Climate Hope, Regenerative Agriculture and Soil Restoration
Up to 40% of the world’s land is degraded
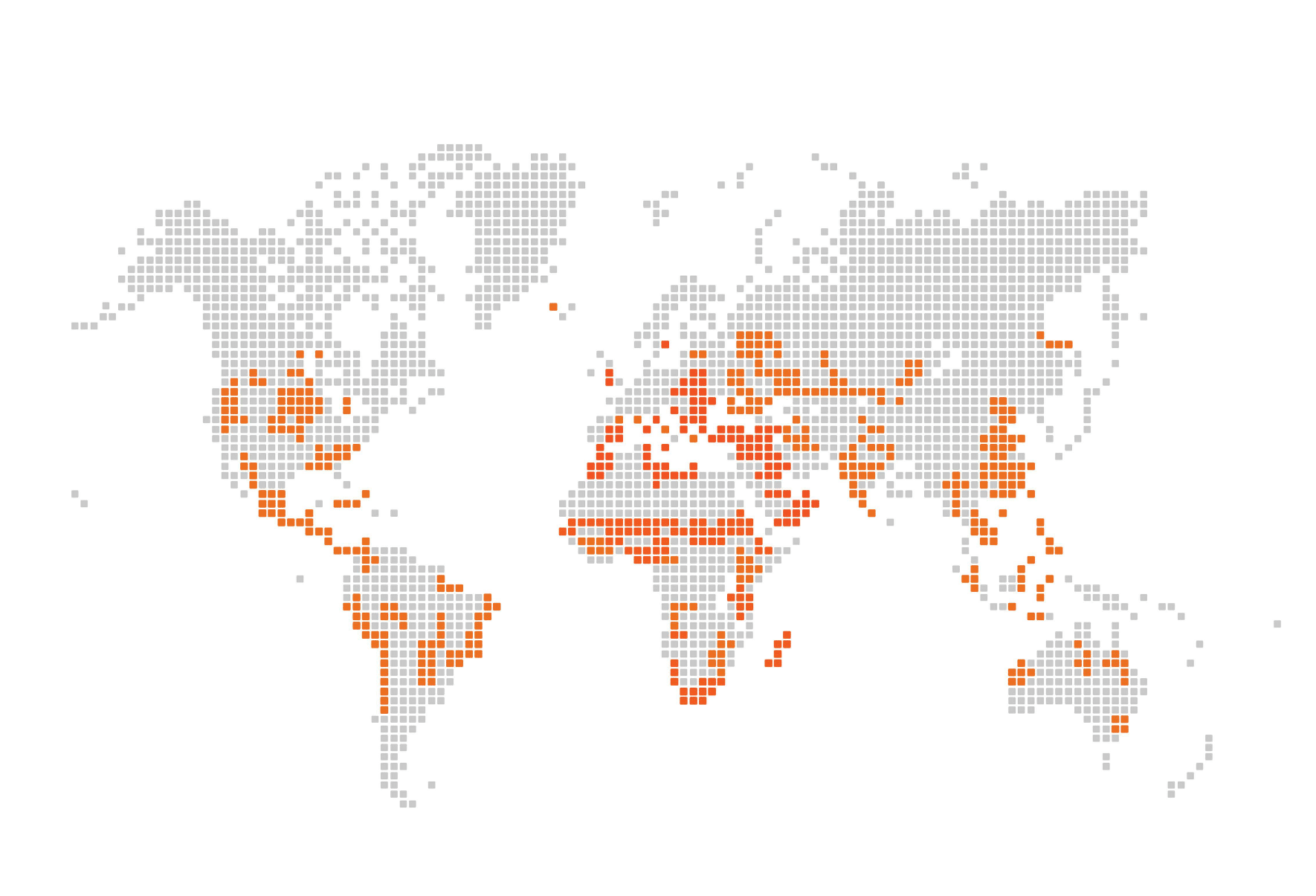
Poor land management and conventional agricultural practices have degraded soils, reducing their ability to store carbon and absorb water, accelerating climate change and threatening food systems.
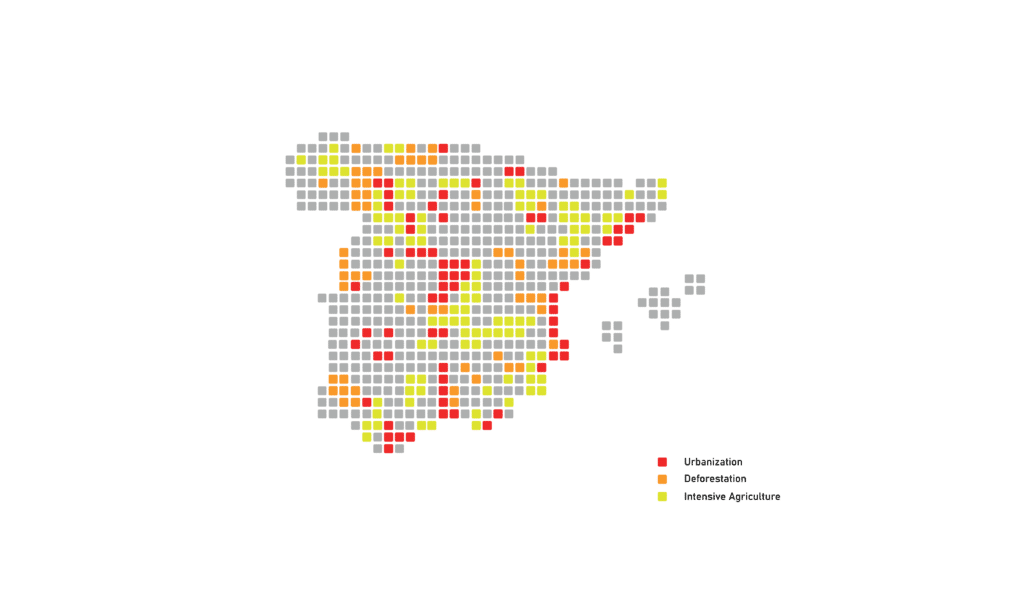
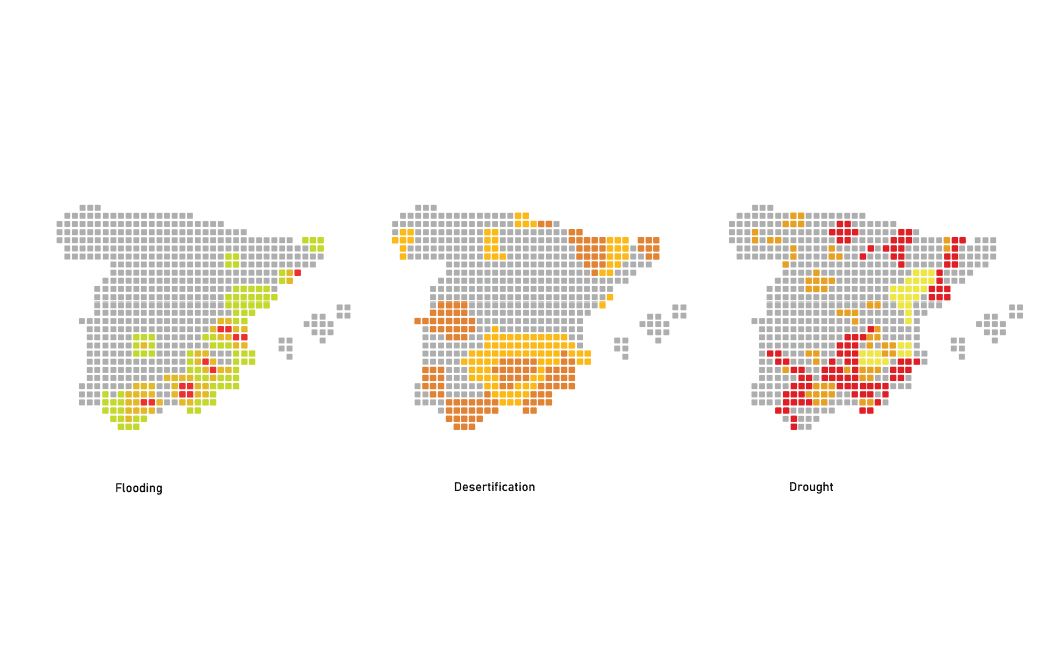
Soils store 3x more carbon than the atmosphere, but 50-70% of their natural carbon has been lost. The loss of carbon sequestration capacity in degraded soils accelerates climate change. Depleted soils hold up to 60% less water, leading to extreme droughts, increased flooding.
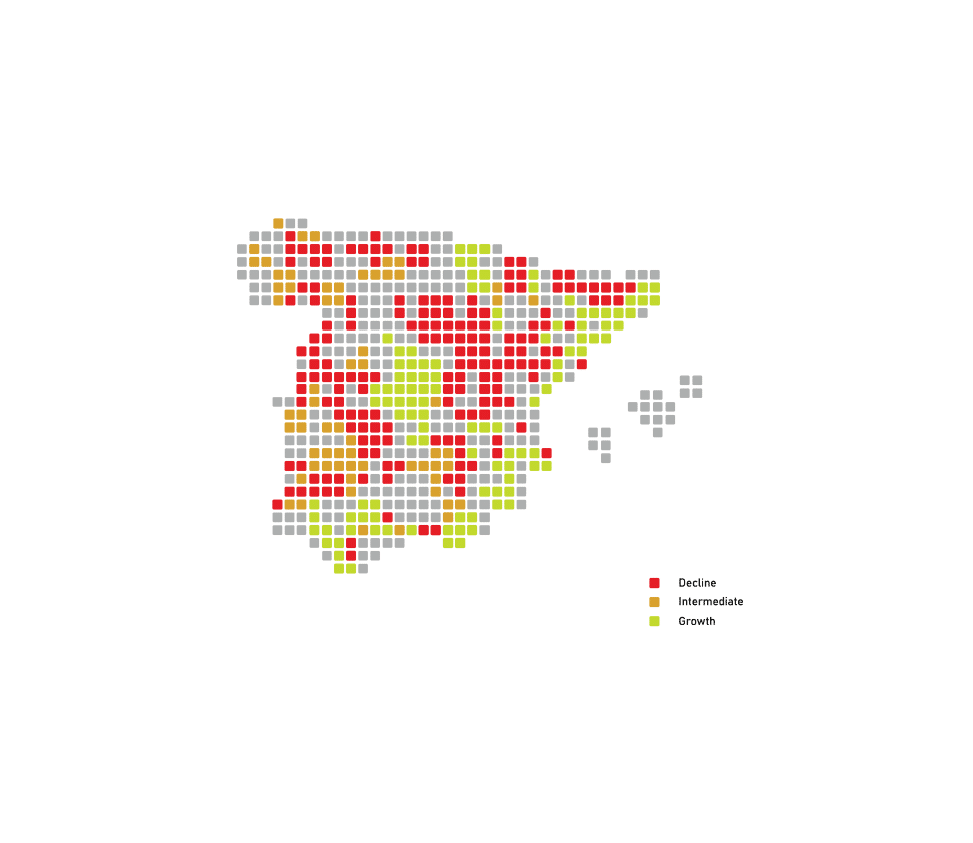
Regenerative agriculture offers solutions, but since 2005, EU farms have declined by nearly 40%, displacing 5.3 million farmers. Carbon farming remains unviable due to labor demands and tech barriers. An aging workforce (55+) and declining interest among young people worsen the crisis.
Farming games are widely popular, showing strong interest in interactive agriculture. Gamification simplifies complex land management, making it engaging and accessible. Farming games provide a risk-free way to explore different practices.,

After My Analysis from the first term, where I determined 6 principles of foundations at the large scale, framework scale and tool scale; as well as an analysis of multiple farming platforms that help mitigate the problem. I have determined 6 key takeaways and implementable tools to move forward with my project.

Research question:

Looking into a Game Design:

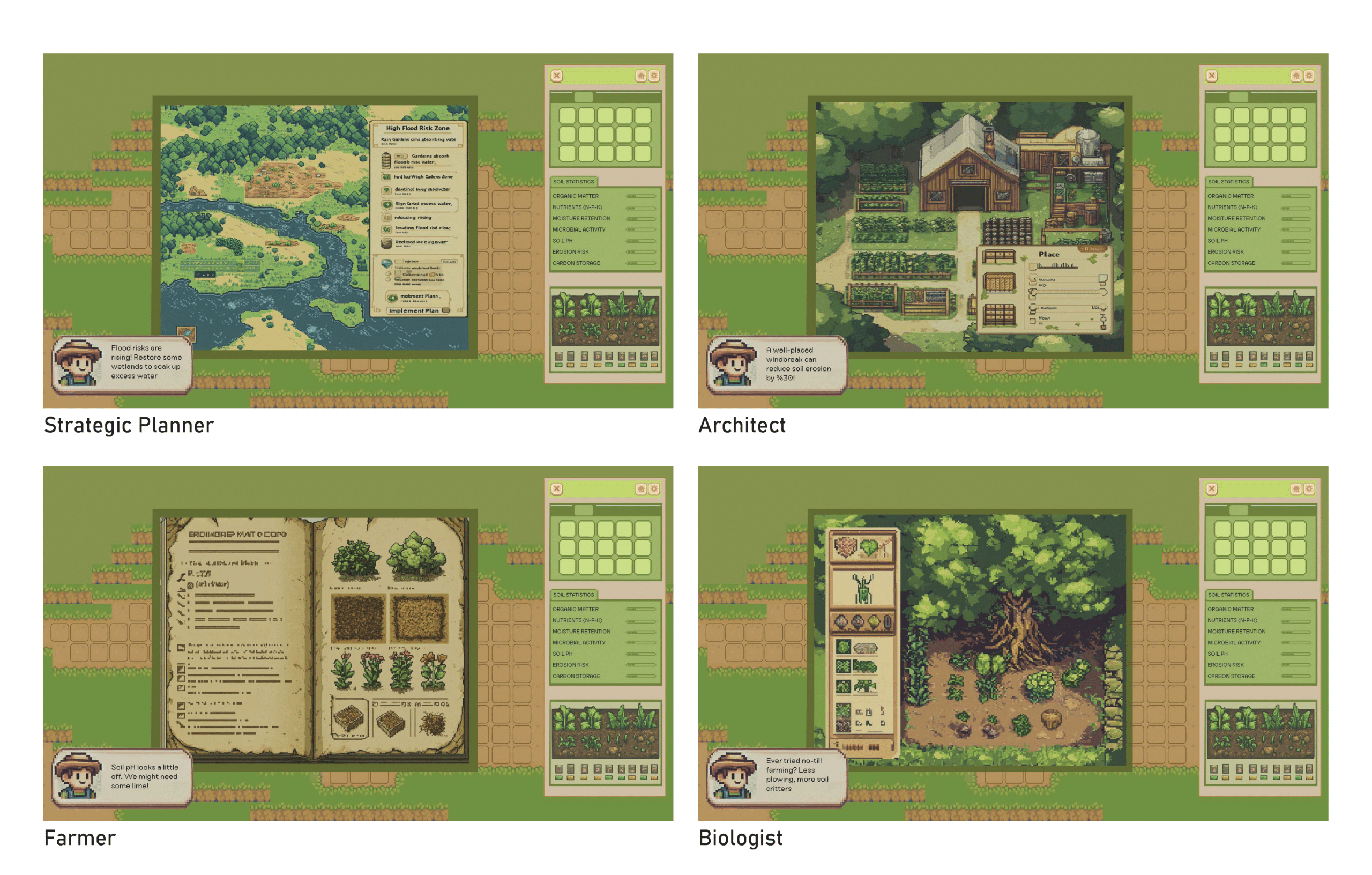
Providing accessible, location-specific soil quality information to support sustainable land management decisions. how does it work?
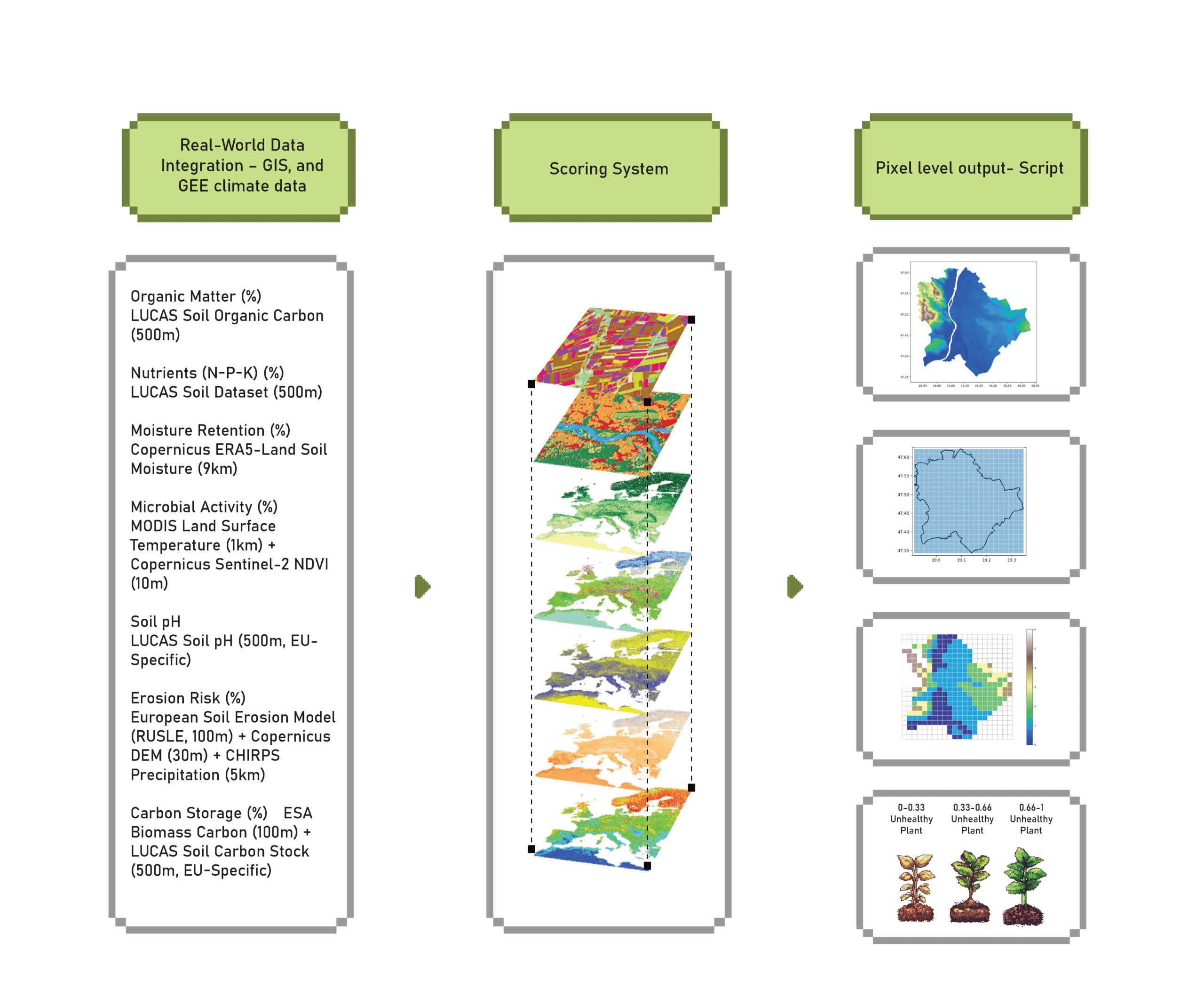
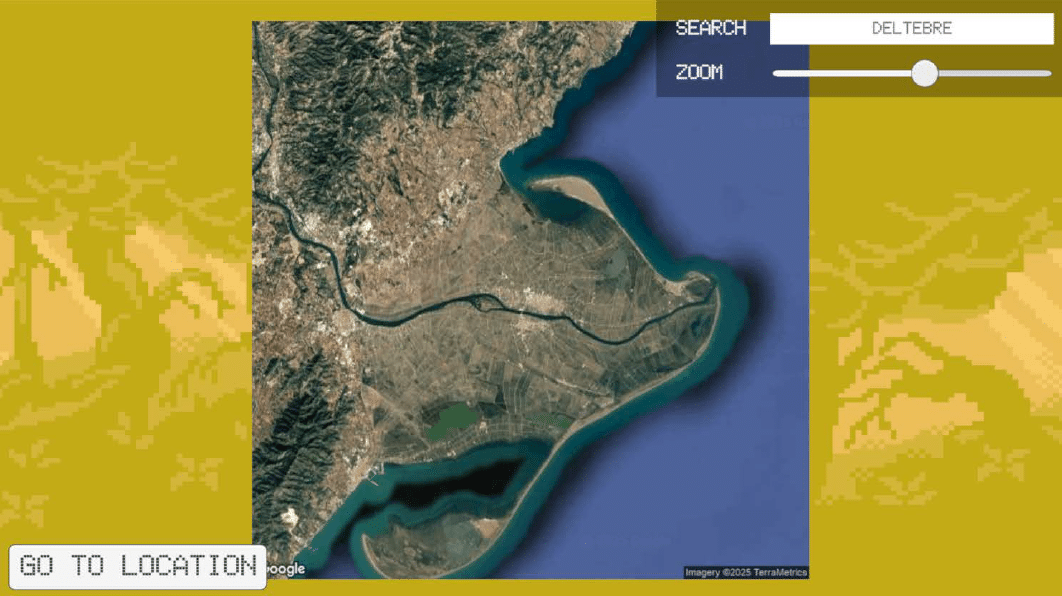
Players navigate a dynamic grid overlay that maps soil health across the landscape, identifying degraded areas in need of restoration through real-time data visualization.
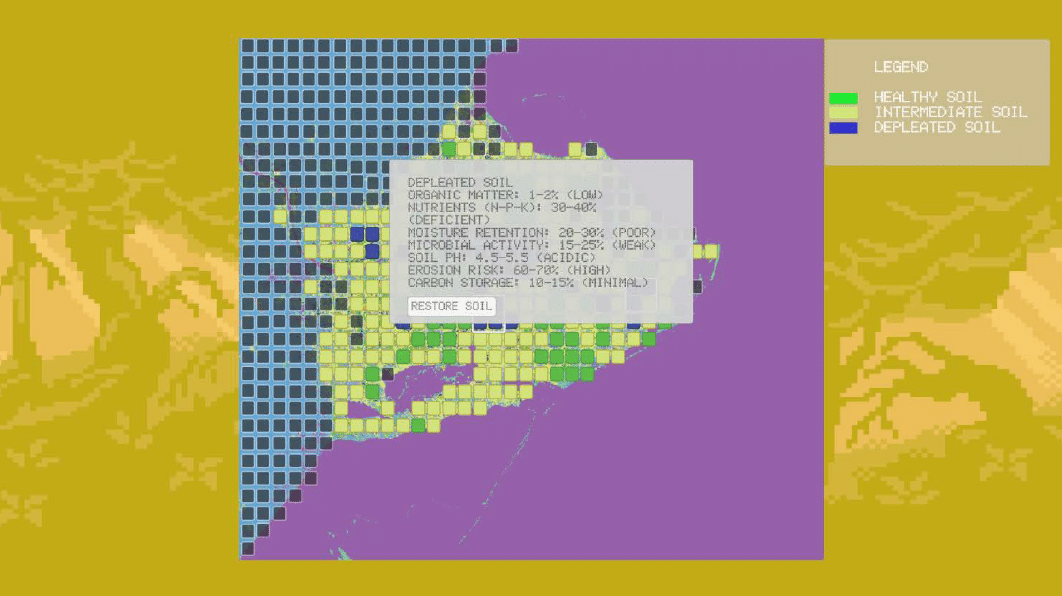
Clicking on an unhealthy soil grid reveals key metrics such as carbon content, pH levels, and moisture retention, providing insight into soil depletion and guiding restoration strategies.
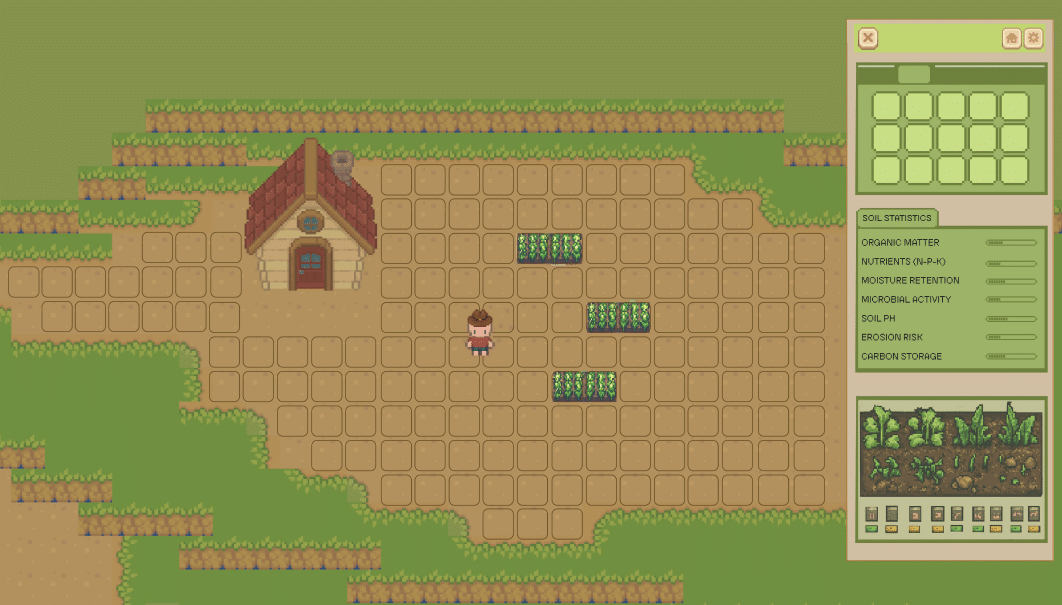
Jumping into sandbox mode allows players to interact with the soil up close, experimenting with regenerative techniques in real-time to restore balance and improve ecosystem health.
One of the key aspects of the game is the ability to collaborate with other players. Improving the environment is not something that can be done by one person or one discipline, You have to work together to make an impact.
Each character has its own role in different regenerative agriculture practices that lead to soil restoration.
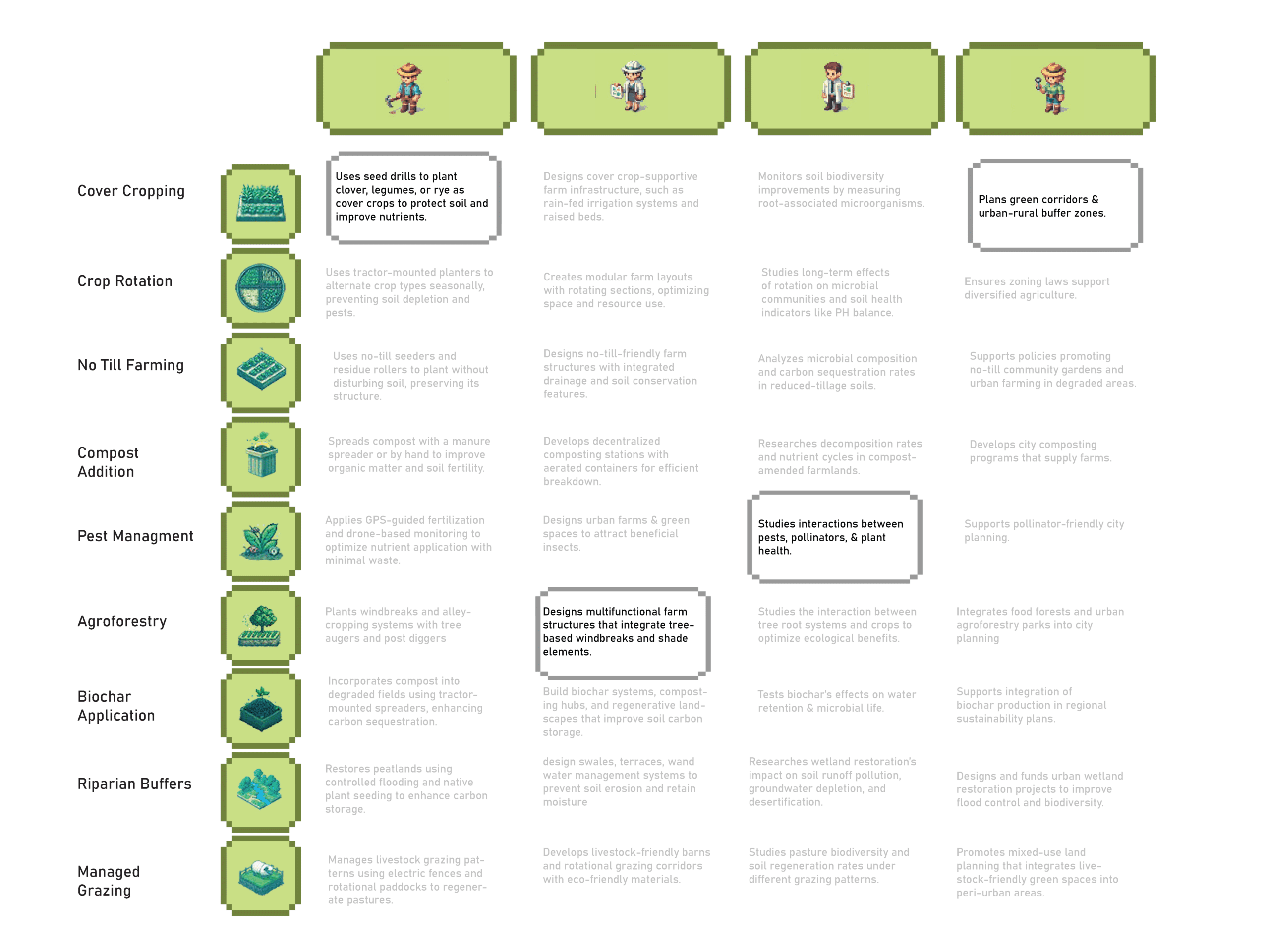
and I have been building a step by step Library on which practices work, where and when. To Experiment with different farming and land management techniques. Implement a player evolution system where players unlock more sustainable farming techniques as they progress.

As well as which character should be involved at which stage of the soil restoration.
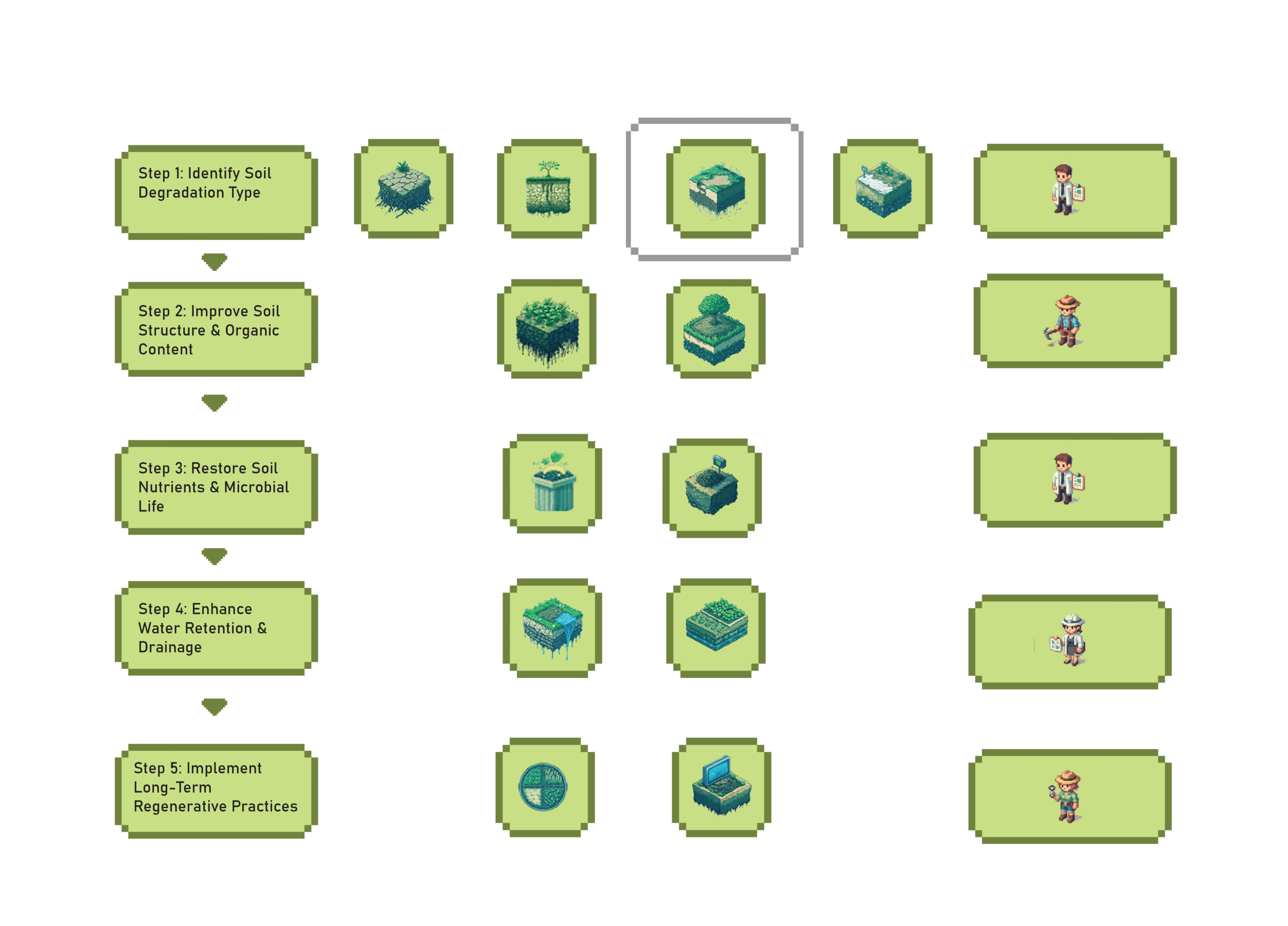
I have also been building an inventory system where players can learn what tools and items to use according to the crops they are dealing with and the conditions of their soils.
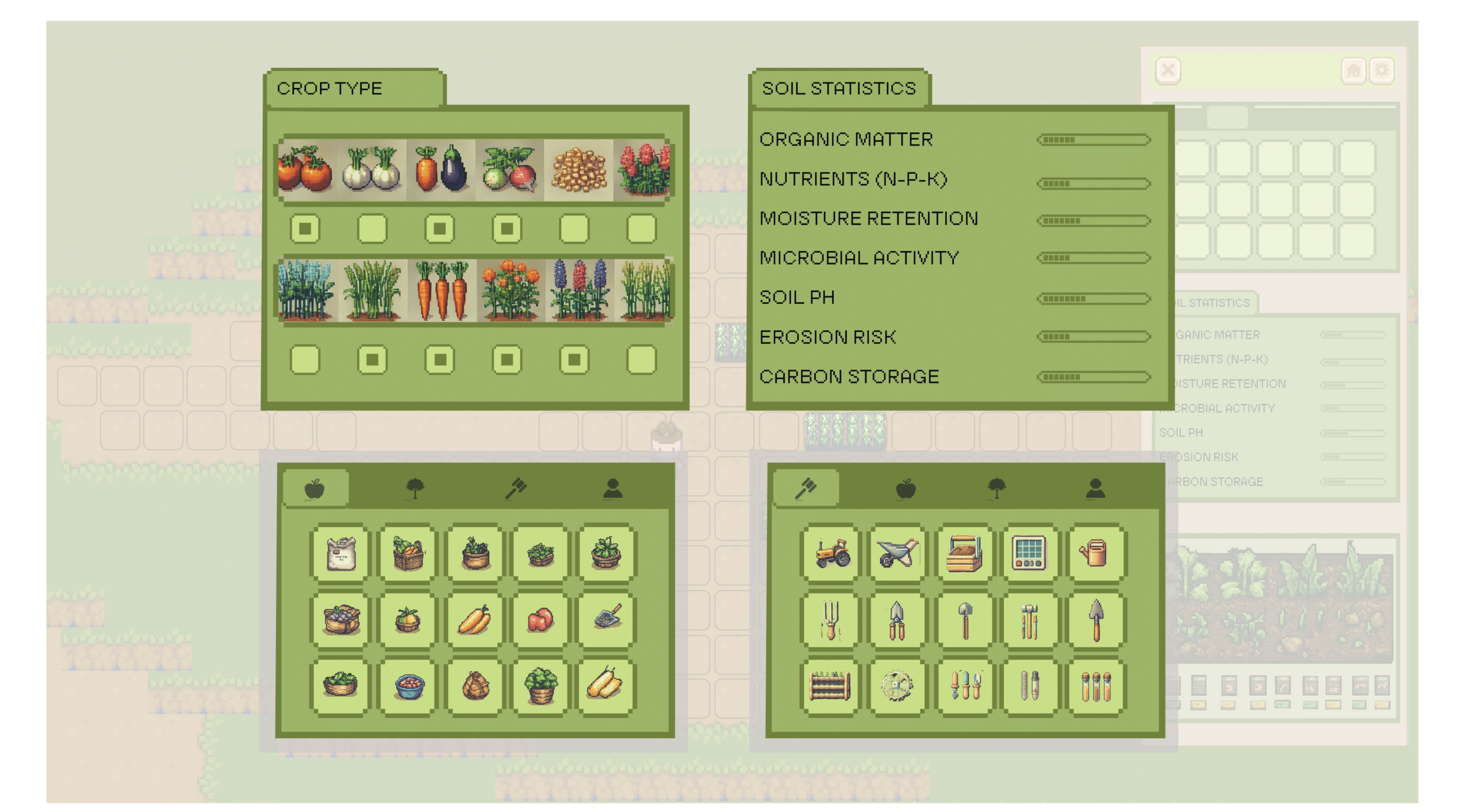
Finally, Living ecosystem where interactions between soil, water, crops, and climate evolve based on player actions.Encourages strategic thinking. Different locations require different restoration strategies, reinforcing game depth and replayability.
Consequence Scenarios give a speculative, futuristic aspect and Creates urgency – Players feel motivated to act because they see direct consequences of soil mismanagement. Ties gameplay to climate resilience. Players restore soils to prevent catastrophic events in a simulated yet realistic environment.
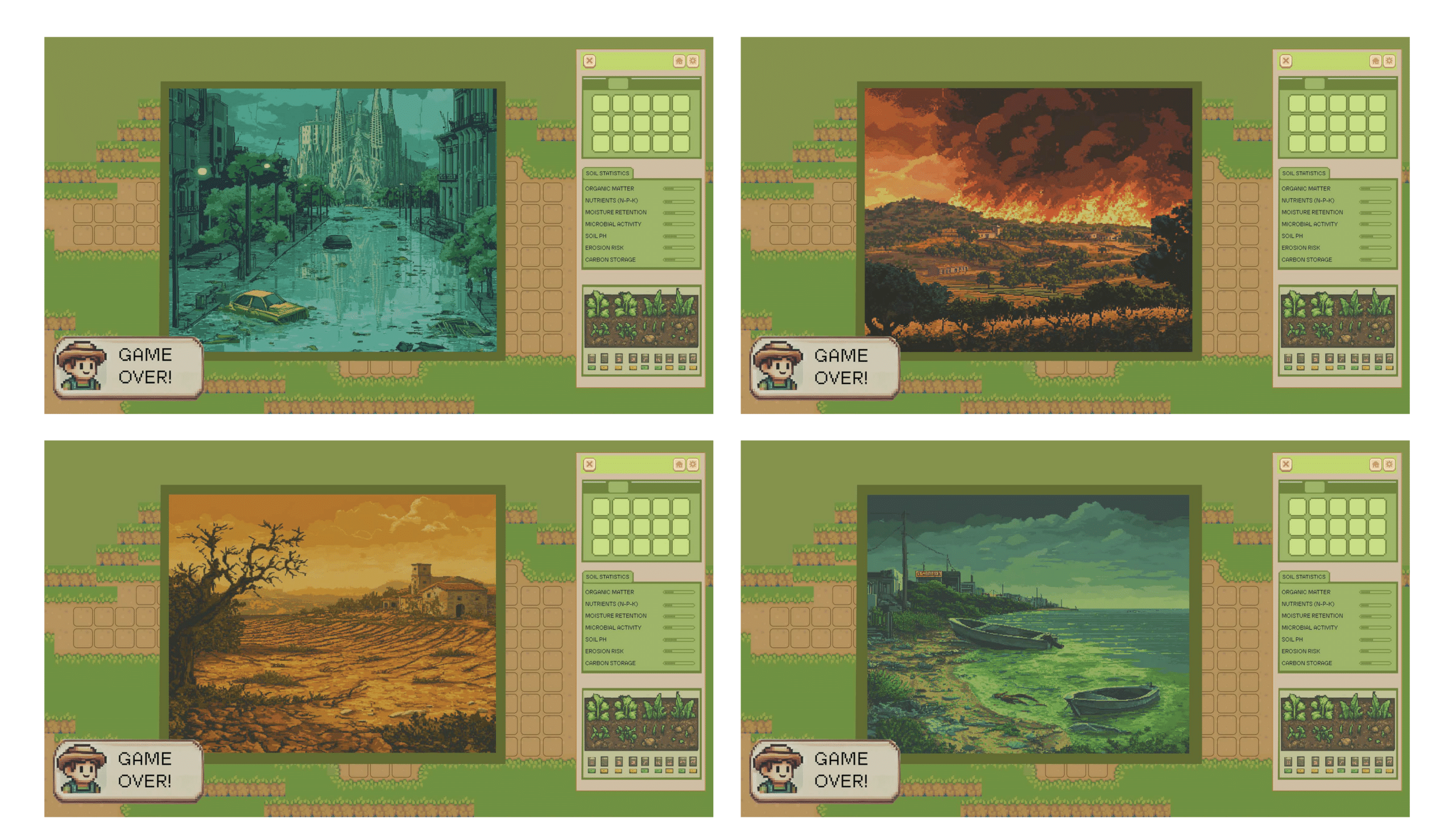
We often look at the effects at the global food chain level, but we need to be much better at considering the environmental effects at the local level. Soil degradation and restoration dynamically affect land productivity and biodiversity.

