the 6-axes of the robotic arm.
Context
Recently we have clearly observed immense changes in architectural design development. Architecture has been influenced by computer-aided design tools and computational methods. Architects are looking for new approaches like generative and parametric techniques in order to find solutions to form finding processes.
Building in this context, the seminar invites students to explore the technique of Additive Manufacturing 3D printing with biomaterials using robotic fabrication. Hence, students will work with cork-paste-based material recycled from cork stoppers to explore new possibilities of biomaterials in additive manufacturing construction.
Aim

Students will explore different architectural systems through the application of topology optimisation tools. Topology Optimisation is an already-known engineering procedure for effective implementation in the architectural design process. The existing attempts of complex engineering algorithms implementation, as a form-finding approach will be explored during the workshop. By intersecting architectural form evaluation with engineering analysis complemented by optimisation algorithms, a new quality of contemporary architecture design process may appear.
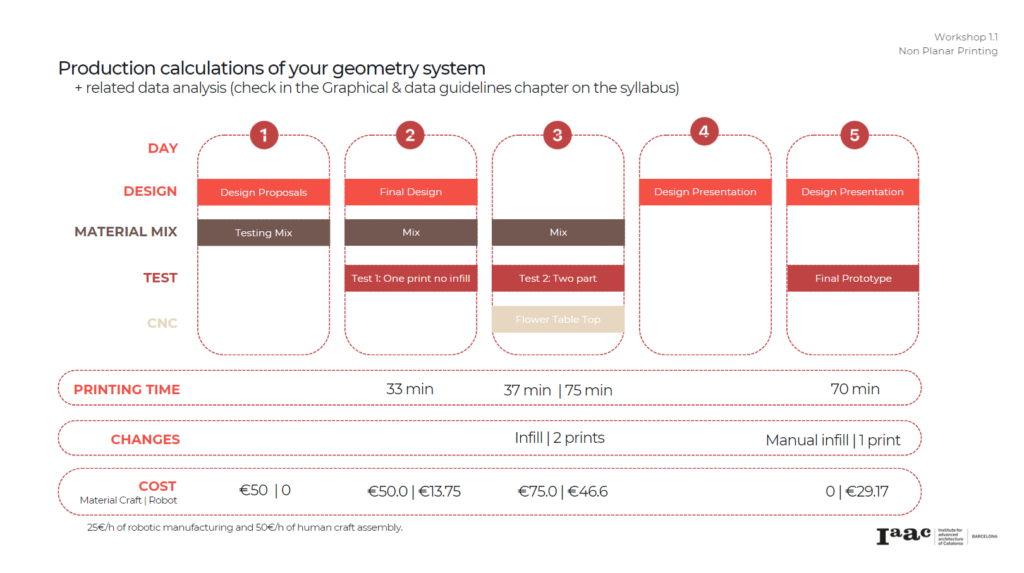
Day 1.
Brainstorming
SimpleTable
OneFootTable
Flower Iterations
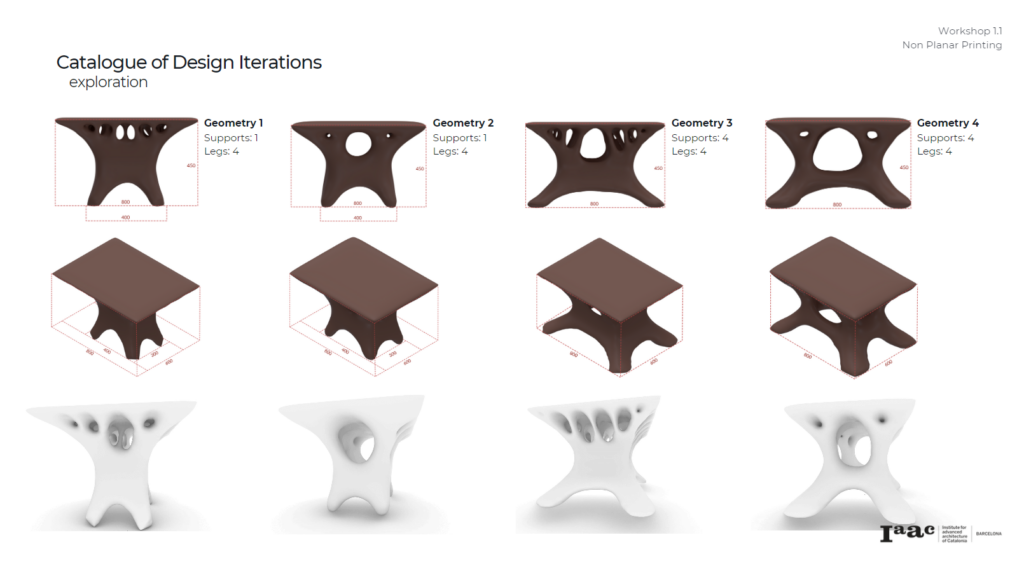
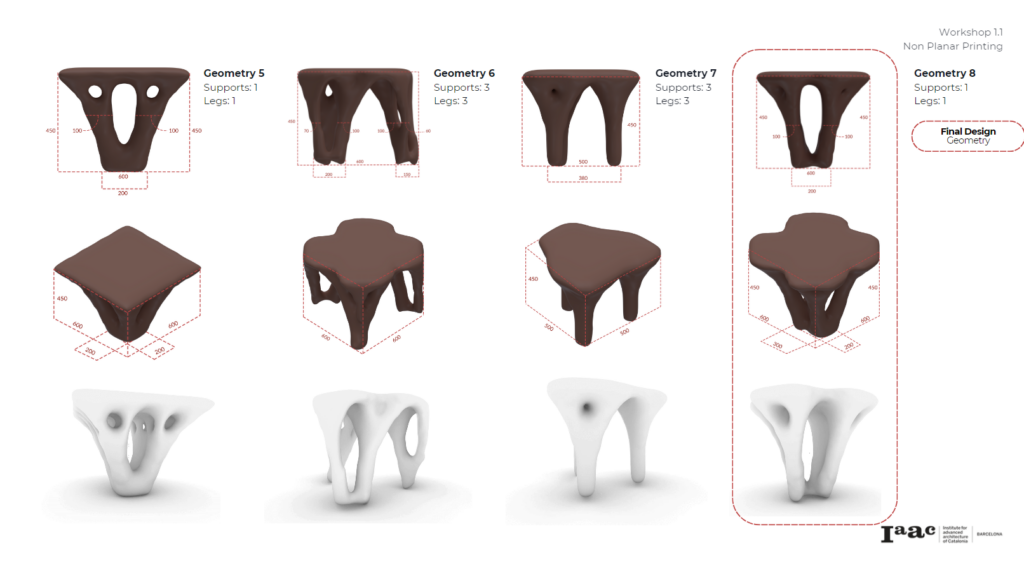

Day 2.
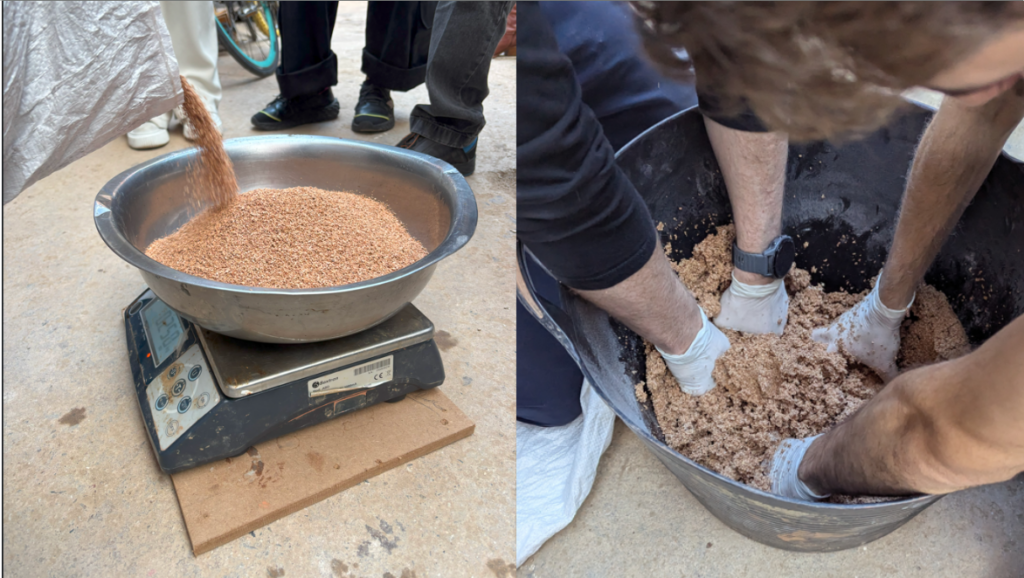
Material Mix:
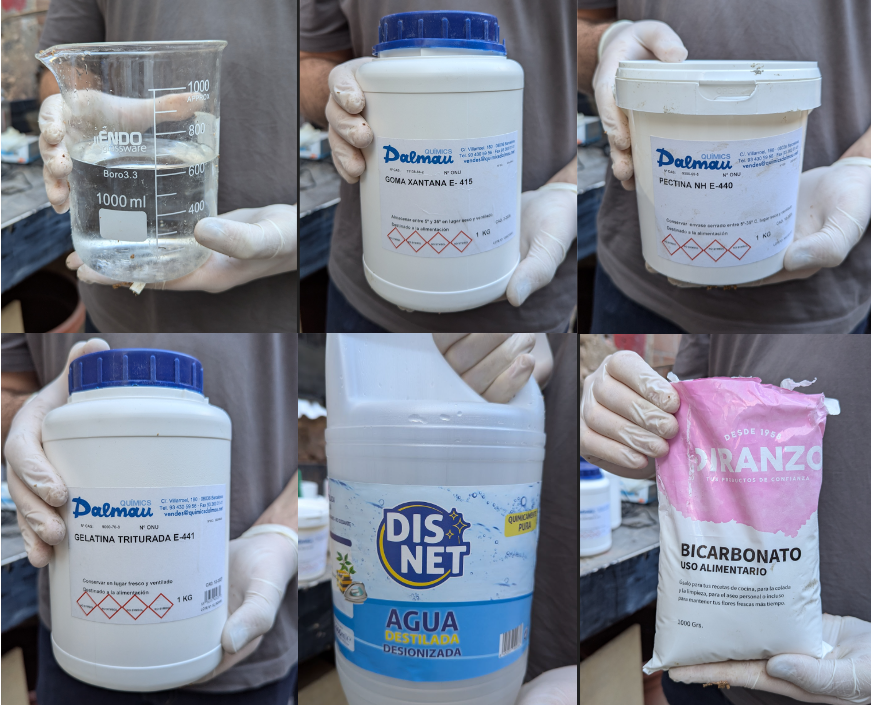
Initial Mixing ratio for 1kg of cork with other materials:

FINAL MATERIAL:
Second Mixing ratio for 1kg of cork with other materials:
Cork – 1 kg (11.29%)
Gelatine – 600g (6.77%)
Xanthan gum – 350 g (3.95%)
Bicarbonato – 125 g (1.41%)
Pectine -285 g (3.22%)
Distilled water -3.25 L (36.68%)
Tap water -3.25 L (36.68%)
Mixing steps:
Mix gelatin powder with cold desalinated water, It is important to add both gelatine and water little by little while whisking/ mixing until it becomes spongy. Then set aside fot a few minutes to let it set. Mix cork granules with xanthan gum, Pectin powder and bicarbonate of soda. Mix the powders and the granules together thoroughly until cork granules are coated with the powder. Mix the gelatin mixture into the cork mixture and mix thoroughly to avoid any clumps forming. ( extra desalinated water could be added into the mixture if it needs extra liquid). Mix the cork-gelatin mixture until a homogenous, viscous mixture is formed. Then the material is ready to be loaded Into WASP pump (Any extra material left should be covered with cellophane to avold exposure to air and becoming dry.)

‘
Material Costs:
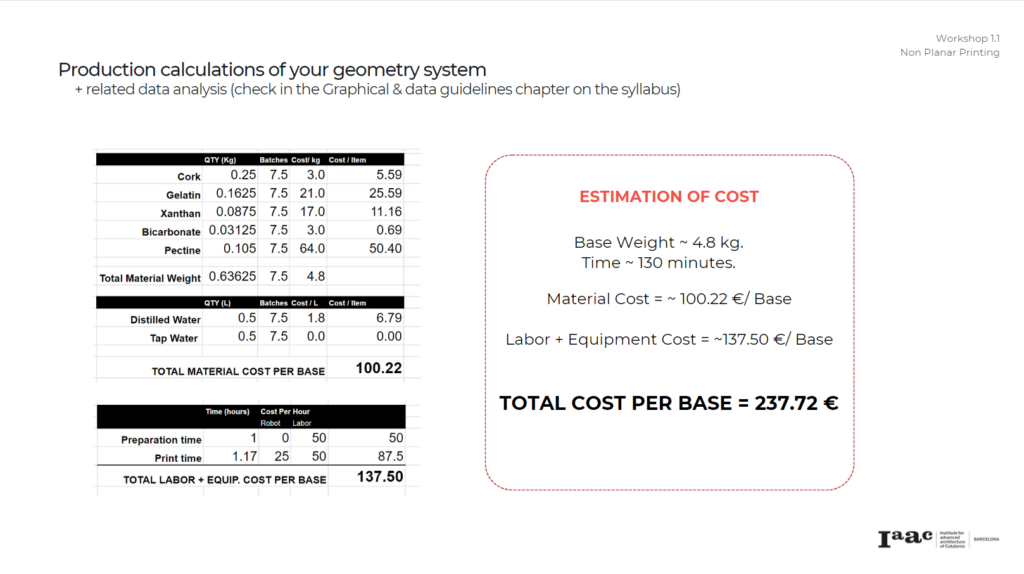

Material Results:
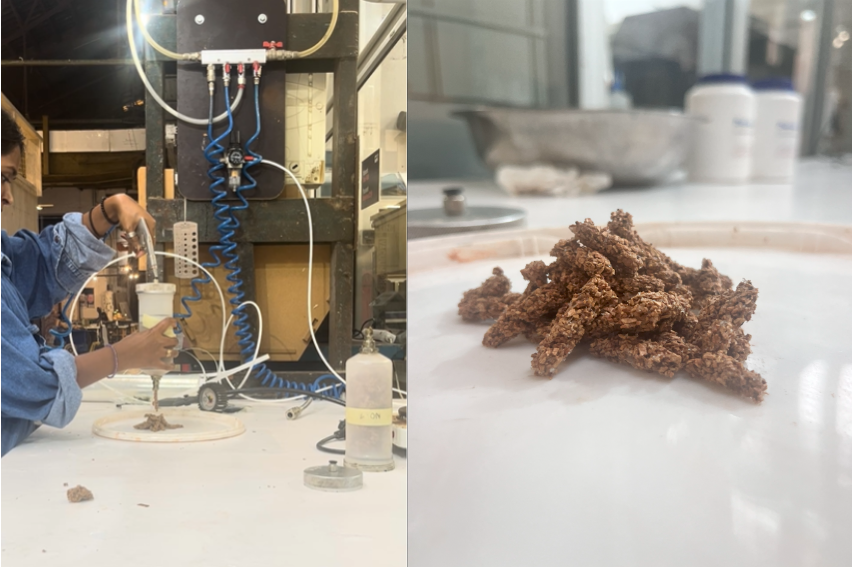

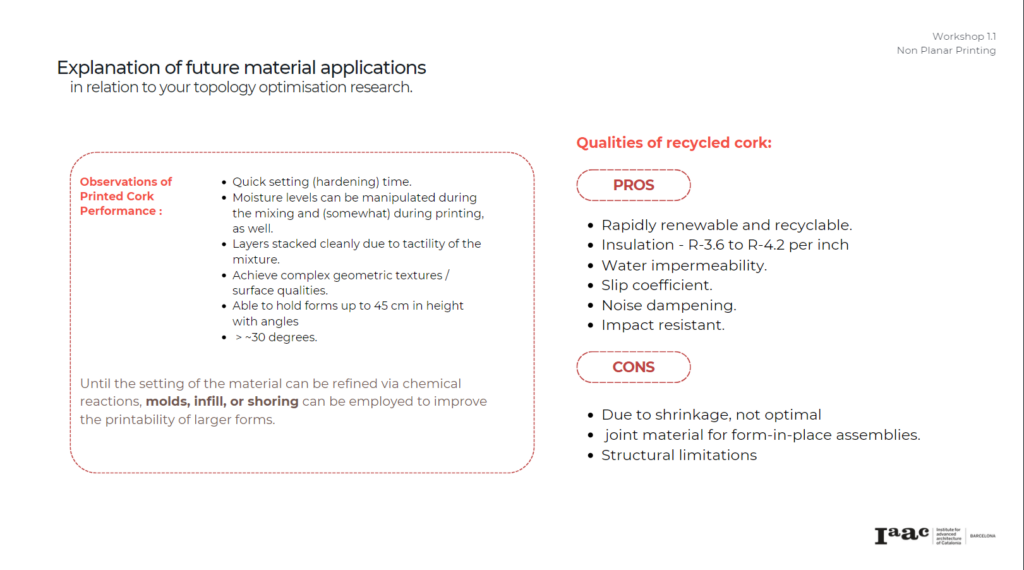
Design & Analysis:
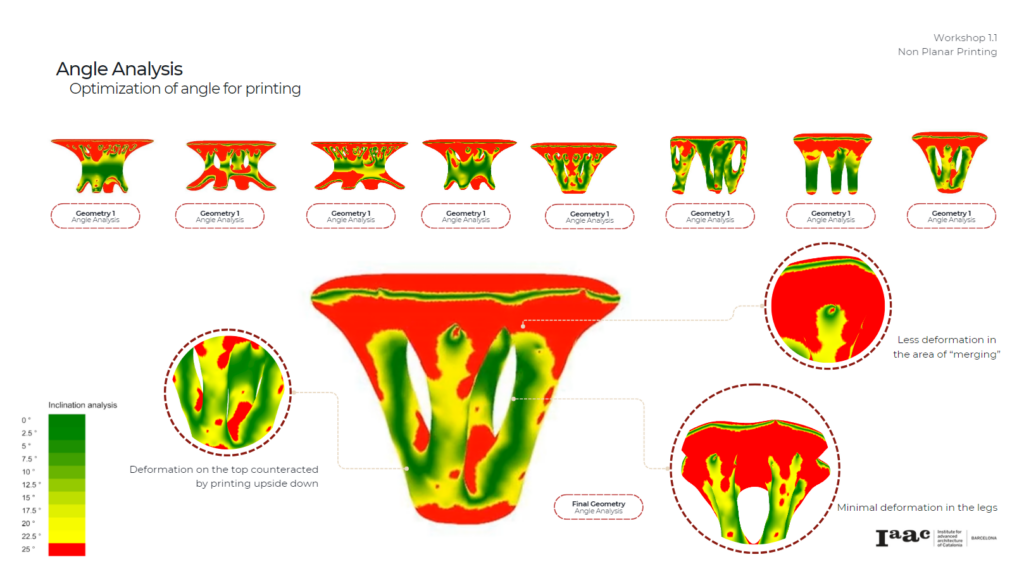
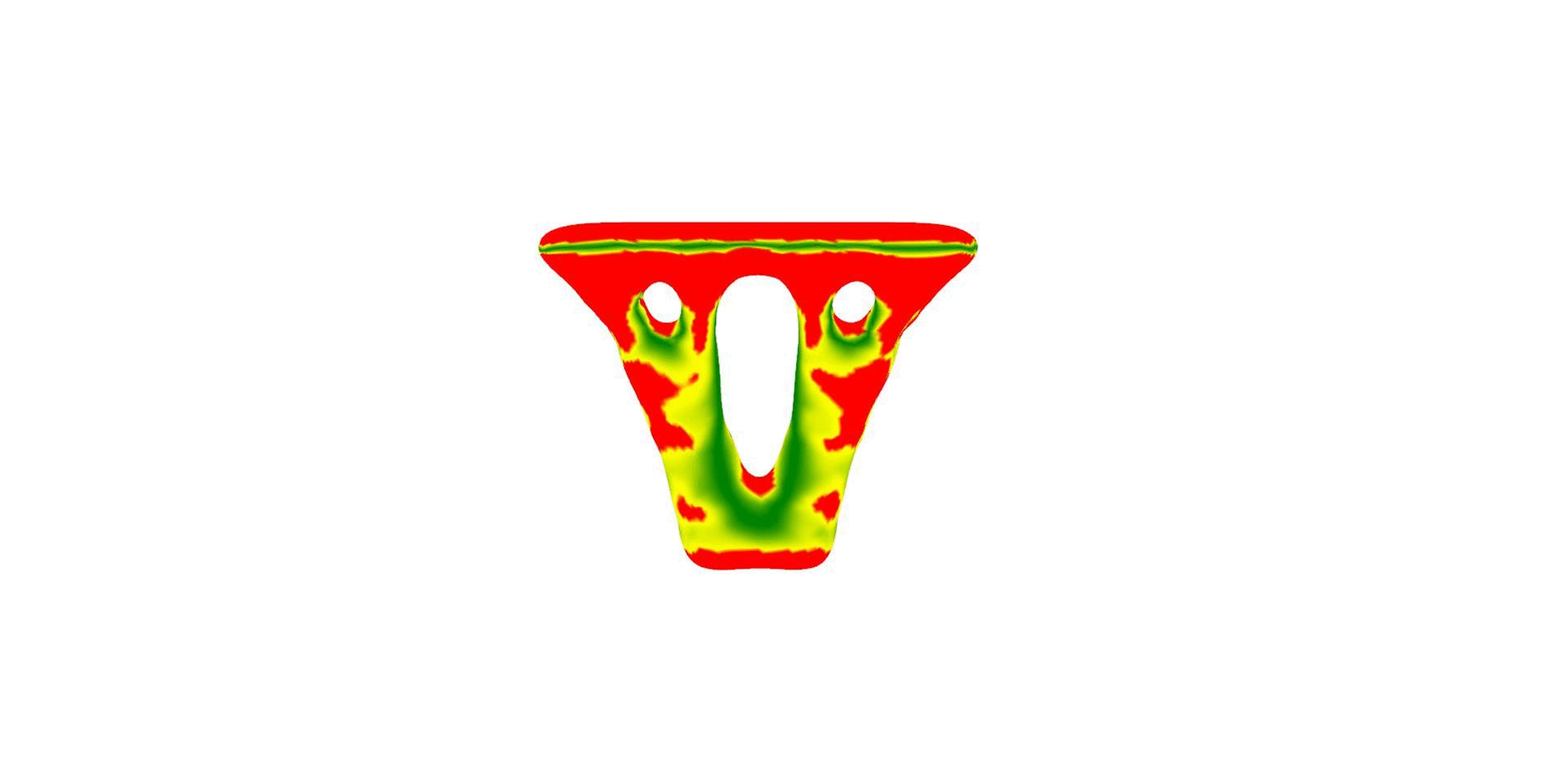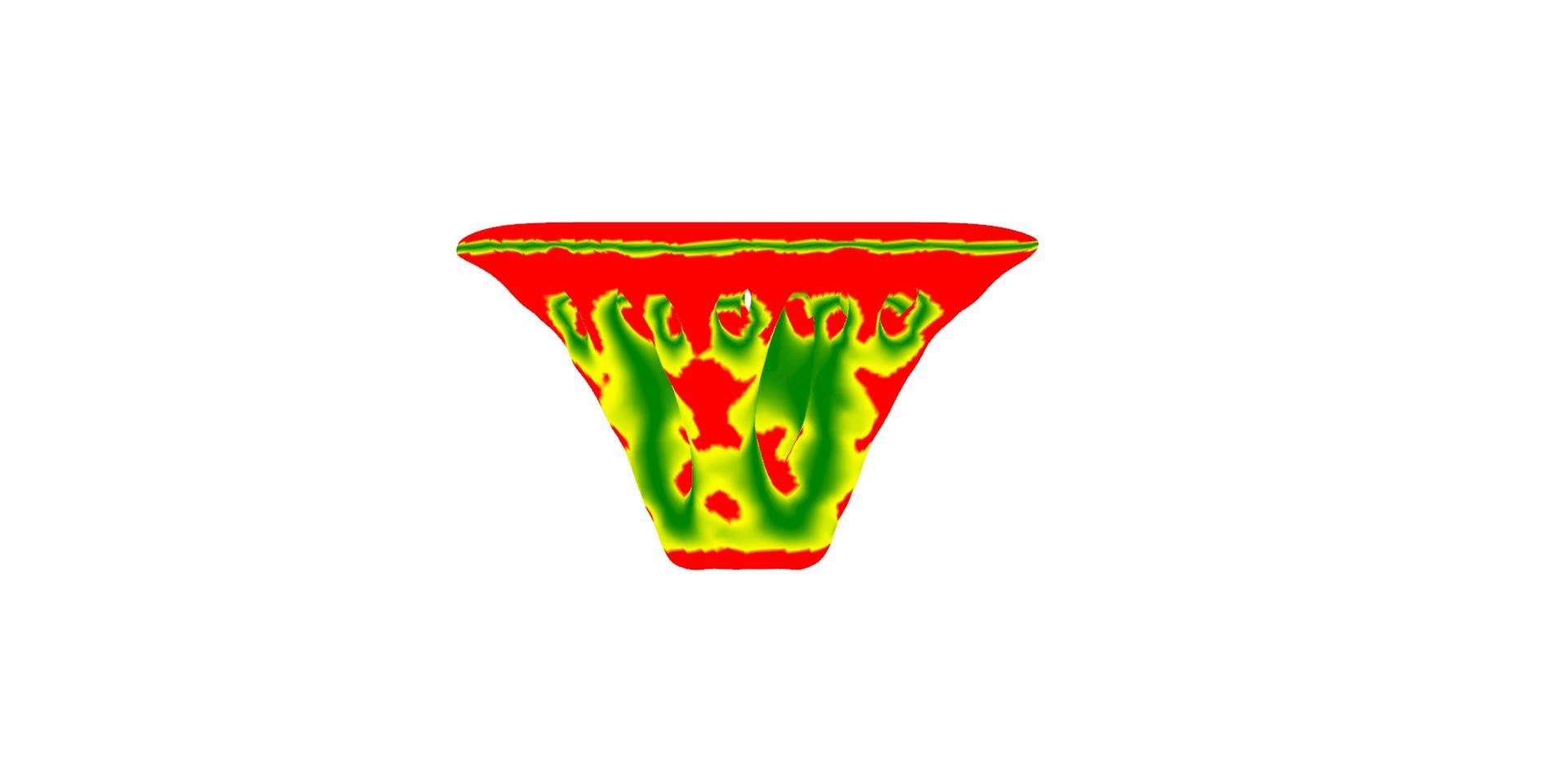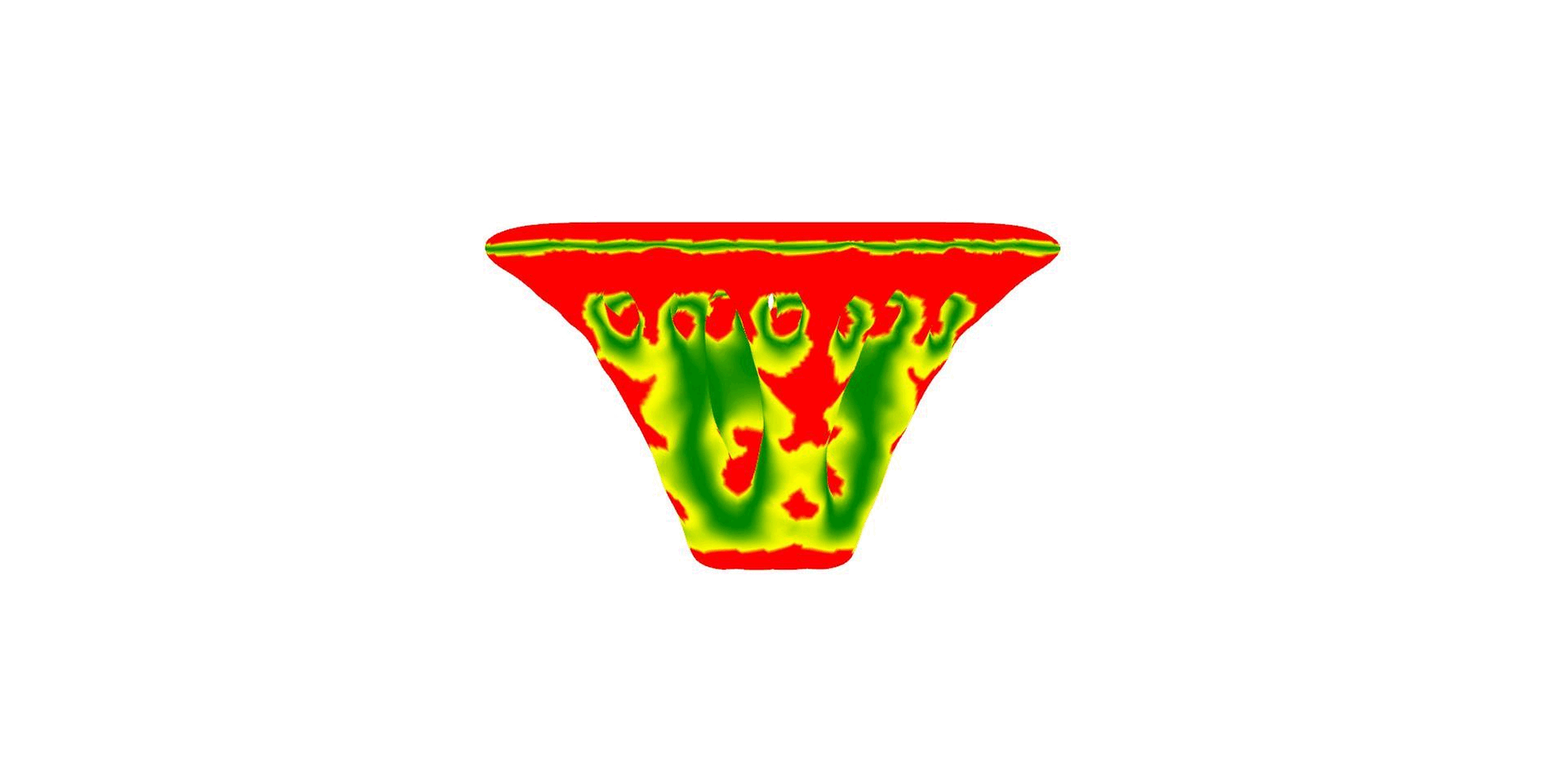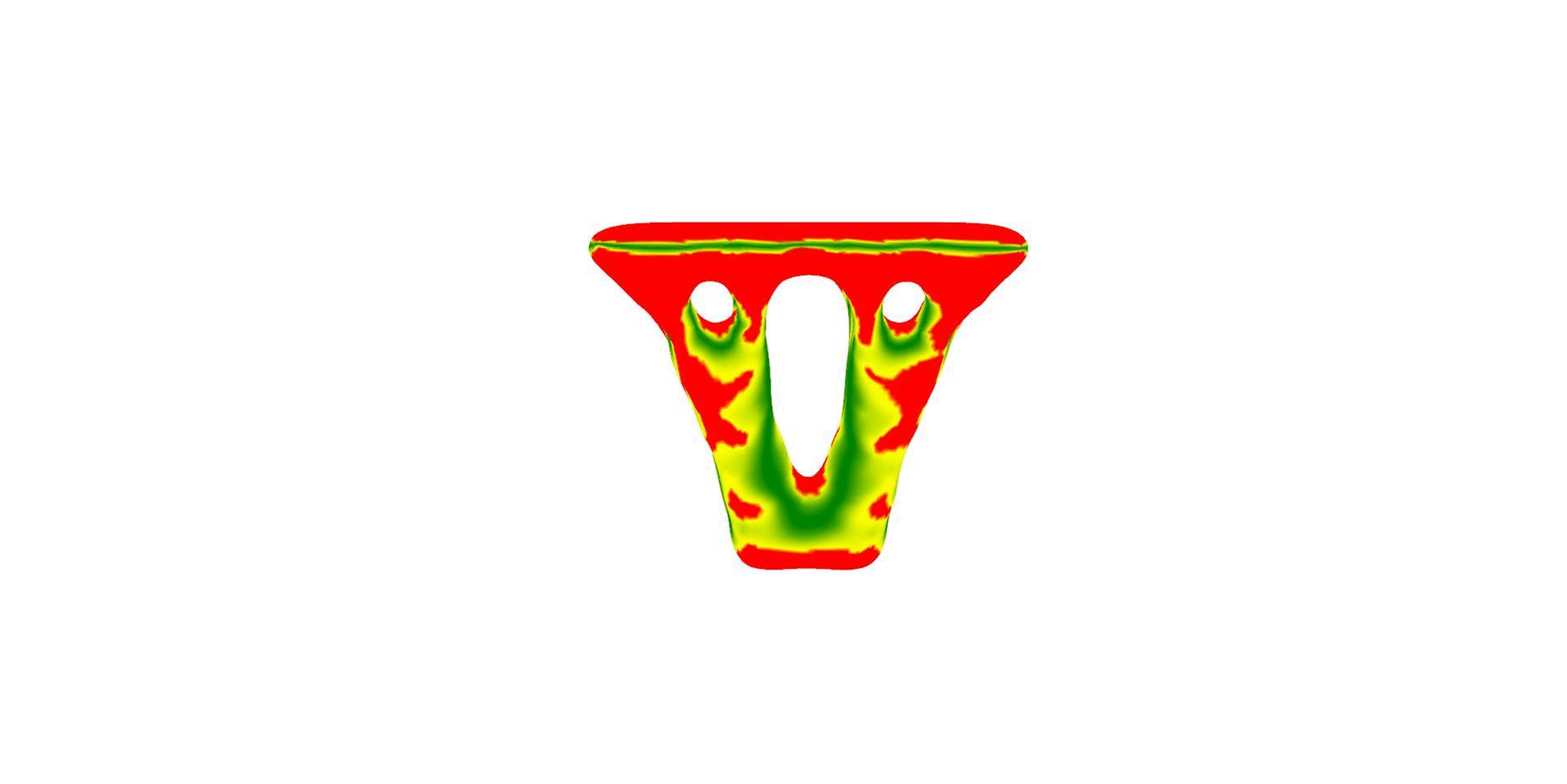
3D Printing
Equipment Parameters :
Tool:
- Tool Type : Extruder
- Tool Diameter (mm) = 5mm
- Nozzle width = 4mm
- SystemAbb : Robotic Arms – 6 Axis
- Industrial Robotic
- ABB IRB 6700
Arduino ( WASP Extruder ):
- PUMP = PRESSURE – ( 15 – 50 )
- EXTRUDER = MOTOR SPEED 300-5.000 (LONG INT VALUE)
Extrusion :
- Layer width
- 1.5 cm 50% robot speed
- 2 cm 25% robot speed
- Extrusion height = 5 mm
- Pressure of the Pump
TEST1.& TEST 2: 12.9 TEST 3 : 13.9
- Motor Speed = 300-5.000
TEST / PROTOTYPE 1 :

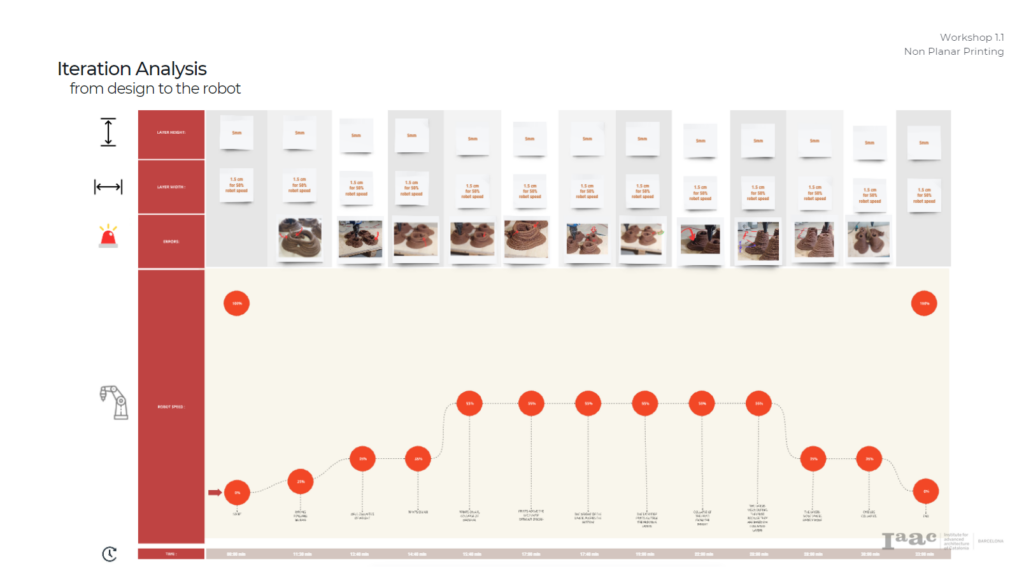
IMAGE SOURCE:
IMAGE SOURCE
PROTOTYPE 1 RESULTS:
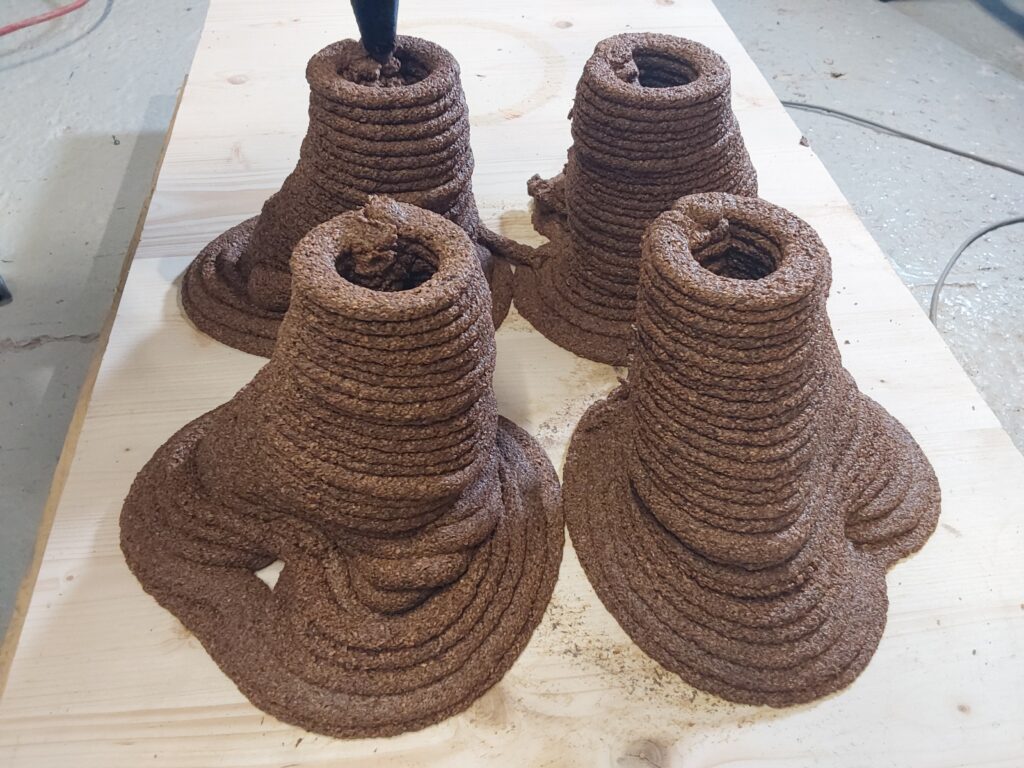
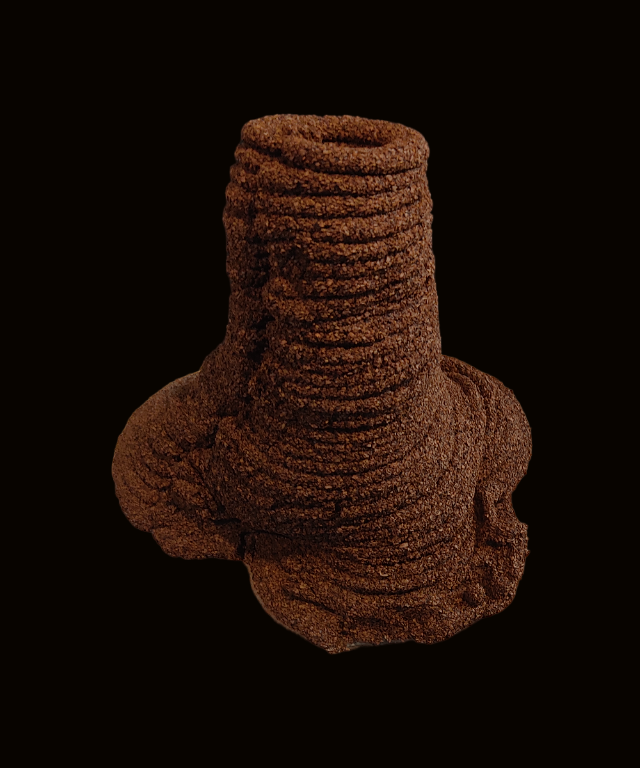


Day 3.
CNC Milling:
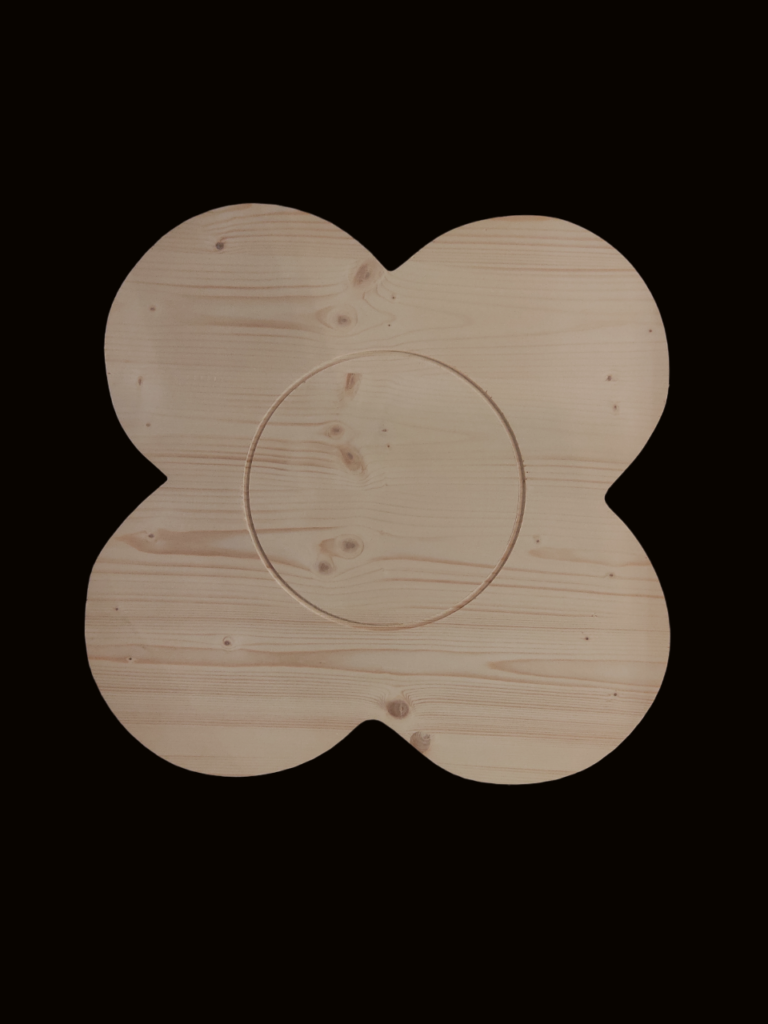

DESIGN / PROTOTYPE 2 :

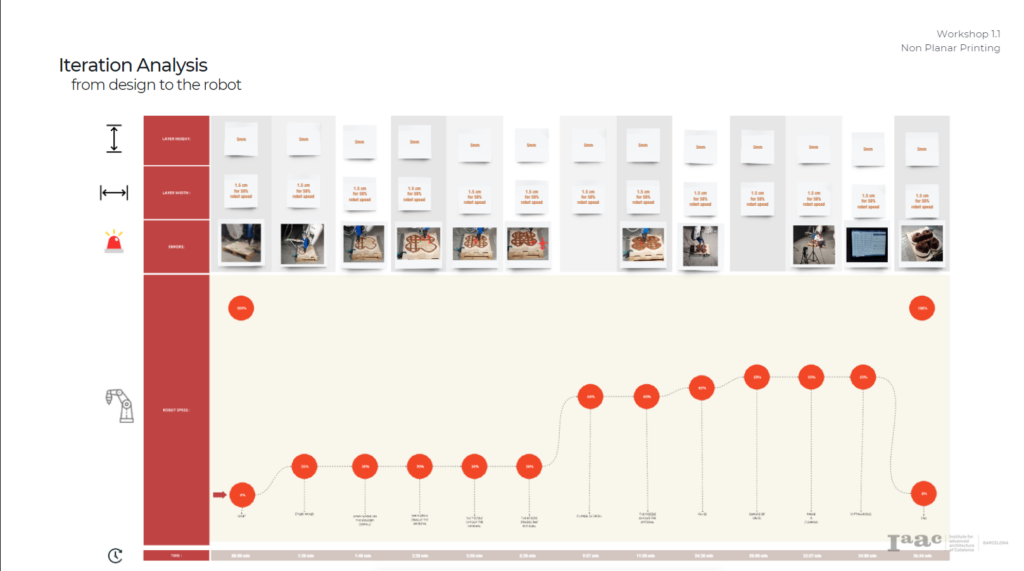
IMAGE SOURCE:
PROTOTYPE 2 RESULTS:
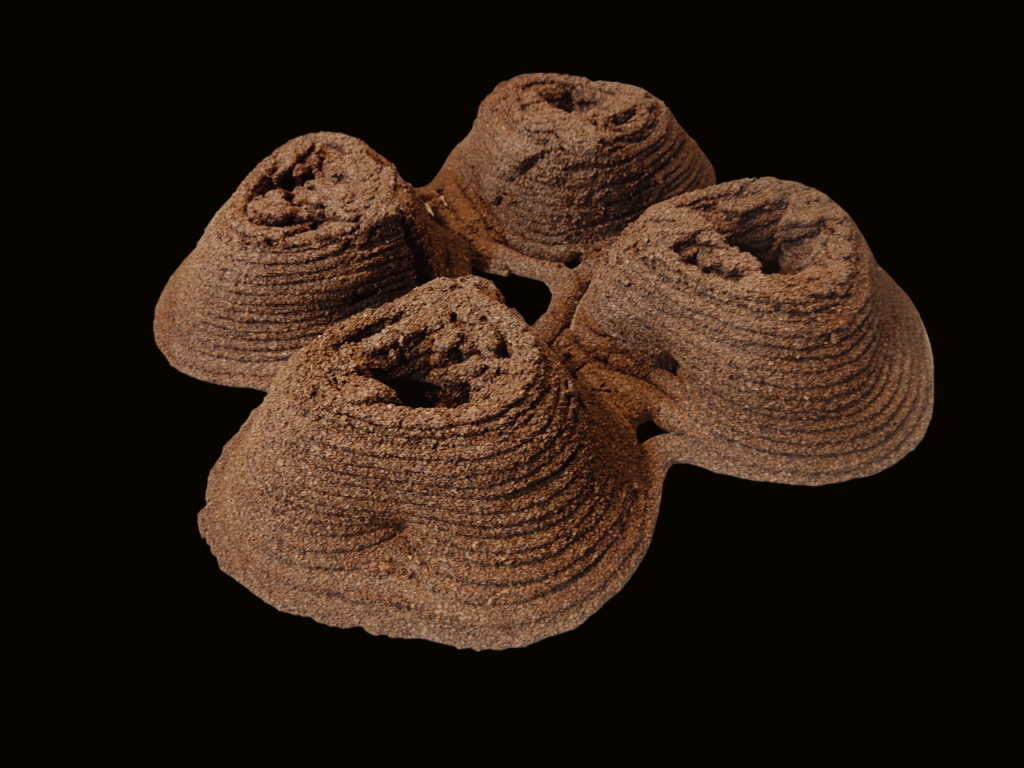

TEST / PROTOTYPE 3 :

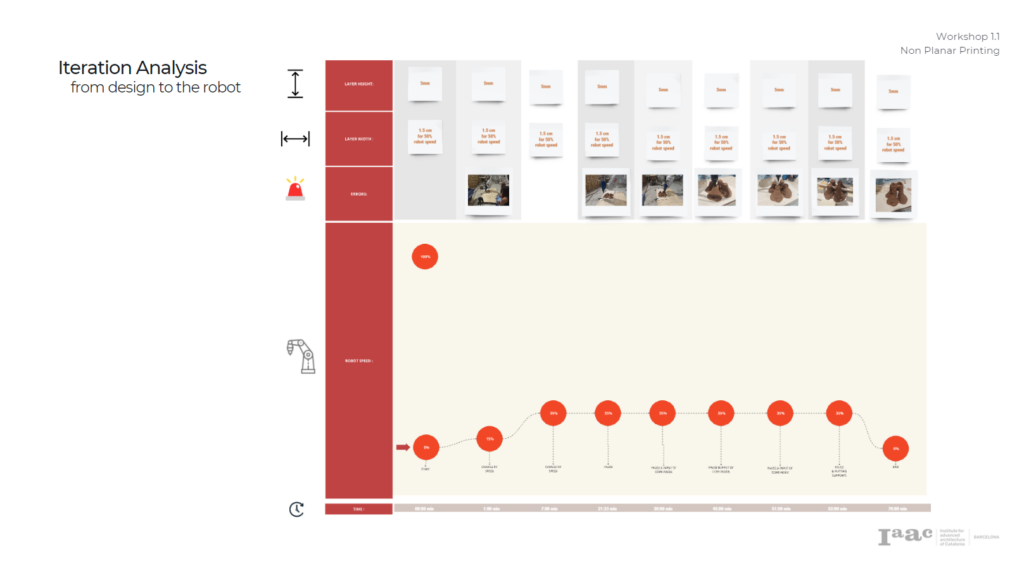
IMAGE SOURCE:
PROTOTYPE 2 RESULTS:
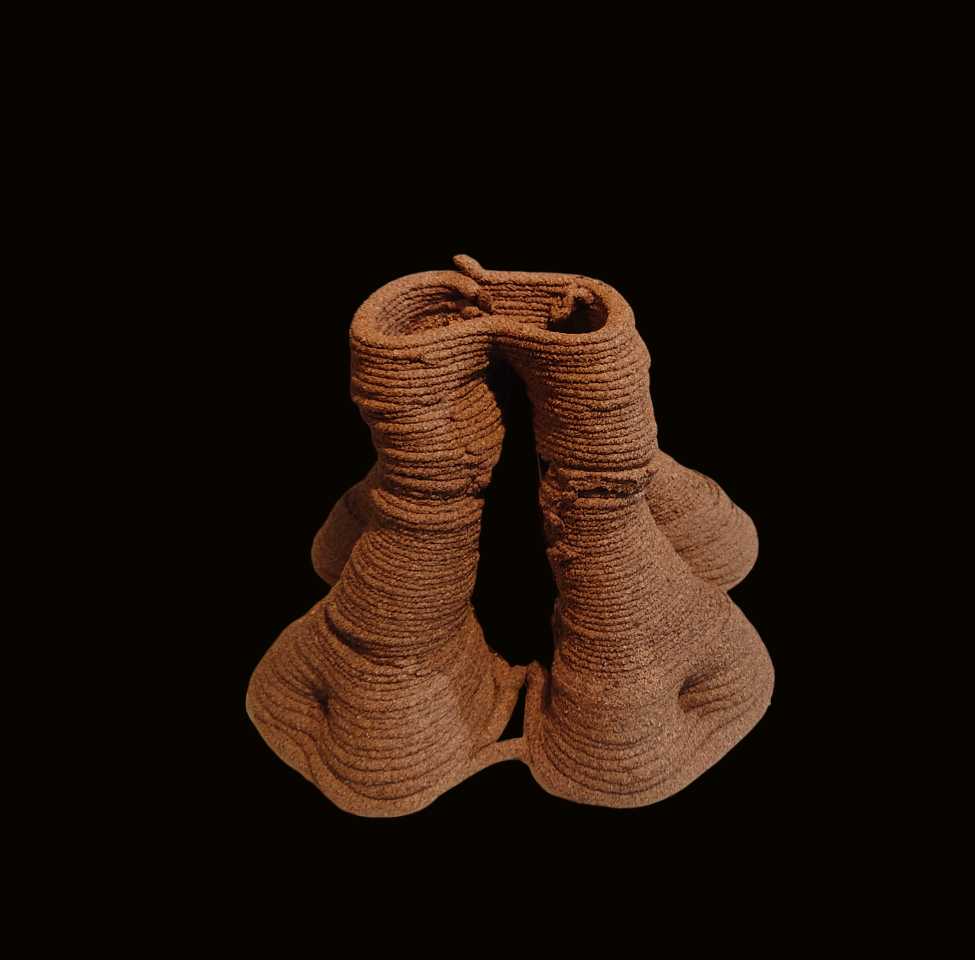

Final Result:
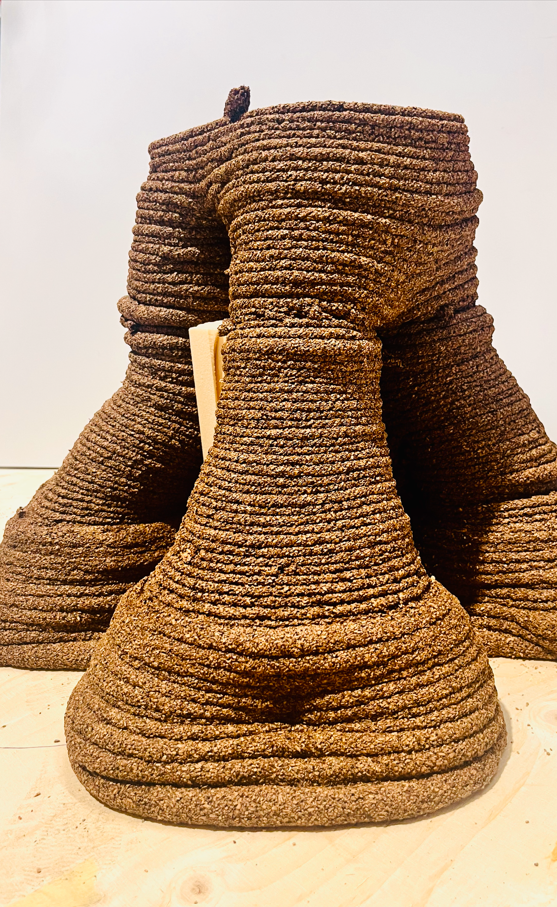



Final Render:



