Abstract
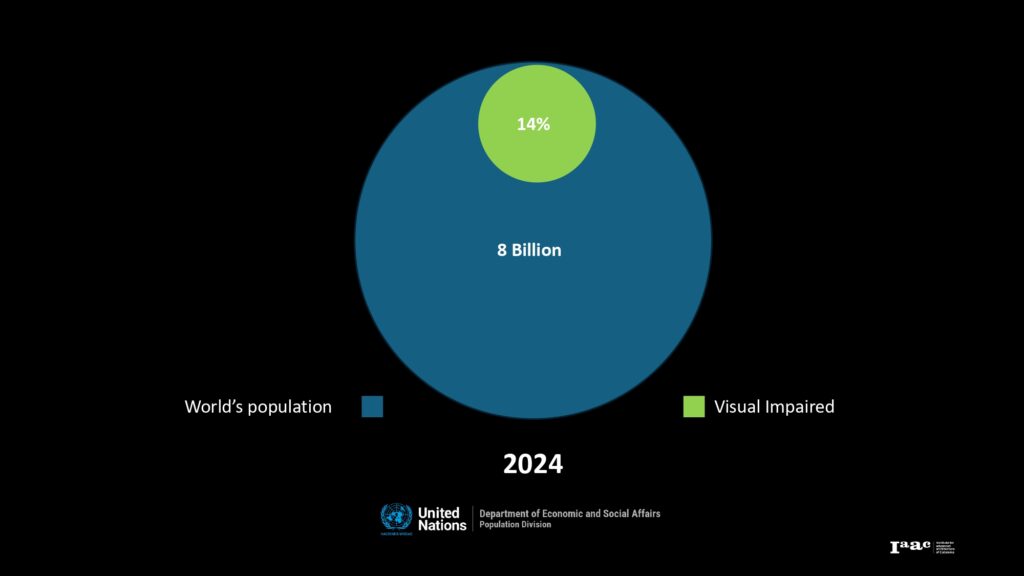
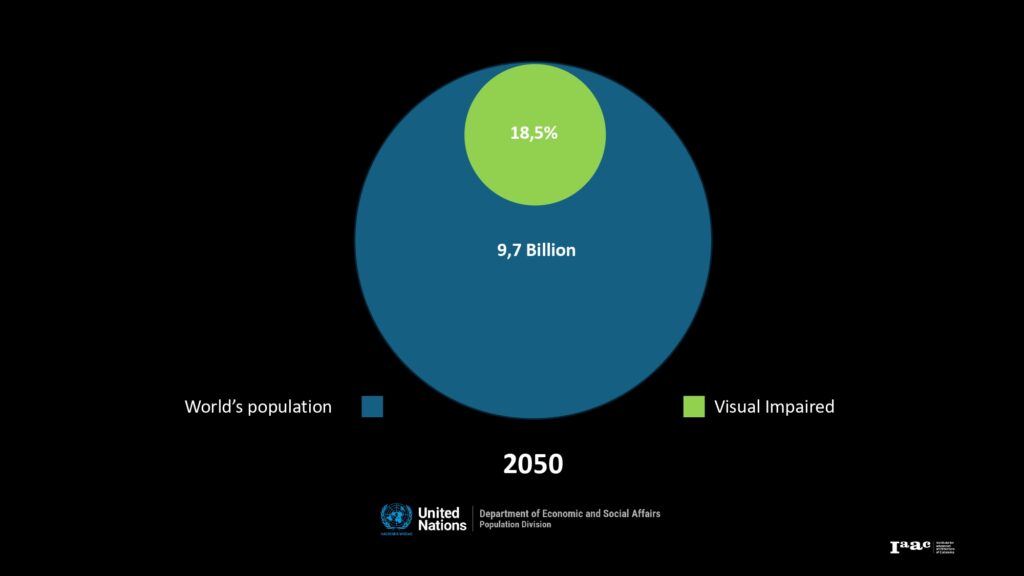
In response to the increasing global population of visually impaired individuals, projected to reach 18.5% by 2050, our project focuses on enhancing the accessibility of architectural spaces, particularly in primary healthcare centers. We have developed the Building Analysis Tool (BAT), an solution designed to assist architects in creating environments that cater to the needs of visually impaired users. By integrating BAT into the architectural workflow, we aim to improve navigation and safety within healthcare facilities, ensuring inclusivity and accessibility for all.

Why Design for Visually Impaired?
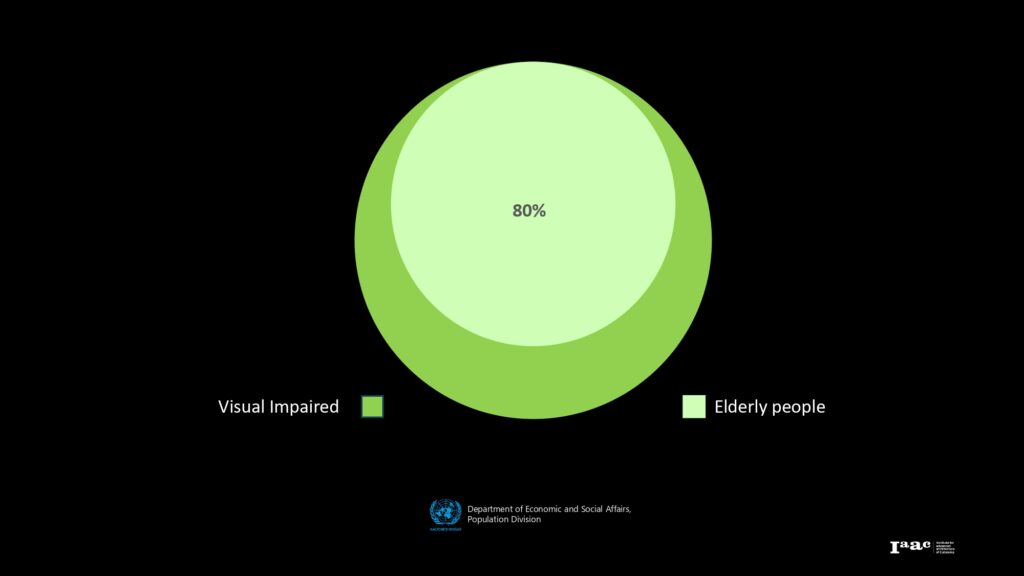
Emphasizing that 80% of visually impaired individuals are elderly, underscoring the need for accessible design in spaces frequently used by this demographic.
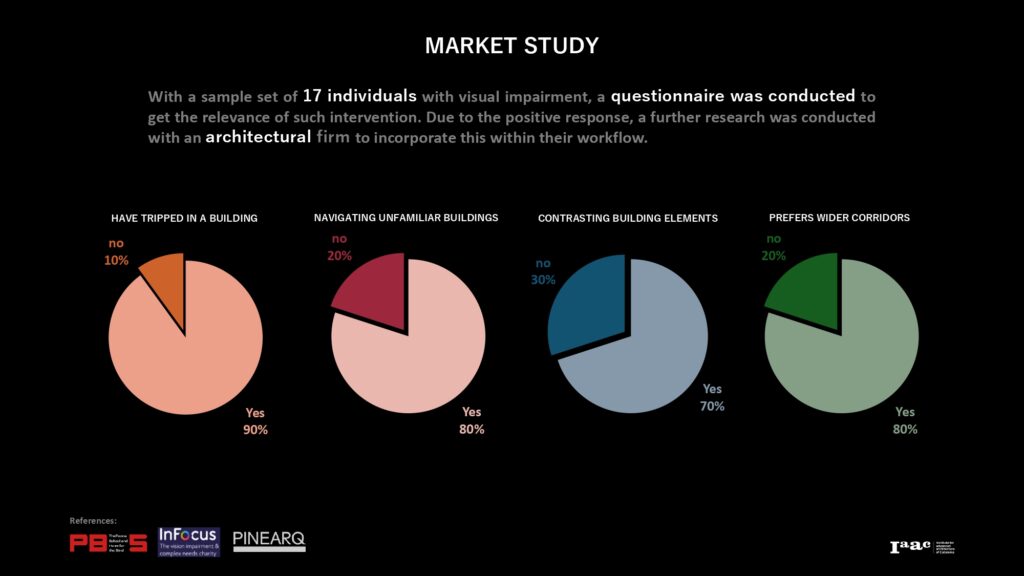



Introducing BAT as a solution to bridge the gap in accessible design for visually impaired users.

User Personas

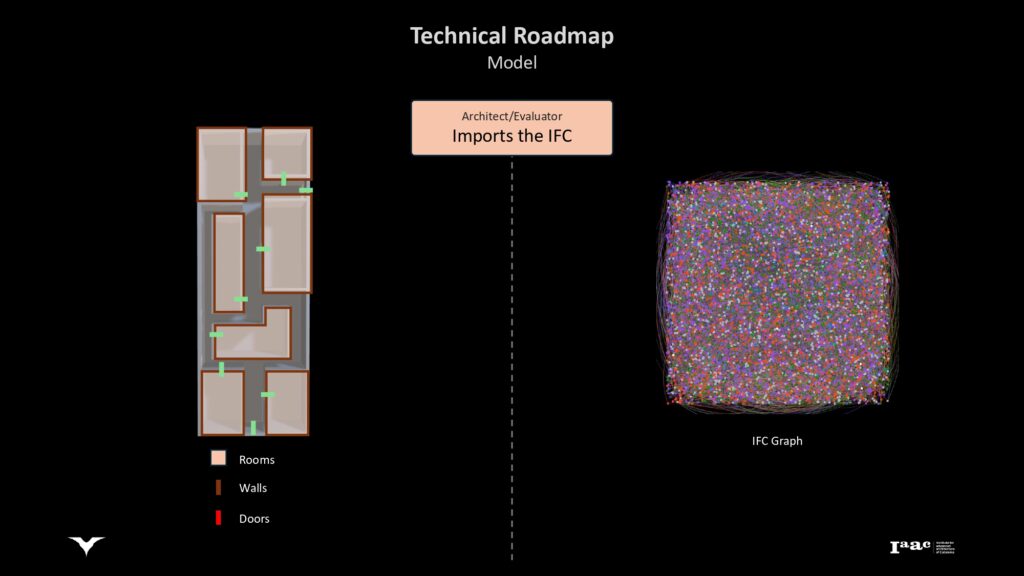
IDEAL PATH – TECHNICAL ROADMAP
Explanation of how architects or evaluators can import IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) models into BAT.
Describing the steps to modify and filter IFC models to focus on relevant elements for accessibility analysis.
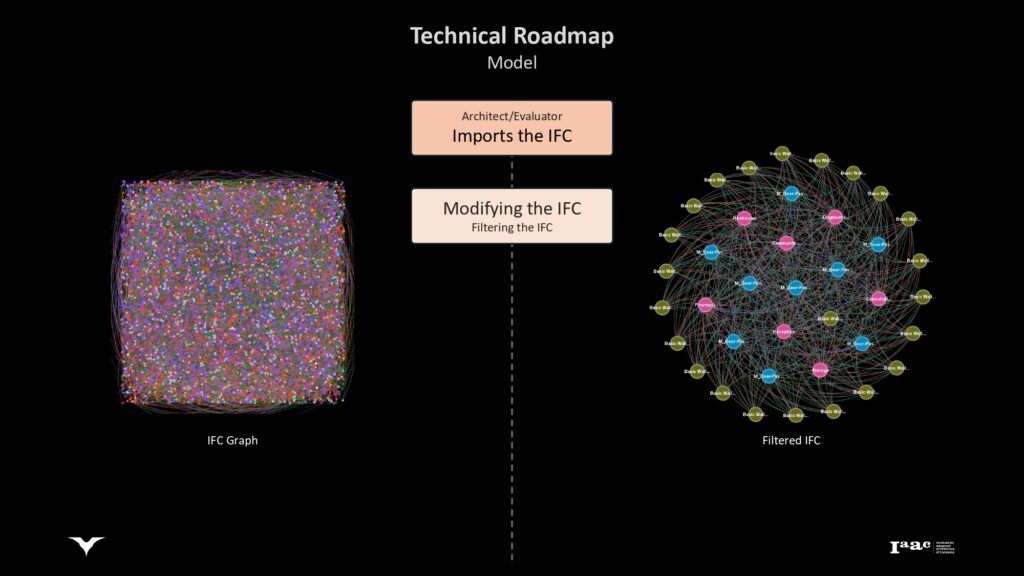
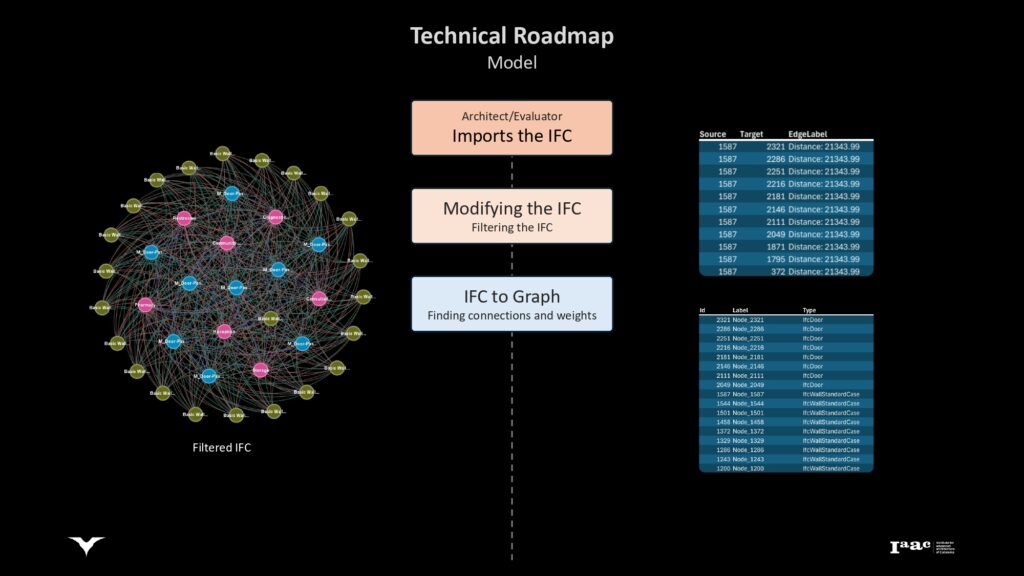
Detailing the process of converting IFC models into graphs to analyze connections and weights within the building structure
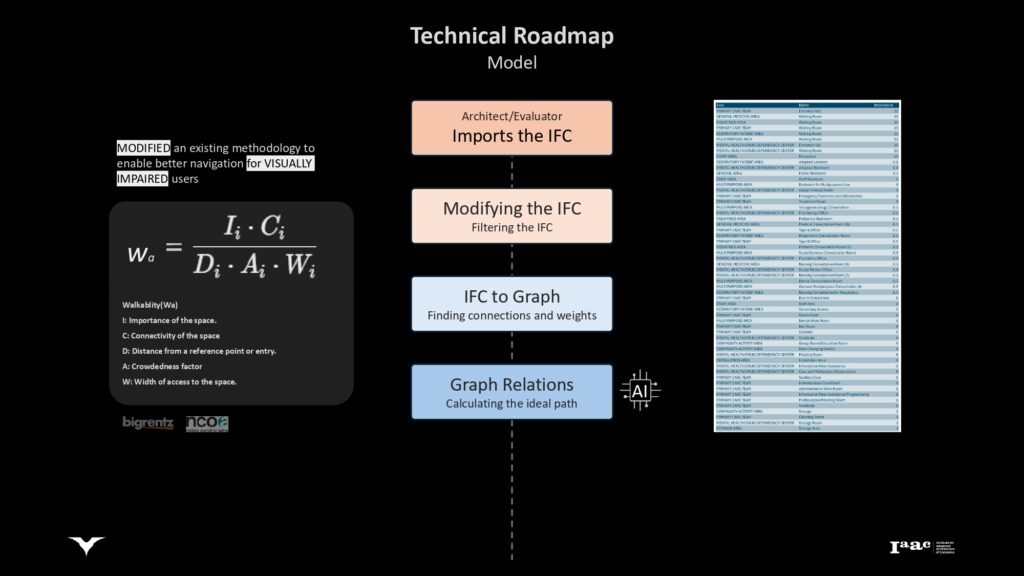
Outlining the calculation of ideal paths within the building to enhance navigation for visually impaired users.
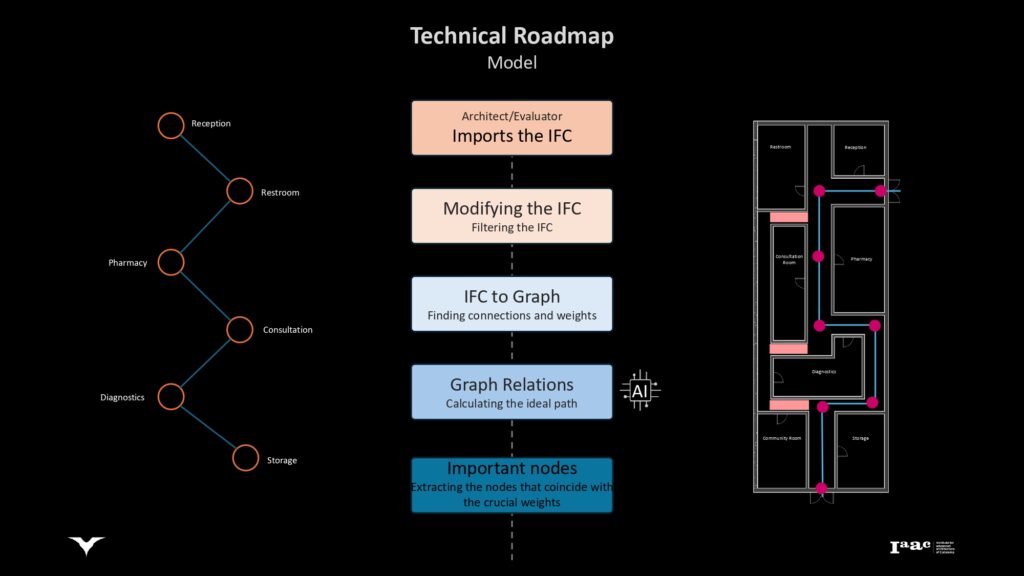
Identifying crucial areas within the building that require attention to improve accessibility.
DESIGN SUGGESTION CHANGE – TECHNICAL ROADMAP
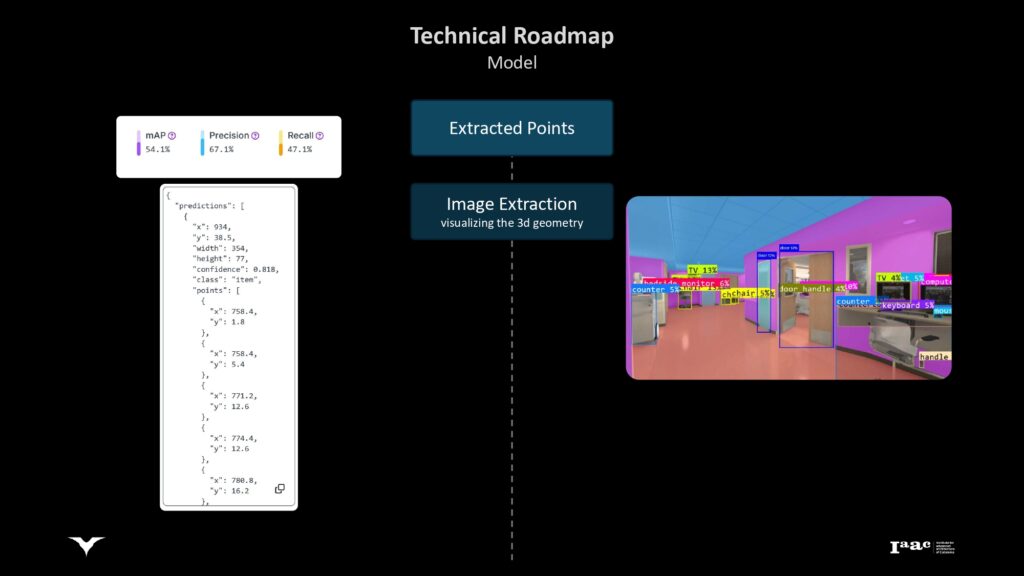
Image Segmentation
Utilizing predefined datasets to detect and analyze building elements relevant to accessibility.
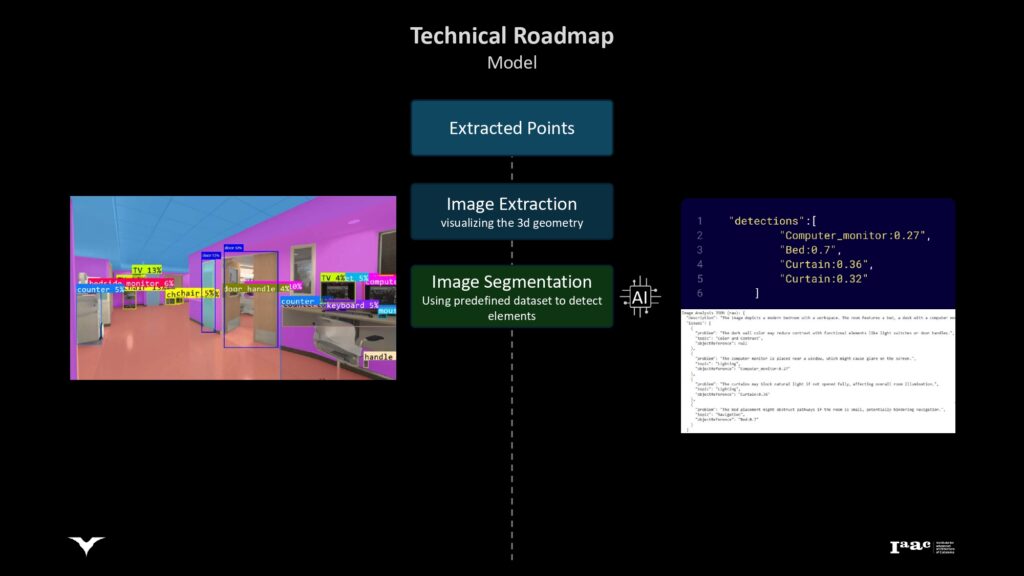
Context Data Extraction
Extracting information from guidelines to inform design decisions and ensure compliance with accessibility standards.
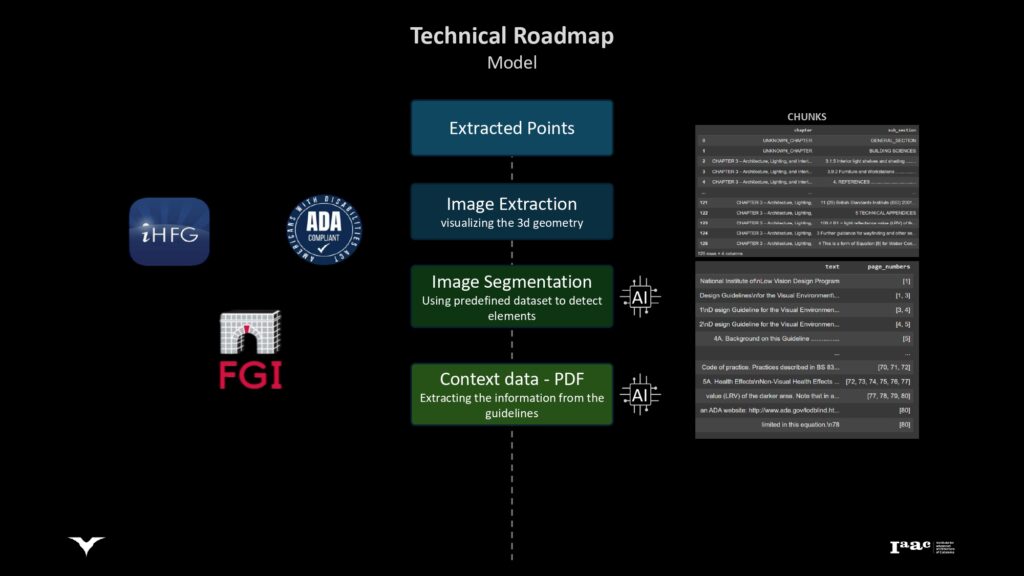
Language Model Integration
Employing language models to correlate interventions with visual data, enhancing the decision-making process.
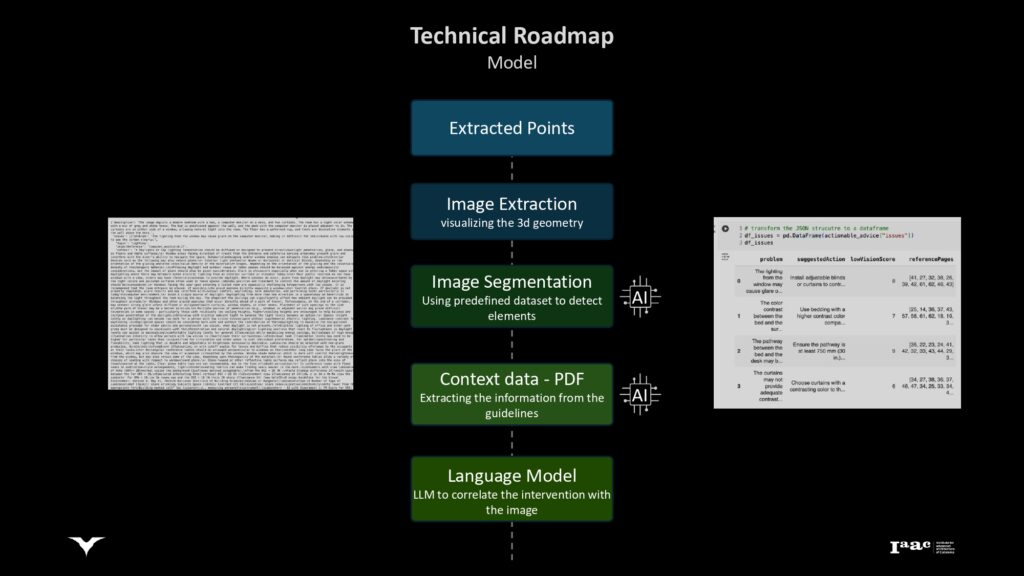
Ideal Path & Suggestion Model
Presenting the model that suggests optimal navigation paths within the building for visually impaired users.