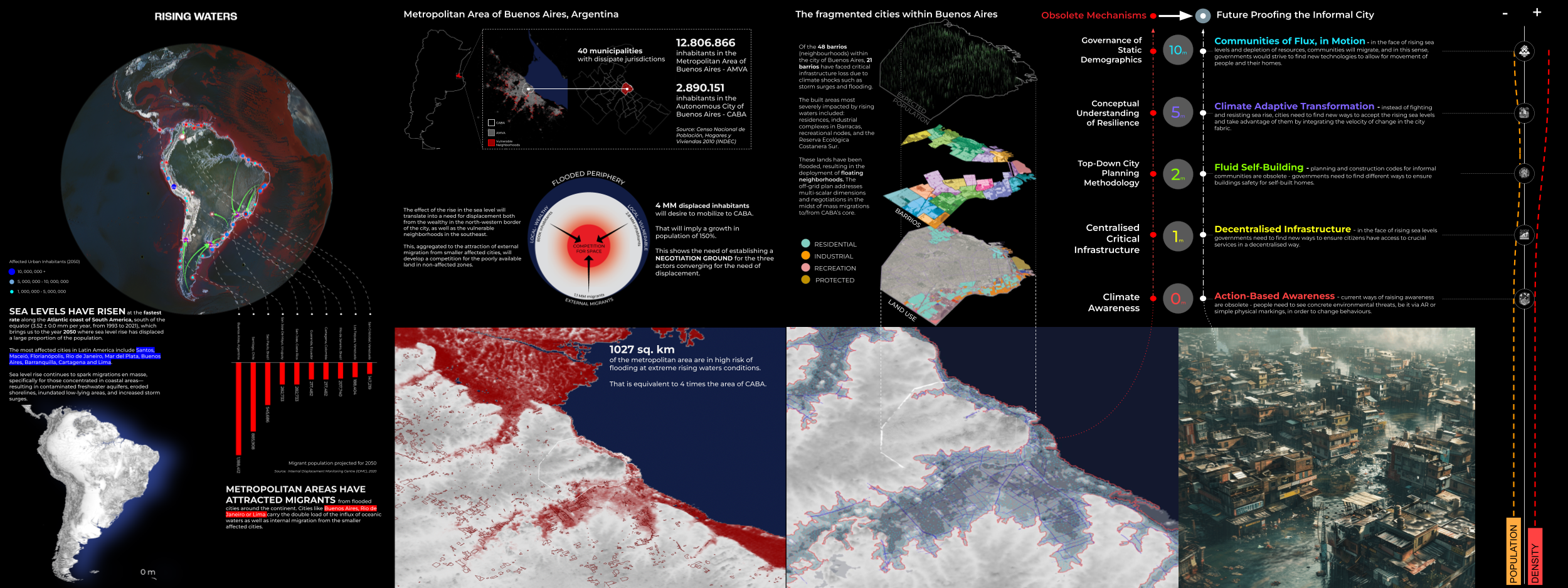
Rising Waters
The year is 2100. Latin America is sinking. Due to global warming the polar icecaps have almost melted completely. In addition the increased temperature has caused the global water mass to expand by almost 1%. As a consequence sea levels are rising at unprecedented levels globally. The coastline in South America is hard-hit by these … Read more