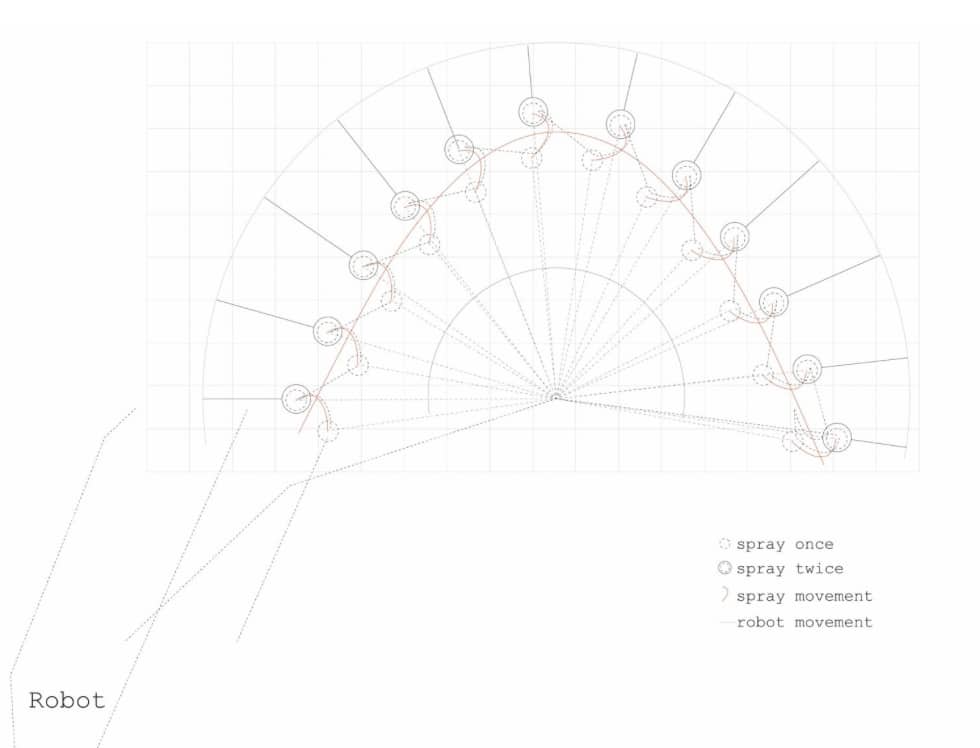
ARCS: Automated Reality Construction Scanner
The construction industry remains one of the least digitized sectors globally, yet it manages a $177 trillion market. Despite this massive scale, approximately 12–20% of total project costs are routinely lost to rework, largely driven by discrepancies between design plans and as-built site conditions. As a proposal developed for our Software II course, we present … Read more