GENETIC OPTIMIZATION THROUGH COMPUTATIONAL DESIGN
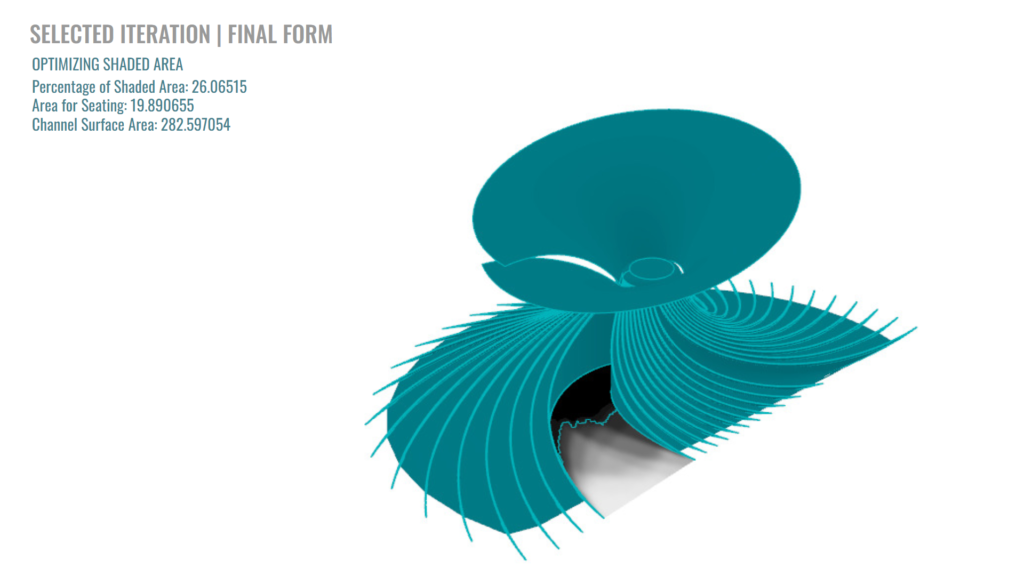
This work aimed to genetically optimize through computational design of a rainwater filtration tower. The tower is part of the design developed for the Digital Matter Studio. The group proposes to create a landscape structure that can collect and filter rainwater through chitosan, a bio-based material made from mussel shells waste, to increase water independence in areas of need.
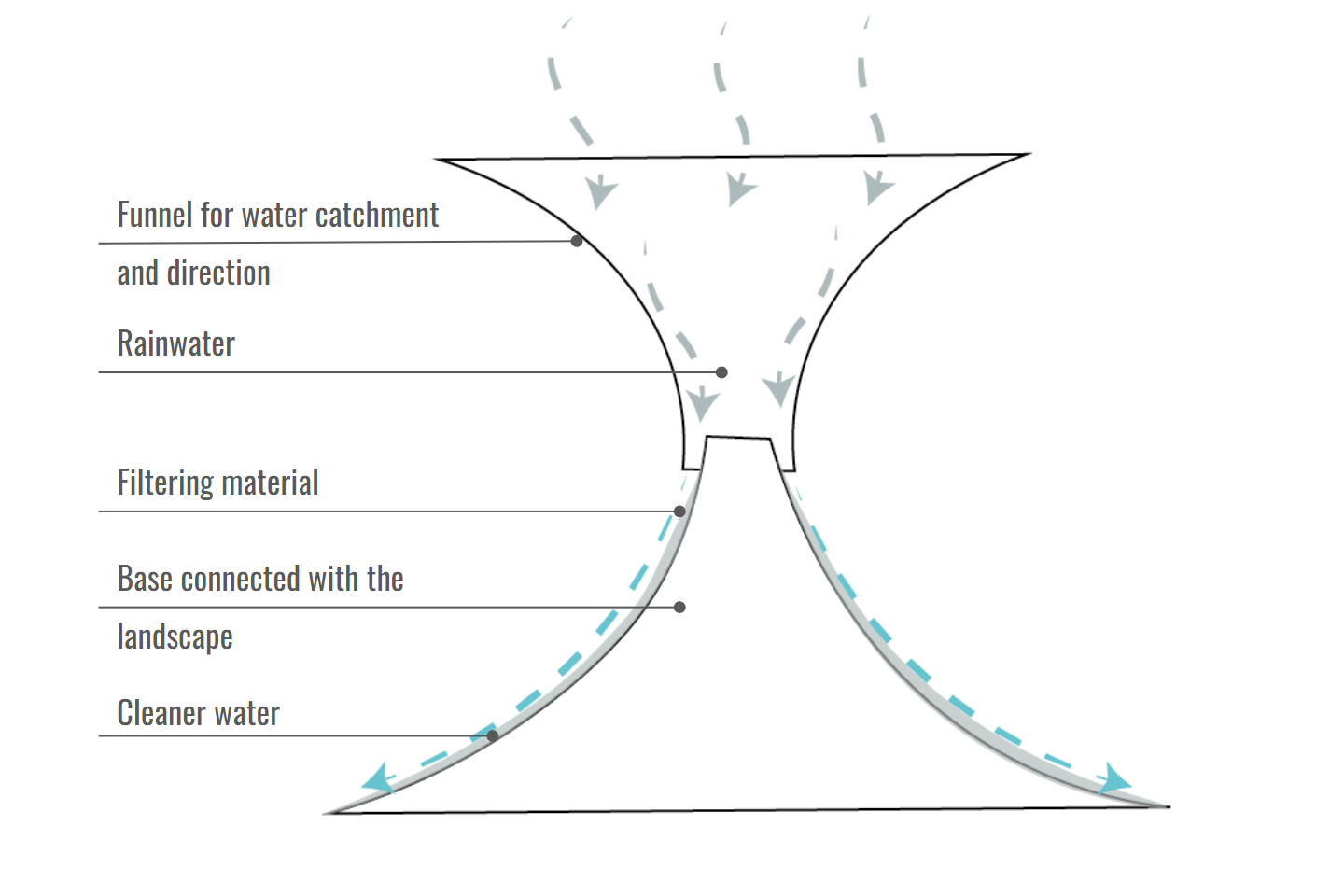
Diagram of how the structure works
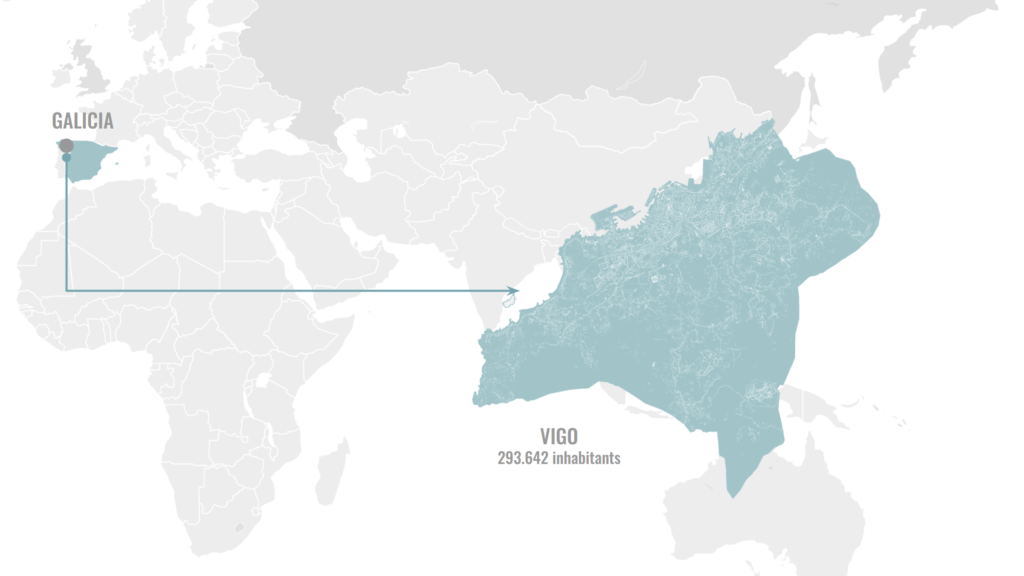
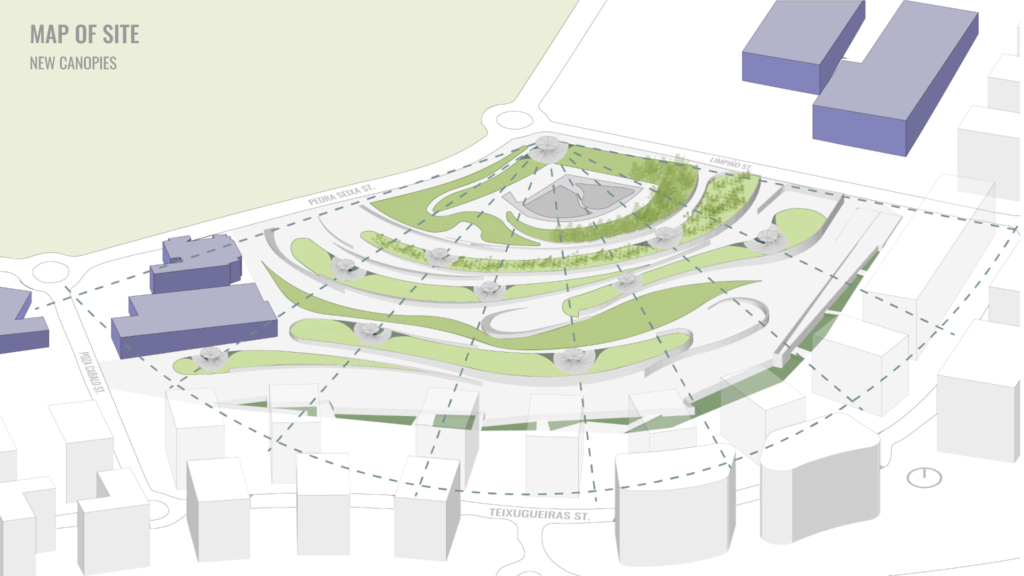
The site chosen in order to showcase the potential of the structure is in Spain, more specifically the region of Galicia in a city called Vigo. This place was chosen because not only the material is available but also because the community suffers from water scarcity even though they have abundant rain seasons.
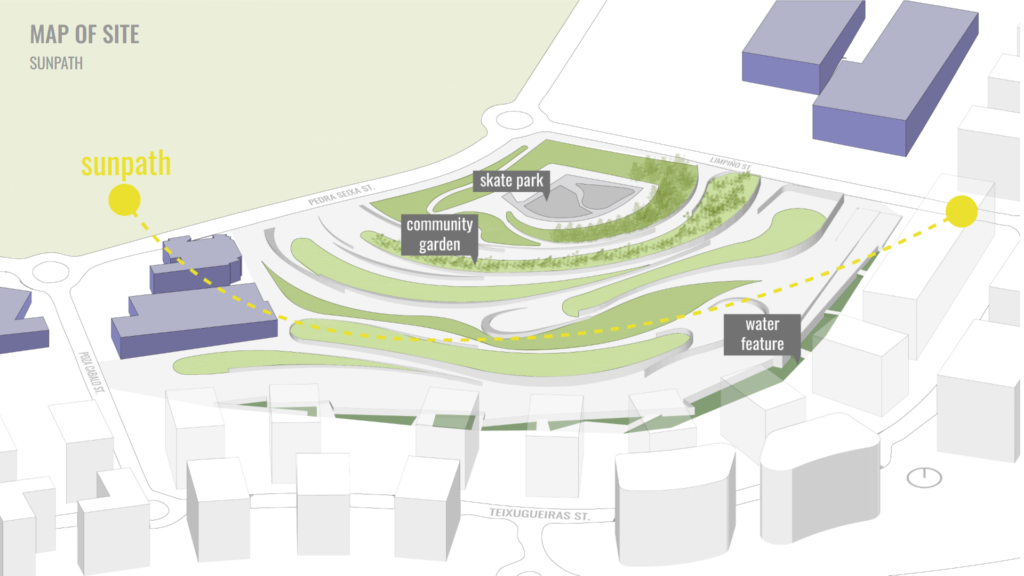

The public space we chose to intervene in is Navia Park, and one of the complaints of the community is the lack of shade during the summer months.
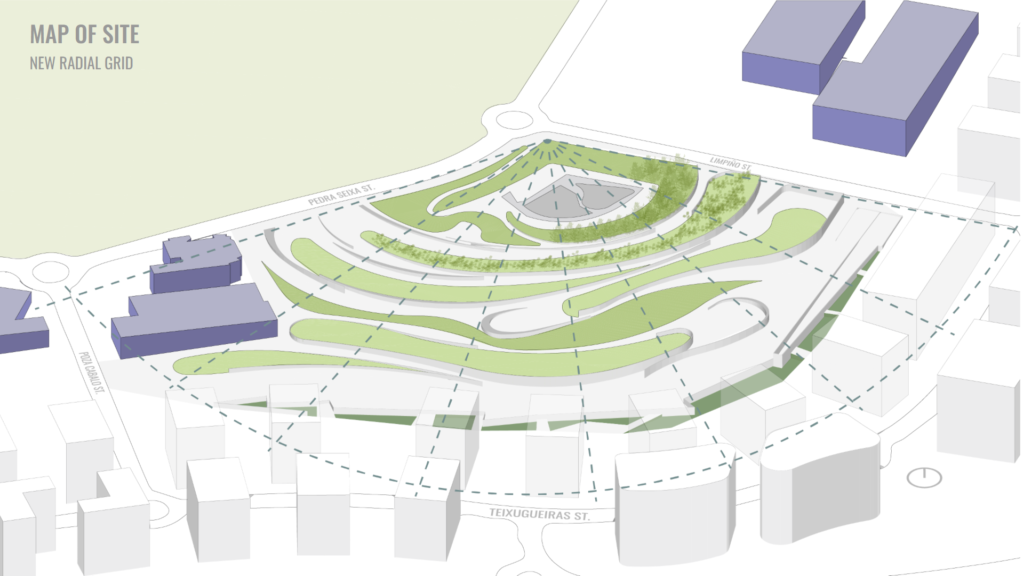
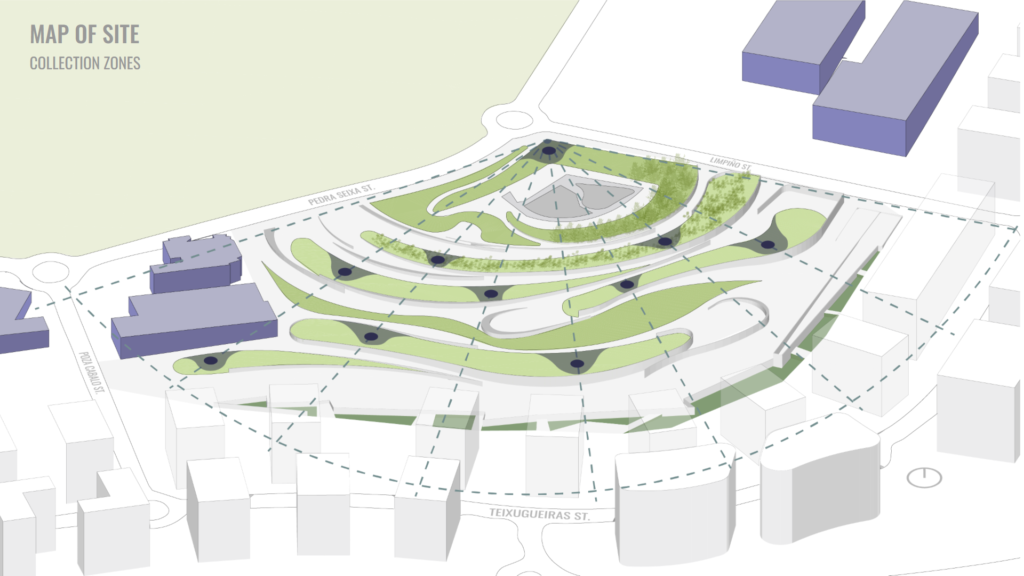
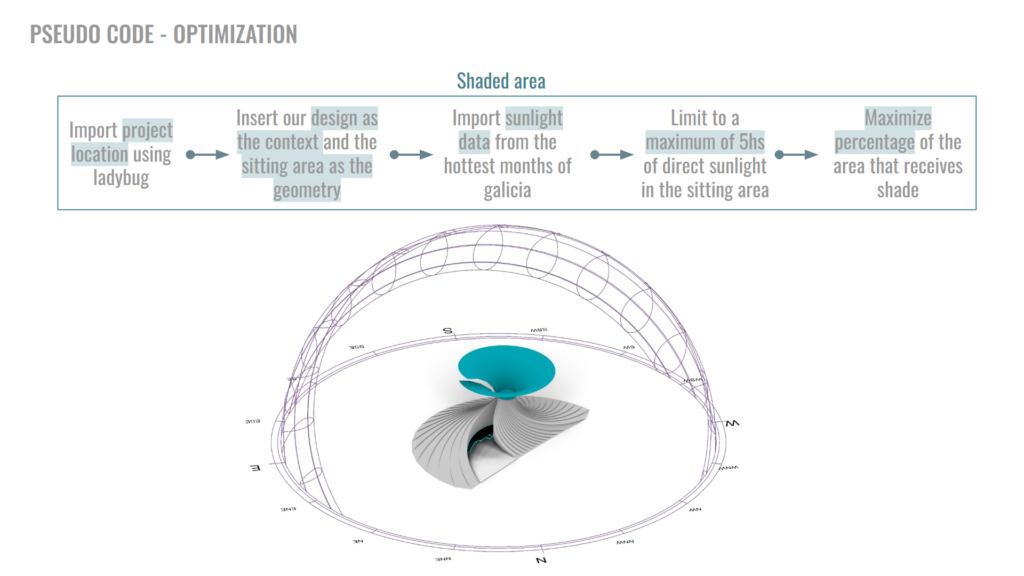
The sun’s path was analyzed and a new radial grid was proposed in the existing landscape, to find the new collection zones.
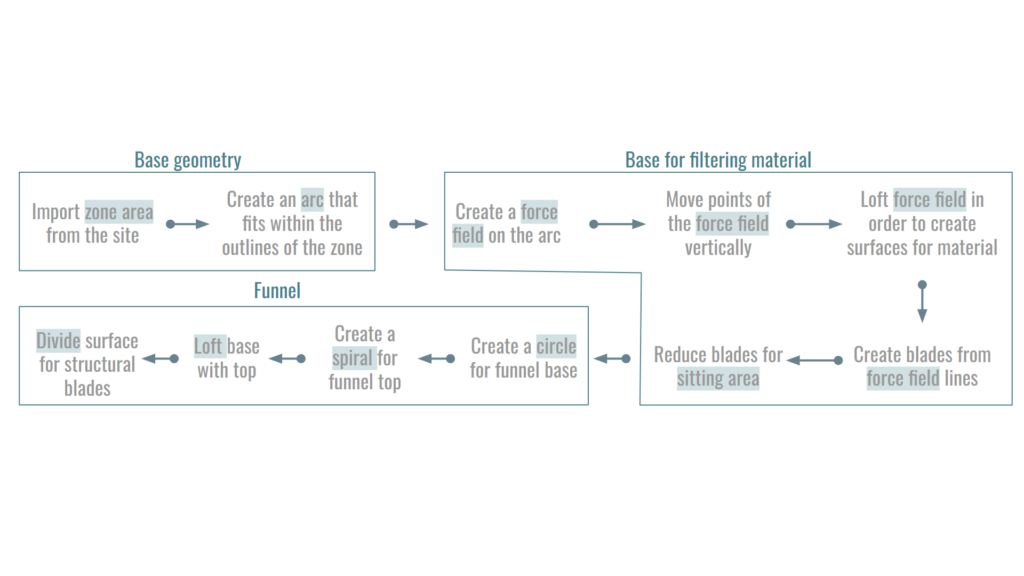
PSEUDO CODE FOR THE DESING
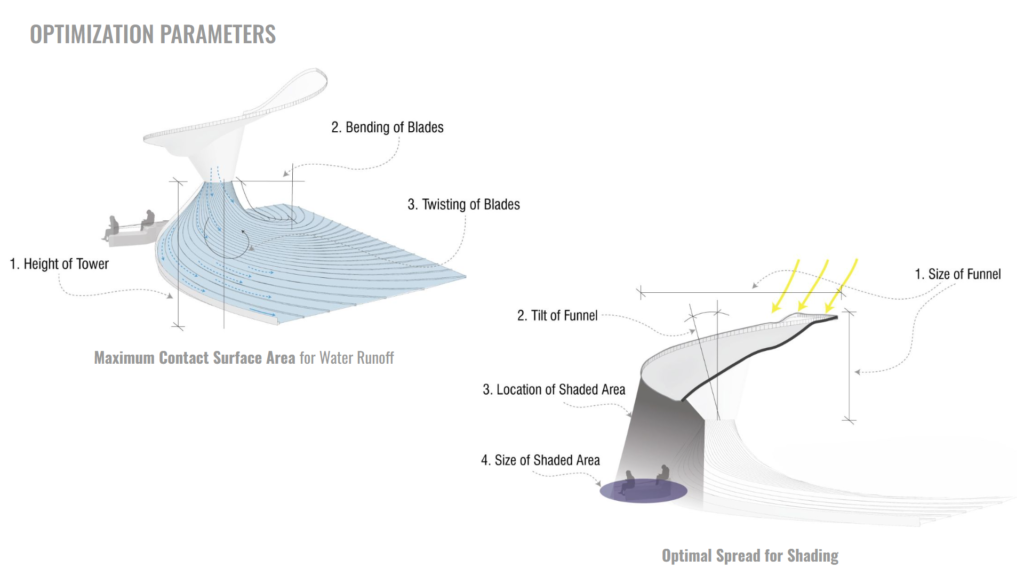
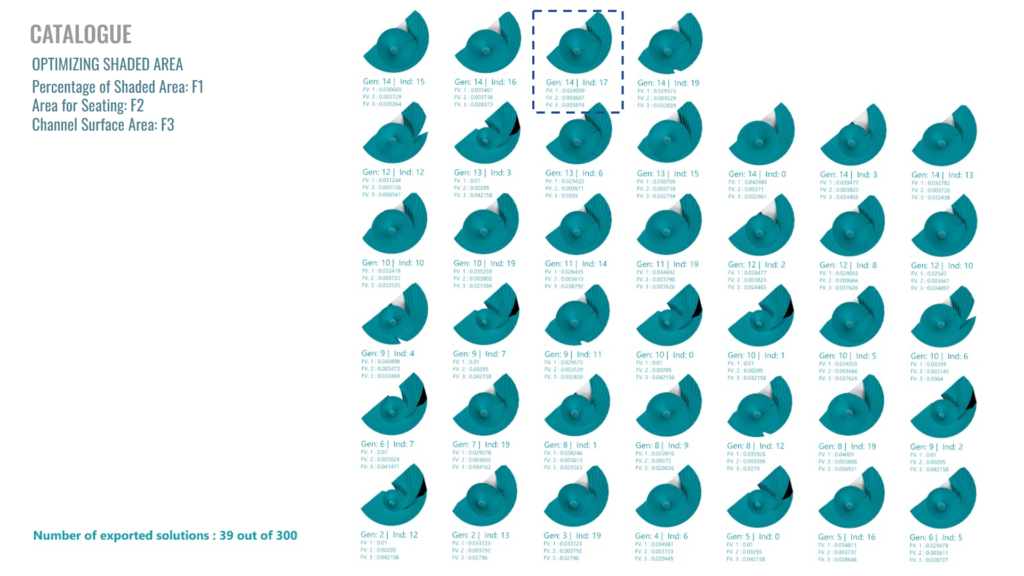
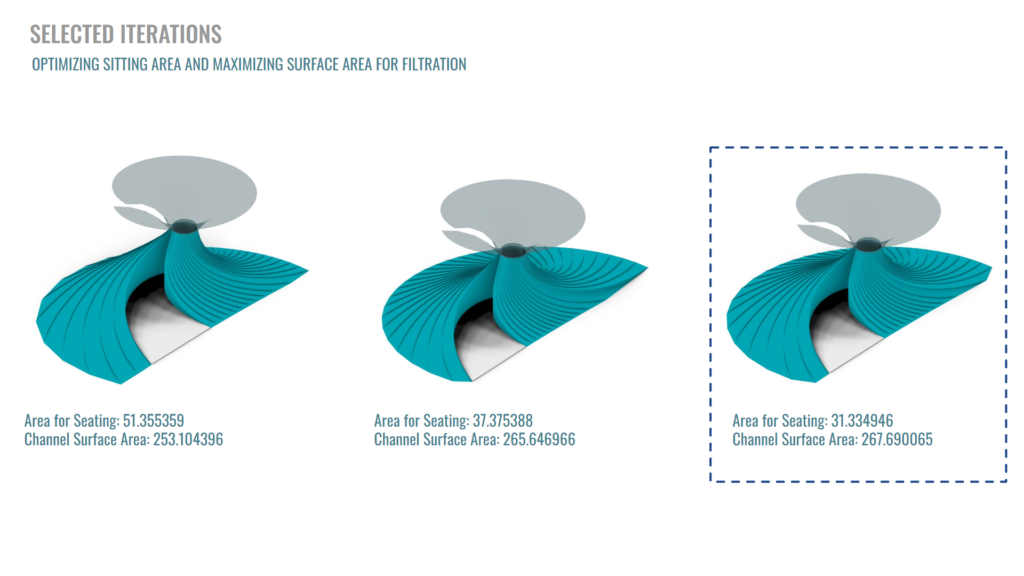
The two parts of the optimization consist of achieving the Maximum Surface Area to apply our filtration material, and also, taking into consideration that one of the issues of the site is the lack of shade, We want to create a sitting area inside of our structure and provide shade for it. So, the Optimal Spread for shading is another parameter to optimize.
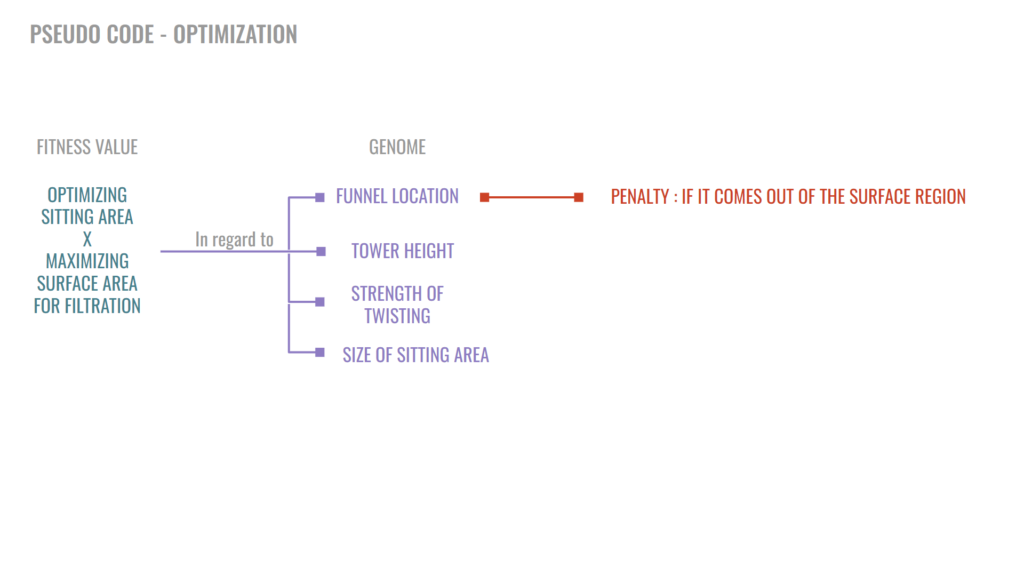
………….FUNNEL LOCATION………………………………………….TOWER HEIGHT…………………………………….STRENGTH OF TWISTING…………………………………..SIZE OF SITTING AREA
Range – According to Penalty…………………………………………..Range – 3m to 4m………………………………………………………Range – 1 to 8…………………………………………………..Range – 80% to 95%
Penalty : Location within offset surface region
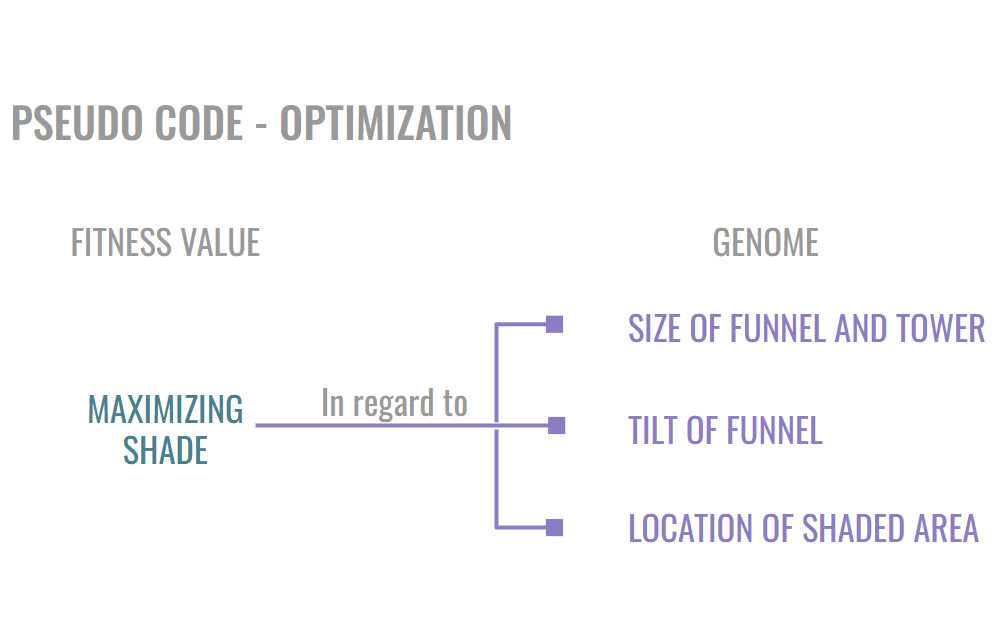
…………………………………………….SIZE OF FUNNEL AND TOWER…………………………………………. TILT OF FUNNEL…………………………………….. LOCATION OF SHADED AREA
………………………………………………….
……………………..Range – Tower radius – 0.8m to 1.8m Funnel scale – 1.2 to 1.8………………….Range – X – 0 to 1 Y – 0.75 to 1………………………………………….Range – 0 to 1