Credits: Thomas Burns
In today’s world, we use countless electronic devices daily. Yet, many of us don’t really understand how they work. Often, these devices are designed more for use than for understanding, leaving us in the dark about their inner workings.
Enter the world of open-source. This approach lets us look under the hood, revealing how tech works and even allowing us to create our own customised technology.
In a digital age where gadgets and gizmos are the norm, understanding their heartbeat often feels like a distant concept. While we’re surrounded by technology, the blueprint of their magic remains veiled.
Welcome to a transformative exploration of the digital universe with The Introduction to Programming and Physical Computing.
What Awaits You:
- Dive headfirst into the foundational pillars of programming and the tactile world of physical computing.
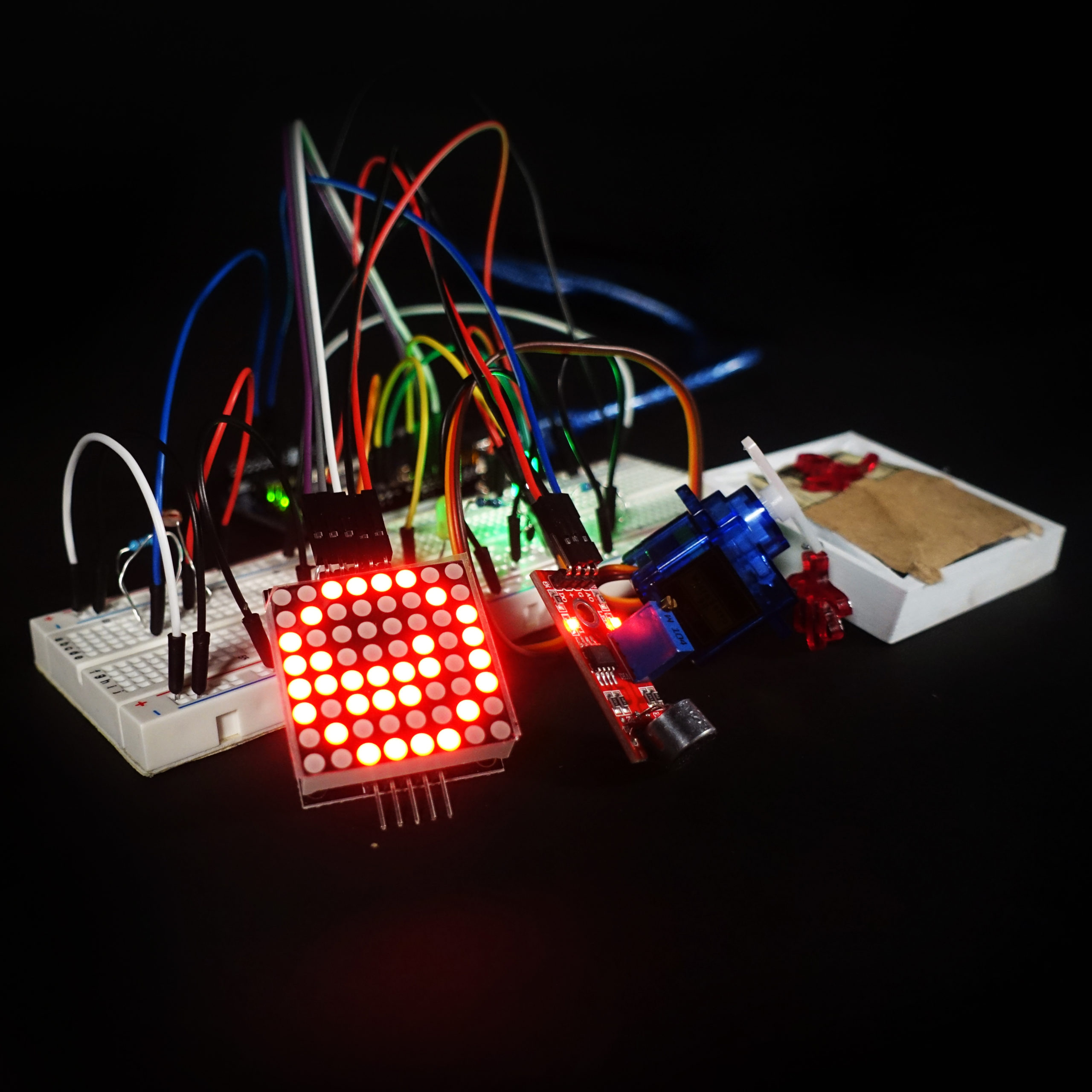
- Familiarise yourself with the versatile Arduino platform, enabling you to bring ideas to life.
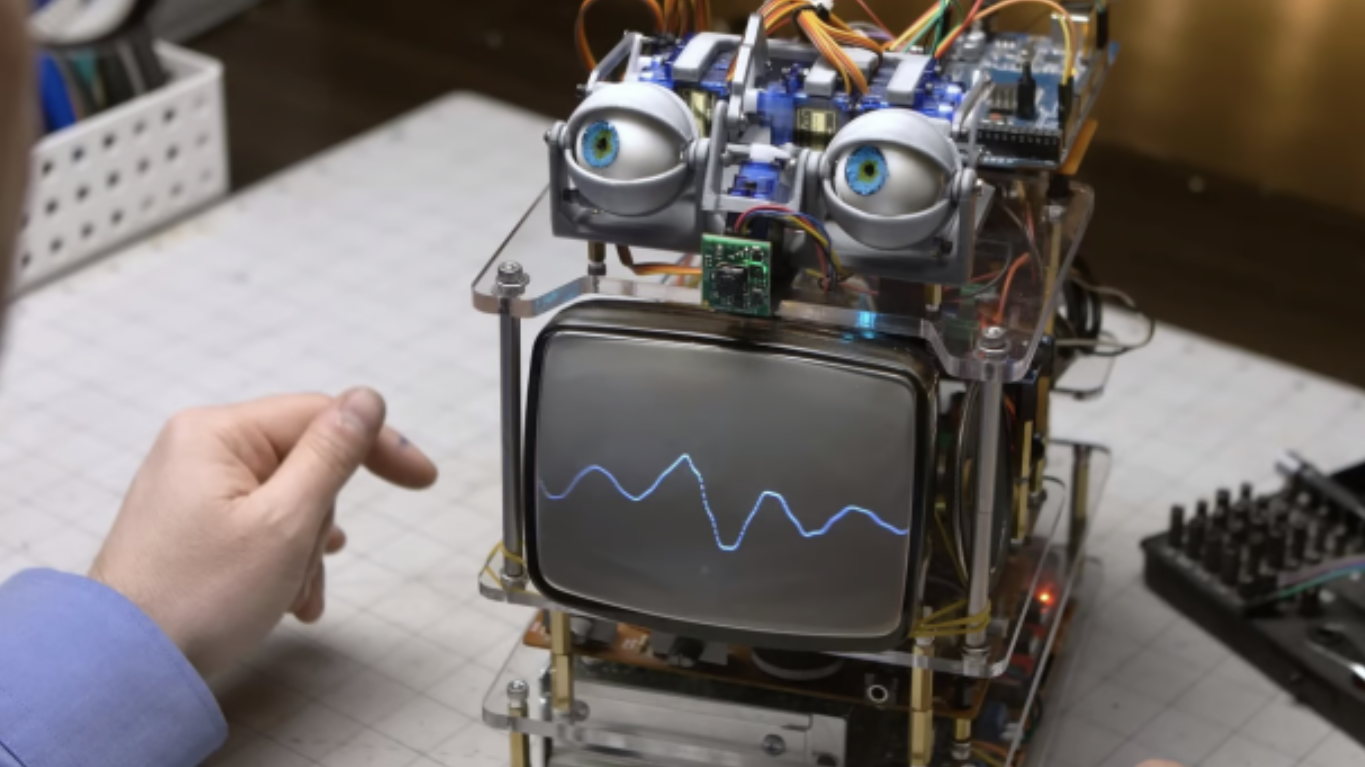
- Step into a hands-on lab experience, where you’ll craft devices that sense and respond to their environment.
By the end of this seminar, not only will you decipher the digital language of everyday devices, but you’ll also be able to dive deeply in this field and embed smart features in your studio projects.
Learning Objectives
At course completion the students will:
- learn the basic concepts of programming that will allow them to reach more depth in various Physical Computing topics as well as to jump to different programming languages;
- be able to sense the environment and act back through actuators;
- to develop smart apparatus that react to external conditions.