A sun-chasing system is a mechanism that automatically tracks the movement of the sun across the sky to maintain the optimal angle for capturing sunlight. When applied to solar panels, this technology can increase energy efficiency by up to 30–40% compared to fixed panels, as it maximizes exposure throughout the day.
Beyond energy generation, the same principle can be used architecturally to design smart shading systems that dynamically follow the sun, creating adaptive shadows and improving comfort and energy performance for users.
Schematic
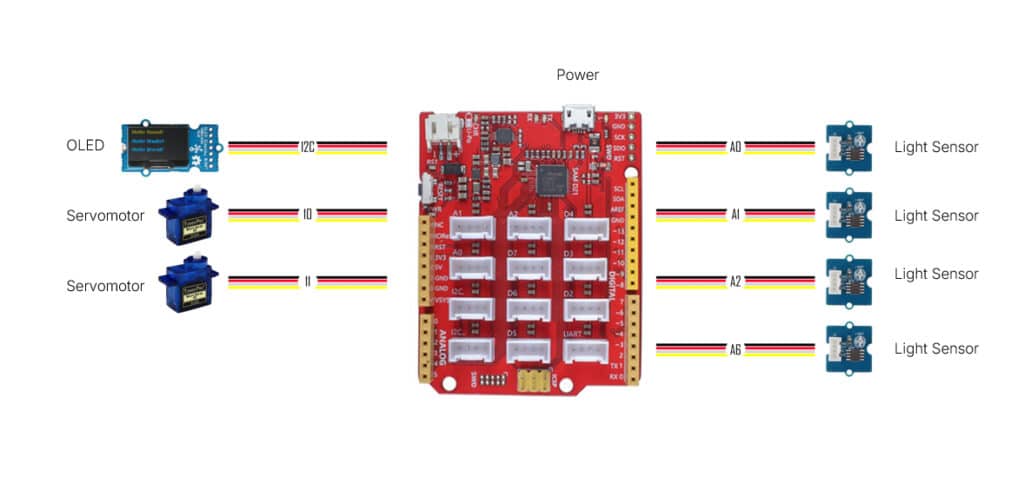

1. Light Detection
- Four light sensors continuously measure light intensity from different directions.
- Small shading walls between the sensors create variations in readings depending on the angle of sunlight, allowing the system to sense directional differences.
2. Decision Making
- The system compares sensor pairs to calculate the horizontal and vertical orientation of the light source:
- By summing the two left and two right sensors, it determines the horizontal angle (east–west direction).
- By summing the two upper and two lower sensors, it detects the vertical angle (altitude of the sun).
- Based on these comparisons and the magnitude of differences, the algorithm identifies the light direction — for example, N, S, E, W, NE, NW, SE, or SW.
3. Action
- Before movement begins, the OLED screen displays the current position of the sun (direction and angle), providing real-time feedback.
- Then, the first servo motor rotates horizontally until both sides of the sensors register equal light intensity, aligning the system in the XY plane with the sun.
- Simultaneously, the second servo motor adjusts the vertical tilt, ensuring the surface directly faces the light source.
4. Feedback Loop
- detecting, calculating, and adjusting in real time.
- When all four sensors read equal values, the plane has perfectly aligned with the sun, achieving maximum light orientation.
Prototype

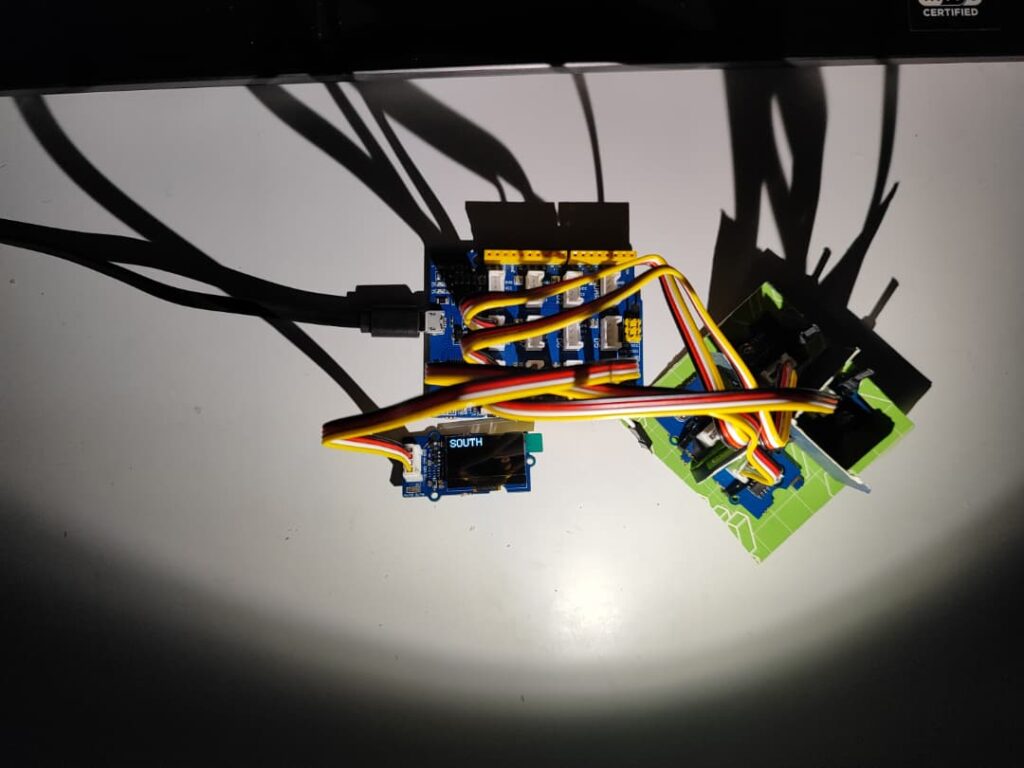
I built a prototype using an Arduino board equipped with four light sensors arranged in a grid. By casting a small shadow grid over the sensors and comparing their light intensity values, the system can accurately determine the sun’s direction. The Arduino processes the sensor data and displays the detected orientation on an OLED screen in real time. Based on this information, two servo motors , one controlling rotation on the XY plane and the other adjusting the horizontal angle ,enable the system to continuously face the sun, creating a fully responsive sun tracking mechanism for solar or shading applications.
The next phase of the project aims to make the system fully responsive to environmental and human factors. It will detect people passing by and adjust its shade to cover them, while also reacting to rain, temperature, or light conditions. This evolution transforms it into an intelligent, adaptive outdoor installation that merges technology with environmental awareness.

